Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Convert quantum bases, states or operators in Hilbert space to functions in phase space
ResourceFunction["QuantumWignerTransform"][QuantumBasis[…]] performs a Wigner transform on the specified QuantumBasis, mapping from the Hilbert space picture to the phase space picture. | |
ResourceFunction["QuantumWignerTransform"][QuantumDiscreteState[…]] performs a Wigner transform on the specified QuantumDiscreteState. | |
ResourceFunction["QuantumWignerTransform"][QuantumDiscreteOperator[…]] performs a Wigner transform on the specified QuantumDiscreteOperator. | |
ResourceFunction["QuantumWignerTransform"][QuantumMeasurementOperator[…]] performs a Wigner transform on the specified QuantumMeasurementOperator. | |
ResourceFunction["QuantumWignerTransform"][QuantumHamiltonianOperator[…]] performs a Wigner transform on the specified QuantumHamiltonianOperator. | |
ResourceFunction["QuantumWignerTransform"][QuantumCircuitOperator[…]] performs a Wigner transform on the operator representation of the specified QuantumCircuitOperator. |
Compute the Wigner transform of a single-qubit Pauli-X QuantumBasis object to obtain a single-qubit QuantumBasis object in the phase space picture:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= | 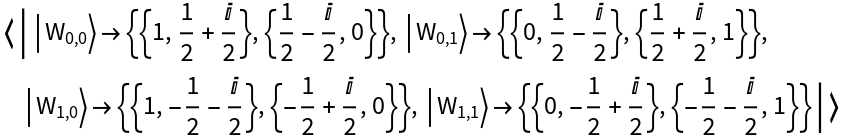 |
Compute the Wigner transform of a two-qubit Pauli-X QuantumBasis object to obtain a two-qubit QuantumBasis object in the phase space picture instead:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |  |
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
Compute the Wigner transform of an arity-1 QuantumDiscreteOperator object in the computational basis (default) to obtain a corresponding arity-1 QuantumDiscreteOperator object in the phase space picture:
| In[7]:= | ![operator = ResourceFunction["QuantumWignerTransform"][
ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteOperator"]["Hadamard", {1}]];
operator["Operator"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/be2/be210202-fa19-443f-aea0-1a42043ca75d/34c54b2956cc2481.png) |
| Out[7]= |
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
Compute the Wigner transform of an arity-2 QuantumDiscreteOperator object to obtain a corresponding arity-2 QuantumDiscreteOperator object in the phase space picture instead:
| In[9]:= | ![operator2 = ResourceFunction["QuantumWignerTransform"][
ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteOperator"]["CNOT", {1, 2}]];
operator2["Operator"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/be2/be210202-fa19-443f-aea0-1a42043ca75d/1413e5fcabae1b9f.png) |
| Out[9]= | 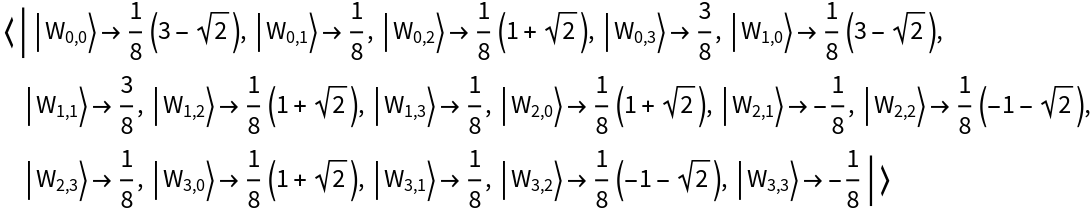 |
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
Compute the Wigner transform of an arity-2 projection-valued QuantumMeasurementOperator object in the computational basis (default) to obtain a corresponding arity-2 QuantumMeasurementOperator object in the phase space picture:
| In[11]:= | ![operator = ResourceFunction["QuantumWignerTransform"][
ResourceFunction["QuantumMeasurementOperator"][
"FourierBasis", {1, 2}]];
operator["Operator"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/be2/be210202-fa19-443f-aea0-1a42043ca75d/52534ef036924dc8.png) |
| Out[11]= | 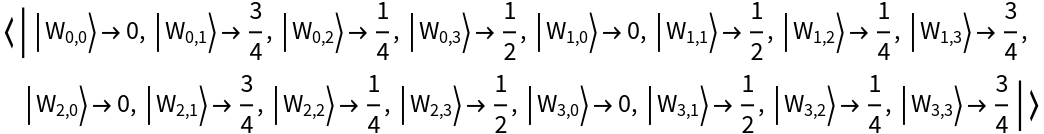 |
Compute the Wigner transform of an arity-1 QuantumHamiltonianOperator object in the computational basis (default) to obtain an arity-1 QuantumHamiltonianOperator object in the phase space picture:
| In[12]:= | ![hamiltonian = ResourceFunction["QuantumWignerTransform"][
ResourceFunction[
"QuantumHamiltonianOperator"][{{1 + \[FormalT]^2, 1 - \[FormalT]^2}, {1 - \[FormalT]^2, 1 + \[FormalT]^2}}]];
hamiltonian["Operator"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/be2/be210202-fa19-443f-aea0-1a42043ca75d/7df00b9adbc91bf0.png) |
| Out[12]= |
Compute the Wigner transform of an arity-2 QuantumCircuitOperator object in the computational basis (default) to obtain an arity-2 QuantumDiscreteOperator object in the phase space picture:
| In[13]:= | ![circuit = ResourceFunction[
"QuantumCircuitOperator"][{ResourceFunction[
"QuantumDiscreteOperator"]["CNOT", {1, 2}], ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteOperator"]["Hadamard", {2}], ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteOperator"]["SWAP", {1, 2}]}];
circuit["Diagram"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/be2/be210202-fa19-443f-aea0-1a42043ca75d/1d326fbcc2aa7cc6.png) |
| Out[13]= | 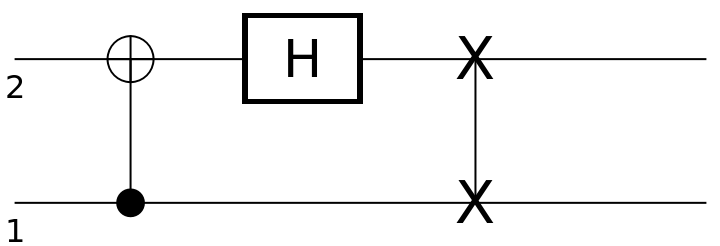 |
| In[14]:= |
| Out[14]= |
Show the operator association of the resulting QuantumDiscreteOperator:
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= | 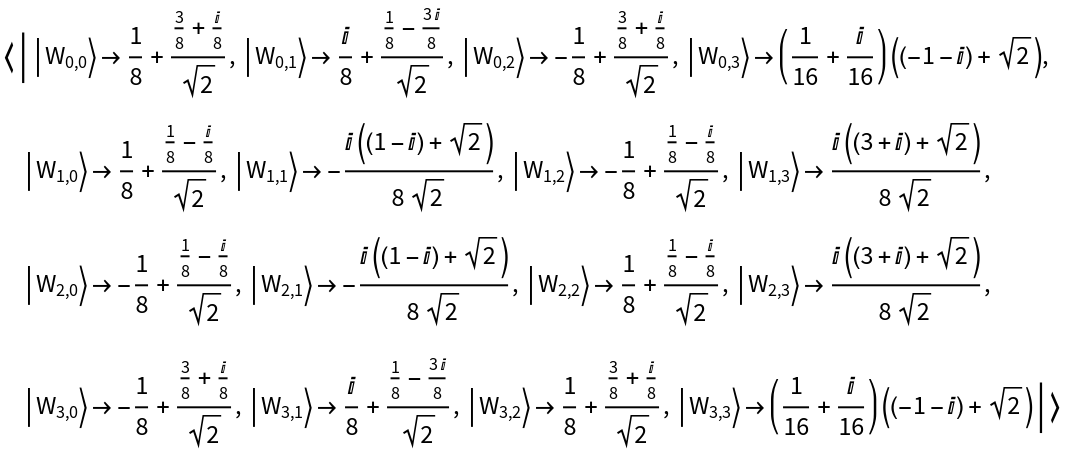 |
Compute the Wigner transform of a single-qubit QuantumDiscreteState object in the computational basis (default) to obtain a single-qudit 4-dimensional QuantumDiscreteState object in the phase space picture:
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= |
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= | 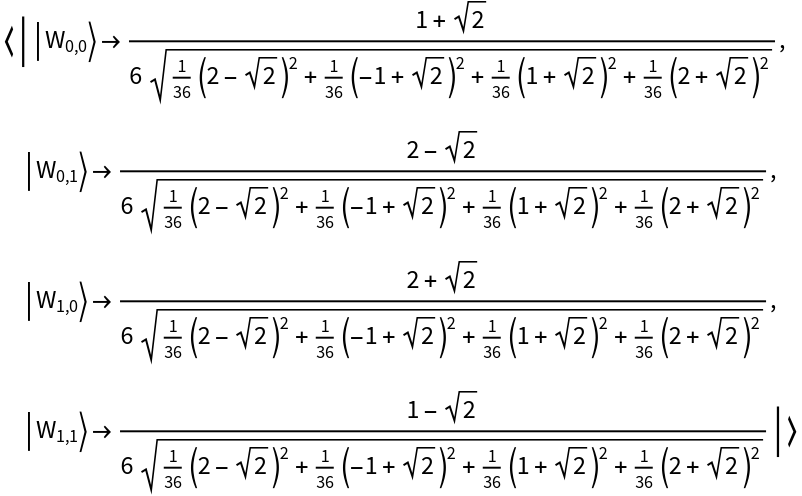 |
Compute the Wigner transform of higher-dimensional quantum objects:
| In[18]:= | ![state = ResourceFunction["QuantumWignerTransform"][
ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteState"][{1, 1 + I, 1 - I}, 3]];
state["Amplitudes"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/be2/be210202-fa19-443f-aea0-1a42043ca75d/4eba24e7ec289aff.png) |
| Out[18]= | 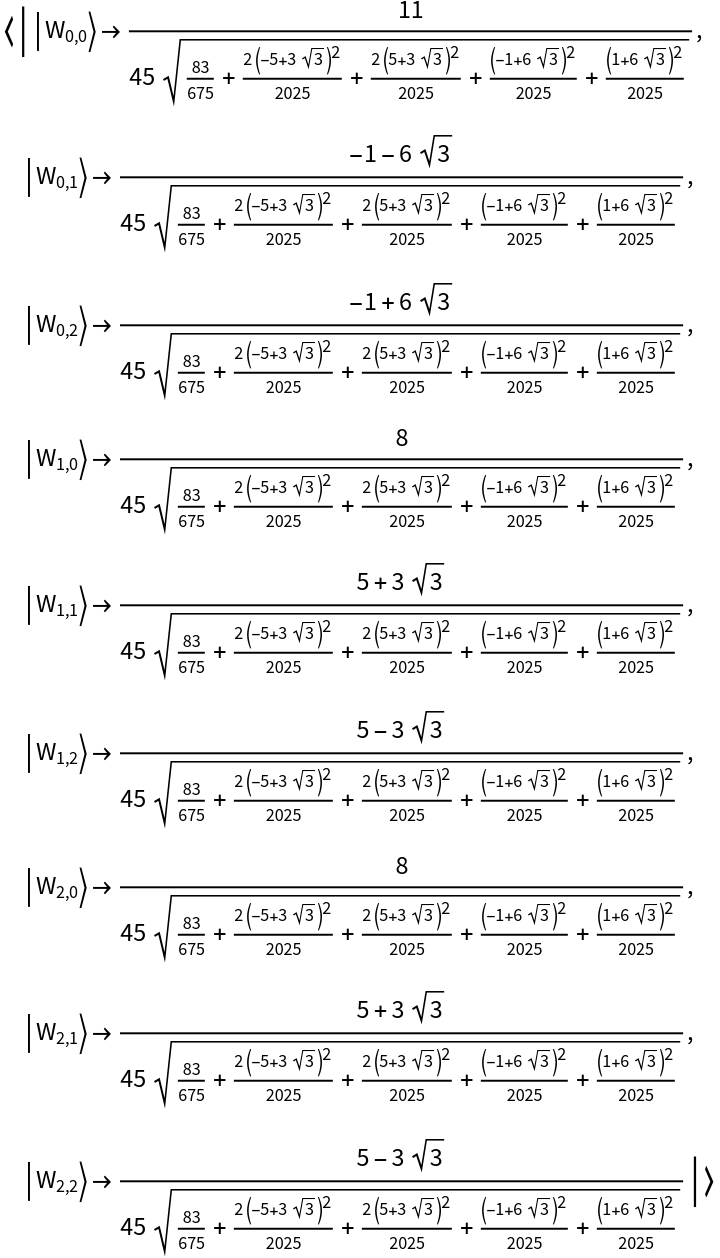 |
| In[19]:= |
| Out[19]= |
Wigner transforms can be computed for quantum objects in arbitrary bases:
| In[20]:= | ![operator = ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteOperator"][
ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteOperator"]["Fourier", {1, 2}], ResourceFunction["QuantumBasis"]["PauliY", 2]];
operator["Basis"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/be2/be210202-fa19-443f-aea0-1a42043ca75d/7f021dd541e15506.png) |
| Out[20]= |
| In[21]:= |
| Out[21]= |
However, the input object must be in either the "Schrodinger", "Heisenberg" or "Interaction" picture. If the input object is already in the "PhaseSpace" picture, then QuantumWignerTransform will not evaluate:
| In[22]:= |
| Out[22]= |
By default, QuantumWignerTransform performs all computations using exact arithmetic:
| In[23]:= | ![operator = ResourceFunction["QuantumWignerTransform"][
ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteOperator"]["Hadamard"]];
operator["Operator"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/be2/be210202-fa19-443f-aea0-1a42043ca75d/42d9b5f06a824b94.png) |
| Out[23]= |
However, in some cases, performance can be improved by using the option "Exact"→False, in which case QuantumWignerTransform performs all computations using numerical approximations instead:
| In[24]:= | ![operator2 = ResourceFunction["QuantumWignerTransform"][
ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteOperator"]["Hadamard"], "Exact" -> False];
operator2["Operator"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/be2/be210202-fa19-443f-aea0-1a42043ca75d/20074ca0744574e3.png) |
| Out[24]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License