Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Perform a spectral decomposition (diagonalization) on a quantum state or operator
ResourceFunction["QuantumSpectralDecomposition"][QuantumDiscreteState[…]] performs a spectral decomposition on the specified QuantumDiscreteState. | |
ResourceFunction["QuantumSpectralDecomposition"][QuantumDiscreteOperator[…]] performs a spectral decomposition on the specified QuantumDiscreteOperator. | |
ResourceFunction["QuantumSpectralDecomposition"][QuantumMeasurementOperator[…]] performs a spectral decomposition on the specified QuantumMeasurementOperator. | |
ResourceFunction["QuantumSpectralDecomposition"][QuantumHamiltonianOperator[…]] performs a spectral decomposition on the specified QuantumHamiltonianOperator. | |
ResourceFunction["QuantumSpectralDecomposition"][QuantumCircuitOperator[…]] performs a spectral decomposition on the specified QuantumCircuitOperator, represented as a QuantumDiscreteOperator. |
Create a two-qubit pure discrete quantum state in the computational basis (default):
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |
Perform a spectral decomposition of the state, resulting in a pure state with a diagonalized density matrix and a new (spectral-decomposed) basis:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
Show the basis elements of the new (spectral-decomposed) basis:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |
Perform a spectral decomposition of a single-qubit mixed discrete quantum state in the computational basis instead, resulting in a mixed state with a diagonalized density matrix:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= |
Show the new (spectral-decomposed) basis:
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |
Perform a spectral decomposition of an arity-2 QuantumDiscreteOperator object, resulting in a QuantumDiscreteOperator object with a diagonalized matrix representation:
| In[14]:= | ![operator = ResourceFunction["QuantumSpectralDecomposition"][
ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteOperator"]["Fourier", {1, 2}]];
operator["Operator"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fcf/fcffb732-eec5-4876-8932-62a361e0b12f/5d8d951c7778a51e.png) |
| Out[14]= |  |
Show the new (spectral-decomposed) basis:
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= |
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= |
Perform a spectral decomposition of an arity-3 projection-valued QuantumMeasurementOperator object, resulting in a projection-valued QuantumMeasurementOperator object with a diagonalized matrix representation:
| In[17]:= | ![measurement = ResourceFunction["QuantumSpectralDecomposition"][
ResourceFunction["QuantumMeasurementOperator"][
"FourierBasis", {1, 2, 3}]];
measurement["MatrixRepresentation"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fcf/fcffb732-eec5-4876-8932-62a361e0b12f/3007f78ca36b84b0.png) |
| Out[17]= |
Show the new (spectral decomposed) basis:
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= |
| In[19]:= |
| Out[19]= | 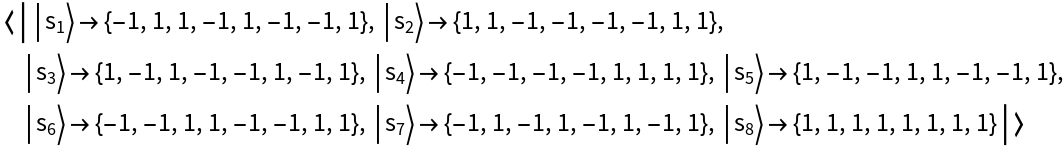 |
Perform a spectral decomposition on an arity-1 QuantumHamiltonianOperator object, resulting in a QuantumHamiltonianOperator object with a diagonalized matrix representation:
| In[20]:= | ![hamiltonian = ResourceFunction["QuantumSpectralDecomposition"][
ResourceFunction[
"QuantumHamiltonianOperator"][{{1 + \[FormalT]^2, 1 - \[FormalT]^2}, {1 - \[FormalT]^2, 1 + \[FormalT]^2}}]];
hamiltonian["Operator"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fcf/fcffb732-eec5-4876-8932-62a361e0b12f/00705f438c2a87b3.png) |
| Out[20]= |
Show the new (spectral-decomposed) basis:
| In[21]:= |
| Out[21]= |
| In[22]:= |
| Out[22]= |
Perform a spectral decomposition of an arity-2 QuantumCircuitOperator object, resulting in a QuantumDiscreteOperator object with a diagonalized matrix representation:
| In[23]:= | ![circuit = ResourceFunction[
"QuantumCircuitOperator"][{ResourceFunction[
"QuantumDiscreteOperator"]["Hadamard", {1}], ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteOperator"]["CNOT", {2, 1}], ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteOperator"]["S", {1}]}];
circuit["Diagram"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fcf/fcffb732-eec5-4876-8932-62a361e0b12f/74094302795e3e88.png) |
| Out[23]= |  |
| In[24]:= |
| Out[24]= |
Show the resulting operator association:
| In[25]:= |
| Out[25]= | 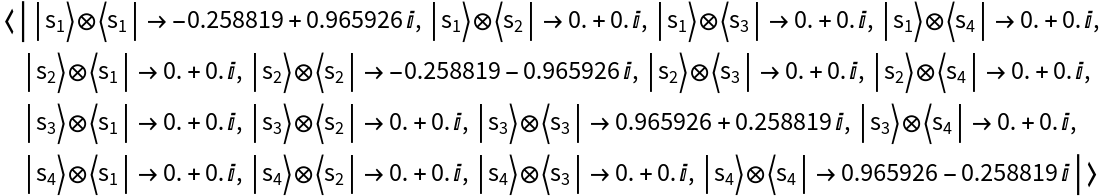 |
Show the new (spectral-decomposed) basis:
| In[26]:= |
| Out[26]= |
| In[27]:= |
| Out[27]= |  |
QuantumSpectralDecomposition can perform spectral decompositions of quantum objects in arbitrary bases:
| In[28]:= | ![operator = ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteOperator"][
ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteOperator"]["CNOT", {1, 2}], ResourceFunction["QuantumBasis"]["PauliX", 2]];
operator["Operator"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fcf/fcffb732-eec5-4876-8932-62a361e0b12f/4cf5700c63e2d87a.png) |
| Out[28]= | 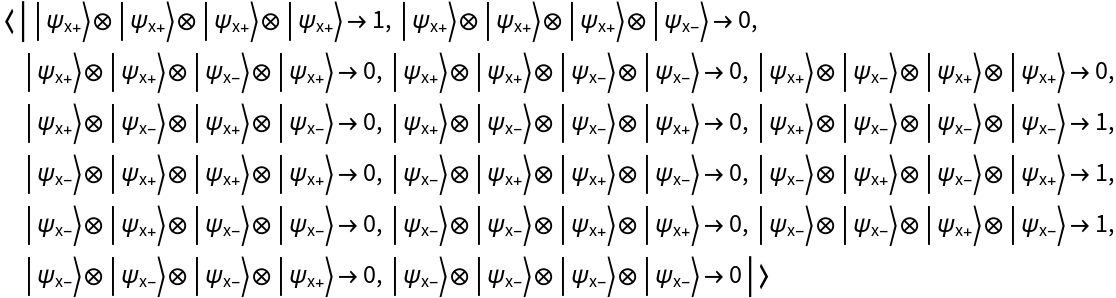 |
| In[29]:= |
| Out[29]= | 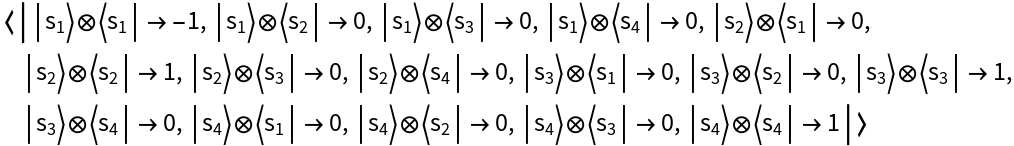 |
| In[30]:= |
| Out[30]= |
Perform spectral decompositions of higher-dimensional quantum objects:
| In[31]:= |
| Out[31]= |
| In[32]:= |
| Out[32]= |
| In[33]:= |
| Out[33]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License