Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Warning: This resource is provisional
Function Repository Resource:
Compute a variety of integral transforms on input expressions
ResourceFunction["GenericIntegralTransform"][f,z,t,transform] gives the integral transform 𝒯transform[f(z)](t) of the input function f(z), in terms of new variable t. | |
ResourceFunction["GenericIntegralTransform"][] prints a table of all available transforms and their definitions. | |
ResourceFunction["GenericIntegralTransform"][patt] prints a table of available transforms whose names match the string pattern patt. | |
ResourceFunction["GenericIntegralTransform"][…, form] prints a table of transforms with definitions displayed in the specified form. |
| GenerateConditions | False | whether to provide conditions under which the given result is valid |
| "FoxHForm" | False | whether to provide results (where possible) in terms of the FoxH function |
| Fourier transform | "Fourier" | "FourierExp" | |
| Fourier cosine transform | "FourierCos" | |
| Fourier sine transform | "FourierSin" | |
| G-transform | ||
| Hankel transform | {"Hankel",ν} | |
| Hankel transform with Power | {"Hankel",ν,α} | |
| Hartley tranform | "Hartley" | |
| Hilbert transform | "Hilbert" | |
| Hilbert transform with Power | {"Hilbert",α} | |
| Integrate transform | "Integrate" | |
| Integrate transform with Power | {"Integrate",α} | |
| Laplace transform | "Laplace" | |
| Laplace transform with Power | {"Laplace",α} | |
| Laplace transform (2‐sided) | "LaplaceTwoSided" | |
| Mellin transform | "Mellin" | |
| Mellin transform with Power | {"Mellin",α} | |
| Neumann transform | {"Neumann”, ν} | |
| Neumann transform with Power | {"Neumann”, ν,α} | |
| Riesz transform | {"Riesz”, α} | |
| Stieltjes transform | {"Stieltjes”, ρ} | |
| Struve transform | {“Struve”, ν} | |
| Struve transform with Power | {"Struve”, ν,α} | |
| Weyl transform | {“Weyl”, α} |
Compute the Mellin transform of a Bessel function:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
Compute the Mellin transform of an exponential function:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
Get the conditions of convergence for when the result above is valid:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |
Generically, the result returned is a ConditionalExpression. The conditions under which this result holds can be expanded by clicking the “+“, followed by “Uniconize”, or simply by examining the InputForm:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= | 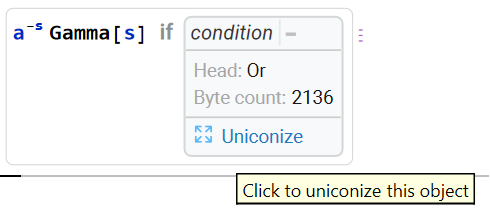 |
| In[5]:= | ![ConditionalExpression[
a^-s Gamma[
s], (Abs[Arg[a]] <= \[Pi]/2 && Re[s] < 1 && Re[s] + Inactive[Max][{}] < 1 && Re[s] + Inactive[Min][{0}] > 0) || (Abs[Arg[a]] < \[Pi]/2 && Re[s] + Inactive[Max][{}] < 1 && Re[s] + Inactive[Min][{0}] > 0)] \[AliasDelimiter]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/2f5/2f5a9641-7e13-420a-8017-969f8b0cc948/5525eb8bc381edb7.png) |
Compute the Laplace transform of a cosine. By default, GenericIntegralTransform gives results in terms of an Inactive MeijerG function:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
Use Activate to allow the Inactive[MeijerG] to evaluate to elementary functions:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |
Compute the Hankel transform of an arctangent:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
To evaluate in terms of simpler functions, use Activate and FunctionExpand:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= | 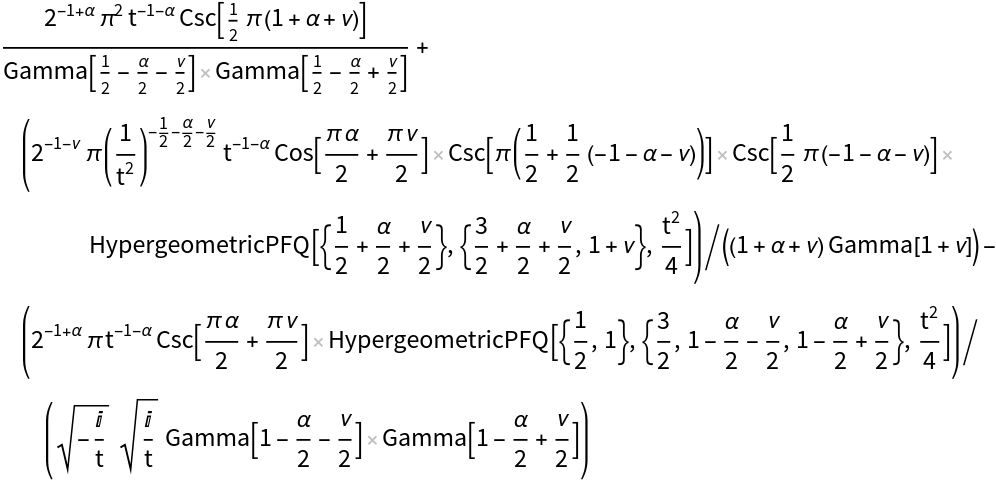 |
Some results are available in terms of the FoxH function. To return this form where possible, use the "FoxHForm" option:
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
Get a table of all available transforms, with definitions in TraditionalForm:
| In[11]:= |

List all transforms starting with the character "H", with definitions given in InputForm:
| In[12]:= |

Compute the G-transform of a sine:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |
Get the result in terms of FoxH:
| In[14]:= |
| Out[14]= |
Compute the Hankel transform of a sine:
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= |
Get the result in terms of FoxH:
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= |
Compute the Hilbert transform of a sine:
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= |
Get the result in terms of FoxH:
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= |
Compute the "Integrate transform" of a sine:
| In[19]:= |
| Out[19]= |
Get the result in terms of FoxH:
| In[20]:= |
| Out[20]= |
Compute the Laplace transform of a sine:
| In[21]:= |
| Out[21]= |
Get the result in terms of FoxH:
| In[22]:= |
| Out[22]= |
Compute the Liousville transform of a sine:
| In[23]:= |
| Out[23]= |
Get the result in terms of FoxH:
| In[24]:= |
| Out[24]= |
Compute the Meijer transform of a sine:
| In[25]:= |
| Out[25]= |
Get the result in terms of FoxH:
| In[26]:= |
| Out[26]= |
Compute the Mellin transform of a sine:
| In[27]:= |
| Out[27]= |
A result in terms of FoxH is not available:
| In[28]:= |
| Out[28]= |
Compute the Mellin transform of BesselJ:
| In[29]:= |
| Out[29]= |
Compute the Neumann transform of a sine:
| In[30]:= |
| Out[30]= |
Get the result in terms of FoxH:
| In[31]:= |
| Out[31]= | 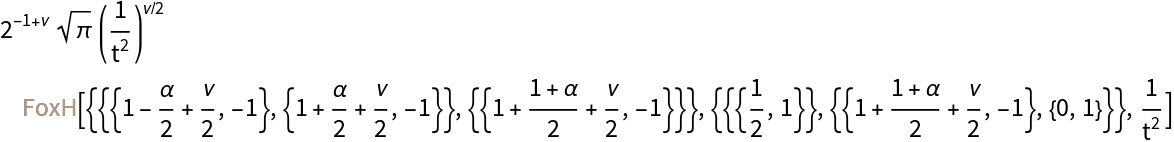 |
Compute the Riesz transform of a sine:
| In[32]:= |
| Out[32]= | 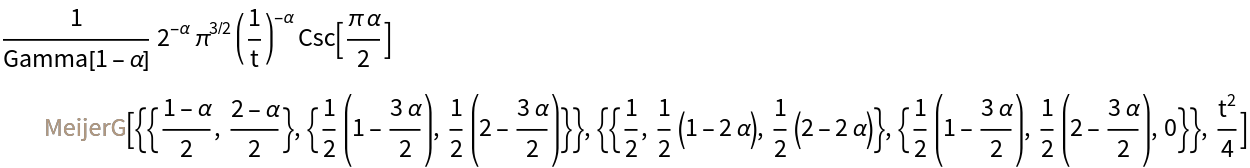 |
Get the result in terms of FoxH:
| In[33]:= |
| Out[33]= |
Compute the Stieltjes transform of a sine:
| In[34]:= |
| Out[34]= |
Get the result in terms of FoxH:
| In[35]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"GenericIntegralTransform", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Sin[z], z, t, {"Stieltjes", \[Rho]}, GenerateConditions -> False, "FoxHForm" -> True]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/2f5/2f5a9641-7e13-420a-8017-969f8b0cc948/1eb010c0a359da70.png) |
| Out[35]= |
Compute the Struve transform of a sine:
| In[36]:= |
| Out[36]= |
Get the result in terms of FoxH:
| In[37]:= |
| Out[37]= |  |
Compute a G-transform of a BesselY function:
| In[38]:= |
| Out[38]= |
Get the result instead in terms of FoxH:
| In[39]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"GenericIntegralTransform", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][
BesselY[\[Nu], z], z, t, {"G", {{{}, {\[Alpha]}}, {{0}, {}}}}, GenerateConditions -> False, "FoxHForm" -> True]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/2f5/2f5a9641-7e13-420a-8017-969f8b0cc948/62586ce7a28e2f06.png) |
| Out[39]= |
The default setting GenerateConditions→False returns a result only, without regard to conditions of convergence:
| In[40]:= |
| Out[40]= |
With GenerateConditions→True, the result can be a ConditionalExpression whose second part gives the conditions of convergence:
| In[41]:= |
| Out[41]= | 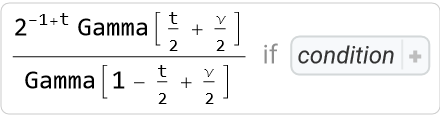 |
| In[42]:= |
| Out[42]= |
| In[43]:= |
| Out[43]= |
Wolfram Language 13.0 (December 2021) or above
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License