Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Visualize the 3D appearance of planets and moons in our solar system
ResourceFunction["TelescopeView3D"][target] display a 3D view of target as observed from your current location at the current time. | |
ResourceFunction["TelescopeView3D"][target,date] display a 3D view of target as observed from your current location on the specified date. | |
ResourceFunction["TelescopeView3D"][target,loc] display a 3D view of target as observed from loc at the current time. | |
ResourceFunction["TelescopeView3D"][target,date,loc] display a 3D view of target as observed from loc on the specified date. |
| "FieldWidth" | Automatic | angular width of the observation field |
| "IncludeSaturnRings" | Automatic | whether to render Saturn's rings |
| "IncludeTextures" | True | whether to include textures on supporting bodies |
| "PointsOfInterest" | {} | locations to be labeled on the target |
| "SatelliteLabels" | False | whether to include text labesl for natural satellites |
| "SatelliteScalingFactor" | 1 | scaling factor for rendering natural satellites for visibility |
| "SatellitesToInclude" | Automatic | additional natural satellites to include in the scene |
| "PointsOfInterestStyle" | "LabeledPoint" | how to render the points of interest locations |
| "Callout" | callout |
| "Point" | red point |
| "Tooltip" | red point with a tooltip |
| “LabeledPoint” | labeled point |
| {"LabeledPoint", style} | labeled point with the specified style |
| {"Point", style} | point with the specified style |
| {"Tooltip”, style} | tooltipped point with the specified style |
Visualize the face of Mars currently visible from Earth:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |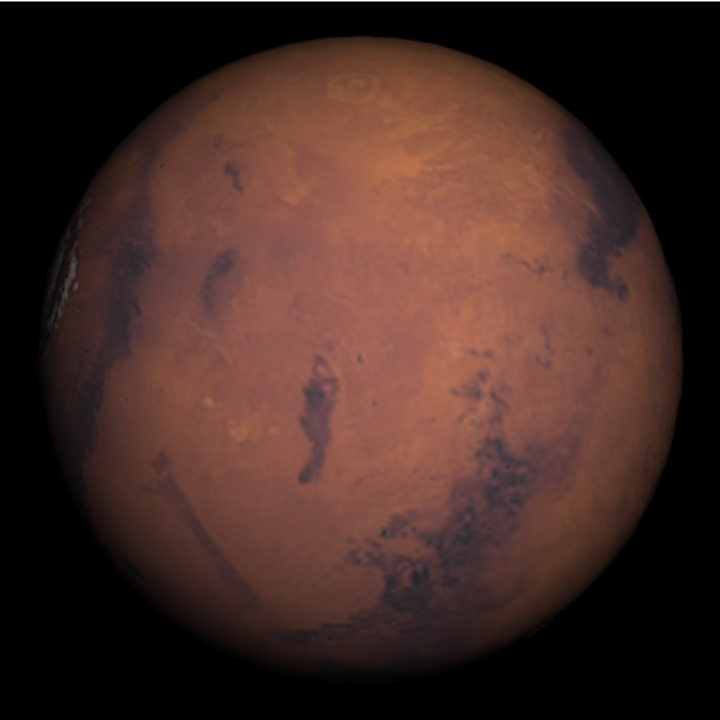  |
Visualize the face of Jupiter visible from Earth on a specific date, including the position of the Great Red Spot:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 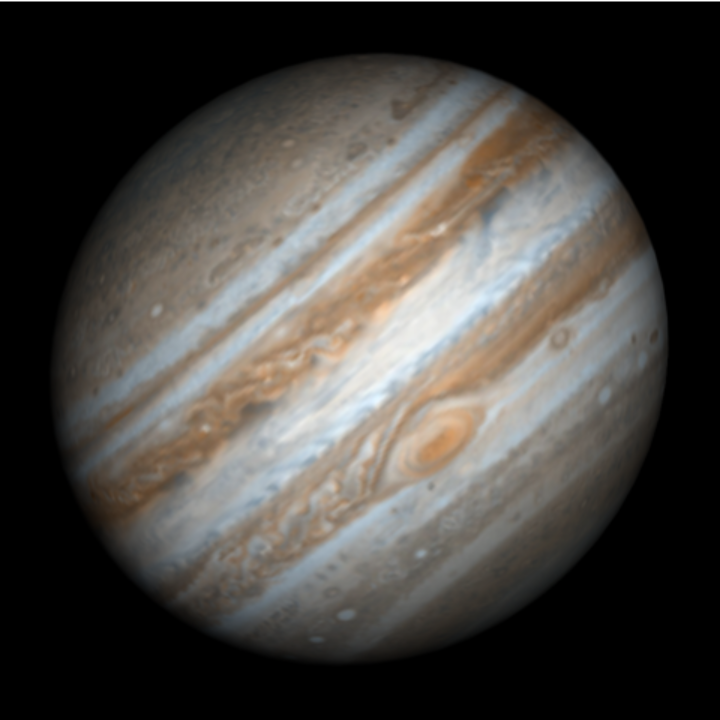 |
Visualize the appearance of the Moon as seen from Earth on a specific date:
| In[3]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Moon"], DateObject[{2023, 3, 31, 3, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "America/Chicago"], GeoPosition[{40.11, -88.22}]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/74ad84e9947fa759.png) |
| Out[3]= |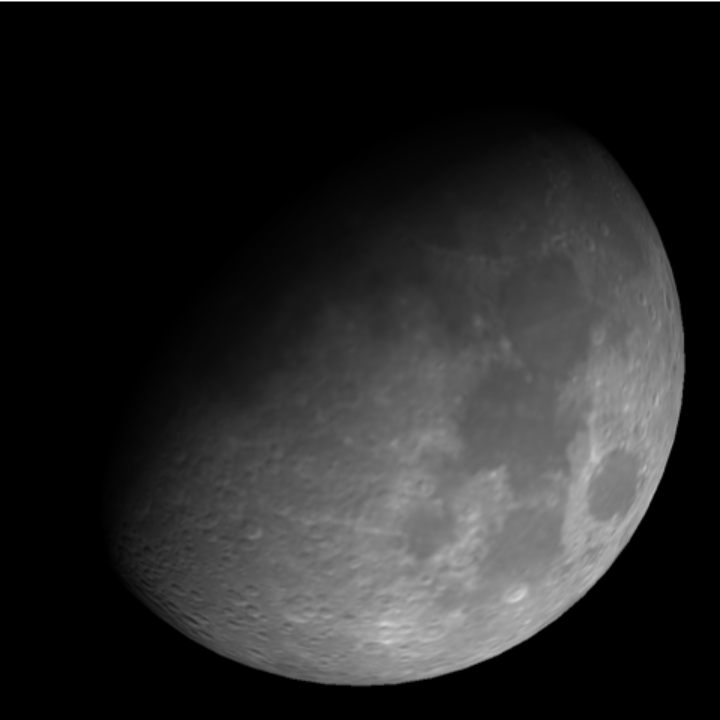  |
Use "FieldWidth" to zoom into a target:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= | 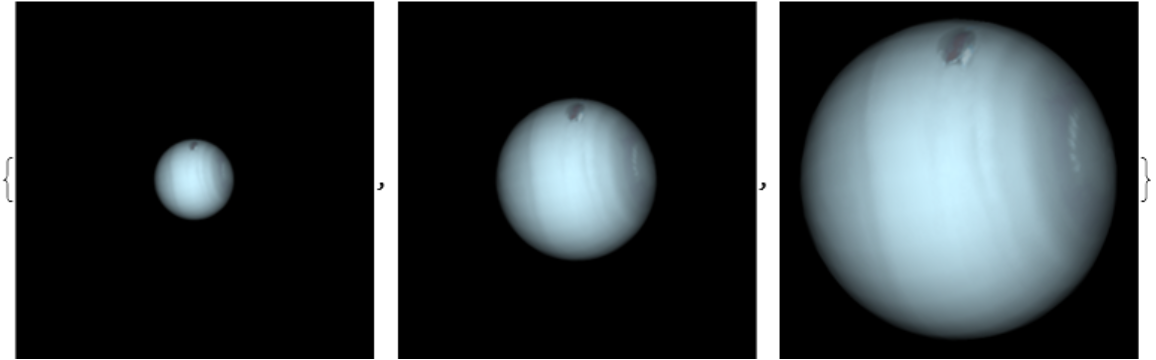 |
View Jupiter's moon Io as seen from the Amergin crater near the equator of Jupiter's moon Europa:
| In[5]:= |
| In[6]:= |
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= | 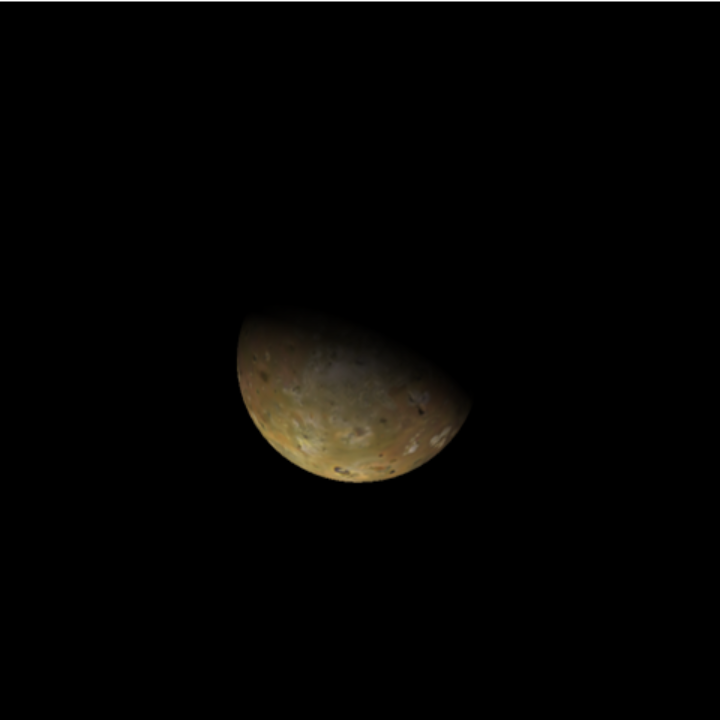 |
Re-orient the camera so that the north ecliptic pole is up:
| In[8]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Io"], date, origin, "FieldWidth" -> Quantity[.01, "Radians"], ViewVertical -> AstroPosition["NorthEclipticPole", {"ICRS", date, origin}, "Cartesian"]["Data"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/10bca23cae2a7f26.png) |
| Out[8]= |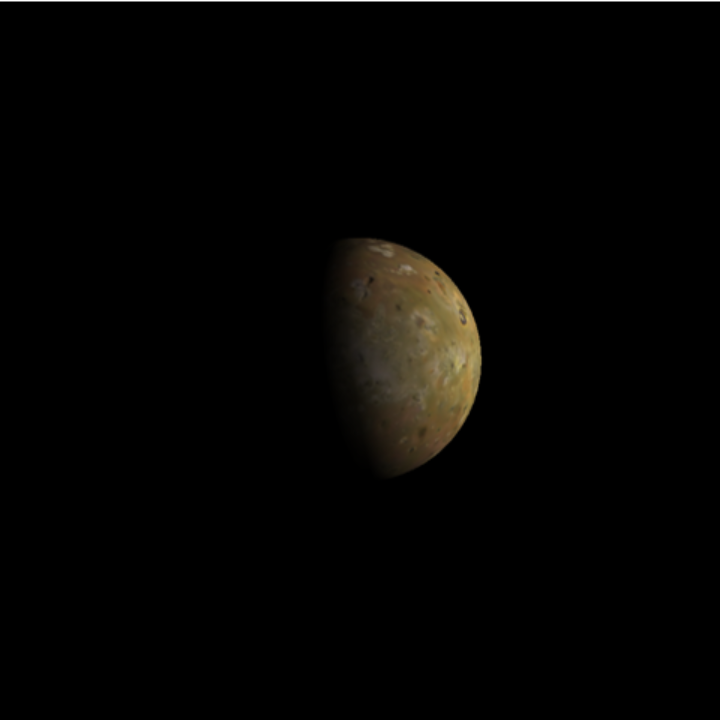  |
By default, Saturn includes the rings:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= | 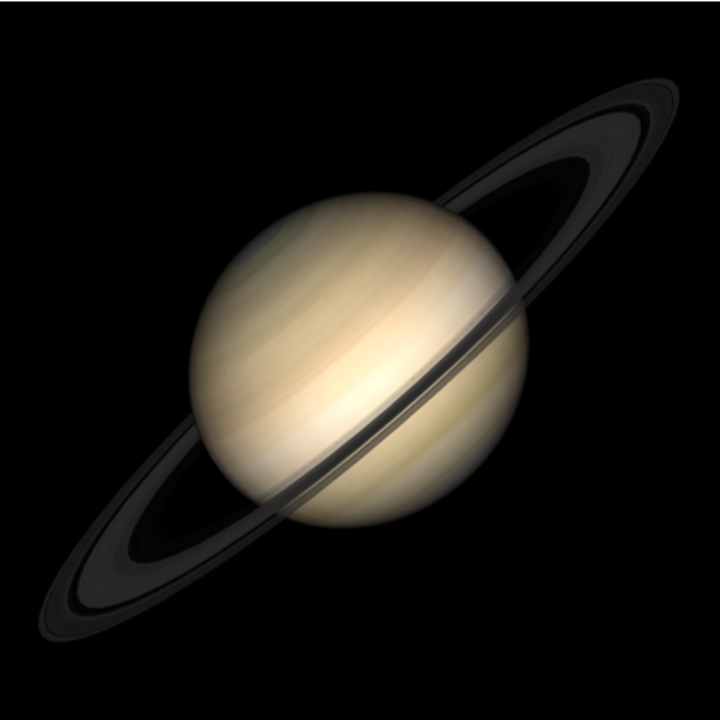 |
For faster rendering, the rings can be turned off:
| In[10]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Saturn"], DateObject[{2023, 3, 4, 10, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "America/Chicago"], "FieldWidth" -> Quantity[30, "Arcseconds"], "IncludeSaturnRings" -> False]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/6e28bfe4bdefb01c.png) |
| Out[10]= |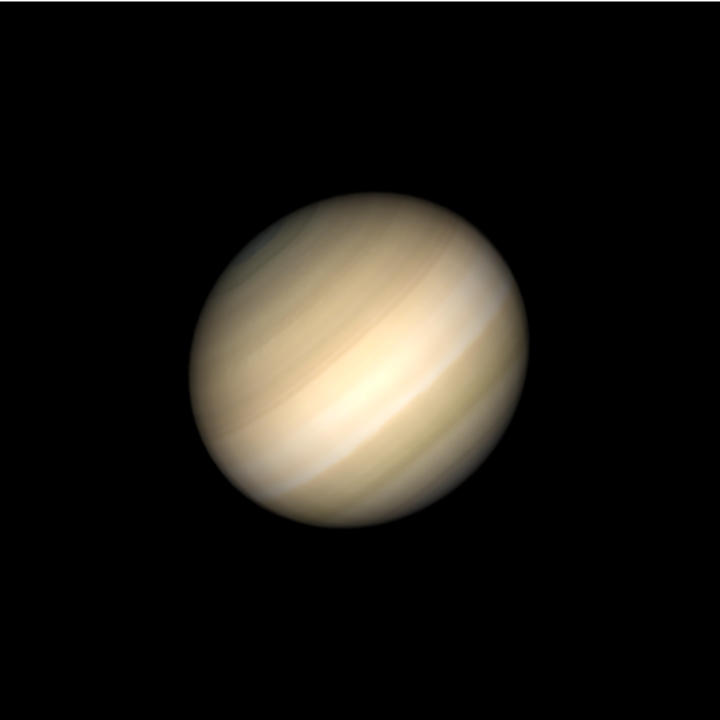  |
View the Earth and Moon from Olympus Mons on Mars:
| In[11]:= |
Turn off the textures for Earth and the Moon so that their dark textures don't make it hard to see them:
| In[12]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Earth"], DateObject[{2023, 3, 6, 17, 23, 58.7402054`}, "Instant", "Gregorian", -6.`], origin, "FieldWidth" -> Quantity[.25, "AngularDegrees"], "SatelliteScalingFactor" -> 2, "IncludeTextures" -> False]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/3a1eb095fbc333e6.png) |
| Out[12]= |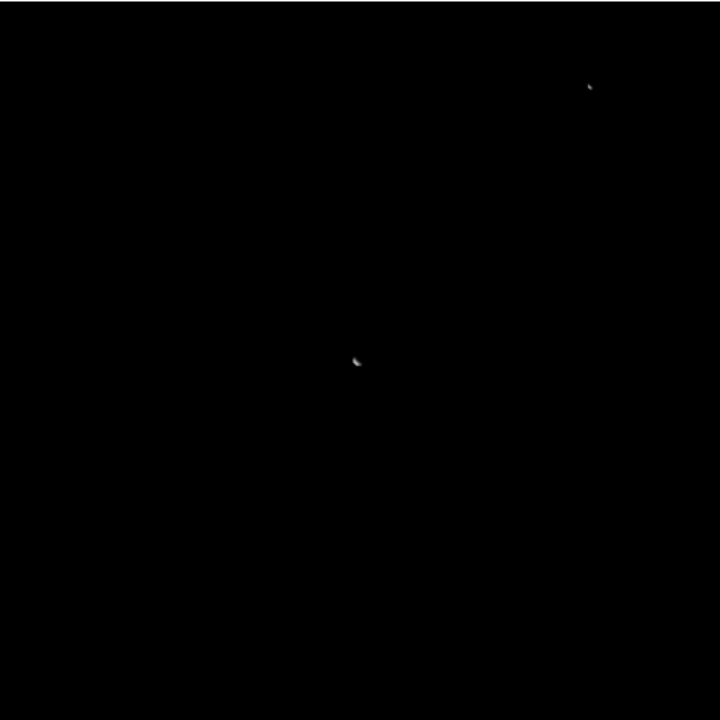  |
Visualize Mars and include both of its moons:
| In[13]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Mars"], DateObject[{2023, 3, 3, 23, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "America/Chicago"], "FieldWidth" -> Quantity[0.5, "Arcminutes"], "SatellitesToInclude" -> EntityClass["PlanetaryMoon", "MarsMoon"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/6d6186f6b479141a.png) |
| Out[13]= |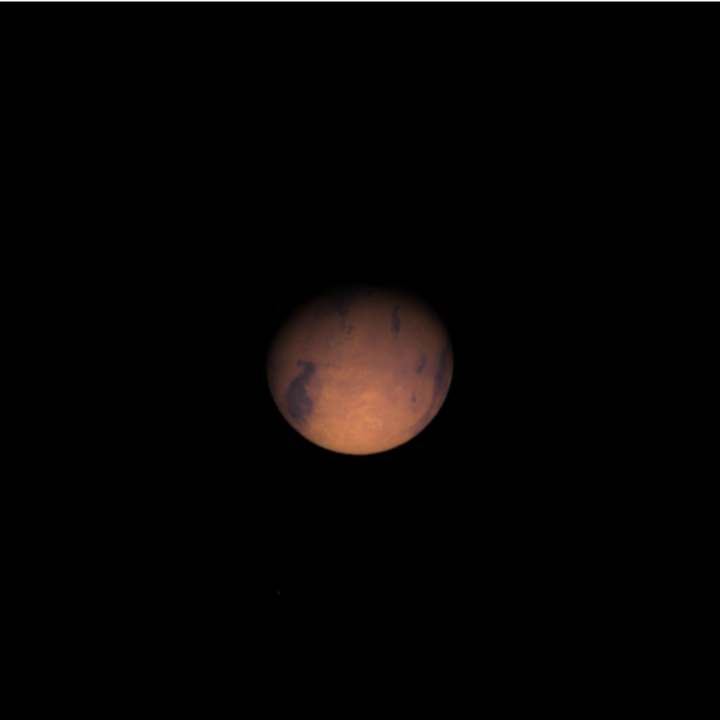  |
Enlarge the moons for better visibility:
| In[14]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Mars"], DateObject[{2023, 3, 3, 23, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "America/Chicago"], "FieldWidth" -> Quantity[0.5, "Arcminutes"], "SatellitesToInclude" -> EntityClass["PlanetaryMoon", "MarsMoon"], "SatelliteScalingFactor" -> 20]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/0a0e2128dc05bce9.png) |
| Out[14]= |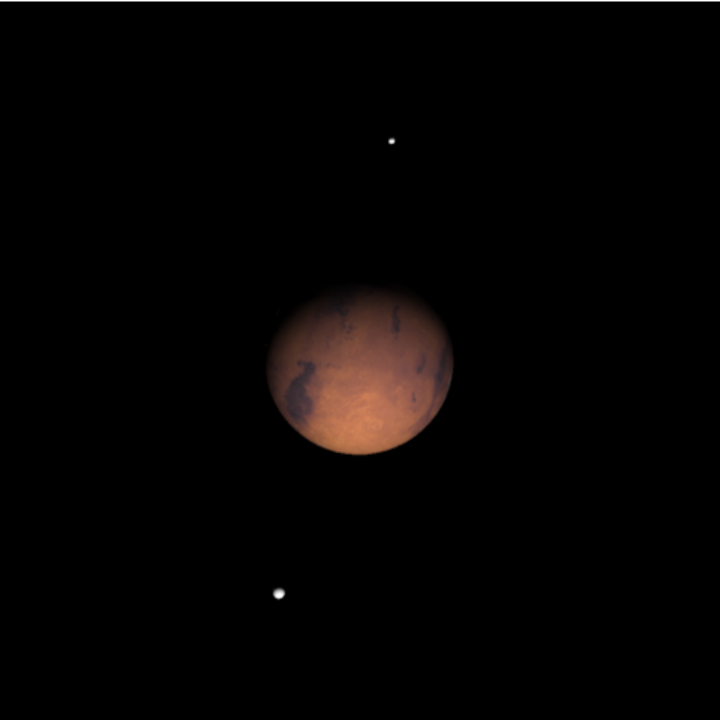  |
Label the moons:
| In[15]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Mars"], DateObject[{2023, 3, 3, 23, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "America/Chicago"], "FieldWidth" -> Quantity[0.5, "Arcminutes"], "SatellitesToInclude" -> EntityClass["PlanetaryMoon", "MarsMoon"], "SatelliteScalingFactor" -> 20, "SatelliteLabels" -> True]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/4a4b703bffe872e9.png) |
| Out[15]= |  |
Label features that are visible on Mars:
| In[16]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Mars"], DateObject[{2023, 5, 15, 15, 16, 44.104283452034`}, "Instant", "Gregorian", -5.`], "PointsOfInterest" -> {Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "OlympusMonsMars"]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/56adb49cce8a1007.png) |
| Out[16]= |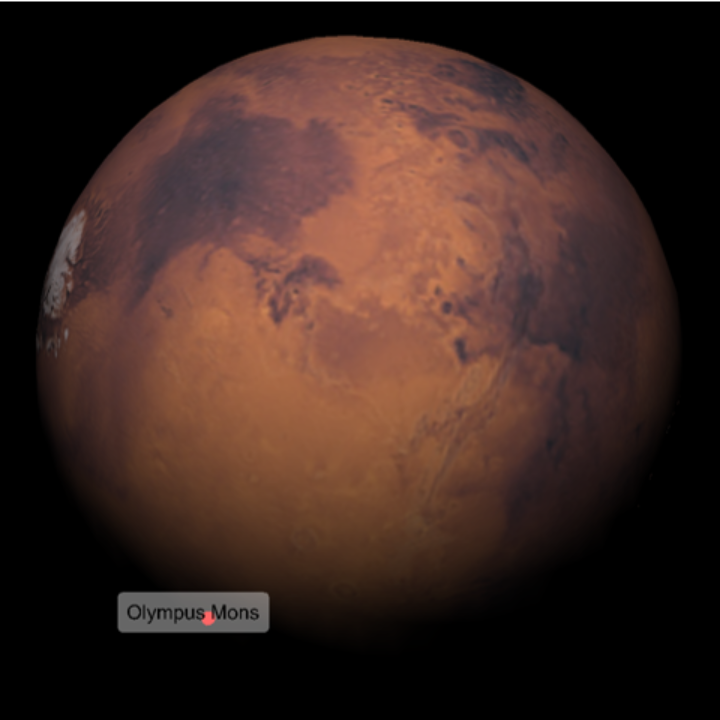  |
| In[17]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Mars"], DateObject[{2023, 5, 1, 8, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "America/Chicago"], "PointsOfInterest" -> {Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "OlympusMonsMars"],
Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "ArsiaMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "PavonisMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "AscraeusMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "VallesMarinerisMars"]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/20bde50f76a419b4.png) |
| Out[17]= | 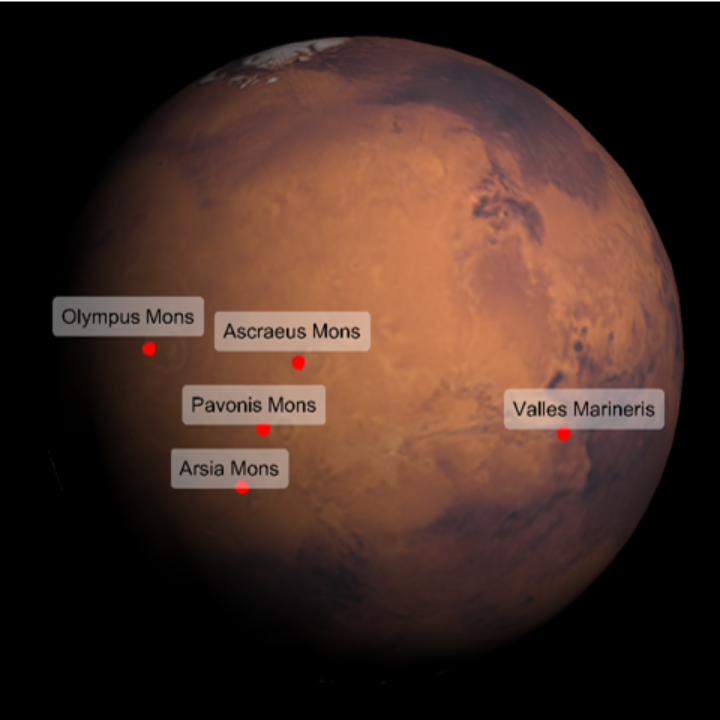 |
Label features on the Moon:
| In[18]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Moon"], DateObject[{2023, 4, 5, 0, 0, 0}, TimeZone -> "America/Chicago"], "PointsOfInterest" -> {Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "MareTranquillitatisMoon"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "CopernicusMoon"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "TychoMoon"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "MareSerenitatisMoon"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "MareImbriumMoon"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "MareNubiumMoon"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "MareFrigorisMoon"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "MareCrisiumMoon"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "MareCognitumMoon"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "MontesApenninusMoon"]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/5a9590d5d9ee6176.png) |
| Out[18]= |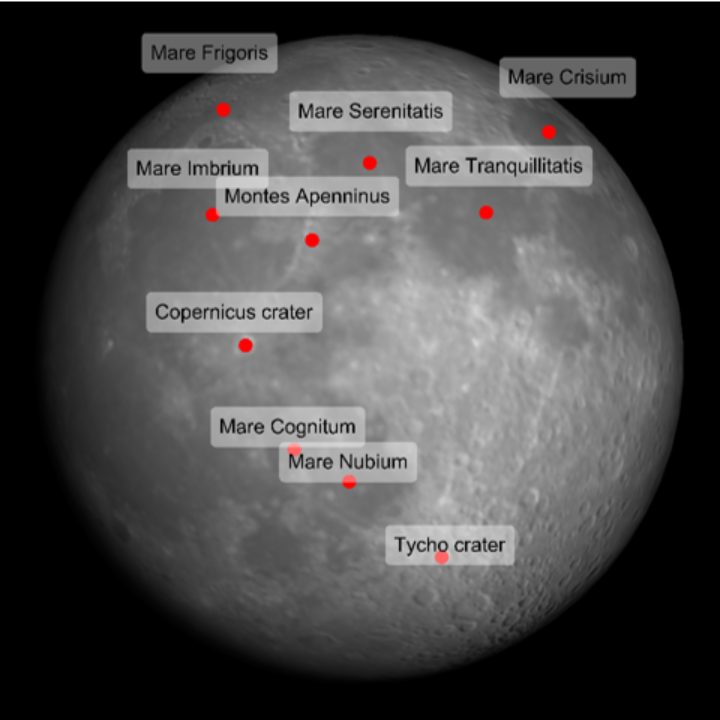  |
Label features on Io:
| In[19]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Io"], DateObject[{2023, 4, 1, 20, 0, 0}, TimeZone -> "America/Chicago"], "PointsOfInterest" -> {Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "LokiPateraIo"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "BabbarPateraIo"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "PeleIo"]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/0587f44cf6053e5d.png) |
| Out[19]= | 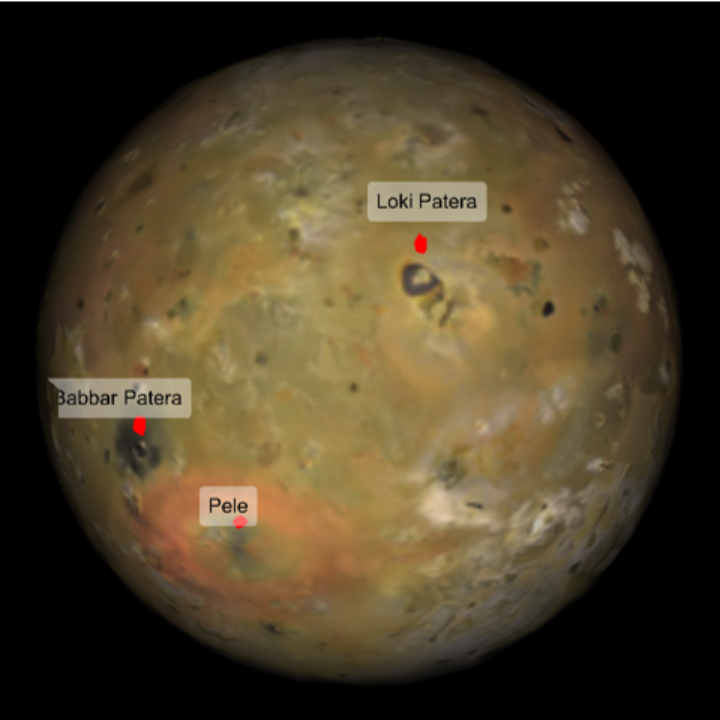 |
| In[20]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Mars"], DateObject[{2023, 5, 1, 8, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "America/Chicago"], "PointsOfInterest" -> {Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "OlympusMonsMars"],
Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "ArsiaMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "PavonisMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "AscraeusMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "VallesMarinerisMars"]}, "PointsOfInterestStyle" -> "Callout"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/3f9bf72ad6c2123b.png) |
| Out[20]= |  |
| In[21]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Mars"], DateObject[{2023, 5, 1, 8, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "America/Chicago"], "PointsOfInterest" -> {Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "OlympusMonsMars"],
Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "ArsiaMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "PavonisMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "AscraeusMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "VallesMarinerisMars"]}, "PointsOfInterestStyle" -> "LabeledPoint"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/77d2f54d6642feae.png) |
| Out[21]= | 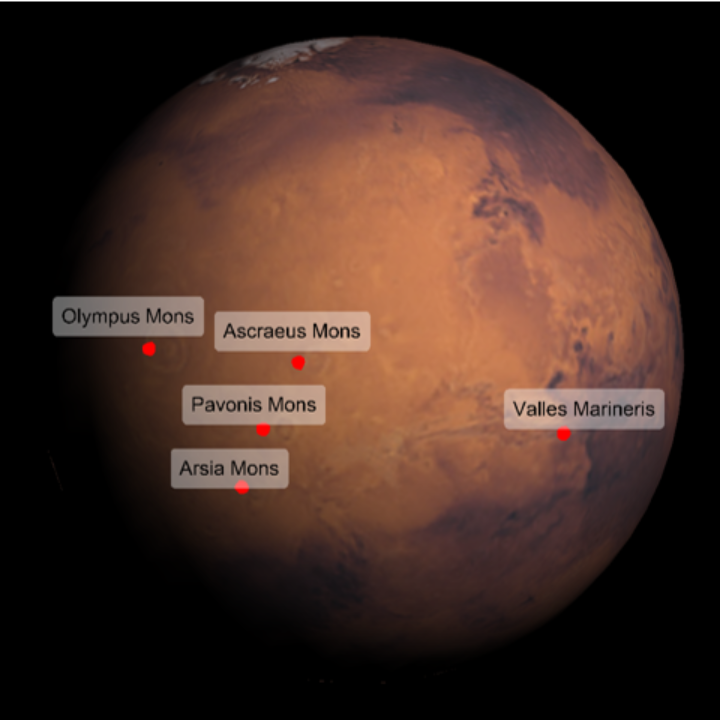 |
| In[22]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Mars"], DateObject[{2023, 5, 1, 8, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "America/Chicago"], "PointsOfInterest" -> {Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "OlympusMonsMars"],
Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "ArsiaMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "PavonisMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "AscraeusMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "VallesMarinerisMars"]}, "PointsOfInterestStyle" -> {"Point", Red, PointSize[.02]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/75e005b07693ae1a.png) |
| Out[22]= |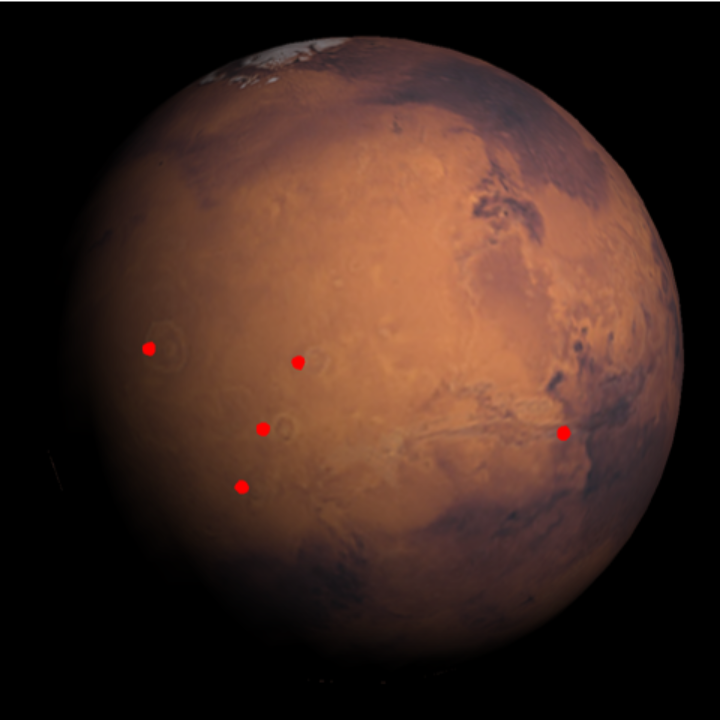  |
| In[23]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Mars"], DateObject[{2023, 5, 1, 8, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "America/Chicago"], "PointsOfInterest" -> {Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "OlympusMonsMars"],
Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "ArsiaMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "PavonisMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "AscraeusMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "VallesMarinerisMars"]}, "PointsOfInterestStyle" -> "Tooltip"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/5691c410c0b1bd85.png) |
| Out[23]= |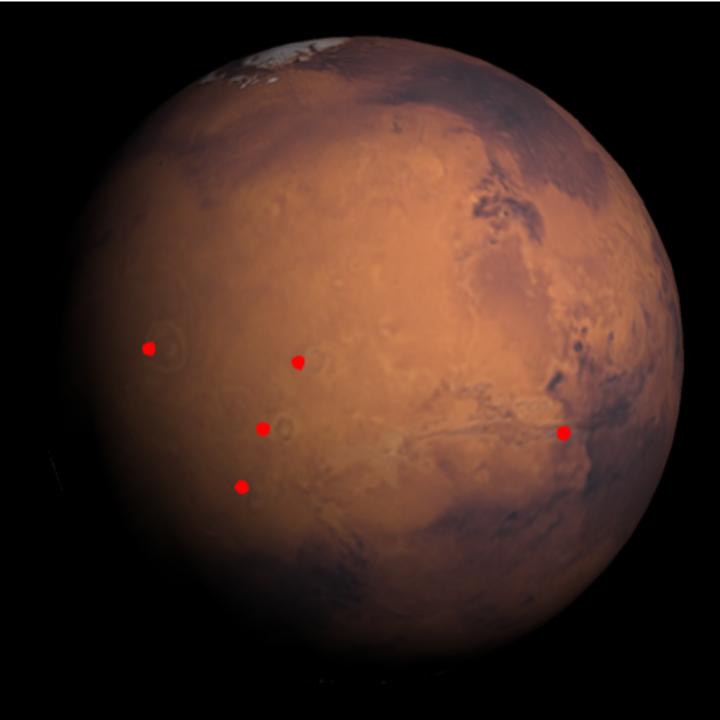  |
| In[24]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Mars"], DateObject[{2023, 5, 1, 8, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "America/Chicago"], "PointsOfInterest" -> {Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "OlympusMonsMars"],
Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "ArsiaMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "PavonisMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "AscraeusMonsMars"], Entity["SolarSystemFeature", "VallesMarinerisMars"]}, "PointsOfInterestStyle" -> {"LabeledPoint", Directive[Blue, PointSize[.01]]}, LabelStyle -> Blue]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/5926ffdadfd35950.png) |
| Out[24]= | 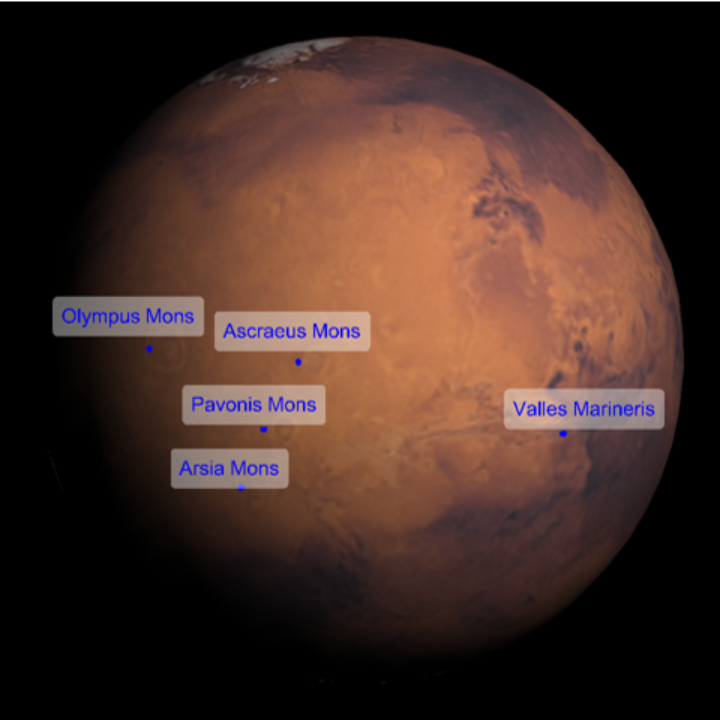 |
Show the appearance of Mars at 10 PM local time:
| In[25]:= |
| Out[25]= | 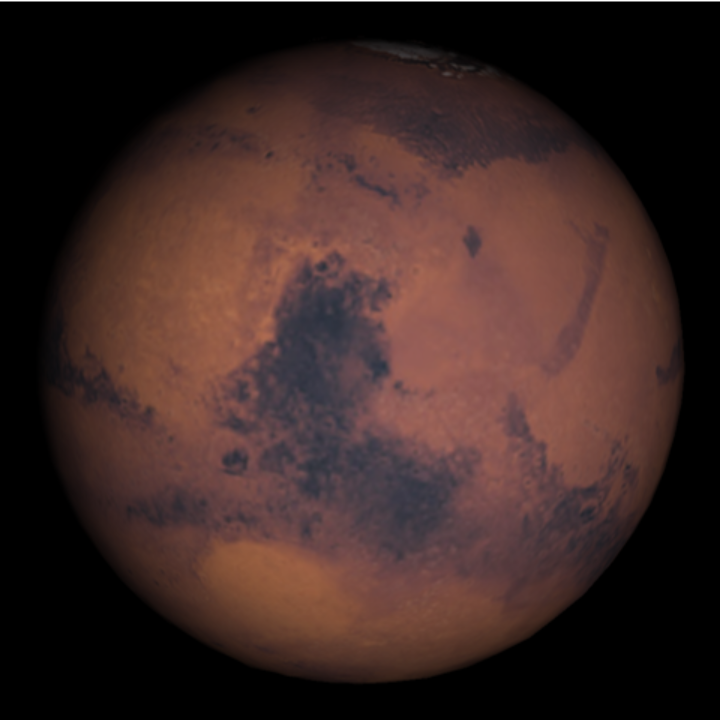 |
Simulate the occultation of Mars by the Moon:
| In[26]:= |
| Out[26]= |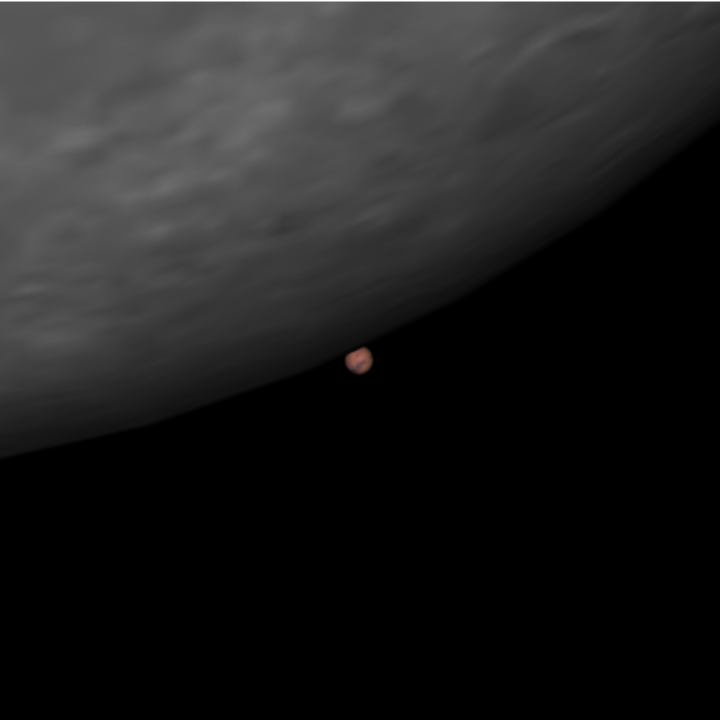  |
Simulate Neptune being occulted by Mercury as observed at the North Pole of the Earth:
| In[27]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Mercury"], DateObject[{2067, 7, 15, 11, 53, 30}, "Instant", "Gregorian", 0.`], GeoPosition[{90, 0}], "FieldWidth" -> Quantity[20, "Arcseconds"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/31ad496ecdb13be8.png) |
| Out[27]= |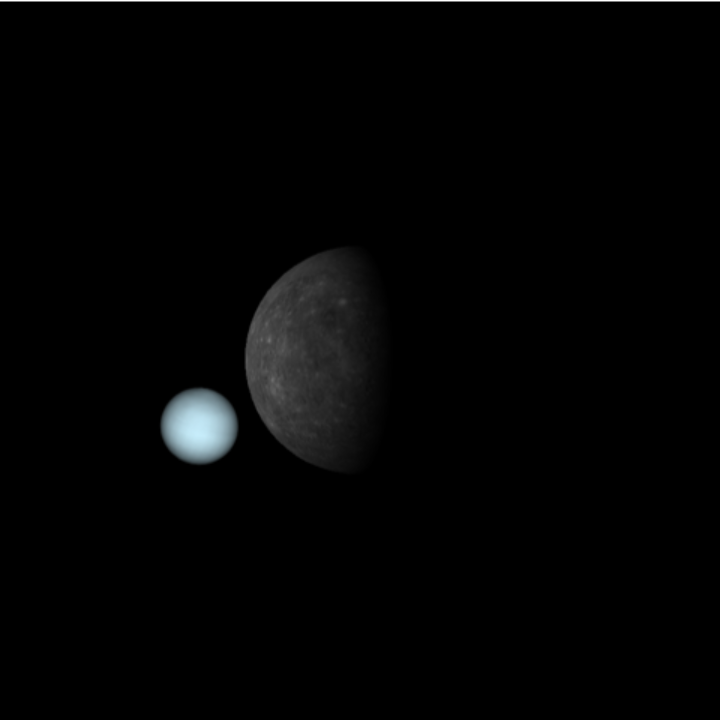  |
Reproduce the observations of Galileo on Jan 8, 1610:
| In[28]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Jupiter"], DateObject[{1610, 1, 8, 18, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "Europe/Rome"], Entity["City", {"Padova", "Veneto", "Italy"}], "FieldWidth" -> Quantity[0.4, "AngularDegrees"], "SatellitesToInclude" -> EntityClass["PlanetaryMoon", "GalileanMoon"],
"SatelliteScalingFactor" -> 10]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/506b32210a6f5f05.png) |
| Out[28]= |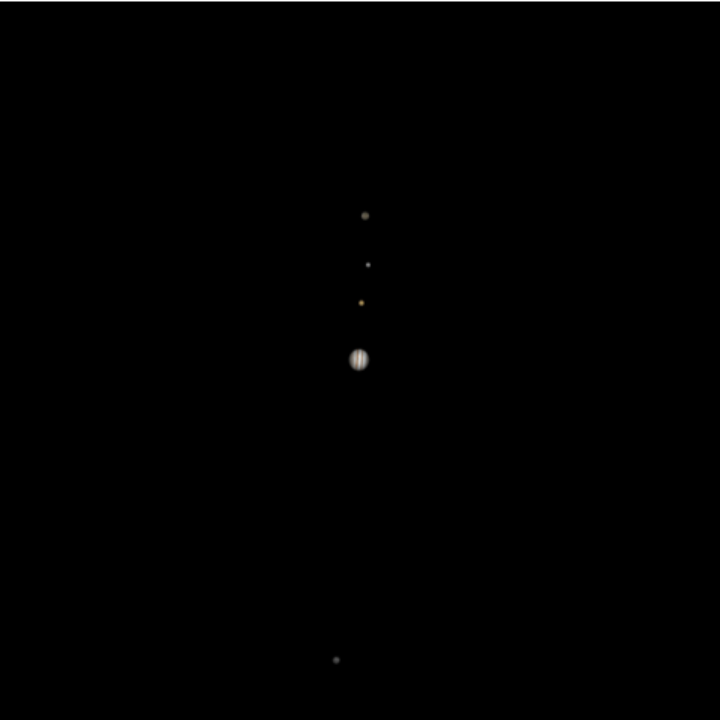  |
Explore the positions of some of Saturn's small moons near the rings:
| In[29]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Prometheus"], DateObject[{2022, 11, 21, 1, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "America/Chicago"], "FieldWidth" -> Quantity[20, "Arcseconds"], "SatelliteLabels" -> True, "SatelliteScalingFactor" -> 10, "SatellitesToInclude" -> {Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Atlas"], Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Pan"], Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Prometheus"], Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Pandora"], Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Telesto"]}, "IncludeSaturnRings" -> True]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/3c7425b20618a986.png) |
| Out[29]= | 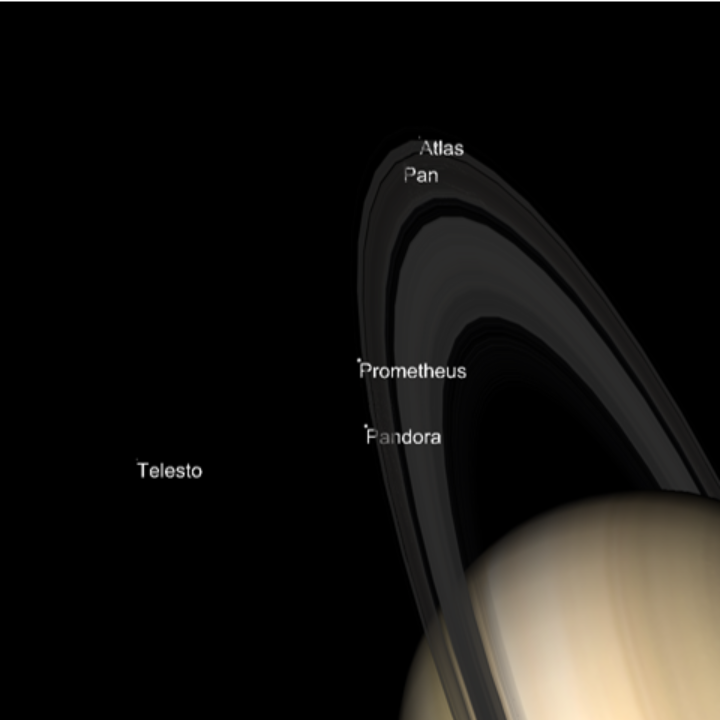 |
Explore a typical backyard telescopic view of Saturn's larger moons:
| In[30]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Saturn"], DateObject[{2022, 11, 21, 1, 0, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", "America/Chicago"], "FieldWidth" -> Quantity[6, "Arcminutes"], "SatelliteScalingFactor" -> 10, "SatellitesToInclude" -> {Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Titan"], Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Rhea"], Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Tethys"],
Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Dione"], Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Enceladus"], Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Mimas"]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/23bc8128a2403e98.png) |
| Out[30]= |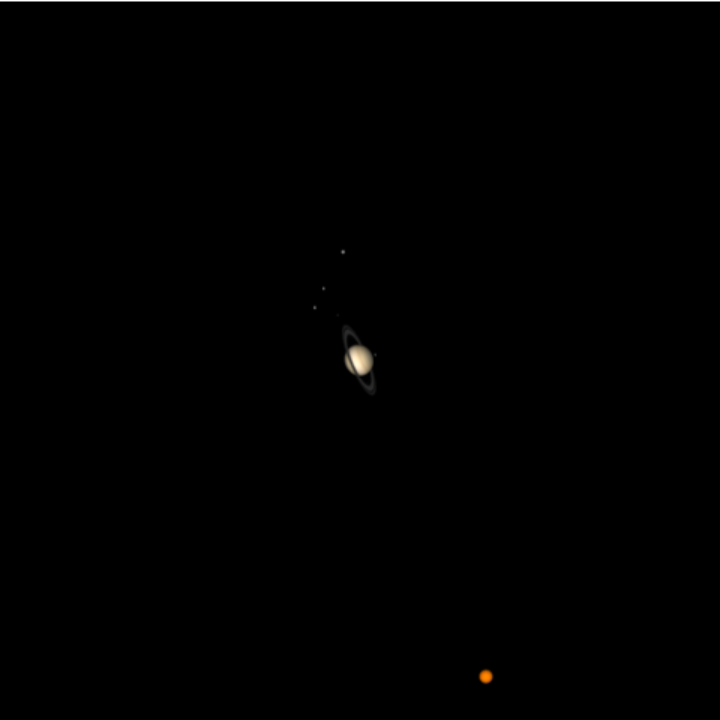  |
Recreate an occultation of Saturn by Venus in 1771:
| In[31]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Saturn"], DateObject[{1771, 8, 29, 19, 38, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", 0.`], GeoPosition[{-26.19, 28.04}], "FieldWidth" -> Quantity[40, "Arcseconds"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/7d5abaf5da3ef4e2.png) |
| Out[31]= | 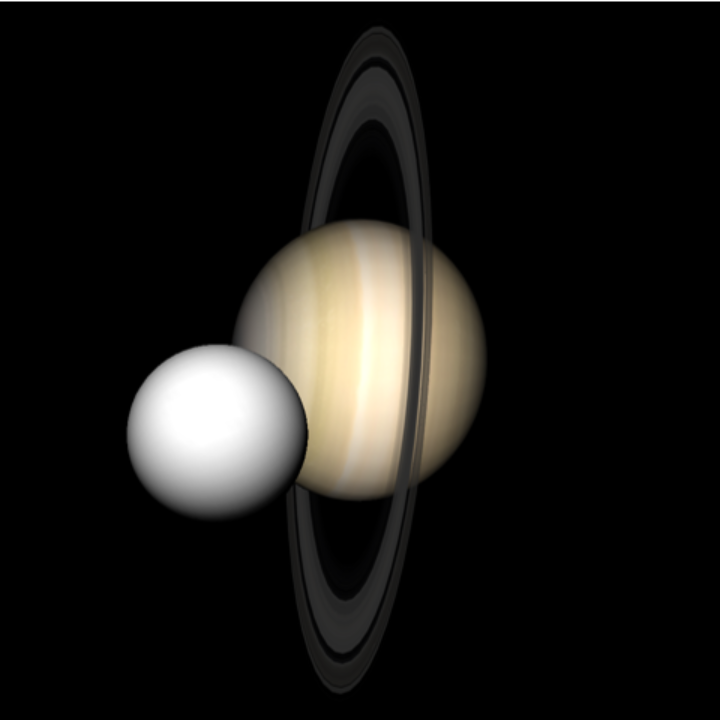 |
Re-create a view of crescent Venus and a crescent Moon next to each other:
| In[32]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Venus"], DateObject[{2020, 6, 19, 4, 19, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", -3.`], GeoPosition[{46.15, -60.17}], "FieldWidth" -> Quantity[13.3, "Arcminutes"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/23c48e1e6c7fb260.png) |
| Out[32]= |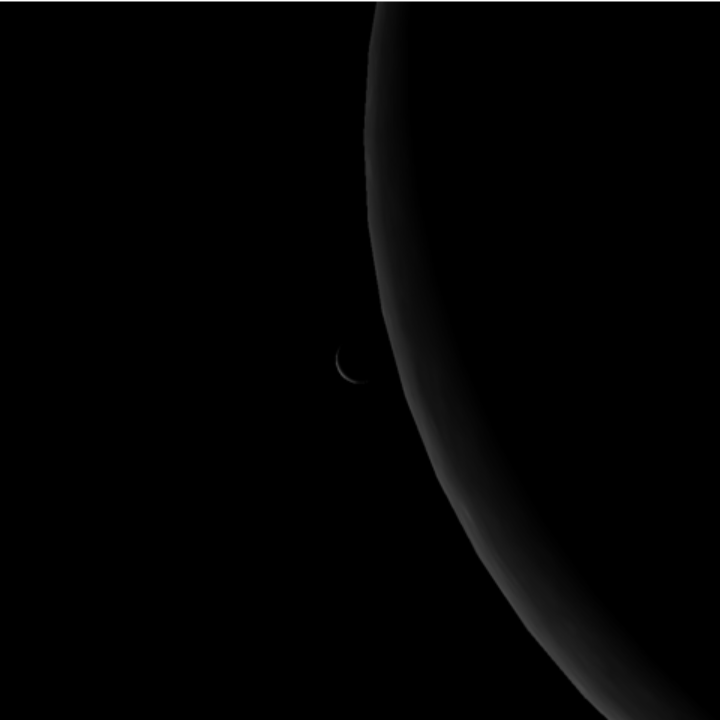  |
Simulate the view from Apollo 8 during the famous "Earthrise" photograph. Assume a position near the equator of the Moon and slightly on the Earth‐side of the Moon. Africa can be seen on the terminator:
| In[33]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Earth"], DateObject[{1968, 12, 24, 15, 40, 0}, "Instant", "Gregorian", 0.`], GeoPosition[{0, 85}, Entity["PlanetaryMoon", "Moon"]], "FieldWidth" -> Quantity[5, "AngularDegrees"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/24b105e7db13757d.png) |
| Out[33]= |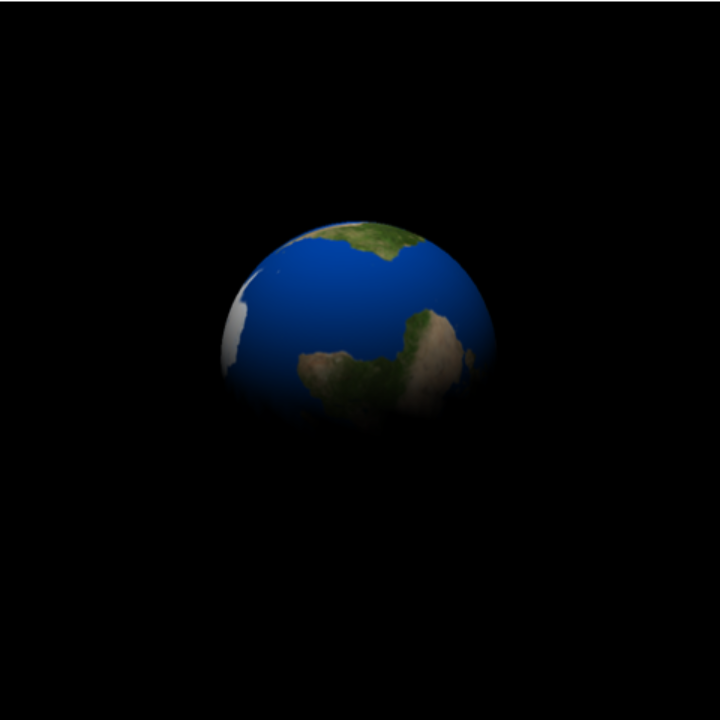  |
Simulate the view of Earth from the Apollo 11 landing site on the Moon:
| In[34]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"TelescopeView3D", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][Entity["Planet", "Earth"], DateObject[{1969, 7, 21, 4, 19, 0}, TimeZone -> 0], Entity["MannedSpaceMission", "Apollo11"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fea/fea7ca51-a57a-43ba-8d6b-79dadb740a1c/53f911de8142b2a5.png) |
| Out[34]= |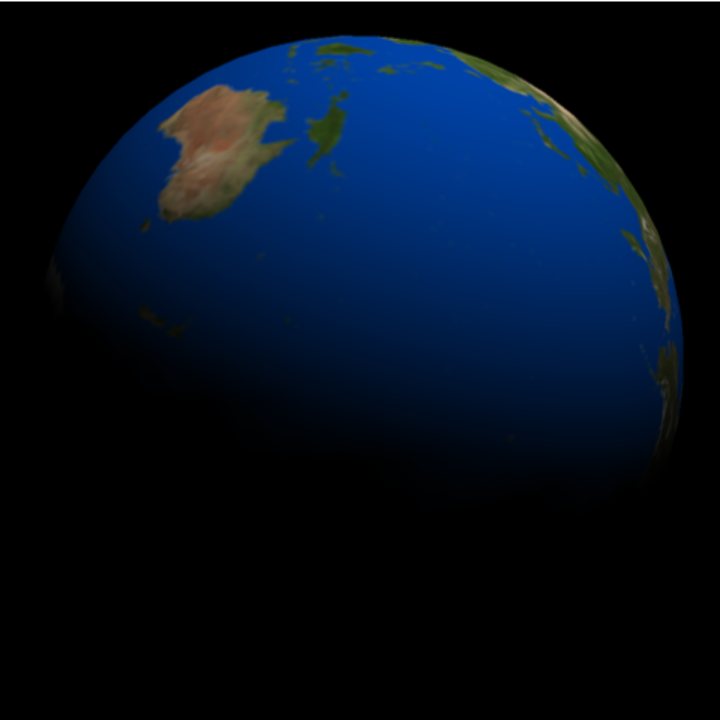  |
Wolfram Language 13.0 (December 2021) or above
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License