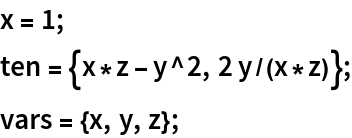Basic Examples (3)
Define a function that takes a matrix of variables as input and returns a vector:
Apply the function:
Use TensorPureFunction with a tensor of rank 3:
Apply the function:
Use TensorPureFunction with a tensor of rank 4:
Apply the function:
Scope (3)
Use TensorPureFunction in combination with Grad:
Use TensorPureFunction in combination with Curl:
Use TensorPureFunction to compute a Jacobian matrix:
Apply the Jacobian function:
Use TensorPureFunction to compute a Hessian matrix:
Apply the Hessian function:
Options (1)
IndexingMethod (1)
The IndexingMethod option allows specifying the method used to indexing elements of argvars in the TensorPureFunction. By default, the method is set to "UseIndexed", which uses the Indexed function. Alternatively, can be set the option to "UsePart" to use the Part function. This option provides flexibility in choosing the preferred method of indexing elements of argvars within the TensorPureFunction:
Applications (4)
Multilinear Functions (2)
Use TensorPureFunction with the following trilinear function:
Apply the trilinear function:
Deformation Gradient and Vorticity Tensor (2)
Define a simple function to compute the deformation gradient given a velocity field at the point :
The calculation of the deformation gradient for the -velocity is as follows:
Now, use TensorPureFunction to obtain a pure function of the above array:
Define a simple function to compute the vorticity tensor given a velocity field at the point :
The calculation of the vorticity tensor for the -velocity is as follows:
Now, use TensorPureFunction to obtain a pure function of the above array:
Properties and Relations (3)
Use TensorPureFunction with the resource function JacobianMatrix:
This is equivalent the computing the Jacobian directly:
Use TensorPureFunction with the resource function HessianMatrix:
This is equivalent the computing the Hessian directly:
Use TensorPureFunction with the resource function DVectorField:
The previous tensors are identical:
Possible Issues (3)
If any of the specified variables have existing definitions, TensorPureFunction issues a warning and returns unevaluated. For example:
To avoid this issue, wrap the variables with Block to prevent conflicts with global definitions:
Since TensorPureFunction explicitly checks for global definitions before proceeding, it remains unevaluated when global definitions of the arguments are found. For example:
Evaluate overrides the hold attribute so that TensorPureFunction behaves as expected with the previously defined inputs:
On the other hand, when using Evaluate explicitly on the function or variable arguments before passing them to TensorPureFunction, and at least one of the variables in the argument list has a global definition, the expected behavior of holding evaluation and issuing a warning will not occur. Instead, the function will be evaluated with the assigned values, potentially leading to incorrect results. For example:
In this case, since Evaluate forces the immediate evaluation of the input, TensorPureFunction does not detect existing global definitions and proceeds incorrectly. To avoid this issue, it is recommended to use Clear to remove any prior definitions before applying the function.
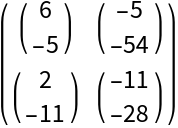
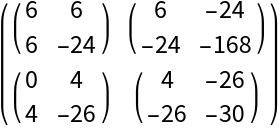
![With[{f = {x^3 - 2 x y, x y^2}, vars = {x, y}}, ResourceFunction[
"TensorPureFunction", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][f, vars, "IndexingMethod" -> "UsePart"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/169/1691b320-b7c2-450f-a089-fc775ad1c045/6da42478ae0712ee.png)
![d3 = ResourceFunction[
"TensorPureFunction", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][{-2 x3 y1 y2 - 2 x2 y1 y3 - 2 x1 y2 y3, 4 x2 x3 y1 + 4 x1 x3 y2 + 4 x1 x2 y3}, {{x1, y1}, {x2, y2}, {x3, y3}}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/169/1691b320-b7c2-450f-a089-fc775ad1c045/1e380e9126b18ee8.png)
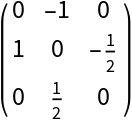
![ResourceFunction[
"TensorPureFunction", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][
Simplify@
ResourceFunction["JacobianMatrix"][{x^3 - 2 x y - y^6, x y^2 - 5 x y}, {x, y}], {x, y}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/169/1691b320-b7c2-450f-a089-fc775ad1c045/0db3537cbf2220ee.png)
![d21 = With[{ten = ResourceFunction["DVectorField"][{x - y^2, 2 y/x}, {x, y}, {1, 2},
2, "MultilinearFunction"]}, ResourceFunction[
"TensorPureFunction", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][ten, {{x1, y1}, {x2, y2}}]];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/169/1691b320-b7c2-450f-a089-fc775ad1c045/1bf37f24dab5cf56.png)
![d22 = ResourceFunction["DVectorField"][{x - y^2, 2 y/x}, {x, y}, {1, 2}, 2, "PureMultilinearFunction"];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/169/1691b320-b7c2-450f-a089-fc775ad1c045/33b6eb2b737961aa.png)
![x1 = 1;
y1 = 2;
ResourceFunction[
"TensorPureFunction", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][{-2 x3 y1 y2 - 2 x2 y1 y3 - 2 x1 y2 y3, 4 x2 x3 y1 + 4 x1 x3 y2 + 4 x1 x2 y3}, {{x1, y1}, {x2, y2}, {x3, y3}}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/169/1691b320-b7c2-450f-a089-fc775ad1c045/03184ccb46a3843a.png)
![Block[{x1, y1}, ResourceFunction[
"TensorPureFunction", ResourceSystemBase -> "https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/api/1.0"][{-2 x3 y1 y2 - 2 x2 y1 y3 - 2 x1 y2 y3, 4 x2 x3 y1 + 4 x1 x3 y2 + 4 x1 x2 y3}, {{x1, y1}, {x2, y2}, {x3, y3}}]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/169/1691b320-b7c2-450f-a089-fc775ad1c045/59e15571797d6624.png)