Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Compute the Pfaffian of an antisymmetric (skew-symmetric) matrix
ResourceFunction["Pfaffian"][m] gives the Pfaffian of a skew-symmetric matrix m. |
| "ParlettReid" | Parlett–Reid tridiagonalization |
| "Householder" | Householder tridiagonalization |
| "Hessenberg" | Hessenberg decomposition |
| "Pauli" | uses the second Pauli matrix |
| "Det" | uses the built-in Det |
Pfaffian of an antisymmetric matrix:
| In[1]:= | ![ResourceFunction["Pfaffian"][( {
{0, a, b, c},
{-a, 0, d, e},
{-b, -d, 0, f},
{-c, -e, -f, 0}
} )] // Simplify](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4cc/4cca8ff7-3513-4642-9095-4c5bb7d8ac8b/4b14f3004d7bf624.png) |
| Out[1]= |
The Pfaffian of a real antisymmetric matrix:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |  |
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |
A complex matrix:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |  |
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
A symbolic matrix:
| In[6]:= | ![ResourceFunction["Pfaffian"][( {
{0, a, b, c, d, e},
{-a, 0, f, g, h, i},
{-b, -f, 0, j, k, l},
{-c, -g, -j, 0, m, n},
{-d, -h, -k, -m, 0, o},
{-e, -i, -l, -n, -o, 0}
} )] // Simplify](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4cc/4cca8ff7-3513-4642-9095-4c5bb7d8ac8b/656abb5f1e854bda.png) |
| Out[6]= |
Methods applicable to real matrices:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |  |
| In[8]:= | ![Table[ResourceFunction["Pfaffian"][mat, Method -> method], {method, {"ParlettReid", "Householder", "Hessenberg", "Pauli", "Det"}}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4cc/4cca8ff7-3513-4642-9095-4c5bb7d8ac8b/6cfb328745b95c10.png) |
| Out[8]= |
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
Methods applicable to complex matrices:
| In[10]:= |
| In[11]:= | ![Table[ResourceFunction["Pfaffian"][mat, Method -> method], {method, {"ParlettReid", "Householder", "Pauli", "Det"}}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4cc/4cca8ff7-3513-4642-9095-4c5bb7d8ac8b/49f6d1a237a6fb1e.png) |
| Out[11]= |
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |
Methods applicable to symbolic matrices:
| In[13]:= | 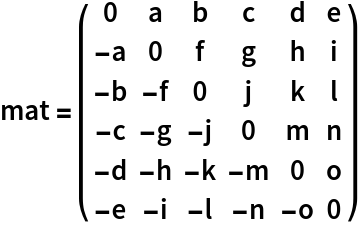 |
| Out[13]= |
| In[14]:= |
| Out[14]= |  |
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= |
The Pfaffian of an antisymmetric matrix of odd dimension is zero:
| In[16]:= | ![ResourceFunction["Pfaffian"][( {
{0, a, b},
{-a, 0, c},
{-b, -c, 0}
} )]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/4cc/4cca8ff7-3513-4642-9095-4c5bb7d8ac8b/093b7f071adf57f3.png) |
| Out[16]= |
For a 2n×2n skew-symmetric matrix m, the Pfaffian of the matrix transpose mT is equal to (-1)nPfaffian[m]:
| In[17]:= |
| In[18]:= |
| In[19]:= |
| Out[19]= |  |
| In[20]:= |
| Out[20]= |
For such matrices, the Pfaffian of λm is equal to λnPfaffian[m]:
| In[21]:= |
| Out[21]= |
Also, for such matrices, the square of the Pfaffian is equal to the determinant of the matrix:
| In[22]:= |
| Out[22]= |
For a 2n×2n skew-symmetric matrix m and an arbitrary 2n×2n matrix x, Pfaffian[x.m.xT]⩵Det[x]*Pfaffian[m]:
| In[23]:= |
| In[24]:= |
| Out[24]= |  |
| In[25]:= |
| Out[25]= | 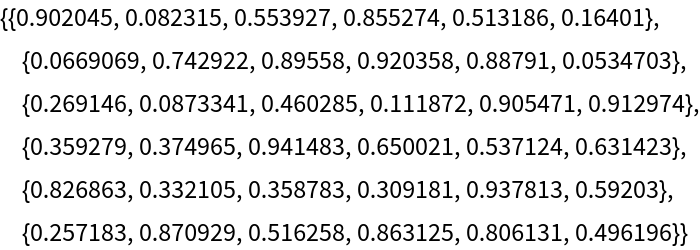 |
| In[26]:= |
| Out[26]= |
The Pfaffian of a 2n×2n skew-symmetric block diagonal matrix is the product of its non-zero superdiagonal values:
| In[27]:= |
| In[28]:= |
| Out[28]= |  |
| In[29]:= |
| Out[29]= |
The Pfaffian of a 2n×2n skew-symmetric tridiagonal matrix is the product of the entries at odd positions on the superdiagonal:
| In[30]:= |
| In[31]:= |
| Out[31]= |  |
| In[32]:= |
| Out[32]= |
Reducing an antisymmetric matrix to its tridiagonal form gives a numerically stable way to compute the Pfaffian from the superdiagonal values:
| In[33]:= |
| In[34]:= |
| Out[34]= |  |
Tridiagonalize using the resource function SkewLTLDecomposition:
| In[35]:= |
| In[36]:= |
| Out[36]= | 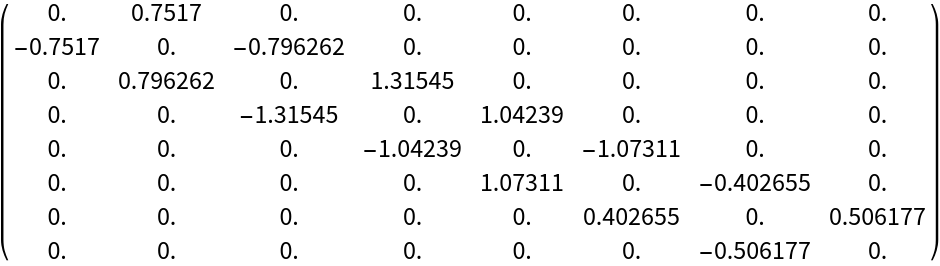 |
| In[37]:= |
| Out[37]= |
Using the resource function SkewTridiagonalDecomposition:
| In[38]:= |
| In[39]:= |
| Out[39]= | 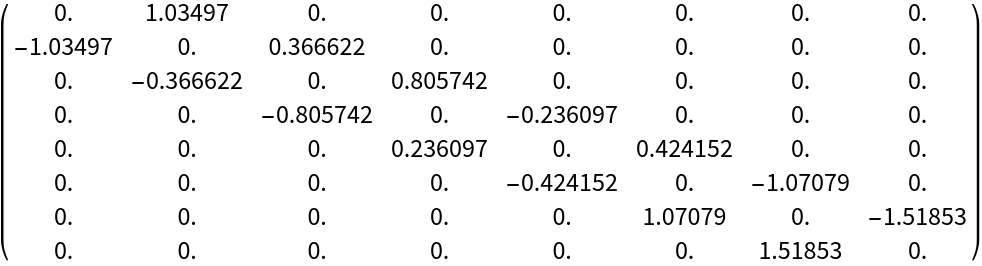 |
| In[40]:= |
| Out[40]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License