Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Compute the skew-tridiagonal decomposition of an antisymmetric matrix
ResourceFunction["SkewTridiagonalDecomposition"][m] gives the skew-tridiagonal decomposition of antisymmetric matrix m. |
Construct a a skew-symmetric matrix:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |  |
The skew-tridiagonal decomposition:
| In[2]:= |
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |  |
The skew-tridiagonal decomposition of a real antisymmetric matrix:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |  |
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= | 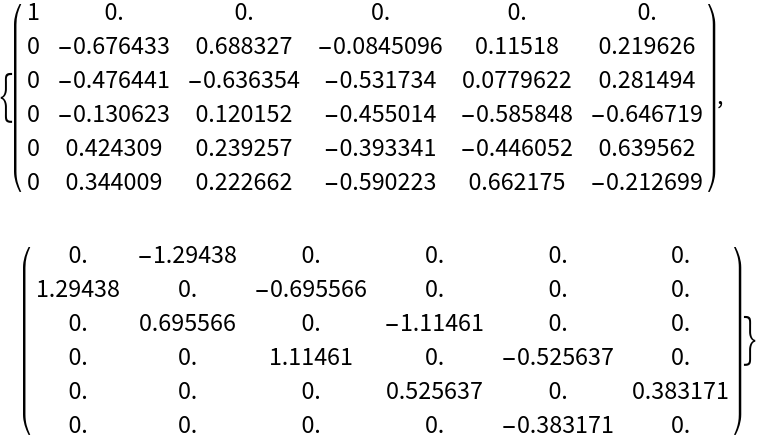 |
The skew-tridiagonal decomposition of a complex antisymmetric matrix:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |  |
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |  |
Compute the Pfaffian of an antisymmetric matrix by reducing it to the tridiagonal form:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |  |
| In[9]:= |
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |  |
| In[11]:= |
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |
Compare with the result of the resource function Pfaffian:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |
In the result of {q,t}=SkewTridiagonalDecomposition[m], the matrix q is unitary and t is tridiagonal:
| In[14]:= |
| In[15]:= |
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= |
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= |
The original matrix is given by q.t.Transpose[q]:
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= |
For real matrices, SkewTridiagonalDecomposition gives result similar to HessenbergDecomposition:
| In[19]:= |
| In[20]:= |
| In[21]:= |
| In[22]:= |
| Out[22]= |
| In[23]:= |
| Out[23]= |
The resource function SkewLTLDecomposition also produces a tridiagonal matrix t with the same Pfaffian, possibly up to the sign:
| In[24]:= |
| In[25]:= |
| In[26]:= |
| Out[26]= |  |
| In[27]:= |
| In[28]:= |
| Out[28]= |  |
| In[29]:= |
| Out[29]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License