Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Generate a Hartley matrix
ResourceFunction["HartleyMatrix"][n] returns an n×n Hartley matrix. |
A 4×4 Hartley matrix:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= | 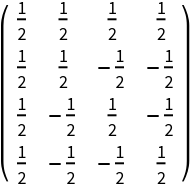 |
Visualize the basis sequences of the Hartley transform:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[3]= |  |
By default, an exact matrix is computed:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= | 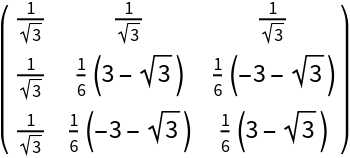 |
Use machine precision:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
Use arbitrary precision:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
The Hartley matrix is symmetric and orthogonal:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= | 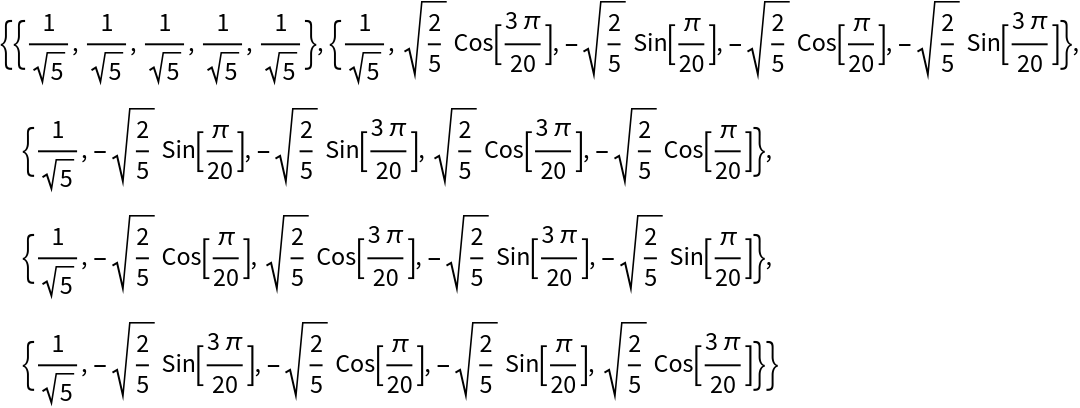 |
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
The Hartley matrix is thus its own inverse:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
Compute the discrete Hartley transform of a vector by multiplying it with the Hartley matrix:
| In[10]:= |
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= |
It is faster to use the resource function DiscreteHartleyTransform:
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License