Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Compile a color function for improved performance in colorizing images
ResourceFunction["CompileColorFunction"][f] creates a CompiledFunction from the color function f. |
| "ColorSamples" | 16 | number of data points to use in the compiled function |
| ColorSpace | "RGB" | what color space the output values should represent |
| CompilationOptions | Automatic | options for the complation process |
| CompilationTarget | $CompilationTarget | the target runtime for code generation |
| Parallelization | True | parallel controls for compiled function execution |
| RuntimeAttributes | {Listable} | evaluation attributes for the compiled function |
| RuntimeOptions | "Speed" | runtime options for the compiled function |
Compile a color function:
| In[1]:= |
|
| Out[1]= |
|
| In[2]:= |
|
| Out[2]= |
|
See the resulting color:
| In[3]:= |
|
| Out[3]= |
|
Compile a built-in color function from ColorData:
| In[4]:= |
|
| Out[4]= |
|
Apply it to some data:
| In[5]:= |
![cf[({
{0, 1/8, 1/4},
{3/8, 1/2, 5/8},
{3/4, 7/8, 1}
})]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/dc0/dc0f250b-3227-4b8e-a635-eb5acbe45581/06acfcae7fd3ebb5.png)
|
| Out[5]= |

|
Get the resulting image:
| In[6]:= |
|
| Out[6]= |
|
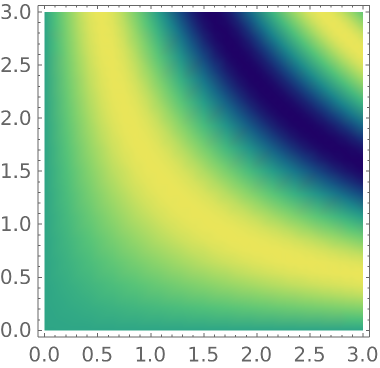
Use a compiled color function in a plot:
| In[7]:= |
|
| Out[7]= |
|
| In[8]:= |
|
| Out[8]= |
|
Generate colorized images from tables of data:
| In[9]:= |
|
| Out[9]= |
|
| In[10]:= |
|
| In[11]:= |
|
| Out[11]= |

|
Create a fast color function from a slow one:
| In[12]:= |
|
| In[13]:= |
|
| Out[13]= |
|
| In[14]:= |
|
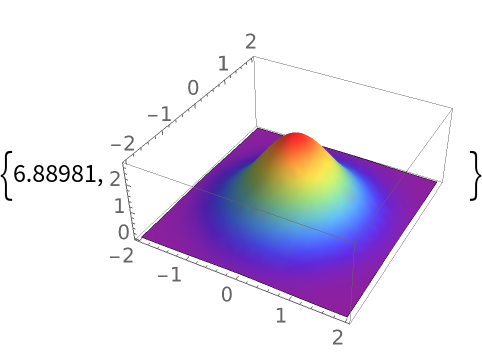
Compare the performance:
| In[15]:= |
|
| Out[15]= |
|
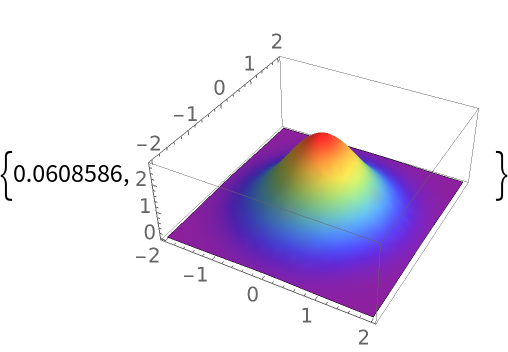
| In[16]:= |
|
| Out[16]= |
|
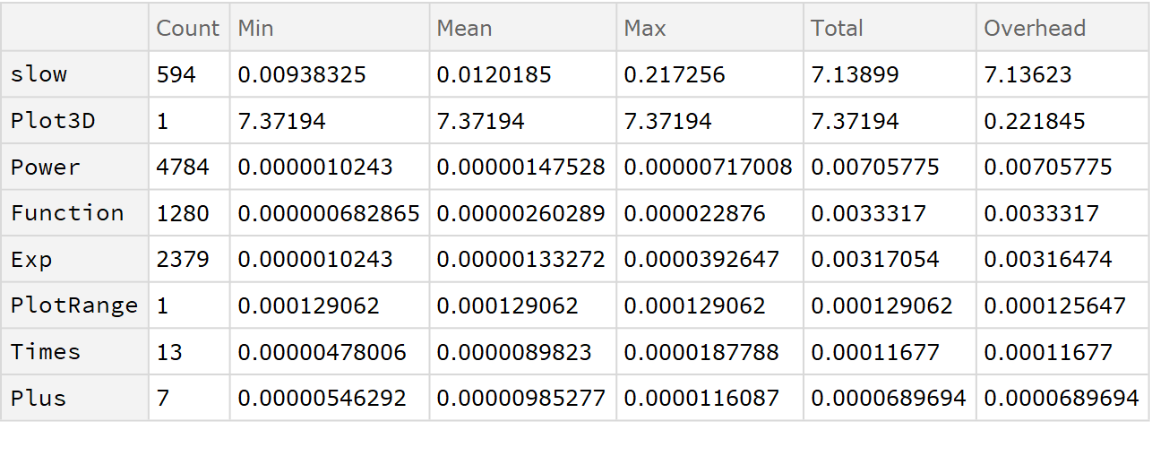
Inspect timing details:
| In[17]:= |
![ResourceFunction["EvaluationTiming"][
Plot3D[Exp[1 - x^2 - y^2], {x, -2, 2}, {y, -2, 2}, ColorFunction -> Function[{x, y, z}, slow[z]], PlotRange -> All, Mesh -> None]]["Summary"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/dc0/dc0f250b-3227-4b8e-a635-eb5acbe45581/012156c30e8fabab.png)
|
| Out[17]= |
|
| In[18]:= |
|
| Out[18]= |
|
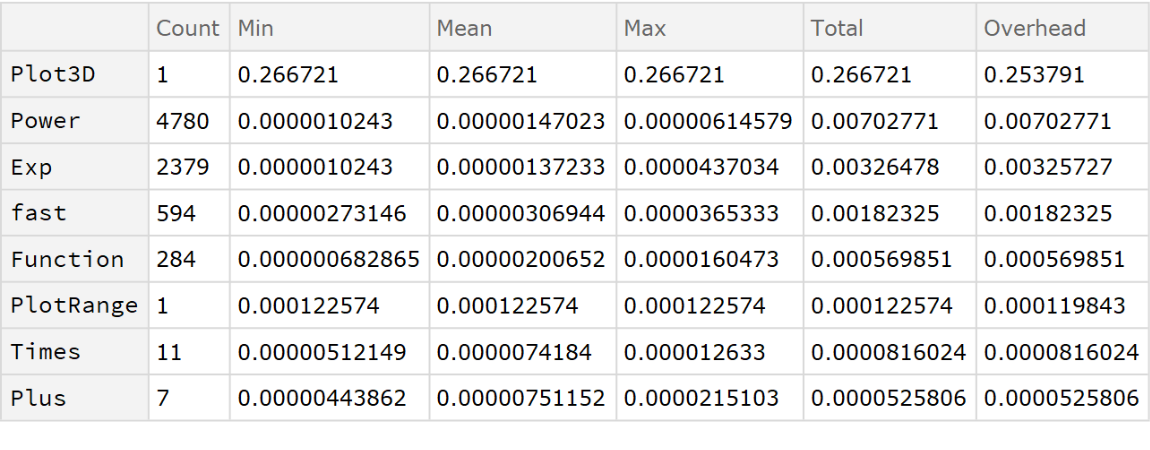
The compiled version contributes an insignificant amount of overhead:
| In[19]:= |
![ResourceFunction["EvaluationTiming"][
Plot3D[Exp[1 - x^2 - y^2], {x, -2, 2}, {y, -2, 2}, ColorFunction -> Function[{x, y, z}, fast[z]], PlotRange -> All, Mesh -> None]]["Summary"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/dc0/dc0f250b-3227-4b8e-a635-eb5acbe45581/439b8c97ffa0f7ec.png)
|
| Out[19]= |
|
| In[20]:= |
|
| Out[20]= |
|
Gradients that have a high amount of variance can lose some detail when compiled:
| In[21]:= |
|
| Out[21]= |
|
| In[22]:= |
|
| In[23]:= |
|
| Out[23]= |
|
| In[24]:= |
|
| Out[24]= |
|
| In[25]:= |
|
| Out[25]= |
|
Use more initial color samples to increase the quality:
| In[26]:= |
|
| Out[26]= |
|
| In[27]:= |
|
| Out[27]= |
|
By default, CompileColorFunction will use Listable in the RuntimeAttributes:
| In[28]:= |
|
| Out[28]= |
|
This allows the compiled function to be applied directly to an array of data:
| In[29]:= |
|
| Out[29]= |
|
| In[30]:= |
|
| Out[30]= |
|
If compiled without the Listable attribute, the function needs to be applied to individual values directly:
| In[31]:= |
|
| Out[31]= |
|
| In[32]:= |
|
| Out[32]= |
|
It works if mapped:
| In[33]:= |
|
| Out[33]= |
|
By default, Parallelization is set to True for CompileColorFunction:
| In[34]:= |
|
| Out[34]= |
|
| In[35]:= |
|
| In[36]:= |
|
| Out[36]= |

|
Force the function to evaluate on a single thread:
| In[37]:= |
|
| Out[37]= |
|
| In[38]:= |
|
| Out[38]= |

|
If a C compiler is available on the current machine, additional performance may be obtained by setting CompilationTarget to "C":
| In[39]:= |
|
| Out[39]= |
|
| In[40]:= |
|
| In[41]:= |
|
| Out[41]= |
|
Use the default value of "WVM":
| In[42]:= |
|
| Out[42]= |
|
| In[43]:= |
|
| Out[43]= |
|
By default the values output by the compiled function will represent RGB values:
| In[44]:= |
|
| Out[44]= |
|
| In[45]:= |
|
| In[46]:= |
|
| Out[46]= |

|
Specify a different color space:
| In[47]:= |
|
| Out[47]= |
|
| In[48]:= |
|
Now the ColorSpace needs to be specified for Image as well:
| In[49]:= |
|
| Out[49]= |

|
| In[50]:= |
|
| Out[50]= |

|
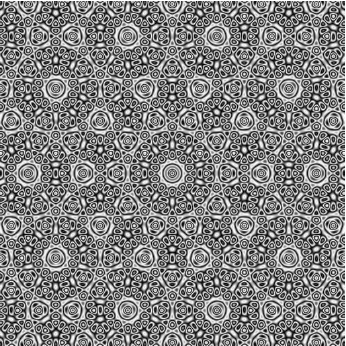
Compiling a color function and applying directly to image data can improve performance over Colorize:
| In[51]:= |
|
| Out[45]= |
|
| In[52]:= |
|
| Out[52]= |
|
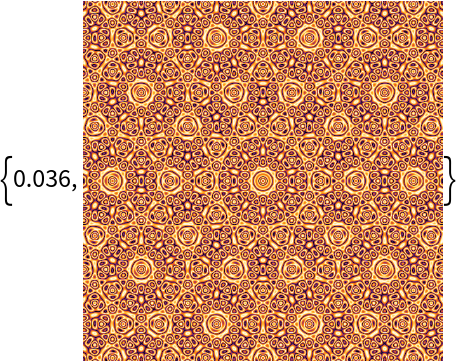
| In[53]:= |
|
| Out[53]= |
|
Compare to using an uncompiled color function:
| In[54]:= |
|
| Out[54]= |

|
In CompileColorFunction[f], if the function f does not produce a smooth gradient when evaluated from 0 to 1, the compiled function can have low quality results:
| In[55]:= |
|
| Out[55]= |
|
| In[56]:= |
|
| In[57]:= |
|
| Out[57]= |
|
| In[58]:= |
|
| Out[58]= |
|
| In[59]:= |
|
| Out[59]= |
|
The compiled function will be deterministic, even if the input function is not:
| In[60]:= |
|
| Out[60]= |
|
| In[61]:= |
|
| Out[61]= |
|
| In[62]:= |
|
| Out[62]= |
|
The results won’t change when given the same input:
| In[63]:= |
|
| Out[63]= |
|
Compare to the original function:
| In[64]:= |
|
| Out[64]= |
|
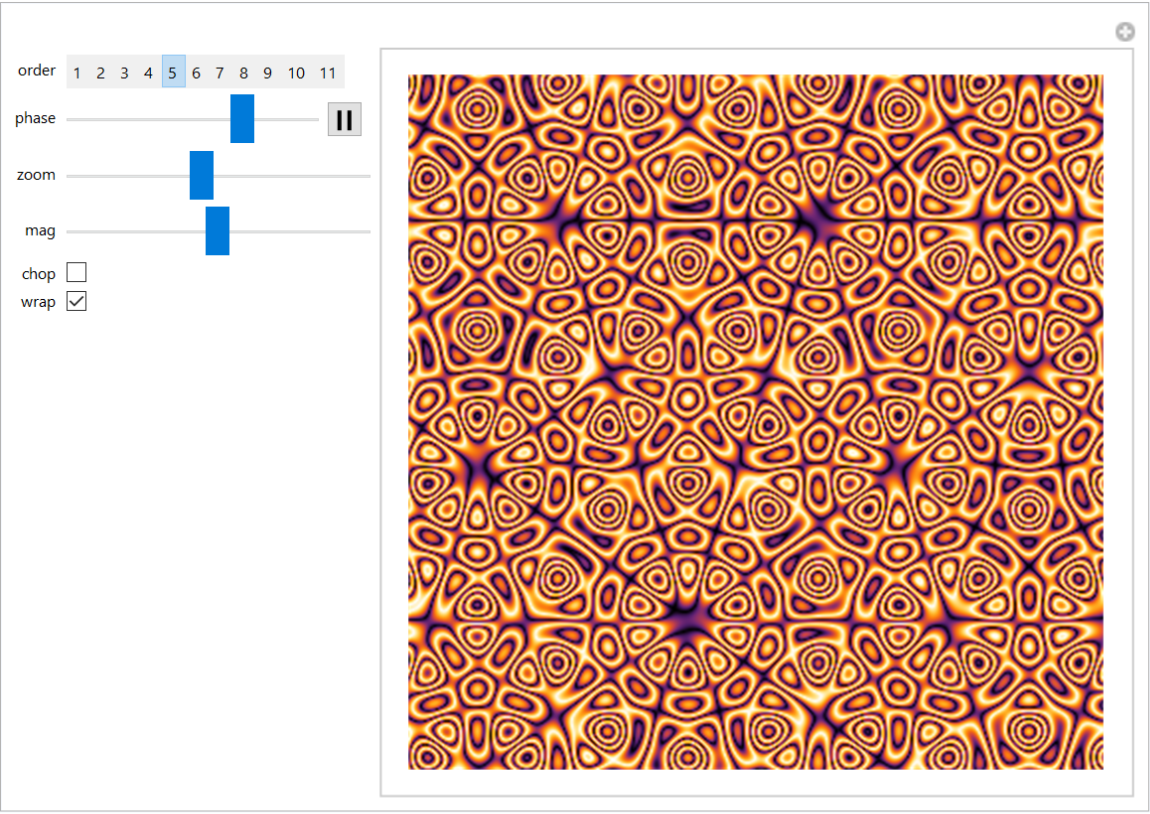
Colorize data quickly for for interactive visualizations:
| In[65]:= |
![Manipulate[
Image[qcc[qc[grid, zoom, phase, order, mag, chop, wrap]]],
{{order, 5}, 1, 11, 1, Sequence[
ControlType -> SetterBar, ImageSize -> {153, 25}]},
{phase, 0.0, 2.0 Pi, Sequence[
ControlType -> Animator, ImageSize -> {153, 25}, AnimationRunning -> True, AppearanceElements -> {"ProgressSlider", "PlayPauseButton"}]},
{{zoom, 0.25}, 0.05, 0.5, Sequence[
ControlType -> Slider, ImageSize -> {153, 25}]},
{{mag, 1.0}, 0.0, 2.0, Sequence[
ControlType -> Slider, ImageSize -> {153, 25}]},
{{chop, False}, {False, True}, ControlType -> Checkbox},
{{wrap, True}, {False, True}, ControlType -> Checkbox},
ControlPlacement -> Left,
Initialization :> (
$compilationTarget := ($compilationTarget = If[
Quiet[
TrueQ[
Not[Check[
Compile[{}, 1 + 1, CompilationTarget -> "C"], $tag,
MessageName[CCompilerDriver`CreateLibrary, "nocomp"]] === $tag]]], "C", "WVM"]);
qcc = ResourceFunction["CompileColorFunction"][
ColorData["SunsetColors"], CompilationTarget -> $compilationTarget];
xres = 350;
yres = 350;
grid = Array[{# - yres/2., #2 - xres/2.}& , {yres, xres}];
qc = Compile[{{pt,
Blank[Real], 1}, {scale,
Blank[Real]}, {phase,
Blank[Real]}, {order,
Blank[Real]}, {mag,
Blank[Real]}, {chop,
Alternatives[True, False]}, {wrap,
Alternatives[True, False]}},
Block[{x = Part[pt, 1], y = Part[pt, 2], sum = 0.}, Do[
AddTo[sum,
Cos[phase + (scale x) Cos[i (Pi/order)] - (scale y) Sin[
i (Pi/order)]]], {i, order}]; sum = mag sum; sum = If[wrap,
If[
OddQ[
Floor[sum]], 1 - Mod[sum, 1],
Mod[sum, 1]], 0.5 Tanh[sum] + 0.5]; If[
chop, sum = 0.6 Floor[sum + 0.5] + 0.2]; sum], Parallelization -> True, RuntimeAttributes -> {Listable}, RuntimeOptions -> "Speed", CompilationTarget -> $compilationTarget];
),
SynchronousInitialization -> False
]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/dc0/dc0f250b-3227-4b8e-a635-eb5acbe45581/64ee062790bc9489.png)
|
| Out[65]= |
|
Wolfram Language 11.3 (March 2018) or above
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License