Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Build a causal graph from an expression evaluation trace
ResourceFunction["TraceCausalGraph"][expr] evaluate an expression and return a causal graph of its trace. | |
ResourceFunction["TraceCausalGraph"][expr,n] trace only up-to n steps of evaluation. | |
ResourceFunction["TraceCausalGraph"][expr,n,patt] prune trace by a specifying a pattern of expressions to include. | |
ResourceFunction["TraceCausalGraph"][expr,…,prop] returns the specified property prop. |
| "CausalGraph" (default) | causal graph of the trace |
| "Path" | path as an interspersed list of HoldComplete expressions and positions |
| "PathGraph" | path as a PathGraph |
| "PathEventsGraph" | intersperse a path graph with corresponding event vertices |
| "PathCausalGraph" | add causal dependency edges to the "PathEventsGraph" |
| "IncludeInitialEvent" | False | whether to include an additional event that produces original expression |
| "ShowIndices" | False | show event indices |
| "ShowEventOrder" | False | show evaluation order with a path between events |
| "ShowPositions" | False | show event position with negative position indicating internal evaluations |
| "ShowExpressions" | True | show complete or partial expressions |
| "PruneIdentities" | True | prune events that evaluate expression to itself |
| "PruneSideEvents" | False | prune expressions that do not correspond to any part of original expression |
| "PruneTerminatedEvaluation" | True | prune expression with TerminatedEvaluation |
Make a causal graph from a standard evaluation of an expression:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= | 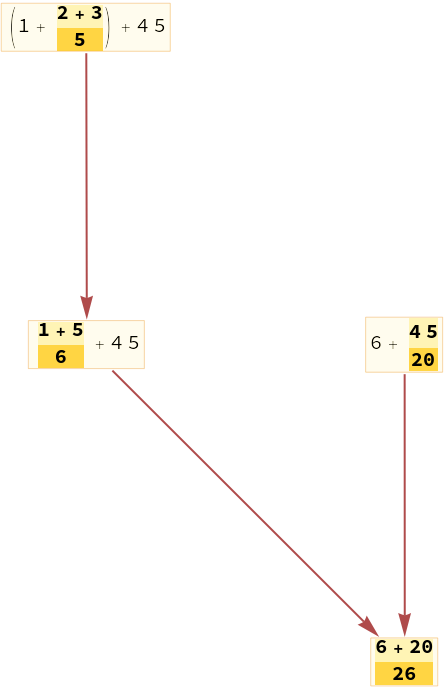 |
Make a path consisting of intermediate expressions together with subexpression positions being evaluated:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
Make a path graph of expressions in a trace:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= | 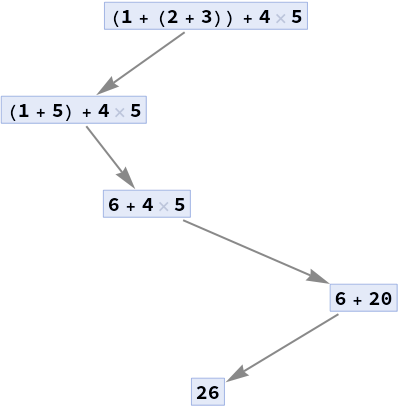 |
Make a path with interspersed events between expressions:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= | 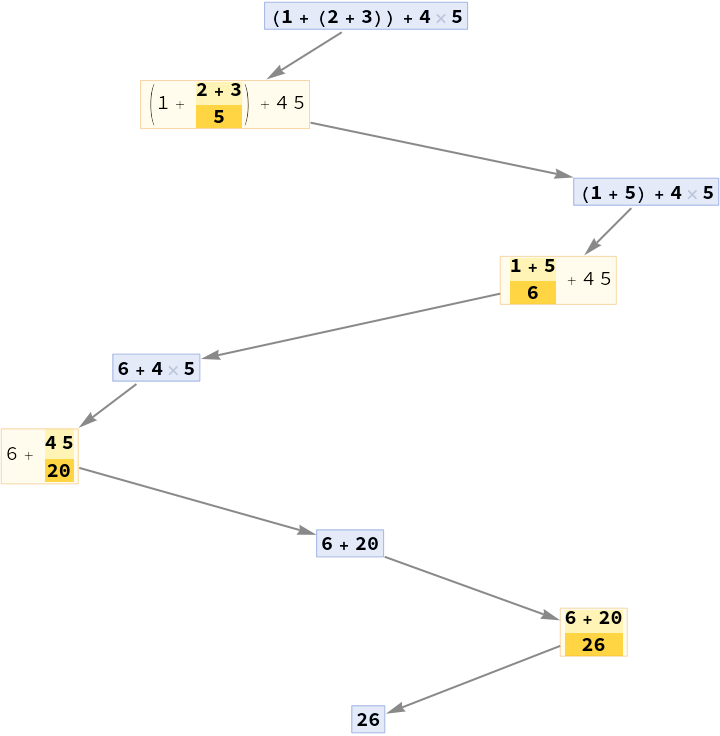 |
Add dependency edges between events:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= | 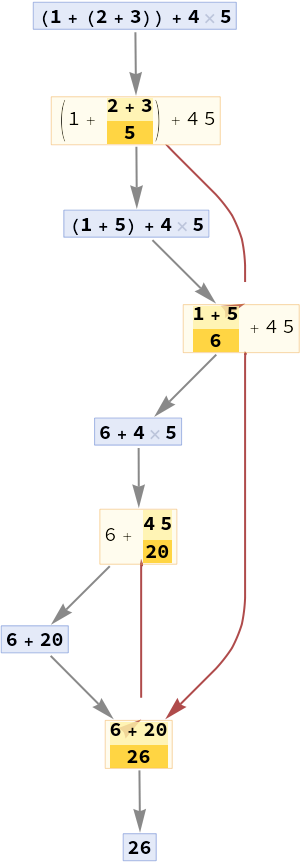 |
Trace a more complicated expression:
| In[6]:= | ![ClearAll[fib]
fib[n_] := fib[n - 1] + fib[n - 2]
fib[0 | 1] = 1;
ResourceFunction["TraceCausalGraph"][fib[3]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fd5/fd5d319f-74a4-4f61-8a5d-a22498ee40c6/6a7bb35d14857b43.png) |
| Out[7]= | 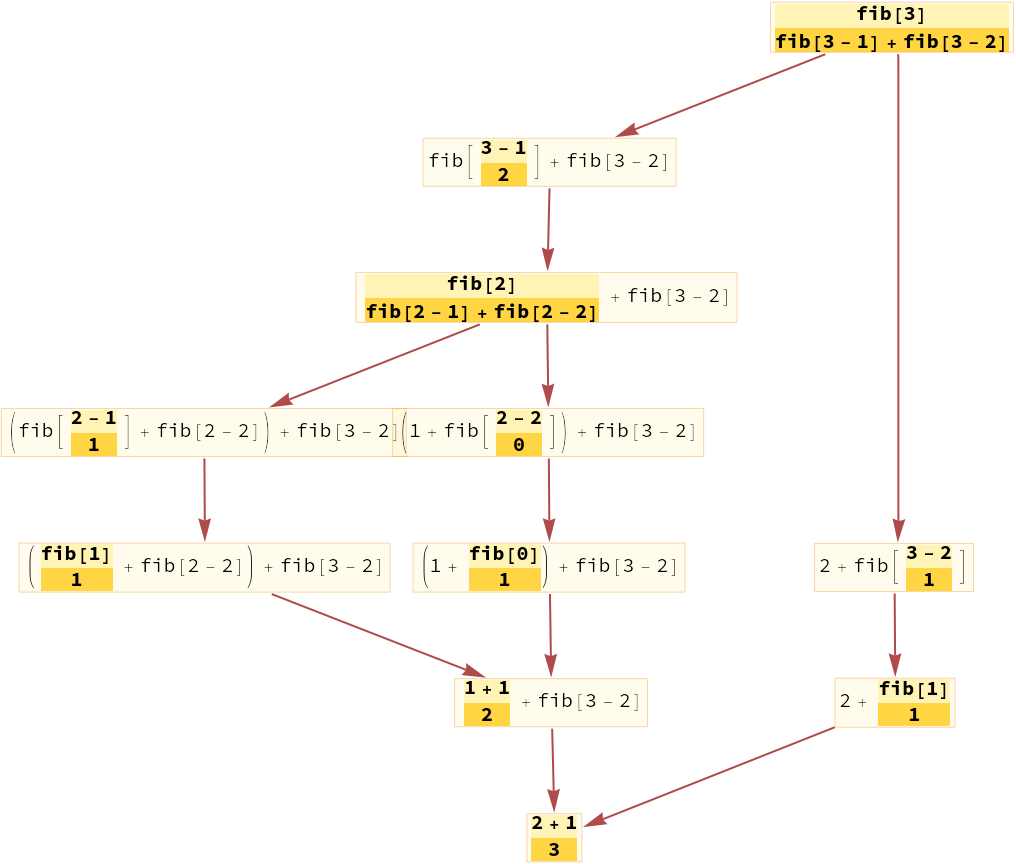 |
Tracing internal functions would result in side-events (indicated by a dashed boundary):
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= | 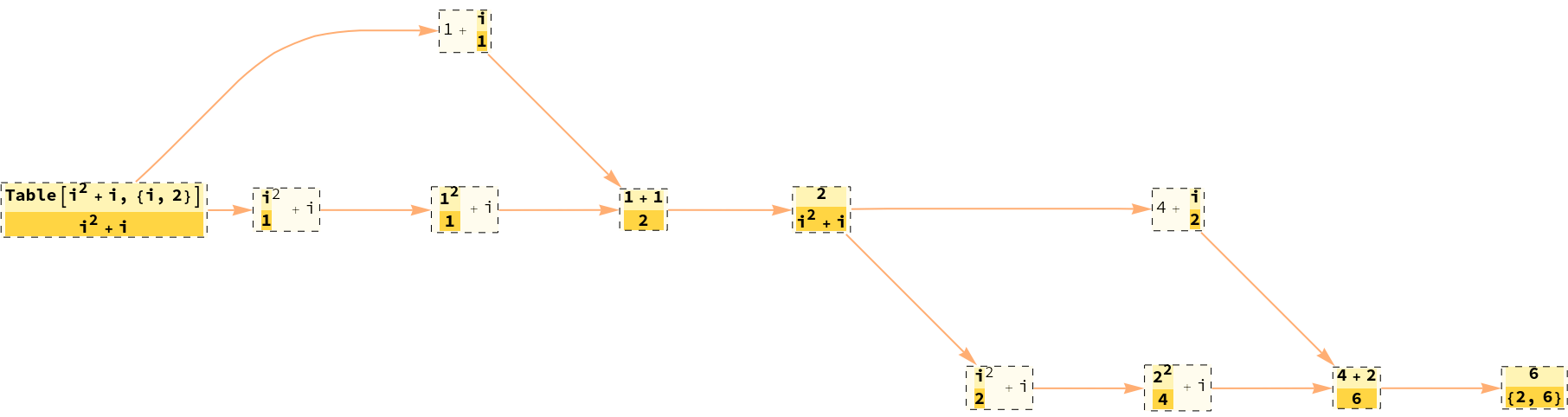 |
Include an additional event that all events causally depend on:
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= | 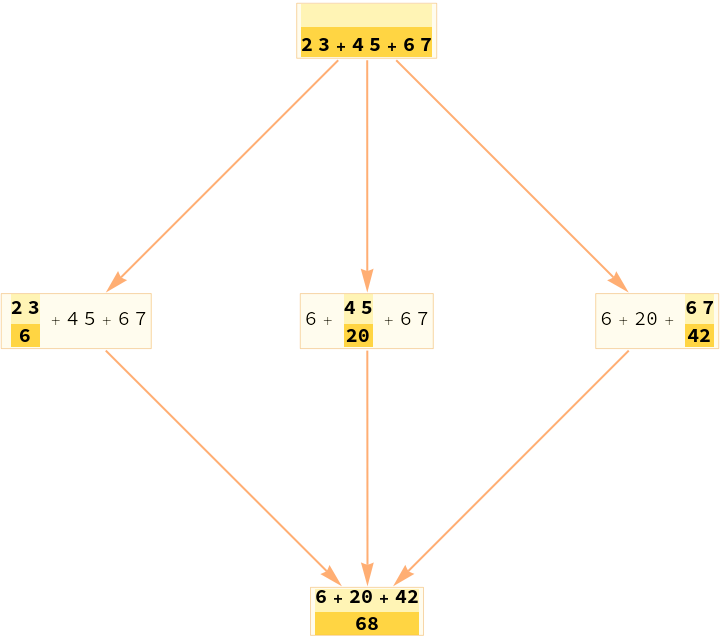 |
Show indices of events in evaluation order:
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= |
Indicate an actual order of events during evaluation:
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= | 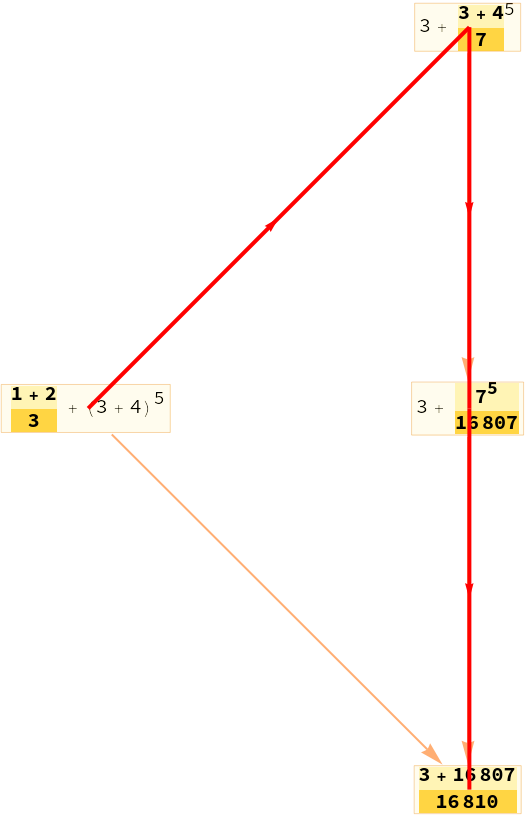 |
Show positions of subexpressions being evaluated:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |
With side-events having decreasing negative part numbers:
| In[14]:= |
| Out[14]= |
Instead of the whole expression show only subexpressions under evaluation:
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= |
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= |
Trivial identity events are pruned by default:
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= |
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= | 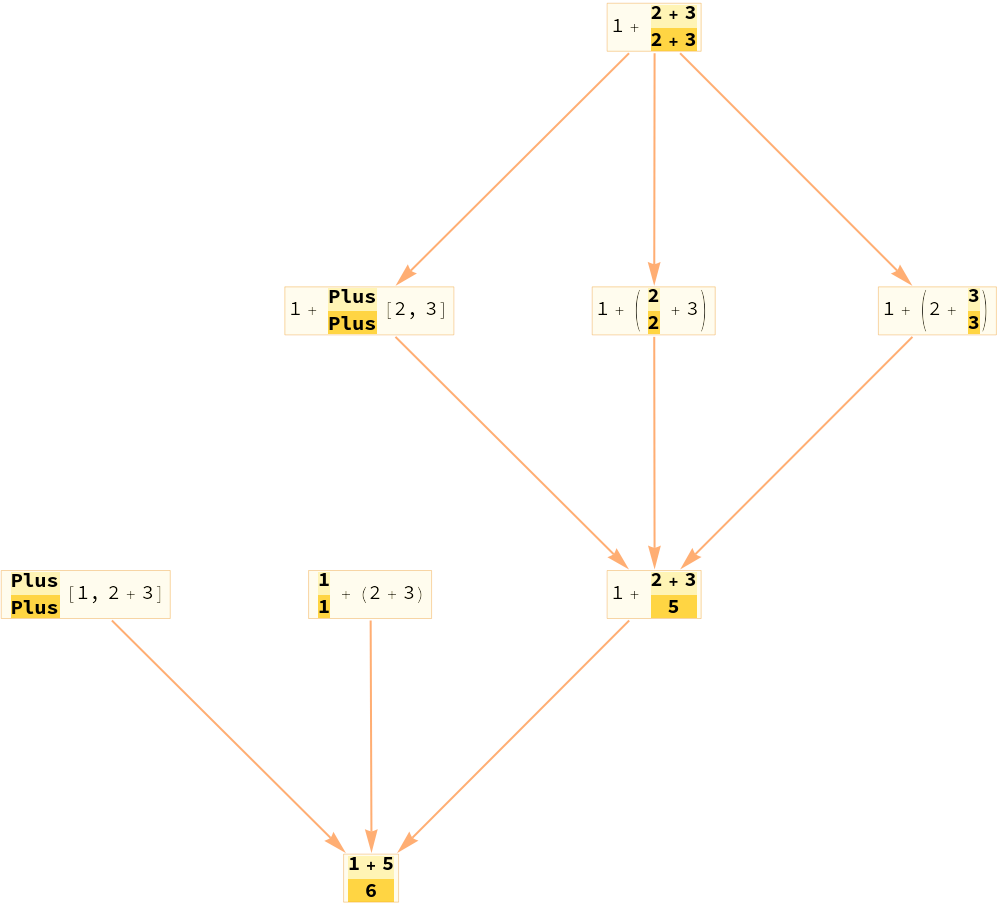 |
Prune side-events from a trace PathGraph and corresponding events:
| In[19]:= |
| In[20]:= |
| Out[20]= |
| In[21]:= |
| Out[21]= | 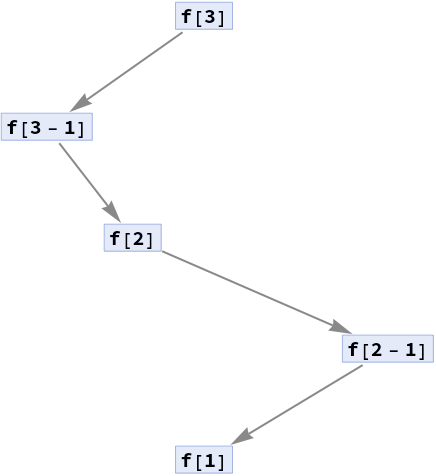 |
| In[22]:= |
| Out[22]= |
Terminating after non-terminal amount of steps results in TerminatedEvaluation inside of the last event, which is pruned by default:
| In[23]:= | ![GraphicsRow[
Table[ResourceFunction["TraceCausalGraph"][(1 + 2)^3, n, "PruneTerminatedEvaluation" -> False, PlotLabel -> Row[{n, If[n == 1, "step", "steps"]}, " "], GraphLayout -> "SpiralEmbedding"], {n, 4, 12, 2}], Frame -> All]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fd5/fd5d319f-74a4-4f61-8a5d-a22498ee40c6/11c133ef05620396.png) |
| Out[23]= | 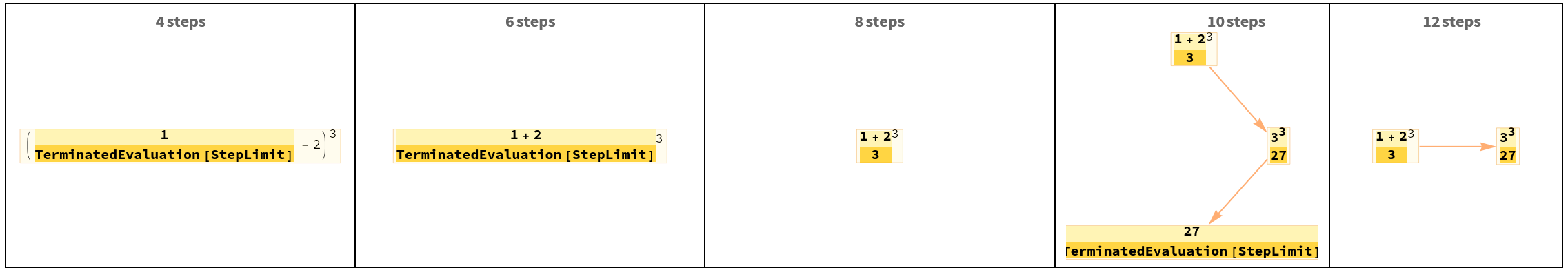 |
Non-standard evaluation, like flattening of Flat subexpressions results in incorrect reconstruction of intermediate expressions:
| In[24]:= | ![ClearAll[f]
SetAttributes[f, Flat]
f[x, a] := f[a, x]
ResourceFunction["TraceCausalGraph"][f[x, a, a], "PathGraph"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fd5/fd5d319f-74a4-4f61-8a5d-a22498ee40c6/1248dfb1c5ba5637.png) |
| Out[25]= | 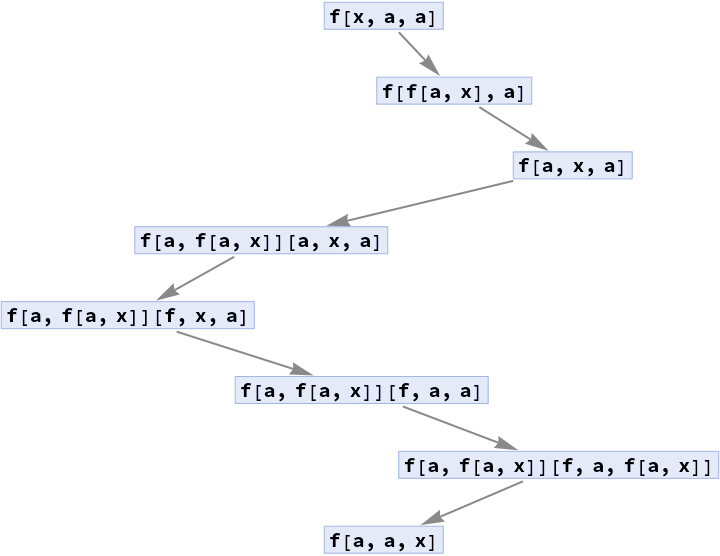 |
Trace a Fibonacci function with memoization:
| In[26]:= |
| In[27]:= |
| Out[27]= | 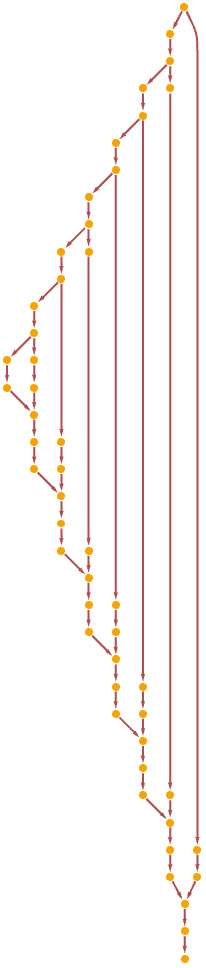 |
Make a causal graph of a nested recursive function:
| In[28]:= | ![Clear[f]
f[n_] := f[n - f[n - 3]] + f[n - 2]
f[n_ /; n < 1] = 1;](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/fd5/fd5d319f-74a4-4f61-8a5d-a22498ee40c6/5b9fbd43aaba4cc4.png) |
| In[29]:= |
| Out[29]= | 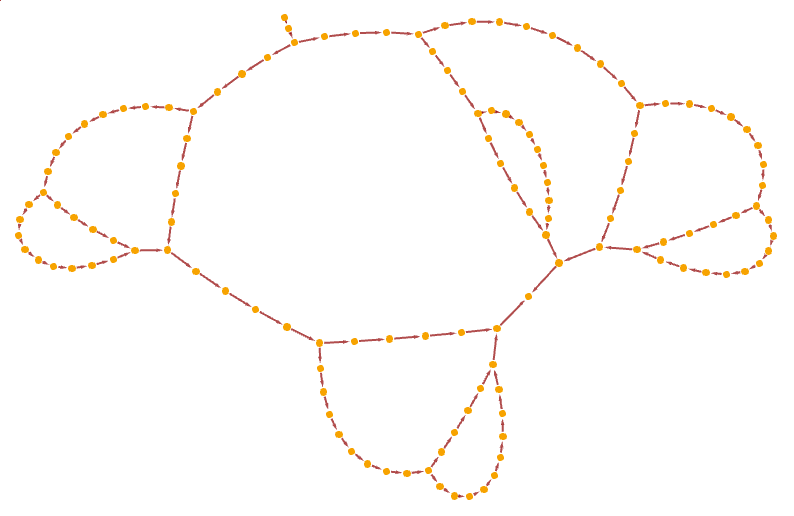 |
| In[30]:= |
| Out[30]= | 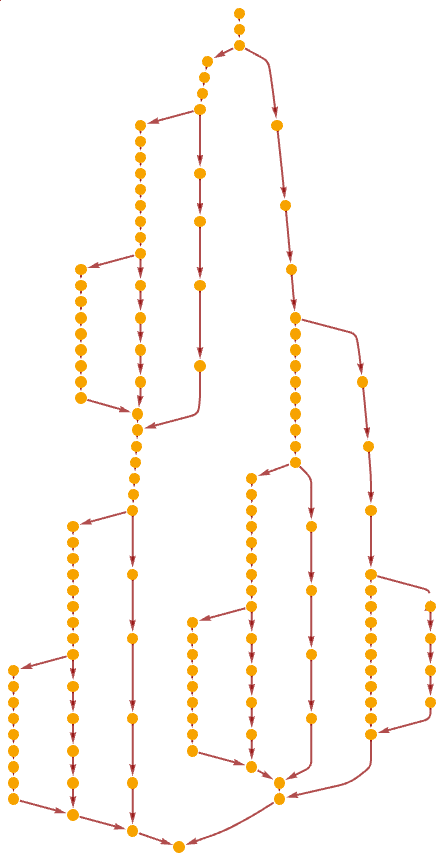 |
Divide-and-conquer factorial:
| In[31]:= |
| In[32]:= |
| Out[32]= | 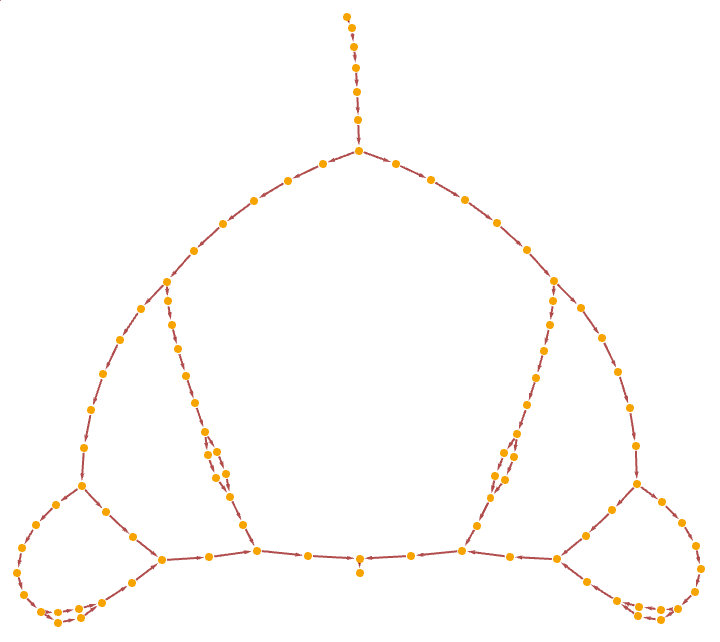 |
Wolfram Language 13.0 (December 2021) or above
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License