Get a pure function whose argument is a vector for a given multivariable scalar function
Contributed by:
E. Chan-López, Jorge Luis Ramos Castellano, Bhaskar Shukla & Alex Trounev
Examples
Basic Examples (2)
Define a function of two variables taking as input a vector of variables:
Apply the function:
Scope (2)
Use ScalarPureFunction to obtain a linear pure function of three variables and evaluate it at (1,-2,1):
Use ScalarPureFunction to obtain a transcendental pure function of three variables and evaluate it at (1,1,1):
Options (1)
IndexingMethod (1)
The IndexingMethod option allows specifying the method used to indexing elements of argvars in the ScalarPureFunction. By default, the method is set to "UseIndexed", which uses the Indexed function. Alternatively, can be set the option to "UsePart" to use the Part function. This option provides flexibility in choosing the preferred method of indexing elements of argvars within the ScalarPureFunction:
Applications (3)
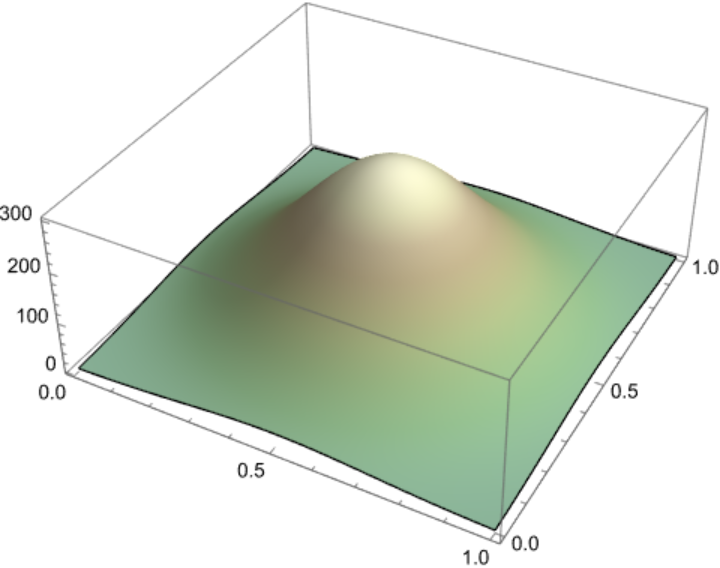
Generate a Height Map (1)
To generate a height map for an imaginary mountain in the shape of a two-dimensional Gaussian function, use ScalarPureFunction to represent the height at each point of the mountain as follows:
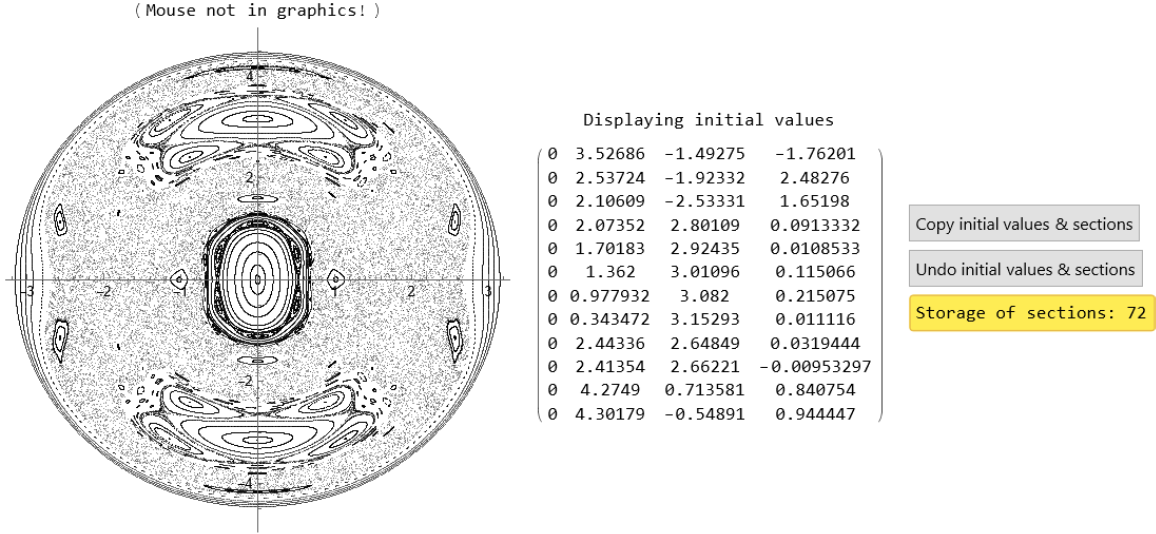
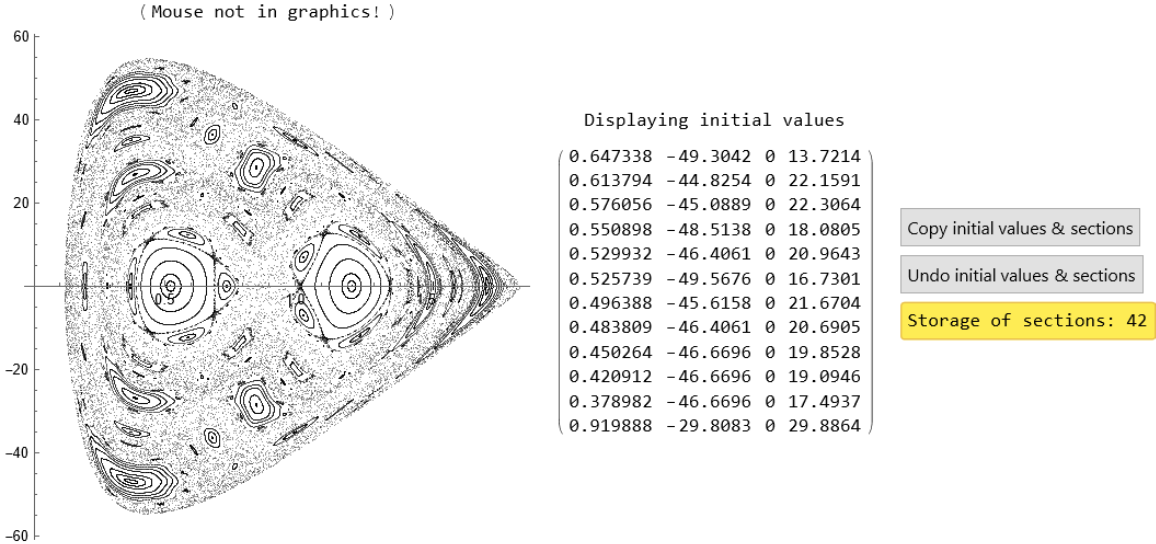
Poincaré Sections of Hamiltonian Systems with Two Degrees of Freedom (2)
Use ScalarPureFunction in combination with ClickPoincarePlot2D to plot Poincaré sections of particle motion near a black hole horizon:
Poincaré sections of the Yang-Mills-Higgs system:
Publisher
Ramón Eduardo Chan López
Related Links
Requirements
Wolfram Language 13.0
(December 2021) or above
Version History
-
1.1.0
– 26 March 2025
-
1.0.0
– 20 March 2024
Related Resources
![H = ResourceFunction["ScalarPureFunction"][
1/2 (100 - 200 x + 2 Sqrt[x] Sqrt[1 + py^2 + px^2 x] + 100 (x^2 + y^2)), {x, px, y, py}];
eq1 = x'[t] == px[t]* x[t] Sqrt[x[t]/(1 + py[t]^2 + px[t]^2*x[t])];
eq2 = px'[t] == 100 - 100 x[t] - px[t]^2 Sqrt[
x[t]/(1 + py[t]^2 + px[t]^2*x[t])] - ((1 + py[t]^2) Sqrt[
x[t]/(1 + py[t]^2 + px[t]^2*x[t])])/(2 x[t]);
eq3 = y'[t] == py[t] Sqrt[x[t]/(1 + py[t]^2 + px[t]^2 x[t])];
eq4 = py'[t] == -100 y[t];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/abd/abd01fcf-c882-4b21-9a02-93c88743209c/1-0-0/7a6569efb25dbea5.png)
![ResourceFunction["ClickPoincarePlot2D"][{eq1, eq2, eq3, eq4}, H, 40, t, 4000, y[t], {x[t], px[t]}, {PlotStyle -> {{
AbsolutePointSize[1],
GrayLevel[0],
Opacity[0.4]}}, AspectRatio -> 1, PlotHighlighting -> None}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/abd/abd01fcf-c882-4b21-9a02-93c88743209c/1-0-0/7e6072ab9cfcb3a2.png)
![H = ResourceFunction["ScalarPureFunction"][
1/2 (px^2 + py^2) + x^2 + y^2 + 1/2*x^2 y^2, {x, px, y, py}];
eq1 = x'[t] == px[t];
eq2 = px'[t] == -(2 x[t] + x[t]*y[t]^2);
eq3 = y'[t] == py[t];
eq4 = py'[t] == -(2 y[t] + x[t]^2*y[t]);](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/abd/abd01fcf-c882-4b21-9a02-93c88743209c/1-0-0/5298b02fea0e43c6.png)
![ResourceFunction["ClickPoincarePlot2D"][{eq1, eq2, eq3, eq4}, H, 10, t, 4000, x[t], {y[t], py[t]}, {PlotStyle -> {{
AbsolutePointSize[1],
GrayLevel[0],
Opacity[0.4]}}, AspectRatio -> 1, PlotHighlighting -> None}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/abd/abd01fcf-c882-4b21-9a02-93c88743209c/1-0-0/1c4f27b3390fee37.png)