Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Compute the radical inverse of an integer to a given base
ResourceFunction["RadicalInverse"][n] gives the base 10 radical inverse of the integer n. | |
ResourceFunction["RadicalInverse"][b,n] gives the base-b radical inverse of the integer n. |
The base-10 radical inverse of 42:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
The base-2 radical inverse of 42:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
Plot the binary radical inverse:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= | 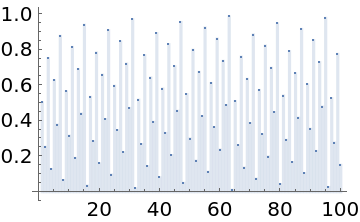 |
Evaluate for large arguments:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |
RadicalInverse automatically threads over lists:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
Demonstrate the filling of the unit interval with the decimal radical inverse, also known as the van der Corput sequence:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
Generate a 2D Halton sequence with bases 2 and 3:
| In[7]:= | ![ListPlot[Table[
ResourceFunction["RadicalInverse"][{2, 3}, k], {k, 256}], AspectRatio -> Automatic, PlotRange -> {{0, 1}, {0, 1}}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/238/238c8723-47a4-47e1-aa5b-5980d566bfab/7153da582a63d43e.png) |
| Out[7]= | 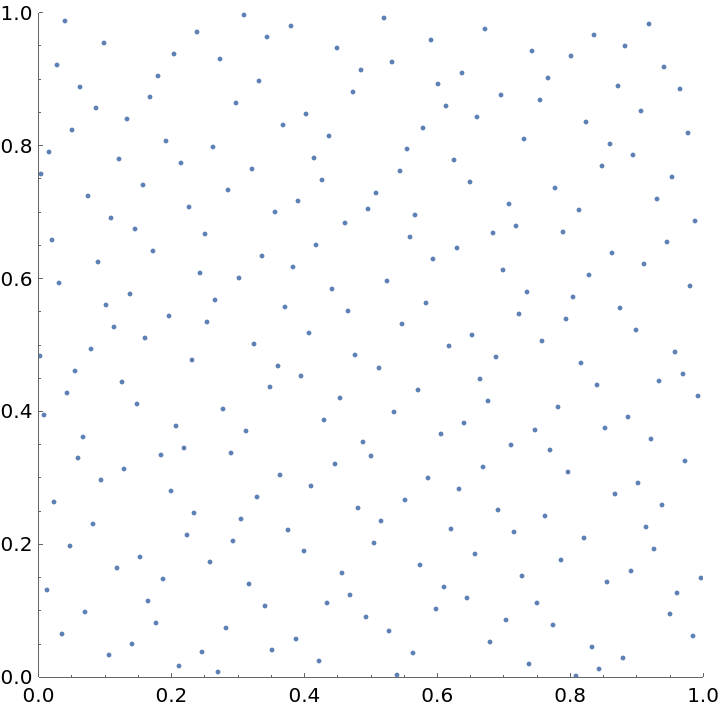 |
Generate a 2D binary Hammersley sequence:
| In[8]:= | ![With[{n = 256}, ListPlot[Table[{k/n, ResourceFunction["RadicalInverse"][2, k]}, {k, n}], AspectRatio -> Automatic, PlotRange -> {{0, 1}, {0, 1}}]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/238/238c8723-47a4-47e1-aa5b-5980d566bfab/5900c7f8533fb58d.png) |
| Out[8]= | 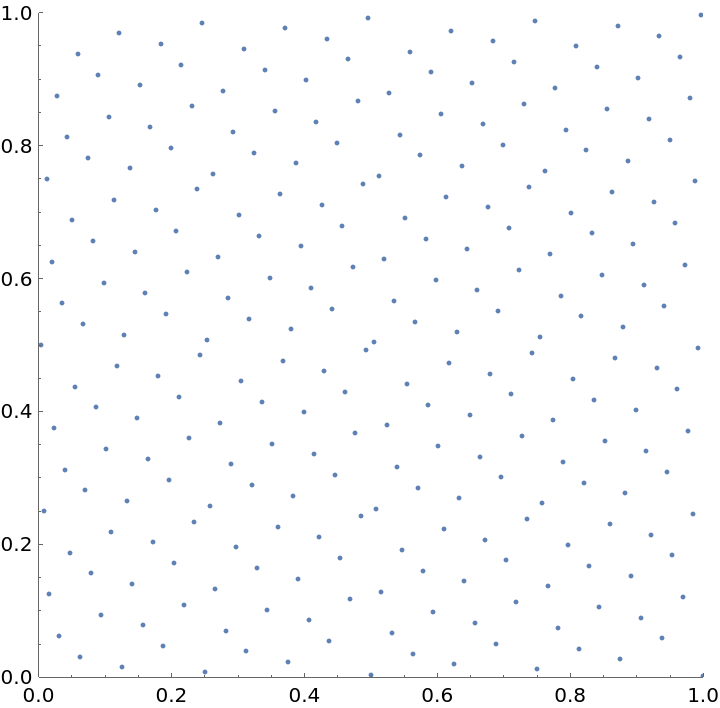 |
Compare the Halton and Hammersley sequences for approximating π by quasi-Monte Carlo integration:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License