Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Compute the LU decomposition of a matrix with different pivoting methods
ResourceFunction["PivotedLUDecomposition"][m] generates a representation of the LU decomposition of a matrix m. |
| "Complete" | use complete pivoting |
| "Partial" | use partial pivoting (equivalent to LUDecomposition) |
| "Rook" | use rook pivoting (default) |
Compute the LU decomposition of a matrix:
| In[1]:= | ![{lu, rp, cp} = ResourceFunction["PivotedLUDecomposition"][\!\(\*
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"1", "1", "1"},
{"2", "4", "8"},
{"3", "9", "27"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\)]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/b2a/b2a62176-090a-4be0-8f03-cea3b821db97/23f65d9d342a4b1e.png) |
| Out[1]= |
l is the strictly lower triangular part of lu with ones assumed along the diagonal:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 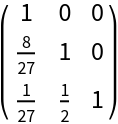 |
u is the upper triangular part of lu:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= | 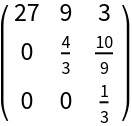 |
Multiplying l and u gives a permuted version of the original matrix, with the permutations determined by rp and cp. Verify the decomposition:
| In[4]:= | ![l . u == \!\(\*
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"1", "1", "1"},
{"2", "4", "8"},
{"3", "9", "27"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\)[[rp, cp]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/b2a/b2a62176-090a-4be0-8f03-cea3b821db97/095412bfef3cc113.png) |
| Out[4]= |
Find the LU decomposition of a machine-precision matrix:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[6]= |
Verify the decomposition:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[8]= |
LU decomposition for a complex matrix:
| In[9]:= | ![ResourceFunction["PivotedLUDecomposition"][\!\(\*
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{
RowBox[{"2", "+",
RowBox[{"4", " ", "I"}]}],
RowBox[{"9", "+",
RowBox[{"9", " ", "I"}]}],
RowBox[{"9", "+",
RowBox[{"2", " ", "I"}]}]},
{
RowBox[{"2", "+",
RowBox[{"9", " ", "I"}]}],
RowBox[{"1", "+",
RowBox[{"3", " ", "I"}]}],
RowBox[{"4", " ", "I"}]},
{
RowBox[{"3", "+",
RowBox[{"8", " ", "I"}]}], "0",
RowBox[{"7", "+",
RowBox[{"4", " ", "I"}]}]}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\)]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/b2a/b2a62176-090a-4be0-8f03-cea3b821db97/485f8f4be0646d22.png) |
| Out[9]= |
LU decomposition of a non-square matrix:
| In[10]:= | ![m = \!\(\*
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"4", "4", "1", "4"},
{"1", "4", "1", "7"},
{"7", "5", "6", "3"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\);
{lu, rp, cp} = ResourceFunction["PivotedLUDecomposition"][m]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/b2a/b2a62176-090a-4be0-8f03-cea3b821db97/7016c8db5f924ad2.png) |
| Out[11]= |
Reconstruct the l and u matrices:
| In[12]:= |
| Out[13]= | 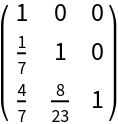 |
| In[14]:= |
| Out[14]= | 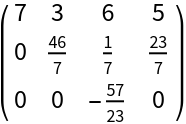 |
Verify the decomposition:
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= |
Use different pivoting methods in computing the LU decomposition:
| In[16]:= | ![ResourceFunction["PivotedLUDecomposition"][\!\(\*
TagBox[
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"3", "1", "5"},
{"2", "4", "6"},
{"8", "7", "9"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\), Pivoting -> "Complete"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/b2a/b2a62176-090a-4be0-8f03-cea3b821db97/671a67e66736a66c.png) |
| Out[16]= |
| In[17]:= | ![ResourceFunction["PivotedLUDecomposition"][\!\(\*
TagBox[
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"3", "1", "5"},
{"2", "4", "6"},
{"8", "7", "9"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\), Pivoting -> "Partial"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/b2a/b2a62176-090a-4be0-8f03-cea3b821db97/26aefca371d801a3.png) |
| Out[17]= |
| In[18]:= | ![ResourceFunction["PivotedLUDecomposition"][\!\(\*
TagBox[
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"3", "1", "5"},
{"2", "4", "6"},
{"8", "7", "9"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\), Pivoting -> "Rook"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/b2a/b2a62176-090a-4be0-8f03-cea3b821db97/54aacb1be1260228.png) |
| Out[18]= |
LU decompositions are mainly used to solve linear systems. Here is a 5×5 random matrix:
| In[19]:= |
Compute its LU decomposition:
| In[20]:= |
Extract the lower and upper parts of the decomposition:
| In[21]:= |
Solve the system m.x=b for x with two backsolves and two permutations:
| In[22]:= | ![b = ConstantArray[1, 5];
y = LinearSolve[l, b[[rp]]];
x = Permute[LinearSolve[u, y], cp]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/b2a/b2a62176-090a-4be0-8f03-cea3b821db97/147a2e376e4b76eb.png) |
| Out[23]= |
Compute the residual, which should be tiny:
| In[24]:= |
| Out[24]= |
With the setting Pivoting→"Partial", PivotedLUDecomposition is equivalent to the built-in LUDecomposition:
| In[25]:= | ![ResourceFunction["PivotedLUDecomposition"][\!\(\*
TagBox[
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"3", "1", "5"},
{"2", "4", "6"},
{"8", "7", "9"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\), Pivoting -> "Partial"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/b2a/b2a62176-090a-4be0-8f03-cea3b821db97/0fe632876ceeece3.png) |
| Out[25]= |
| In[26]:= | ![LUDecomposition[\!\(\*
TagBox[
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"3", "1", "5"},
{"2", "4", "6"},
{"8", "7", "9"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\)]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/b2a/b2a62176-090a-4be0-8f03-cea3b821db97/7af91a4a5d916dbc.png) |
| Out[26]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License