Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Invert a zero-frequency shift
ResourceFunction["FourierShiftInverse"][data] rearranges a zero-frequency-shifted Fourier transform data back to the original transform output. | |
ResourceFunction["FourierShiftInverse"][data, dim] operates along the dimension dim of data. |
Swap the left and right halves of a vector:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
If a vector has an odd number of elements, then the middle element is considered part of the right half of the vector:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
Swap the first quadrant of the matrix with the third, and the second quadrant with the fourth:
| In[3]:= | ![ResourceFunction["FourierShiftInverse"][\!\(\*
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"1", "2", "3", "4"},
{"5", "6", "7", "8"},
{"9", "10", "11", "12"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\)] // MatrixForm](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d6a/d6a6aa8a-5551-4925-9aad-dd4db679baf1/4b05d95bf94375c3.png) |
| Out[3]= |
Swap halves of each column of matrix:
| In[4]:= | ![ResourceFunction["FourierShiftInverse"][\!\(\*
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"1", "2", "3", "4"},
{"5", "6", "7", "8"},
{"9", "10", "11", "12"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\), 1] // MatrixForm](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d6a/d6a6aa8a-5551-4925-9aad-dd4db679baf1/0ca24f0d2eaa0eb2.png) |
| Out[4]= |
Swap halves of each row of matrix:
| In[5]:= | ![ResourceFunction["FourierShiftInverse"][\!\(\*
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"1", "2", "3", "4"},
{"5", "6", "7", "8"},
{"9", "10", "11", "12"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\), 2] // MatrixForm](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d6a/d6a6aa8a-5551-4925-9aad-dd4db679baf1/24e8242745e4e533.png) |
| Out[5]= |
FourierShiftInverse can be applied to a multidimensional array:
| In[6]:= | ![ResourceFunction["FourierShiftInverse"][\!\(\*
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"1", "2"},
{"3", "4"},
{"5", "6"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"7", "8"},
{"9", "10"},
{"11", "12"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}]},
{
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"13", "14"},
{"15", "16"},
{"17", "18"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"19", "20"},
{"21", "22"},
{"23", "24"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}]}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\)] // MatrixForm](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d6a/d6a6aa8a-5551-4925-9aad-dd4db679baf1/799fe364805465c1.png) |
| Out[6]= | 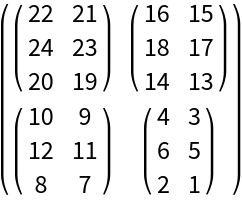 |
The dimension can be any valid part specification:
| In[7]:= | ![ResourceFunction["FourierShiftInverse"][\!\(\*
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"1", "2"},
{"3", "4"},
{"5", "6"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"7", "8"},
{"9", "10"},
{"11", "12"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}]},
{
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"13", "14"},
{"15", "16"},
{"17", "18"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"19", "20"},
{"21", "22"},
{"23", "24"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}]}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\), -2 ;;] // MatrixForm](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d6a/d6a6aa8a-5551-4925-9aad-dd4db679baf1/66e2572d6faf5528.png) |
| Out[7]= | 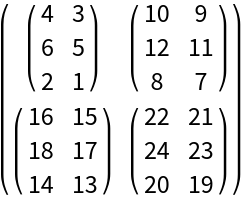 |
| In[8]:= | ![ResourceFunction["FourierShiftInverse"][\!\(\*
TagBox[
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"1", "2"},
{"3", "4"},
{"5", "6"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"7", "8"},
{"9", "10"},
{"11", "12"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}]},
{
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"13", "14"},
{"15", "16"},
{"17", "18"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
RowBox[{"(", "", GridBox[{
{"19", "20"},
{"21", "22"},
{"23", "24"}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}]}
},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Center}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {
Offset[0.27999999999999997`], {
Offset[0.7]},
Offset[0.27999999999999997`]}, "Rows" -> {
Offset[0.2], {
Offset[0.4]},
Offset[0.2]}}], "", ")"}],
Function[BoxForm`e$,
MatrixForm[BoxForm`e$]]]\), {1, -1}] // MatrixForm](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d6a/d6a6aa8a-5551-4925-9aad-dd4db679baf1/7846b02e223cca31.png) |
| Out[8]= | 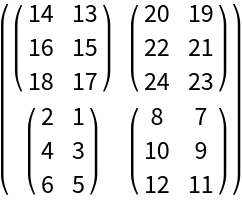 |
An optical low-pass filter model:
| In[9]:= | ![opticalLowpass[data_, r_] := InverseFourier[
Fourier@data*
ResourceFunction["FourierShiftInverse"]@
DiskMatrix[r, Dimensions@data]]
opticalLowpass[image_Image, r_] := Image@Abs@opticalLowpass[ImageData@image, r]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d6a/d6a6aa8a-5551-4925-9aad-dd4db679baf1/4b1c0c8bb8abc2cb.png) |
Apply the filter to a image:
| In[10]:= | ![opticalLowpass[\!\(\*
GraphicsBox[
TagBox[RasterBox[CompressedData["
1:eJztXQdAFEf3v5nZvQYcvVsoCoJYENtnVzSJJiq2WKLYSzQ2NDFqNBoTkxhL
1NgTKWqSLxbsHaOoqLHEWDCxYrBrFFGjxxX+U3avwN0Bd6D5f+HBwZW93fnN
e/PmtZkNHjC68xAokUjGyfGfzv0ntExI6D+xixt+0W3UuHeHjho8qO2o8YOH
Dk5oOIAcJgHCo5zKqZzKqZzKqZzKqZzKqZzKqZzK6SXQv90FBZhedRteJf3L
4ZfT/yr9y8Wajut/cx9wXLFU2/9WFxkRA1d3JAGwBN/4XyADGoB4GZTA/ylw
JSIi/OBfjJ+Iwv+WbBdJgBqzgD19OSTqF2B8+soIAMTmPCr5L+2SwgXRqxc2
CBj/AYIvqTEEPJM1AF75TAoAx0EIEaGXxH8CGwII/xFeJMbPB7R+s93rlXj+
ZSl+Mu4BE7yXc0FbbQEocvHZixfPr2khfXn4MXK58h9hbAPedfbjy4lf/fL3
mhDuZV1TAiE/Ya7yFY1+WkNhMPm40DNXeri61Dt8t7e07MY/FnYoFm8Q9qve
vnLAucyuVhQBZuOSB0QVVy8O5eVeC/UzXctQ/5lyGvBBk27o0l8VfjrfQWHe
w+o/sIqM46vtfTJKWWb4KffpcCcyz/l89VvawwNOZXW1ohqDJx8gEkQQSnnO
bW7unmiu7IYjkXkyybKp1ndo16YXXiH/kSy6UdPGhJo0dEeQQ26zH57vLi/L
6QifGskUckpSmQsXdBbjf0X6H6ufn+/ff/DgAf5ztSmEXODcR6c7y1FZXhFr
Gq/uEz/8cOLECRPfRlKu0plXOf6VY77+as6cObNnz/k0DKLQRY/PtkdlbIsD
WPX7Wzdu3ryRfXsNz8GKZw+6lOXlbLWExDlEkiIUvOhRZlcOUZO0DC8KVa16
de/Ro3uPd1pgNYDxO70i84/qIoMCRO6f5fw5KqRihQpYE5TlJemUgx8QAQ6C
CmfTnYgiLqsr2m6OScQPRl7SPfrjwoXM38e78GV3RezpQyh4feT6Fc7sd4Kv
0vwVp3/UNvPC7xd+x5SgKrurMexCpAG/AhW3/uj0qtgvMZEAAINaN2/ZokXL
Vi2r8mXGDWAMrNFugJyyYYyU2mBldUnb7TFeGE9/HLVMOFh2/p/hekAQPMQh
onHLED6wGqU3vsssUmoPQqqehIiMobHAYpjGdquBUdLZc4kxqGw8O72YaVPs
wWirFfSats4KgKkapEEZYzAUAsMYMZFd+hIW6bYaLX0BJusFKIY8gMW4VymH
3wB1OW0Q/tzU4jOwCopCQJtrlAXhMHKErfMyrwKwGY95vfR8iAQ9ScAT+z8W
0AOzTnacaDTX+gkNUi++AVlzRb9QYAfFQvloiFkDq8UPokal5oXYD4IQAMHp
Yn0BC/OaxgRLVwCAjUwOEJ1g8SViETnKdci8VTqECHCTAyXi4LBxWRrcZB0A
TSwtxM4svl3ga7C08QPAOzkpbZHUhKkcPhb/8pAYaFL8XOnkzBPoUOZEPlIg
wziAUG7rvPgzXhhLSKp0dpIjgPC7TniCwX/xP2II8YqCbVMgVLryz8G39/+c
fsAG9ZAhQWYBCNqafiB9f1o3oqSchx7cf3B/+vY2hCGyDw4cSP/5yCIVFA9F
blMO7bdyynRMB/ZEE+4SmHW27Dv4RQBXcd3BQz/48ZXmHNyfWo2KVd21h8y+
tz9jlj8q1fkXa5qxT7U6vXXSjVNwBgUfeQ+/o3k0CnMHuX2m1+l1uvs9iaTK
lql1+TpdupchOMJ5Jutsnje3ORMsCJtn52nXBXNVsrS6zCA+fKtG82cMHRqx
F3RanUDkiUazKZhKDZQIcULH8cMxT/MMF7FAmrFy4wQXfgdj0jwcSUav6lMd
xd+DcIpf8kKr12oPeJrht3Ve7eNmQMDfLFutWRuEQq9ptecrc2FbNJrrdaha
jf09T6NlRP+r8zYGS5lZUEqjAKugsc80+VYJM2qsnAW8ySWr3cXvaR+NxNxB
Lp/SAx70IOpKukStJ/z3NCgsziNJp7N+4nx9bnOGH4Cmf2p06zD+LJ0uk+DX
av+sQyfQqFmJSYkCJWFKTB7nA4W5pZSGAeLGPNZqrUupTpugMJp54Xf0+nzM
f6KdXGbg53qB/9KlBvygePjzc5uJ+Jtla7TrgiDFXwlh/DrKfwSkHt4+3qbk
48YhFiXlpGIgyrFugOC9+zm5T6xT7iiFGJLH+An/dY+o/Iv870kkkWf8P1B8
/HqCHwj4tQy/luLfKuDHYsXxSCCOEULCrOvcdrgfLA38sOGUyR9NtkYfffRR
Aymbhgn+MMJ/LcWP5Z/wn8o/Gf9q8iLdExQff3Mz/MEo9DrhPyfix2fybNG2
3RsCtSV/3qznxNGmuA0/eyict8cvFj0Nwa8gpguwRUgM9xj4T8e/wH+Kn+o/
rP8JfsOoLBb/JSJ+nbn8C+O/yf6sayKRZ1eyvqtA8+8geNW5g+F2BuIF2xSI
fp1tCTJaPy8ff+wFE/2Pn+VpNgZxtL1O0YsPh9sVFiHn5aXYqxa4L2a5bPUW
fBX4cdfHZqrzBKJPXqg3BCHKMuQ851CYfWEhiALaxXcNEV1OYE3+xRCE6AC/
dPwQVp+TnJzCiP5PWvO+D/UPAXKafSjcrkwEkkYv/+3s1TURVAIARLxcKZdZ
IJaEkSt4JOiply//nFzKm5AU/yDB+3L6Yr994x+plmWOaTXs8mIP4sth9dZy
9pezLNFXjGY3l6FXxH/ibhYQThYawf8Vse94IXvwA+WYZdV49/SDofTcHBz1
+NnzFzZotPzVyD/G6h7TqNF/RCLPGkXKWZwBO40yzi75h9DJQyHr8uccKWDl
XKOe5uXbcFN0Y+VIUmb4AbP/tXo8/4dg/Oeo/avLiqEBhWYZd+4Z6C7+vZtS
SYw+25uGAhzHu792OCMG0sAy8X90elvtTJDDssNPI15NszV560NQlWtazXls
/2zWabLq0OBH7Pk8jcH9w84Um/8MwRj78CPoNfzc6Y7CcOIwfq2NZmL8Clh2
8k/VfHPi/1H/V5tZmQ/fkpd3vQ6Nesf+rhZdE+pKa7QbQ3hrcbVi41f2uXym
m5JjIUcEMP9t45eXIX4qxxHzE5PHeHO+XycnfeEt8x+/MvHrYKrmo75aSf0+
SonE/0vwcTT+g6Q9L+6M8/dyl3LMABp258GDv6zRw4cPR2D/F4Iywk/1udTX
18+Dg7y3r683Dzl3X18fkmIEQObla05+7pytcG1xCLhuU18+dfrXn6qx0K3E
t2bN2rUsUE1M5J8PB6miLSP5p9FDji4owX9JYAfRF9RARxwyIw5ajysXk5Dr
/F07d+3euagqNLhCtghCKPqZZaL/xQwQZMklSEP/NDRMR0eh5jjq8CLev3LF
SpUqBcrEad22/8eOKSv8AkHB1iFlVlDoBsgkgL02ZB1gEemqIonavPRHiCQU
hd+YkS07/Bh9oxEj4ysAr/7vDW8k51sljGyhIK5H5LCRpjQ2ztUsxWAPQWDI
W9AuhpyUs048L9Z7lyn/EZx88/6RxiD8zIN7U52l8x88mIVPhbg+lx8QHSzQ
g79+COId1X+CQAuSjbu4Z4+evWxQBIJlzn/MiY9z8840lkRk5f09w0m6TKOe
5wkRgvG3X+RpKOXh/y80qcHIQf0nkZgoHSICo56oxSCDRUpQoJeC/0neb41B
5DXti0+dZct1mq+98DVQ58Nnz5030NnziyshliQHdtu/AhTxJRj7VGMrT4Ht
P1Sm/q+Af9qTvDNNJJFZOvVnStkKrW6+J2Y0qtAyNrY1plj2+1odJ04ipE1L
Jf6N9evopxob9r+e2r9iX4XfNca/XWfoSQD0fk/I4p86vU57wBOIeDjPkuAH
Esx/Iv/XdS8+VUqX67TzPaEEmXj4QhCe2CJkBFQa+2UjDprVRtiN36b/kz9W
bsQfcYtY4X+NJNdV0fiv7kFPMndJl7wgsvKzp9hMyHmm2MKv1+c0g8iozA34
9QT/Mp32aw9iBdUa+74JjZ/QzY1kRgH0mrNz5YEYiBzGD7H859lK0+lE/0fC
8h9ajfbhKHxhpJqhI8mwez1IK6TL1Hl6jWa/l5j/lGD+28ir4F583BQaHXhL
+BHmf7/bWDnlkV+mA1NDeMo0vwmvx5zoBaHD2XAE33uQ8zjXOj0eaYI/7Orj
x7mPbr9LWO768ePcnNzcrLdJxl6+4K/Hj3Oe7BDwE2PWY8XTHBunfXyrqckQ
toQfyxDqe0dNI79sDlBj/5f6f9hErr96TTVhTZ4DhJtQc+jgwUOs0+BavJjT
AcCzD35j8MAaxIZQNMDPhwztV4WYZFzzQUMGD3o3TilCgpwidpiN8w4ePCAQ
mI5uC/gxc7qeunjp8qXLly9dunjx4qWLV1dUpOkIxNVJ+TyYc7wWmXgbfAEn
w5ywmyi6nJjpPM1BUWcFChYSq94gZ8EP44BGyOZ5sWVlWiFlET/2i3zqxMTU
jalLf/GjXpiMxqORz5Jra7/9D1agdsUATfBTI7soCxgaDhbKfozfoE+QxHAg
MDmzTc+qQK2clfFPetSkHdgiZFVRFRP3pR1sAxyeAJg3bfEULEMEDC+YwSQ6
oMBoSBRGU2LC3572RHO2CahG5j+FbBmb//D837wlo1b0ERvtJPgsUrmUBTAc
uq7AIauNMtazSaDEhHVC/lCoQ3AcP2byNGL/QoxfPUMhJfafBymN6X72+p/Z
Brp+M6kizxqMOOIjOoxfYj2gwOpMxBdCspT9FQADiVD/VlQNYdGEOIwf8z8y
K+/ZDKV0qUaN+Y+tiL631YL9r8GzgFqTGiQTPJjSqQABDI/Fj0xrzQTkZKQL
PjMVCGKMQ1MVYSchyE29n3uyiaT6H08eTVfKFj3NneNJejX++pOnzwz05Om6
IN5xnpsQhoEVtWUVDREPjMlfROJSHB3/JCqFtT+ZffC3OcQ7viYcwJh+A7r5
S9x79u9fj0dNBg1soiRhkbA+AwYMHGCgQW+4lPK+EwB4RUVapOrVq0dGOhtM
H3lE9epRkWEKskAtsAb51IcEY3zJYdX9HW+UIfQDWGiGxnlMihNo/Id9UpoS
AEG3HXv2WqQ9e3el1hejBCB0HX5jdyK2djiXMXt3792zrQ9WUMr+afjAHSPk
juMnC/+IUGG9hv/SYCfJ1mCLg0yD1OzgeB5KRM1TOn2AILb/Lfr/2Lp/cacN
FPdTr36L2KHna2HLx30hKUd4/BF+33m6TqfVPp8nL4Wm0LgclQJEwn+Qukcs
UgcNq4IALC3Vx4jkPyz7Pzq9Pu9uG0M9Z/Xb2NvRnquJ+e+2gDx9PBkzzXka
KQLE+EtDF8Pw4e8PceebJLwfA4KHThjhjwWMb/FhwrgPxjMaN6Gbq1g16+iU
K1yT+L9W6j+xANxtbcAfeZu4u+dqIYIfP9XlTsYtdp5OfNnnc0sFP4i7+vxK
iGxyzpPBktd+e3qDyJpsxvNnz58/f/GCPJ79vZ7WPwoKwfFLkmzoqCcaazWa
mjttCuLH/EcUv8h/kjsuJfywY5b2aiXZ5KcvBknanHtxB18LymZonxPHj8b/
1LT+lRVAIEcKgQ1GH3ZjBp6/8Psflun3402BCX4s6Wex68e5M/5/hHlgwO84
fHyRuCx9VmXZlGfqoZLXzmvuEfz828mJSSlJScmEkkj+jzEfO8cm3pYd8AWX
DqEAVlpgiRo2cDeEfqoz/tcQ+U/kXyLKf6mMf4I//3pl2Ud/vxgMW5/T3qlF
FJ5rgL9/QECAP/6Hn3jyzK+Crs1j3aj9W+ILA9JvuPuE9Bcp5bXo/9E0jDH0
ReVfR/BT/UfwAyL/pFeez5VZNaEJQeNT04+A6TEm+J+ph4A2hP+kFSo/Xx8f
X/wgf309eBb8dR59+OeV7lBS8q2RsE5xjmjeorYLYgkmiVDhZQG/iT9rH35m
LJstoDH/GAp2dSH8EoK/Fv5cOuJkxtFjR48ewT9HM375OlBK7CJe1bnjsIP+
EJZ8GsBDquXOPy4d7cOzNStAmHMtEA01mum/kuKnkzYU0rYFmkHL2MTQugX8
WoIfyj7XafPF+KxOi/Uf9TsRbLD7aBXRESsRfuSffObDgbv3RbHhA/zqxtSJ
sUD47brRbmLy107+c5CrGKXkICzUTMGR4GzjB9JRp06cPHnqJKXjJ+dX4Gj5
F1cpum16V2hHMQBClee85yWf+sdbtAAQcfEnTp+1SGfOnklvghzBjxsqbfnf
A5/6gEJVG6yKDTWpZxIzKowfHxIQVaNGVM0oQjWiooLlbPbzmPpJvcN24QeA
d1XVGnA6yYcOPh6NfqrWW5r89Xrt8zutgWP8RwFLZ7U5MopmLQo0g4RQW2bM
MukaS/iBk7ubm6urG/4h5MzT+BdQ9D58fKGPqfIoNn5sUyqm/Jo13Zcj+CGx
/yzmP0hy4+7rDuHHA7zGlvb8pg2Fw3TUd64285fZhfgvnfzsxRDQ+pzuLsHP
x30zf/6Chfh34YIF878Z7omY5MhDa6gQZ4cXRLQOX63V/D+HKcjYhnDMszyL
9i/JZzH7D9g//6Ea27vKNqXSSFGBj7Dyc/edNw+KZSj40fGaPquSbNKzF4Mw
/jwy/3PymdoXGuxtURctL4+ufyJE/CLOrqALdGsUrpQ2uJfoTWu/sfxbw6/X
3nodCslf++QfcZHpCfz6RFB4DTcVAPj1PGgI4gPQ6U/99YpyLP+D8fyvvlcb
O8GymTo19kXpL6l/DxZyZoJ7WHJCsPrPi0Kcez34zBnR+pK+Z34985sFOn36
zOmMRg7pf6yn/b5dO/JUb67QnmFUrBCa+zUwJPQBqDltzlRv/o1Zc5rCiIlz
plckY7X9vLlz5s6ZM5c8Zs8d5MUZO9IumxMA1YfZP8y7eqCRsATAycvLw9MC
eXl5envKDaF/O8c/X3/x/iluhFMF5Z+GDj+cRLJZAn4oVTopOSRXKqWIJytP
CYOkLnSxqLBqVA4d3XwDt6ny5E0HFrWSC4Vd1haqs/ivY/YvqWlz8qLxwQJj
lakV6O5lmjOBnJSHZNMZPLR5Gc9RE4yU4Bjr4CCyj+0mF4aczL+6C1kBwqZP
K8FLYYWMvfafGDij8RtJoSC7sJOCEDsWPiNeHUmbQY6k02g/kB8a/KJBV2wu
iZuC2o+fRthIpI31BkCG9JUFF8gC/w3+H8WfT+I/c2Qmg5JCBXJXV5Wbu5uH
CwQKdxe5uzPnil0OGX7Lzc3dXcUjNxc8pfNyMq+zml5ajit/55sZtfnui2bU
gd3nz6iL0VeZ8vW8OXPnkZ85C4YZFpg6FAU1bikCkQKPdQ8LRHWADBXmPyrI
f3P8rKgMxWdkHD6SceToV56o85GvYjdPr5z6bSXQ4tjhY78c++X4qgjPH+au
XrSudp+Tx04ca8TLGFslnGrpixtdlYteZHWB859f7Y5Z3vTC38+esxUKfz9f
V1nK+qp0wl/EQO+RcejQYct0cHdDC/6PCX5USP4pfFLI+l7mH1dI6nqZt2RA
bmqncyvCMneGgg6PddSwOBjt/eumX9Mym3Tbu2X7luiQt5wAXWaFnJfp73aS
Ldff6CJZrMvugQdEg/RrWVevU8rKSqosFTOrjm1DJapcDiVYs3902P55DVrE
L8g/EPlvMv6pXRvmBiN79ujeo3vPns2dwMDHqR3Pfht2YWeoJC6H4tccrOP5
a+oJjD/+zLHjvzRss8KLlbZyLhh/F/my/BtdwFJtdk8sqD6vx3XsENexY8cO
HTt2auzMaoOx/Mq8S2EjPsChUc8s13/ptPpC8T9L4z+f4jeBj7iwDzs7tV/+
3crEpMTkMW5gYM7GOIq/iqRjro6sE807GONzasuptAuNe6Xv3benQUCcirny
yGVF/t3O8uX6W10lBD/mMi9XyOVKsieeQi6TcUK9MuI6zvJyfF8kSNf/W6lQ
0uvE+L8Q/9Ib5V+vFfFT/stN+M+hyFXvKSdhtwJ/pN/gBwfkbIg7j+V/V1VJ
h1wtObEGy3/ays2r99YdfOm3s6eaSFUcK2xHLsv1dzoR/F0w/hu9sAauNm9V
YmJSMvlJXP2+r1AgzUftyAywt/jB+DXcv2OeqC2u08c2t/p2rBH/LbIK82wU
yX8soPkPLP94/JOVKWbxXwD52B+HuUf379+/38D+Q8ZUkAzM3Rh3bkXVzF1Y
/nOxr4WH1sE6spCWI4eMbBc+dlzC2GCOR8JyDJfl+ffI+L/ZRbJEd6Mn7u2m
f7xQa1gSWK3eQO1/fInaq3YcDUBQ4sgsQAiCQafPZV6wQJmZF85mNDMsfQ4/
fP78hcytEXj+d52amZl5/uQIsh/I6AuZF87/Nllh0gqWt2s18/MvP//ii6+m
BlD5P/ctxl8FEvnXU/0ndZrw264zGf/JvJp1ublHZSnbCwc5L8+/20m+DOs/
gPUfxg/r7ckkW4+xJi2ryNjvMf/sgtOvi9uFOkAABMW2bNnKArVsGduyuadB
/7s0aRXbqlVDFYlpRLSOxR+H4iZzVWLxl1uGFbTvEfzgqVqj1Wk0G3yx/t/Q
+Rwe/7uqSNo/JskWXV56tEzxfvraw+nRP27cvKFW7FcVmDlE5B/jX6G/2RUs
097oic0n98b4aq1jY/HVW7WOVrBVARWWrk+7/yErhnQMPmQWmqXoH8cZXSxW
M4+otwao78mixtQNM0tFCJZM8+kzPv30s08/6+MCG0zrUzPhbZ+EgV4gctoM
/N6MT4cG8Ir3D/2UcbD2mnXr19eInVeZ5dCx/hPxS5ZqbvbCE5RM5ebqpsJW
kkpF4h9MHuWVq7ydXh2WwubYYqjXgvVnuv8QCxYLfqwhPw1YCLegBU2Oc8YO
lJenj6czz7u4qpxdVXIXJyThXZzxj4vKiefkmP+H9v/n7JXLF1u4VVbw7KIu
K3QY/9L8m13AEg2d/6OStm/btm07/tm2dfcMP45Z5YjzaeyMHN4HxLi8w/LH
Jk+AoVLKxP5iXze1xug7WFK6rftp/frU9Yurgs7r2vRNaTo+pRIkLgctnSC9
h6r37NorPmTIB++PD+VF/cdh/t+JkxP7ByzC9g+CfNOL2jwt09AazcYgKbsA
rdtwfCskIygL2A05CiE+IxHLwFjYGYjwTb0bModBqJDDfvsPZ2RkHPpvDfD+
nfhPrnVbc6s64xtH6kWJA+I36/sF21tMO7h3dwOfqgqhrsZp2sm0NrIpJ3a9
Bqae2NkOd1nM1l9OnDh+gjyOn1gQiAzXlJj5TvZ3gdXqP9NeElJB4s5U1HFi
xdjmxQgEP/Lo9ppTtfbt33qr/Vst3cH4O72nXu20+mYEUR585ao88b/C/KQV
Vu5be7rNlD1bN9dp/W0Ek2XIVWkQ7cWFNKzjDYMbRntjaXGp3aBBPUJ169Wr
H6FAQmcLPHDMDyBAELTWA0gogGLVCEDcnAxQj5GtRypkgdDiSL/531TsvWXH
rl07d30XAT64Ez/9Wqc1tyLwOTinoZOdsYurmjTSpWLSz+t+aztx56bUmNof
h7K4DlmdS4o9eCknRTKe7LnIUR9YLBtFhtABWxPl4PyP0Vdq2rhxE1NqyqhZ
jEoQLhTQpGmTxvVVuBP88cdN6jvhC/s0w0//Y2lzWoSq/DAvKH5f2s/79+/9
PlIy/nbv6de6rLlZDTsbMu9xCSqZXOnSq53Sd8riL1a1+PjnnVvryj15IbBB
LFu5ylUhdXZz5pRu7jIsZM4s9k3IiXYAq/sUVzE5hh8Nv53z2ALlPNxXjxp/
APF97+Y8fnAwGiJZn5ycnEdnMBLY9dGjRzmXqhb0wohUcC4NoxQhsbRgs5Er
GH87/mMi//hbTnGTRg6a2Gjg2LfHTerqXvHD2R8t6r1117Z6vIuUEyNEEPbc
k9bX5/Mjc1z67j/clUcuEw8cZJSeMTsQifNO6WyBRfIfWvP174L5r86oLxQ3
8gOfaPTqk3UhkvbHhr/+ShiW++4kInurWsG4FtUTxFYYe/fug/sP7h2vLXn/
Vp/pWV2+x8cqY9c/P7VfO/Hknz/e0O8PD/xm49K0nhu3pNar1tcLCMt6MEfG
PcydVGG9bpvqI51+uBSpVmqFhRQ63SZa/08z0wgBq7WbxSaS/3im11nCrznS
gJkXkB/0NF+nPVkXIFk//IH2SjjG3ytPl6+/HV5o/LPldRC2njtv/oL586eE
gjZfNoj7LHrQlwFAEZ385NDB3HcTd3x4Qr+pcoUFG79Ne2fr9u11GkyvJCba
cA+Offh4QoX1+VtUkzX6YVKo7Ltk6dKly5YtW7pk6QgvVv/CcR4xTcPMLBR7
8Y95ZnH9j16XUV/IjGP8er32ZAxC0r4k3HUlHKuNHhrsBN4OK1T4KSpPryqh
VfGvt9yzok8lv8AAD3cecXXScnb8dql524Y9Tudvr+zRd2Tf92M/nv5xuFMF
JTKsMoBjHj7+MHBd/lbXSdr8YVLEqbAhJZArKwiHiH97z77JzBq1BzabOkjA
BQ7LunXXAt25s7OOML3xA59hT/ZUDL5qPzJUroYR/MS9xfwvPAHQ4hQ45DT2
qs6f6iKfsC4mbfCIn8I4gKRvbctKOXJg+KGUn46oD4ejsE++GfZWwqyZYTJv
JwQFs4rwP3dC4Pr8rarJFL+sXqcunToT6tSlsTOb/6HrrIMfRCO76t+BEI5l
Uxn0qRFZI6owVY8KdxaCcub4823iZ5O40o3vunXj5i2bNrVRfHXsP3+Mm3wo
Cis4PuSDHyb8OHbMw7xfVt07Xh9Fp99OHrMwbUvd0Nn1EDBU2Bvx6/LflUG3
FX+rGT1/voGuf8EuWOh3Bw6t9SrGLrOFCLJJhgV9WdmpFfOfA3bgx03iVZ3e
lEbGxXWKi4sLUnxxpMHl8ZOP1CDJ5nYHbq3L+bRXxq97Zh1eVd+n1v7sxROO
Ps1p4/N2EDIodhP8Wv27UuQy6/KVa1evXr127fLV7yrR+Bfi/Ps3bnkqDFgo
LCgSP3HXPAZHCMqNxdUtLXyR8YKPUzL8mM3RBz9WvvtH5oU/zmd2kX15rOHF
8ZMPk8I51PJ49tozHYLbvd62QYemfaaGTVz7xaA5uzbXRQoOQh4JNiDBj/Xf
Noaf46Pbd+zQvn37Dh3ad2zowuSW858xe+F2d3uKAGmh7fBzHaFgwVkp/wFs
KX5J8dNS1cqThyjD32rb/s12bSvLvzhS/9L4SRk1sBHJtz1ye+ue2v/5739n
LN01rP/3oR2OXJg7JHFFzcDh1Yizjd0gYpFR/q/Tb1VN0ujflXHSSrTGmtRk
1wiWCWsvlA0mz2xBzM+S1z9JoKz7pTsd6eo7fLUaAwYOskSDO/kK9nWJ8FPu
OLtxXVLXrk/dkNpa/mVGg9/HTToYhXuTa3zg2V9LvOLuPdr43Y4fmvkpu157
unJg8vJaoV/UgZUGvEmquzBLx5jhh65zs2/dFCi5EtN/2Cp2duGAHaXAZFzX
P3TvdmfIjEiYgOc/C7lvneZoA6E4qYTyD6iExf3w/Q8/rF7TQtbjo7DZ7TpP
q0igRXyeuKK3su6K5WNGfNwcc7vBwu8Gx02bUoWTcxXX/Jz2GdnSCcJ3r2aP
DUx++KMq4e5fA6Wc68J799kOJff/WlOZFzKTCHCAs8P+wV1Xaem15Ve7MH3D
wVFPLO5/qs07Uh/ZhZ/ZZ16R4dWqRQbKA0IqhLlVCZRzdLKRKmRYoBUKmYtK
Sao78Uuli0qKPaLXTkS339yUHAWjhw6PUb05ur283rsj8bCRx44YMeI9/Pve
iFEdXCnThYJCtoFuCYlTjbo0/Y0LHTm6loUj638txf8x/+tzbEoq6fxH7d93
duzesyttovvImQk/1vhuKDFbyKIlBOi6QHwAj5j6odqXQ+/94l97fWdSKUfr
31nBPyLaCZmoKITEHcAkQAwAlBR/o/PHO8VnjQuRkVPxXMITK/mfI/U5tt1I
yfBjrjjVqSJrMe3jTz6Z2dVrTuqCS41PzeTYBtkIO//kZiokJY6kUrqwge7q
iSacCohO7UxTxRi9VKmUyhX44STnEc87K0gSRIH/8sKG4xCIIbgSDgBePvxG
1vlLz6996UMDjrDXL0eP/VKYjh1fE8XBEvOflNOiyC0fePVJ25u2N32S11cb
Fl5pdHImT0075ObnqvTxU7gGuHKczDfA38/Pz98/QIl9/nYHqzZZ/wZb0I2c
RxxLqtrk4Dch7XZ/gy3jhnv2p6cfSE/fn/GVv0wMvwmhyJKyH/BVOr7VdkT2
tNpKdhalu4rkpAuRpzsP7dD/JKIS9NOCSn33/Jy+/+AU77nr519sdPpzVrYI
Rm/oV3Nxakj3HWPcYcSaLZsppcZgcY9MXTBvQQWOORxus/Qnasdp9kX2u/Oz
C8+1vctK9DXajXT/D8DKf+wpf6UBWwQb/N6ZFR5ZjyCItkWJxz+E3gNfd4qd
9eVXM+f18pqzYeHVRlj+qdIGyx991uzkk1qT8r/zQ/Wznz559hRTTmuytqfu
51MieeH2N65f6o/X6qhJi4i/vc8Zwqh5i5csXYIJ+39s0SNE/t0G1LJn/JN6
I4iqzq0HhMouaNH6I3pJyC5h//+pPl9rhh+Cnjbwy5wUcEhm5vnfrnzh9UnS
jEMxuyYKZUvLHs1oejKn5of6b/04z67v9Ord4513evby51R4CKhceCSYwKpZ
+cdrddCkRfa7/bOzBCk83N3xL364SBnHIdczee77havKikHEOwcyLzmtfyHl
oNZ2qFcIRZsMv8j//KLxIyKcwc2aN2/eLMglslb1OpWq+bM6X7As59Omp3Jr
TsT857zeeAsbte3f7PCmX62F9XlyexXhZIjgrx2nZfLPcTUXkgjA0qVLVozy
ZguiOd8lv63vhOwaALSRQu4cC3Isub+XBZqbEMS61zL/rfm/bEk9z/f/9djJ
s+sC31o4LWnEripCJQ3FfzKX8h/W+1PYYvpRbO1vWphW81H+1+6o3RfRF/Of
g69fvUf3//nrr5+CWZ6EC1szYdAq3p7N0Oiop7FDWnCAxlpe/0PsH2gi/7ri
yT91f53rRivaLl+y9NtPfHpuWrF/ytkaYhmtgH9i/go/FPHj1q3btm7btm1T
ff9RTZFJJJHgP8Hw39mPx3+VDyZNmjx50uRJU3u6SZn94zz84zGL5bCIzXst
wTdJ4hBHmKz/s5z+xvafEb+e8b9vPjYMBP5jq8EK/uD18yt2+2n9htRv/Htt
XP7zlLPVxV27lpLx/7jGh3os/07hEdXC8aNaNVfnCF9TT57KP9Z/FL8TRDJa
jUQebpwQi4fhoyc0smc3MEHpsaaSbRzGPlVbNH80R+qxNhH8eO45SfGT6pUr
FD+Nf4UXHn74nOGHlwV2W7tu/aaF/j1Tl6dNPBOBhLI9ij+3BpF/FJa4bu3a
tT/9tPa/tWkxnkmykcp/h7w0Iv8uENUhSdL169av2/iRr4zFbSBSOiO2P2zJ
8At9IOa1EBqZa9hk2ZTU6owGIv7+OXl5L47XgUgar8nT5F0Mx/qtO/6W5oZl
/adsXFs6PPPilau7K3X/cdGOSUcixa3OF9yY2vjgrahxud/4cPWvPsL08NHD
+60Rc+XEkyDVjMfpNd98uDWi9+XtLhx87doDNv4f/hjEC5k4cSmoYzUwGH/b
1SkWac1nVYRF71zLlatWrZ4dgiW7+epVKau+DsTtbfp9csrqxYEWe5+IaK3+
8f36d1aFxjZ+I7qrh3AjZ0nj+Dp+nft41hrQRMl594zH1LdPfO9As0FMwlv1
B3T0rNzvTY+qvdtKAazQu088pf6tVXbNeVYJz1RkM3BLO79JZbQkh4w1bJ5K
ZcRkJ884bLZz2I3g8DellpfgUR8YAbFiQNjVkBV4CJYblVxqZECuwJZmlLXs
buPiZoBiiA6W9r3giKdubQdweqdzGmGkqU6CgTaIhakQK32wqn4hw89qKQAS
tirB+obsagWR6CYz/AV7D9BTI3azSSAxrNBj+EuR/0AsabD0kVDtAYQtAyFj
Klsvh1igw+r8C4X5laWpjTlbwGqhhUgnABbuZySY5cJtwMQzGNpbmvBZB1je
RxqICw0kwh7xQm5DgGxAZuWshjCicAwHxB01BJ3FJlcIxNnI/Nv0KswbNuOP
PSEvG8QYYln+xQoDJo0kr8/6wjRgajX8LORygeisSsQeg2L4RkzCWJhAgVhn
IfawEbHjKb8CF4MyFxdnM3KhD06IM8jxSxcSnpaR98m9UDgnZ2eV0rAnoFX8
YvmI8SBxEEiMNRMmNSamXxW+KR4JTD60LHAmjyIAm6laLGKvf7tixbemhF8t
X74ghJ0PNl64/NvvhnhwfLPl3674bgBWAL5ffbsssa+yDO+DXDIS9YU9I4Pk
P5++MN//QqPRqvMe1BHwx2fnqTVJ/py8/3NsBH2Hr1ElS6PWLHEtVTXkCJEB
xQmxoOI1ymQIQTD6qc48/0/CobqcGEHy4rOxxbsqkJMOVOu06kT8zao39Frt
IteyvA1y8QgYAhhkYxSmjkp6BsL/gtsUEvyPYoT9l+Nv6LTalAAkHfQiX4/x
QxhyU6/VLXJ1cOe10iJipygrV5BR06RY/BftDvoCwhF37tw3o3vkz5Vokf83
cHck+0ulg/L0OvVK/OXQm7hHFv8z8BPmOzed8GPKuzWkxU2FAmiytQHiqnWN
Y9l1keJIpr2jhzD++2Zr9bqUAIpfr07CHRZyA7vHS/4p+JFzn+M5mrx7O95S
Fov/+BjfLv379YtjW1UibH4WrPzl6K5WggHQl/B/VQAvHYz5n5eI36Hyj/lv
b5Pt/F6hswiZ4PB9j5b17JN0d1f14t0aAHFvnL926tT3EayIl+MoXtOtGSHP
yWWciP9mYfz5ReIXomsFbBVgfMMhK0Y0oPEpkKzv7R8jZNKorY/j+eJEQwBS
jnvwUZ3a4QrI1v97R1WvXnDjr6jqEU4O4WcQ7UdY1KmZy0b8RHmr0Y0UnCxs
++Ne0uLEwgDyXnJxdOfXfZhvg1C37Tv37jGj3fixOaIU+G/pg1LoFGpGM9eN
lJRiSZWqRt08WtfSDYMLfxkF78z5/cof8/2o3Y/Q2GcF9v/SkCUtD2Ic5X9B
p958JFjGVXTrqbGHyKJYKb0hFBm++G+rP+4lqLhi6T9Yfdf6bi3XXHuH3j/I
8v5XWt2jug7iB6I2FfwIMWHFbBYgfGTu2lnZh8WE6PEQVlyftguL6e7d+xJU
CEplzU/dmUr2Cy6OeEG5j7eMa3V/gSvbYW/sU7XOfOM3stOyg/zHwNxJctPP
352WmUic/fzJjyeddoFLAP3MW2rSAYD3od+wRf5k+SvgQLWzQkXIrS/deOTW
4czj5ZVoCLVI9Lhlfh8Mcucb3VvmQQAi1PtQxrGCdPTIviiH8ONhOT55ZVJi
YtJoN8r/tkvw85XJdDN9IO2cnERubDqzmmFnJNwR/vPwu0nJSZYpOTkxKTGJ
7X8FPbr3je+Lf+P7Y93nP/bcnWVBPAeKFQwHKDxje7MqX2T14VmhakDDevXN
qEGDhvXr11M5Jv9Qtolt2pDqQ1P14x+S+xdqN6tIhYtyqiZPp9eoTzcVU2wk
XhaSRe/yZPWmueRsG4OJmUejg2xE8cjjw9tXEyqwEEWxxr/TiEunMrJ/DGRL
dREtsjff95MU4CMH5V+eqtcQXyrVj+JP+IveLTjVlZzWaTLuGr1W86sBPwkM
kfufWcpEmHpmqUG0Qgb7e0wb4OY2u/T3D13btWv7RlDxdoMHnOfbiUuHhrE7
zRdYvMV6iHQrdJT/W3TYcM7Xb/Shm3aOe6TNz9fqN7kgzGnlJB1ZNq014T9A
IPg6eTPf6mb8ZEOa1GAk+vnsH+f0pSYv996DB/fv9JEWT/5JRT+iyVYSzOEq
tmzWvIUptSS/Td0d4z+WfzyNYFdyox9d2YD5n5+v0292IUrfaTLjp5H/hJeh
WXqbNyIgNdkbgsSbcbC5BFtzCfvS9u1LS9u7+02+WPcGwWqSVNywuQfzf+i1
a9k3TCn7Jn6dWctB/NItBI1On+pLeTXuIZYFrW4TyV9A5WQSZNBpfm0ihizI
lUKvkbFvcS8m9rZeo9kQzPb/AIINhEXVvWKFwAqBgRUquhQ3FwZM/iNL+T98
tYd1JQb/R6dP8eekg9X52ryVBP8tDGSJa6EtXcwuAaSbsPTn6/UbfemMN+6R
jq5fcCb4FR/pBfk37C9M/OrrReLXbg7hTaJcwspFKEZw7fCtyP0PC65/Jxd7
JMR/UN9srHlT/HnpwBcabV4SvkpoNm7IYlfbsRbL+PUYP5ZAgj+/EP7Aecn0
Nt+Jlojc/i1pZVKCt4m6EmLDJtwsOQFQaP8jsj8D5j+N/0AUfyNPq10dwGH/
X6tRr8Q9HZqNtfcSN9vGRgnxs0CGyqUIUimh2ZJnogDsgm1y2Q7rNmxINaUN
G1M3bEgJE/C3TFy/MXWcJ+LarEtdt2EU1hsBK1LXp46wtPLLfvw0K8LZvBED
c82hWTLA8WwAAErvAvsfeXt5enl7SAXFLPfw8PR2xRdWkAW9ePhKeA8vL++i
lE3J8IvRjKJba7rin2lAh+BLxDpKU4ISQ+ZNIiyDJjWtYuqPrfEq4sIl5b+k
eKWMZiYeqTTjecf4bykDRfN0gmFO2QKFWJNE2H1atD9snbbk8g+Kkn7EMs+G
a0A+8JOxKgcVgCHPZyoAUFhYJJTYklw0S/aiYgeZS4wf8N5+vraI7P/qblgm
hr/C1/zm0UJ3m/Nwkc1EnFChYLrxAYJiqhMJ+84jajFBWpNdrIqrEo5/kof1
m4cnOTLTWZkAVxL/z9vg40PUZP9j9SJ3B++8gGoQP9KM+vTr4EVHOIoZ2Kff
G05I0ahPfJ8m2E2K7Bvf7y23ssCPOVHlKjVzrBhAxP7RajcHi/f/wxbmkuub
bn3j7pD8Aw4Oy8q+ZU43bu6qRWx2iN6/k31rrS/nMevGzT/nySDon519c2tw
GeAn9zoJvaovwv/D3nSQYf87wA3p0PvSAjcH5R+OflIg/qPN0xyLobFhfrpe
rdkVIPNYrNOol/M8fDdPrc0ILZaiLqH9g1VNcJH+j06bGmwC10na/srCYkmj
dYJgbG7BGx/kaY7GIKr0PtZpdLsCeY8lep16BdYAw/M0ukNlgJ9OLiHXme9r
kfXM/8P8N9lJFqK3Ltsl/9TSYutNEei+cy92IE0oLW3fknBEdeM07OnsDOQ8
Fuu16hVSgl+rO1SlOFcsqf2Df0KvYrvb+uin439TkAn/AWh/eWGJ9R8Q9Tit
nUXQK6q6OdWoHlWFlndANE2P+R/AuS/Ox/h5hv9waBngJ+Z/let6m/jJ/b83
hUhN5n+M/5uSjn8y0/h07NOnKhLyZ1ISRjcjmUyKJC8VP2WKz/xVySkpyVYI
f5CStGq8j8k93wDX/uoCtxLKP9Z4bp/8cebK9tqsugoq3IzbSwjkrqJa9mXi
J4PSzb1gQ0yINtLNGZkkeRB48/J89xLmocn2ZMdmRr57eDDddZKDred9vXCB
KS2cv2BCJfhy8VNTu+Ddvi34f2a3/AKo7soRziV0AAAnH3N++Ij3u0aRPdsA
D8c+LbD+U6fRHqv7kvGzar9iIjEcBqVYIErKf957ec5vx7MXh9OtVHg06mle
gelfrT4a87LxS6zdhsx4RmAOng2aEtf8AD7wx1uTYhKuT1YS71kKR+e+KFj5
/hzjN+o/f85jSb4O2z+wRPi3WMK/0br8k40TSYmltUHAPgXmXWAHQc95p5sq
Azeu8mZC99ryJWRzERNaumJqkAn/RfzSkvG/JPipE8p7eHt5e3l52yJX5HDV
GS/tf7aHd73Dy9zZlk7AZJNfAAxvFeL/itLAb8P+g35zE1da9v1EWpk01sfh
/Z+RtM6Og0u3XezJs3wRb9j/QSj8Jxu0gcL8L1v8EglXJct67o8Rtv9COQcD
fvhCyhYLN3/f00MsrRfKwYw5dlrr/5LxY6usaP9PR/w/xyOeSOoe4CtnIR0E
m86a+eUXlL5kNGvmrISKL5f/NJMh+j+28l8bgxyN9xlCmmxtN/Z/c8TtZdSG
bWbo/IfdhML4NdqS4NcXyv+Q/Uug0mL8t+j8H+G/Q+5+YSL1L8+1GjN68eJo
HbpKmJ+iz9PuCOA9Fms1GD8Hh6lf5BUXf6qOrKvUbvChSjVBzP8T7aqcrNVo
ddq8X5uYqt6Qazb9Py3N/wXxpVRAKFyXQ2T/qwIXyvslhi544Kdh/LsDOK+l
Oo36OxkHh6vVmiNVi4MfSreQ+gedJtWHziZjH+aRyiqx/gF3hU6Td9pwezXS
KyFZ1P+zrgNJ/i/Y4fFvjp9H7ZJSUlaZUkpyyqchtEXo7dVJqya6c6qBq5KS
h+L54rXkpFWf+BaL/9z41dRnG+tG/cw3l6esSklKGackfSPrsgpfMznl82oG
9mNLzn/+avyu5cV45INVq5JXfeAjLd0FQBDIvQrvfc+2PsCC6uHuocKzgbOH
uzfJ3JJji1X4i3nu4ulFlq27sCorBT4TORkzLJzINT3dXY3OPIk2ulloSYE9
+UvB/inYTuwQFjQ5ha0RyFRIA0VsjygJTdEVb8UpyRWxXU44IWHENj1Bwi6i
xNiACJkOf7ptvokZUoDY+/bc8amIDih8QmhM8AChbUKVQsGCXtvnNX7dkC4z
rggyW/gjroqyp7VlQMD8mZnPUVIf1QDZxiGOujTlVE7lVE4OkMM7qf7/JmDn
3dT+P5MhoEhLHErEf+uHlrwTi/cNM4OhlDgllrcUXc0itkHCvGdgxQ4BwhFA
OK3J7YPFEItYYmLSBAgl4soIxgYLZharPBHep0vSS8cOBiUy6QQj0FBuWfBj
BtAIU8BvrKox6QAx1igh+z+wm2lIhGWJFtsEOLkTB43LR0pl+SEwL6Fk7xXn
a5YPE0WpQOvFgWap01jcH5gcYuWSCPrXMd77DxSVLSgW0aXDBTyKEghEsS5R
WmMVQKmzYY9wiUEaHTonljaFt1zYC8lwIUdPbPn7Vhkr/iuino4UiCGzN+xq
nPk5IZKqOLaeDhpFsBjftPkhW5kBS1lbl54smZ5SPLNvVVXxR5SthpDFKaSm
zkluzKs40sKXQhB4h7s4qlFYr0BWpgnlUqLVJRIL2sWgJot94lJWShauAC3v
5FT8EwBRJYthE7LZLbnRD+KERQpCmgVxhpRL0Vc0xKFKd9urwtdxUJ8auSq+
piEwag2Yra+n0mFMNRV9XsnLGD+lcCM18UwSg2yLtoy5yWP2qjSuWAoESmMh
gclfpKC79HEWb9BtF0fLuqdKLahOT8S5ktvkSaTyf8weQS+RqO6j5SP/GPku
AZWGVSWx7iH8PyH7my46QCWa4F85mWjjUmo0kEj+0eYfACbTr9E1p2PXMUOw
0JT9z8RPLBFjUsfELEVs2rKz1YZpsAgF8Oo7xcrwJKawxXnb1qmK87H5Qc7u
qIxNWnuphLG14gUOC4VrKlaTlXYqt9SoRJFgWHRGnhiCBU/p5seV7k6upUvF
bhikt6Qs4hheWqiPyM1b/7nwS0DFCERaWjMJSs/k/seTJY+HbWv7b+kBC/Qv
hl5O5VRO5VRO5VRO5VRO5VQm9H9RttB5
"], {{0, 256}, {256, 0}}, {0, 255},
ColorFunction->GrayLevel],
BoxForm`ImageTag[
"Byte", ColorSpace -> Automatic, Interleaving -> None],
Selectable->False],
DefaultBaseStyle->"ImageGraphics",
ImageSizeRaw->{256, 256},
PlotRange->{{0, 256}, {0, 256}}]\), 32]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d6a/d6a6aa8a-5551-4925-9aad-dd4db679baf1/798a095e59fca5fd.png) |
| Out[10]= |  |
FourierShiftInverse is the inverse of the resource function FourierShift:
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= |
FourierShiftInverse does not support ragged arrays:
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License