Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Evaluate the Neumann polynomial
ResourceFunction["NeumannO"][n,z] gives the Neumann polynomial On(z) . |
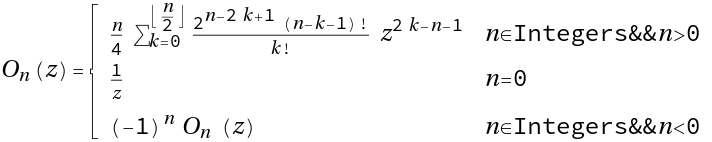
Evaluate numerically:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
Evaluate Neumann polynomials for various orders:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
Plot with respect to z:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= | 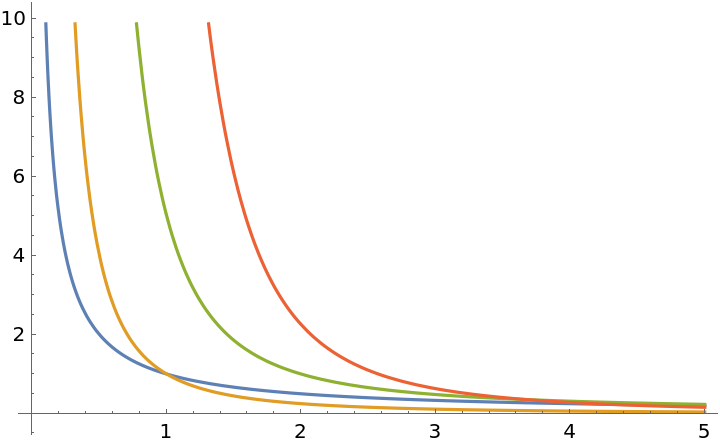 |
Evaluate for complex arguments:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |
Evaluate to high precision:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
The precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
NeumannO threads elementwise over lists:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |
Define a function:
Use NeumannO to expand a function in a Bessel function series:
| In[8]:= | ![(* order of approximation *)
ord = 19; coef = Table[1/(\[Pi] I)
Integrate[
f[z] ResourceFunction["NeumannO"][k, z], {z, -1, -I, 1, I, -1}], {k, 0, ord}];
approx = coef . BesselJ[Range[0, ord], z]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/70f/70fbe704-230e-4c55-9223-d17ae371d128/24013b10ed3d607f.png) |
| Out[8]= |  |
Compare the function with its Bessel series approximation:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= | 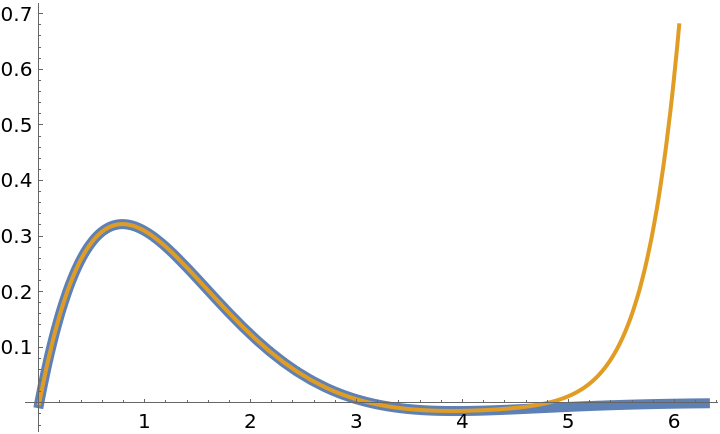 |
Derivatives of Neumann polynomials are related to the polynomials themselves via ![]() :
:
| In[10]:= | ![Table[\!\(
\*SubscriptBox[\(\[PartialD]\), \({z, m}\)]\(\*
InterpretationBox[
TagBox[
DynamicModuleBox[{Typeset`open = False},
FrameBox[
PaneSelectorBox[{False->GridBox[{
{
PaneBox[GridBox[{
{
StyleBox[
StyleBox[
AdjustmentBox["\<\"[\[FilledSmallSquare]]\"\>",
BoxBaselineShift->-0.25,
BoxMargins->{{0, 0}, {-1, -1}}], "ResourceFunctionIcon",
FontColor->RGBColor[
0.8745098039215686, 0.2784313725490196, 0.03137254901960784]],
ShowStringCharacters->False,
FontFamily->"Source Sans Pro Black",
FontSize->0.6538461538461539 Inherited,
FontWeight->"Heavy",
PrivateFontOptions->{"OperatorSubstitution"->False}],
StyleBox[
RowBox[{
StyleBox["NeumannO", "ResourceFunctionLabel",
FontFamily->"Source Sans Pro"], " "}],
ShowAutoStyles->False,
ShowStringCharacters->False,
FontSize->Rational[12, 13] Inherited,
FontColor->GrayLevel[0.1]]}
},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {{0.25}}}],
Alignment->Left,
BaseStyle->{LineSpacing -> {0, 0}, LineBreakWithin -> False},
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
FrameMargins->{{3, 0}, {0, 0}}],
ItemBox[
PaneBox[
TogglerBox[Dynamic[Typeset`open], {True-> DynamicBox[FEPrivate`FrontEndResource[
"FEBitmaps", "IconizeCloser"],
ImageSizeCache->{11., {1., 10.}}], False-> DynamicBox[FEPrivate`FrontEndResource[
"FEBitmaps", "IconizeOpener"],
ImageSizeCache->{11., {1., 10.}}]},
Appearance->None,
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
ContentPadding->False,
FrameMargins->0],
Alignment->Left,
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
FrameMargins->{{1, 1}, {0, 0}}],
Frame->{{
RGBColor[
0.8313725490196079, 0.8470588235294118, 0.8509803921568627, 0.5], False}, {False, False}}]}
},
BaselinePosition->{1, 1},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Left}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxItemSize->{"Columns" -> {{Automatic}}, "Rows" -> {{Automatic}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {{0}}, "Rows" -> {{0}}}], True->GridBox[{
{GridBox[{
{
PaneBox[GridBox[{
{
StyleBox[
StyleBox[
AdjustmentBox["\<\"[\[FilledSmallSquare]]\"\>",
BoxBaselineShift->-0.25,
BoxMargins->{{0, 0}, {-1, -1}}], "ResourceFunctionIcon",
FontColor->RGBColor[
0.8745098039215686, 0.2784313725490196, 0.03137254901960784]],
ShowStringCharacters->False,
FontFamily->"Source Sans Pro Black",
FontSize->0.6538461538461539 Inherited,
FontWeight->"Heavy",
PrivateFontOptions->{"OperatorSubstitution"->False}],
StyleBox[
RowBox[{
StyleBox["NeumannO", "ResourceFunctionLabel",
FontFamily->"Source Sans Pro"], " "}],
ShowAutoStyles->False,
ShowStringCharacters->False,
FontSize->Rational[12, 13] Inherited,
FontColor->GrayLevel[0.1]]}
},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {{0.25}}}],
Alignment->Left,
BaseStyle->{LineSpacing -> {0, 0}, LineBreakWithin -> False},
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
FrameMargins->{{3, 0}, {0, 0}}],
ItemBox[
PaneBox[
TogglerBox[Dynamic[Typeset`open], {True-> DynamicBox[FEPrivate`FrontEndResource[
"FEBitmaps", "IconizeCloser"]], False-> DynamicBox[FEPrivate`FrontEndResource[
"FEBitmaps", "IconizeOpener"]]},
Appearance->None,
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
ContentPadding->False,
FrameMargins->0],
Alignment->Left,
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
FrameMargins->{{1, 1}, {0, 0}}],
Frame->{{
RGBColor[
0.8313725490196079, 0.8470588235294118, 0.8509803921568627, 0.5], False}, {False, False}}]}
},
BaselinePosition->{1, 1},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Left}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxItemSize->{"Columns" -> {{Automatic}}, "Rows" -> {{Automatic}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {{0}}, "Rows" -> {{0}}}]},
{
StyleBox[
PaneBox[GridBox[{
{
RowBox[{
TagBox["\<\"Version (latest): \"\>",
"IconizedLabel"], " ",
TagBox["\<\"1.0.1\"\>",
"IconizedItem"]}]},
{
TagBox[
TemplateBox[{"\"Documentation »\"", "https://resources.wolframcloud.com/FunctionRepository/resources/70fbe704-230e-4c55-9223-d17ae371d128/"},
"HyperlinkURL"],
"IconizedItem"]}
},
DefaultBaseStyle->"Column",
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Left}}},
GridBoxItemSize->{"Columns" -> {{Automatic}}, "Rows" -> {{Automatic}}}],
Alignment->Left,
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
FrameMargins->{{5, 4}, {0, 4}}], "DialogStyle",
FontFamily->"Roboto",
FontSize->11]}
},
BaselinePosition->{1, 1},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Left}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxDividers->{"Columns" -> {{None}}, "Rows" -> {False, {
GrayLevel[0.8]}, False}},
GridBoxItemSize->{"Columns" -> {{Automatic}}, "Rows" -> {{Automatic}}}]}, Dynamic[Typeset`open],
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
ImageSize->Automatic],
Background->RGBColor[
0.9686274509803922, 0.9764705882352941, 0.984313725490196],
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
DefaultBaseStyle->{},
FrameMargins->{{0, 0}, {1, 0}},
FrameStyle->RGBColor[
0.8313725490196079, 0.8470588235294118, 0.8509803921568627],
RoundingRadius->4]],
{"FunctionResourceBox",
RGBColor[0.8745098039215686, 0.2784313725490196, 0.03137254901960784],
"NeumannO"},
TagBoxNote->"FunctionResourceBox"],
ResourceFunction["NeumannO"],
BoxID -> "NeumannO",
Selectable->False][n, z]\)\) == 2^-m \!\(
\*UnderoverscriptBox[\(\[Sum]\), \(k = 0\), \(m\)]\(
\*SuperscriptBox[\((\(-1\))\), \(k\)]\ Binomial[m, k] \*
InterpretationBox[
TagBox[
DynamicModuleBox[{Typeset`open = False},
FrameBox[
PaneSelectorBox[{False->GridBox[{
{
PaneBox[GridBox[{
{
StyleBox[
StyleBox[
AdjustmentBox["\<\"[\[FilledSmallSquare]]\"\>",
BoxBaselineShift->-0.25,
BoxMargins->{{0, 0}, {-1, -1}}], "ResourceFunctionIcon",
FontColor->RGBColor[
0.8745098039215686, 0.2784313725490196, 0.03137254901960784]],
ShowStringCharacters->False,
FontFamily->"Source Sans Pro Black",
FontSize->0.6538461538461539 Inherited,
FontWeight->"Heavy",
PrivateFontOptions->{"OperatorSubstitution"->False}],
StyleBox[
RowBox[{
StyleBox["NeumannO", "ResourceFunctionLabel",
FontFamily->"Source Sans Pro"], " "}],
ShowAutoStyles->False,
ShowStringCharacters->False,
FontSize->Rational[12, 13] Inherited,
FontColor->GrayLevel[0.1]]}
},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {{0.25}}}],
Alignment->Left,
BaseStyle->{LineSpacing -> {0, 0}, LineBreakWithin -> False},
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
FrameMargins->{{3, 0}, {0, 0}}],
ItemBox[
PaneBox[
TogglerBox[Dynamic[Typeset`open], {True-> DynamicBox[FEPrivate`FrontEndResource[
"FEBitmaps", "IconizeCloser"],
ImageSizeCache->{11., {1., 10.}}], False-> DynamicBox[FEPrivate`FrontEndResource[
"FEBitmaps", "IconizeOpener"],
ImageSizeCache->{11., {1., 10.}}]},
Appearance->None,
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
ContentPadding->False,
FrameMargins->0],
Alignment->Left,
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
FrameMargins->{{1, 1}, {0, 0}}],
Frame->{{
RGBColor[
0.8313725490196079, 0.8470588235294118, 0.8509803921568627, 0.5], False}, {False, False}}]}
},
BaselinePosition->{1, 1},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Left}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxItemSize->{"Columns" -> {{Automatic}}, "Rows" -> {{Automatic}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {{0}}, "Rows" -> {{0}}}], True->GridBox[{
{GridBox[{
{
PaneBox[GridBox[{
{
StyleBox[
StyleBox[
AdjustmentBox["\<\"[\[FilledSmallSquare]]\"\>",
BoxBaselineShift->-0.25,
BoxMargins->{{0, 0}, {-1, -1}}], "ResourceFunctionIcon",
FontColor->RGBColor[
0.8745098039215686, 0.2784313725490196, 0.03137254901960784]],
ShowStringCharacters->False,
FontFamily->"Source Sans Pro Black",
FontSize->0.6538461538461539 Inherited,
FontWeight->"Heavy",
PrivateFontOptions->{"OperatorSubstitution"->False}],
StyleBox[
RowBox[{
StyleBox["NeumannO", "ResourceFunctionLabel",
FontFamily->"Source Sans Pro"], " "}],
ShowAutoStyles->False,
ShowStringCharacters->False,
FontSize->Rational[12, 13] Inherited,
FontColor->GrayLevel[0.1]]}
},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {{0.25}}}],
Alignment->Left,
BaseStyle->{LineSpacing -> {0, 0}, LineBreakWithin -> False},
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
FrameMargins->{{3, 0}, {0, 0}}],
ItemBox[
PaneBox[
TogglerBox[Dynamic[Typeset`open], {True-> DynamicBox[FEPrivate`FrontEndResource[
"FEBitmaps", "IconizeCloser"]], False-> DynamicBox[FEPrivate`FrontEndResource[
"FEBitmaps", "IconizeOpener"]]},
Appearance->None,
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
ContentPadding->False,
FrameMargins->0],
Alignment->Left,
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
FrameMargins->{{1, 1}, {0, 0}}],
Frame->{{
RGBColor[
0.8313725490196079, 0.8470588235294118, 0.8509803921568627, 0.5], False}, {False, False}}]}
},
BaselinePosition->{1, 1},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Left}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxItemSize->{"Columns" -> {{Automatic}}, "Rows" -> {{Automatic}}},
GridBoxSpacings->{"Columns" -> {{0}}, "Rows" -> {{0}}}]},
{
StyleBox[
PaneBox[GridBox[{
{
RowBox[{
TagBox["\<\"Version (latest): \"\>",
"IconizedLabel"], " ",
TagBox["\<\"1.0.1\"\>",
"IconizedItem"]}]},
{
TagBox[
TemplateBox[{"\"Documentation »\"", "https://resources.wolframcloud.com/FunctionRepository/resources/70fbe704-230e-4c55-9223-d17ae371d128/"},
"HyperlinkURL"],
"IconizedItem"]}
},
DefaultBaseStyle->"Column",
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Left}}},
GridBoxItemSize->{"Columns" -> {{Automatic}}, "Rows" -> {{Automatic}}}],
Alignment->Left,
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
FrameMargins->{{5, 4}, {0, 4}}], "DialogStyle",
FontFamily->"Roboto",
FontSize->11]}
},
BaselinePosition->{1, 1},
GridBoxAlignment->{"Columns" -> {{Left}}, "Rows" -> {{Baseline}}},
GridBoxDividers->{"Columns" -> {{None}}, "Rows" -> {False, {
GrayLevel[0.8]}, False}},
GridBoxItemSize->{"Columns" -> {{Automatic}}, "Rows" -> {{Automatic}}}]}, Dynamic[Typeset`open],
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
ImageSize->Automatic],
Background->RGBColor[
0.9686274509803922, 0.9764705882352941, 0.984313725490196],
BaselinePosition->Baseline,
DefaultBaseStyle->{},
FrameMargins->{{0, 0}, {1, 0}},
FrameStyle->RGBColor[
0.8313725490196079, 0.8470588235294118, 0.8509803921568627],
RoundingRadius->4]],
{"FunctionResourceBox",
RGBColor[0.8745098039215686, 0.2784313725490196, 0.03137254901960784],
"NeumannO"},
TagBoxNote->"FunctionResourceBox"],
ResourceFunction["NeumannO"],
BoxID -> "NeumannO",
Selectable->False][n - m + 2\ k, z]\)\), {m, 0, 3}, {n, 0, 3}] // Simplify](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/70f/70fbe704-230e-4c55-9223-d17ae371d128/5e0d4c5362ec44fa.png) |
| Out[10]= |
Neumann polynomials satisfy the differential equation ![]() :
:
| In[11]:= | ![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/c4d86f8d-94e0-49fe-86ed-eceb741328fb"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/70f/70fbe704-230e-4c55-9223-d17ae371d128/75e28a133d28d3a5.png) |
| Out[11]= |
Neumann polynomials satisfy the recurrence identity ![]() :
:
| In[12]:= | ![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/0d392399-d7b7-4caf-aec1-7a6a69281797"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/70f/70fbe704-230e-4c55-9223-d17ae371d128/7820b374c0eb9b4b.png) |
| Out[12]= |
The Neumann polynomials have the limiting behavior given by ![]() :
:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |
Neumann polynomials can be represented as the finite sum ![]() :
:
| In[14]:= | ![Table[ResourceFunction["NeumannO"][n, z] == n/4 \!\(
\*UnderoverscriptBox[\(\[Sum]\), \(k = 0\), \(n\)]\(
\*FractionBox[\(Gamma[
\*FractionBox[\(n + k\), \(2\)]]\), \(Gamma[
\*FractionBox[\(n - k\), \(2\)] + 1]\)]
\*SuperscriptBox[\(Cos[
\*FractionBox[\(\[Pi]\), \(2\)] \((n + k)\)]\), \(2\)]
\*SuperscriptBox[\((
\*FractionBox[\(2\), \(z\)])\), \(k + 1\)]\)\), {n, 1, 10}] // Simplify](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/70f/70fbe704-230e-4c55-9223-d17ae371d128/169255e28e9cb9af.png) |
| Out[14]= |
The Neumann polynomials can be expressed in terms of HypergeometricPFQ through the formula ![]() :
:
| In[15]:= | ![Table[ResourceFunction["NeumannO"][n, z] == n^((1 - (-1)^n)/2)/z^((3 - (-1)^n)/2)
HypergeometricPFQ[{-\[LeftFloor]n/2\[RightFloor], \[LeftFloor](
n + 1)/2\[RightFloor], 1}, {}, -(4/z^2)], {n, 1, 10}] // Simplify](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/70f/70fbe704-230e-4c55-9223-d17ae371d128/1a5f618807682273.png) |
| Out[15]= |
Neumann polynomials can be expressed in terms of the Lommel function:
| In[16]:= | ![Table[ResourceFunction["NeumannO"][n, z] == Binomial[n, Mod[n, 2]]/
z ResourceFunction["LommelS"][1 - Mod[n, 2], n, z], {n, 0, 10}] // Simplify](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/70f/70fbe704-230e-4c55-9223-d17ae371d128/4e0462b90708a283.png) |
| Out[16]= |
Neumann polynomials can be expressed in terms of the Schläfli polynomial:
| In[17]:= | ![Table[ResourceFunction["NeumannO"][n, z] == 1/4 (ResourceFunction["SchlaefliS"][n - 1, z] + ResourceFunction["SchlaefliS"][n + 1, z]), {n, 0, 10}] // Simplify](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/70f/70fbe704-230e-4c55-9223-d17ae371d128/56295678ca261535.png) |
| Out[17]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License