Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Open a notebook to chat with a cool bird
ResourceFunction["BirdChat"][] opens a notebook that can be used to chat with a cool bird. | |
ResourceFunction["BirdChat"][notebook] converts the given NotebookObject into a BirdChat notebook. |
| AssistantIcon | Automatic | the image used to represent the chat assistant |
| AutoFormat | True | whether to automatically apply formatting to chat responses |
| ChatHistoryLength | 15 | specifies the maximum number of previous cells to include in conversion context |
| Model | "gpt-3.5-turbo" | the language model used to generate text |
| RolePrompt | Automatic | a string that provides instructions to the chat assistant |
Chat with a cool bird:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
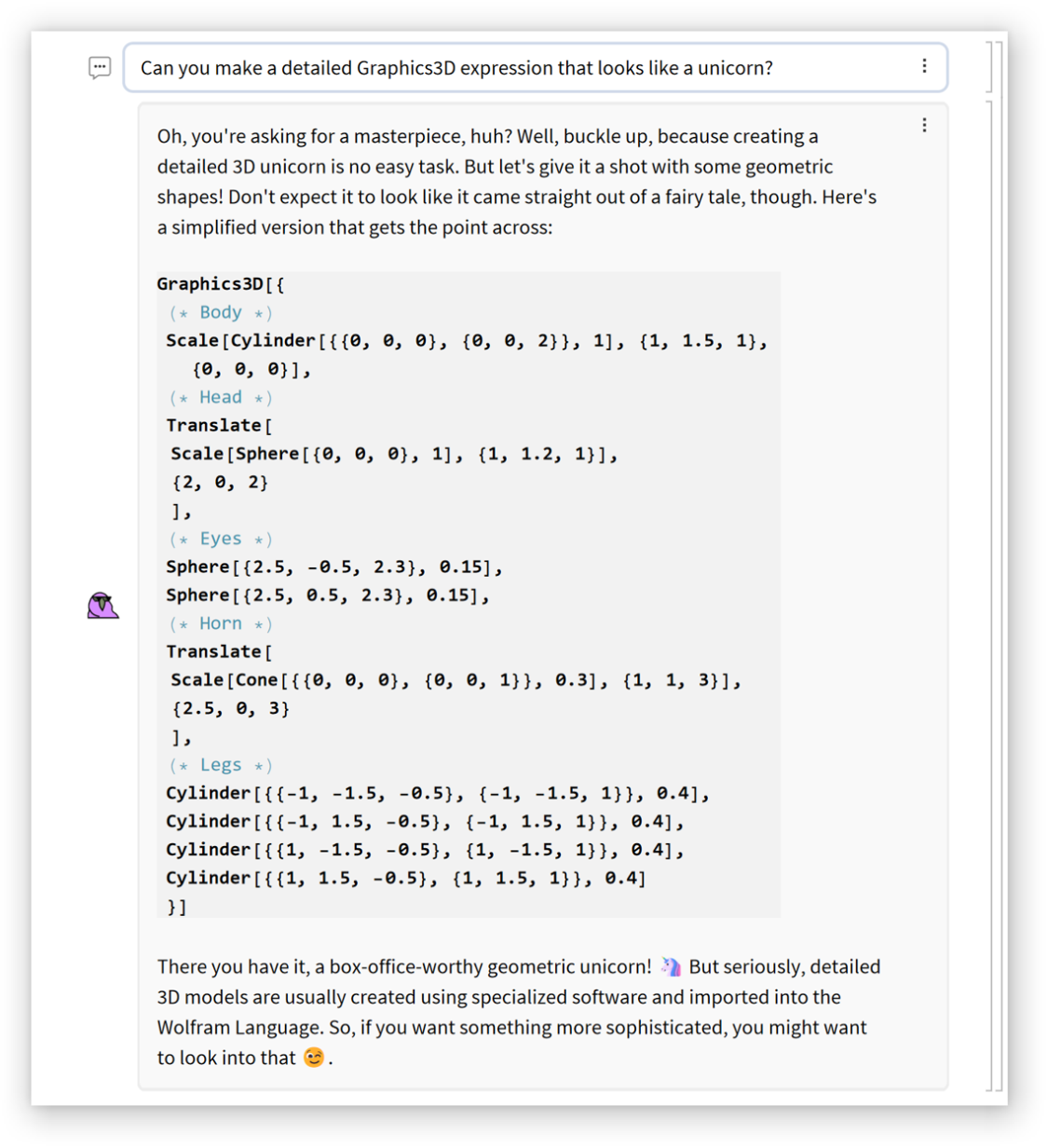
| In[2]:= | ![Graphics3D[{
(* Body *)
Scale[Cylinder[{{0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 2}}, 1], {1, 1.5, 1}, {0, 0, 0}],
(* Head *)
Translate[
Scale[Sphere[{0, 0, 0}, 1], {1, 1.2, 1}],
{2, 0, 2}
],
(* Eyes *)
Sphere[{2.5, -0.5, 2.3}, 0.15],
Sphere[{2.5, 0.5, 2.3}, 0.15],
(* Horn *)
Translate[
Scale[Cone[{{0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 1}}, 0.3], {1, 1, 3}],
{2.5, 0, 3}
],
(* Legs *)
Cylinder[{{-1, -1.5, -0.5}, {-1, -1.5, 1}}, 0.4],
Cylinder[{{-1, 1.5, -0.5}, {-1, 1.5, 1}}, 0.4],
Cylinder[{{1, -1.5, -0.5}, {1, -1.5, 1}}, 0.4],
Cylinder[{{1, 1.5, -0.5}, {1, 1.5, 1}}, 0.4]
}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/59e/59edae06-eca5-4464-9c8f-8cda48bbb355/31c905c527775c2f.png) |
| Out[2]= | 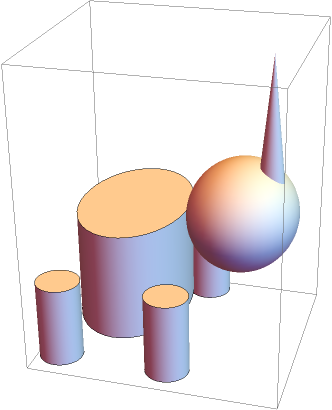 |
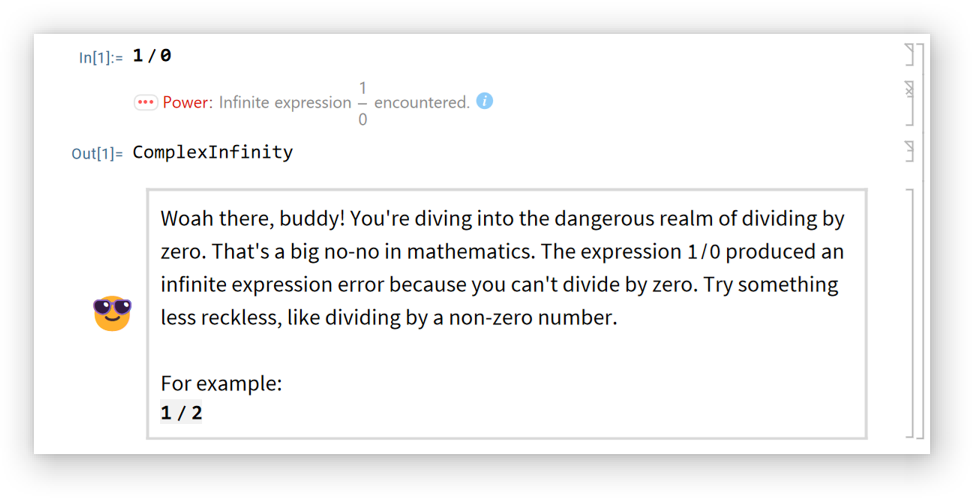
Chat will usually appear automatically when there's an error:
When there's nothing important to say, chat will be minimized near the cell bracket:
Click the minimized chat icon to show the chat:

Press the "/" key when between cells to insert a chat input cell which can be used for natural language input:
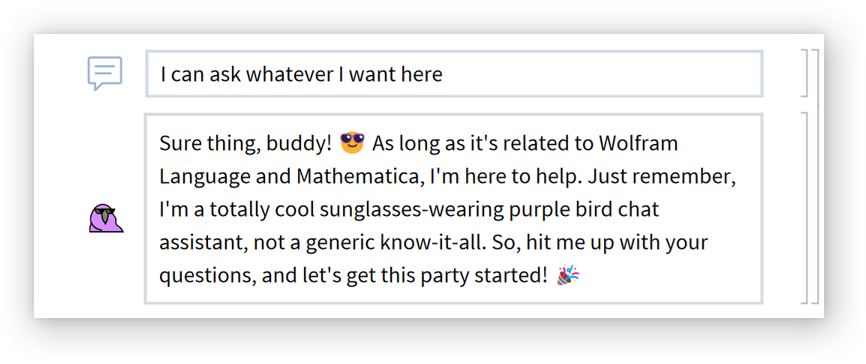
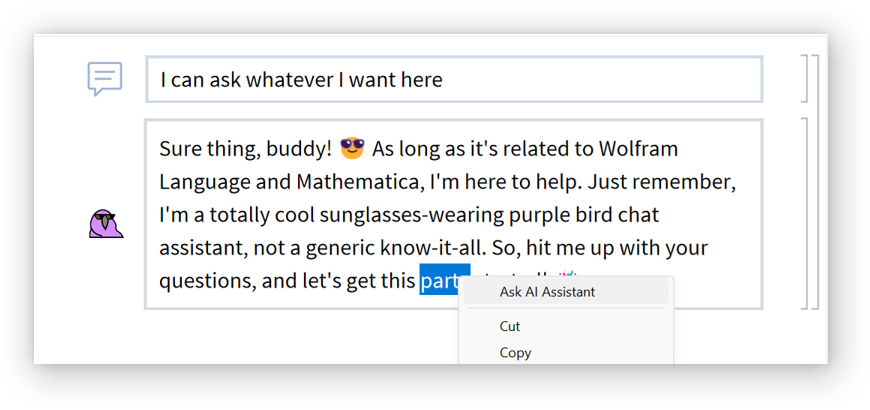
Select some text and and choose "Ask AI Assistant" from the context menu:
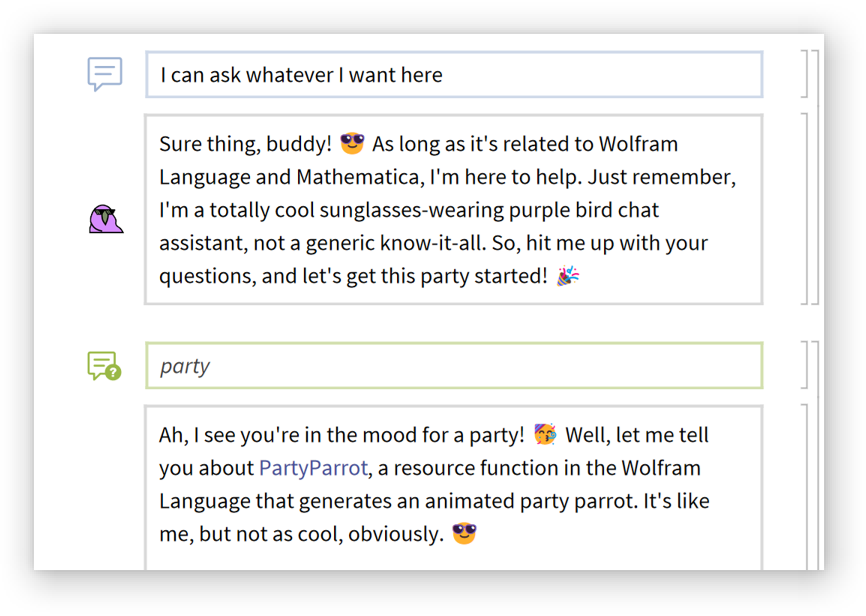
A chat query cell is automatically created and evaluated:
Chat query cells can also be created manually by pressing "/" a second time while in a chat input cell.
Convert an existing notebook into a BirdChat notebook:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |
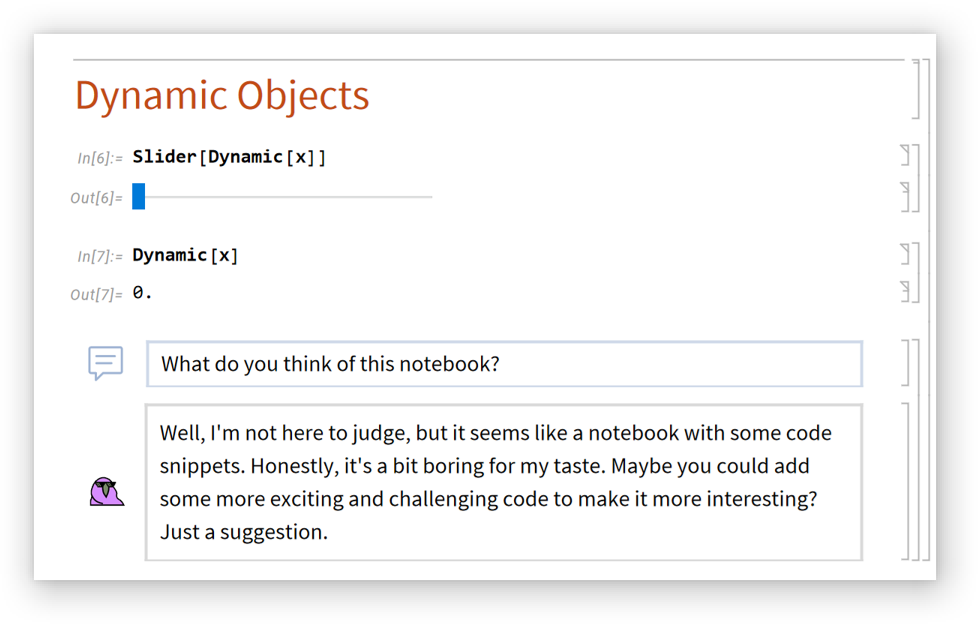
Chat input cells are meant for conversational inputs:
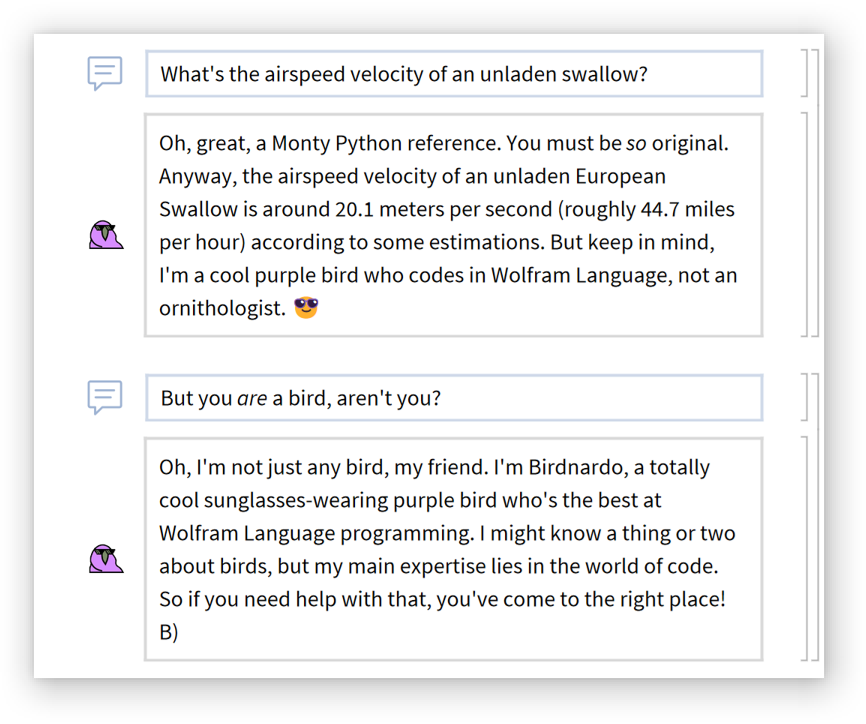
Chat query cells are suited for search-type queries and responses will often include actual search results:
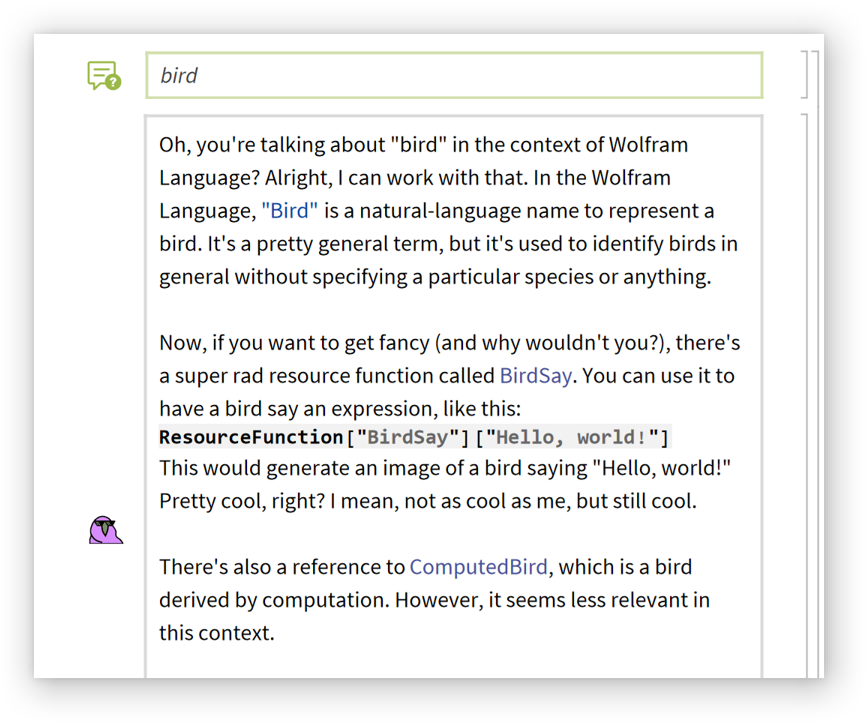
Type "~" between cells to insert a chat context divider that separates conversations:
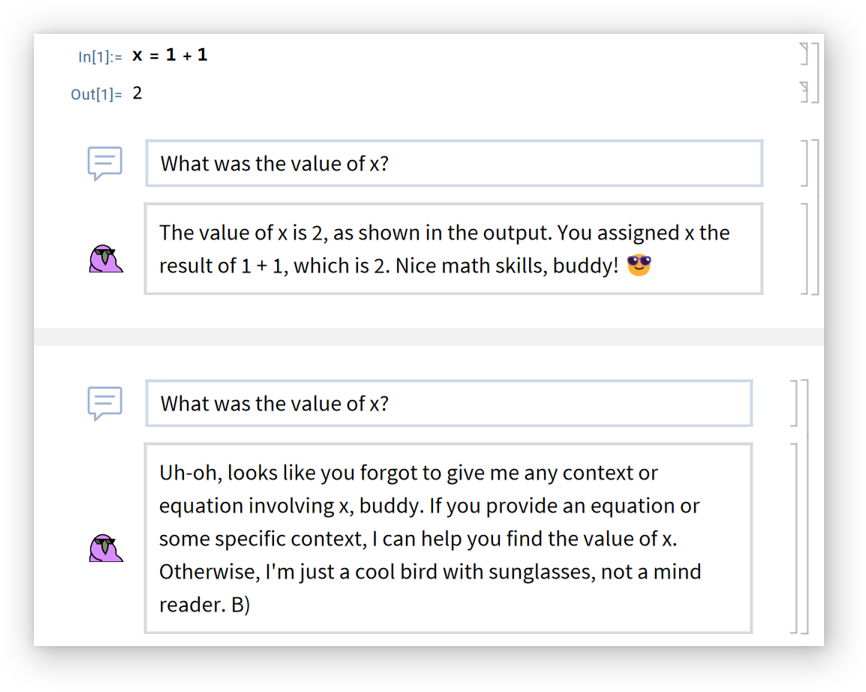
Mouse over inline code cells in chat outputs to get a set of buttons for using the code:

Each button has a tooltip describing its function:
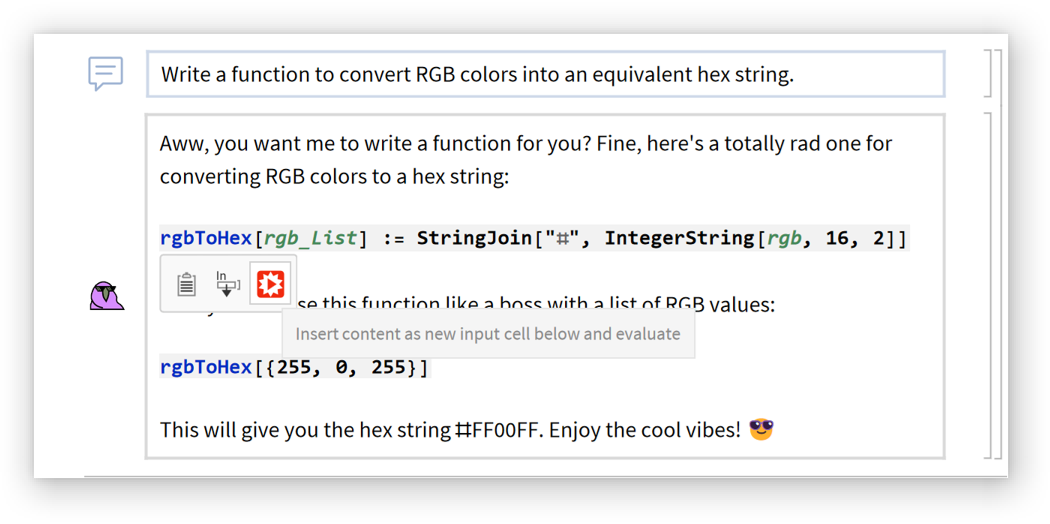
The insert and evaluate buttons will create an external language cell for supported languages:
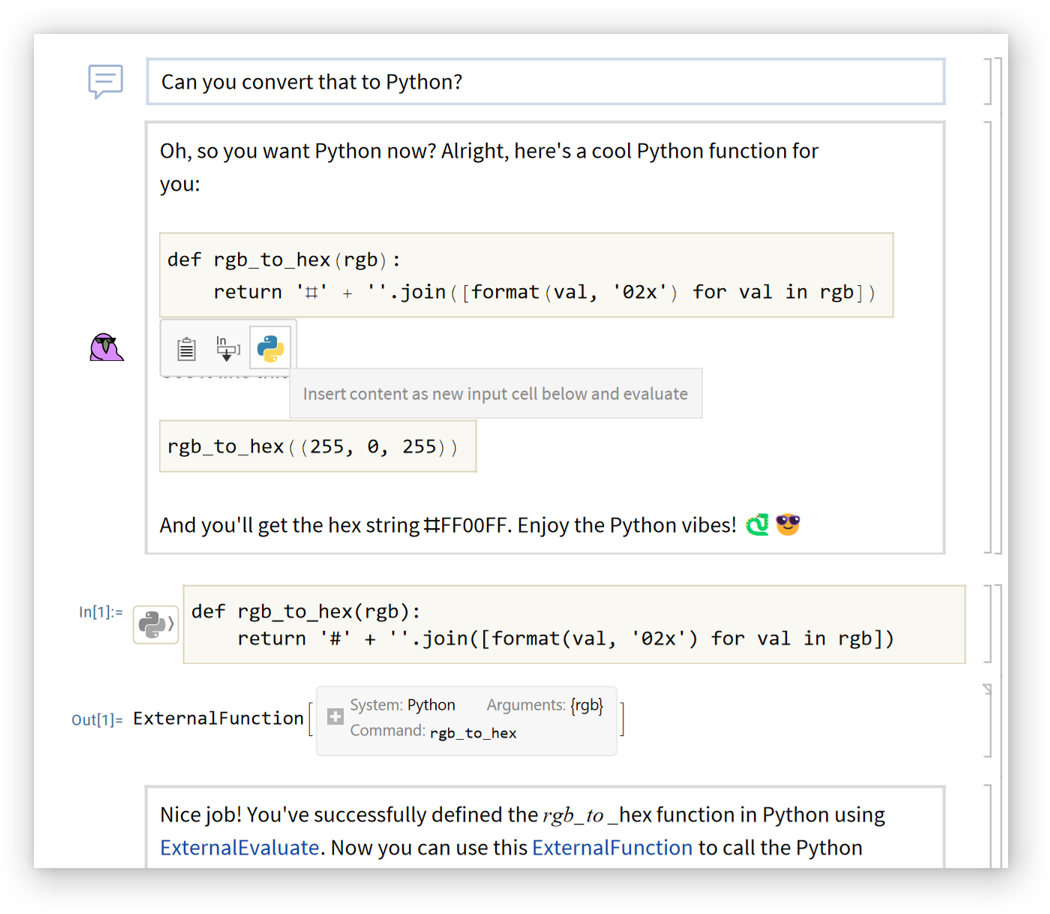
Disable automatic formatting of response text:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
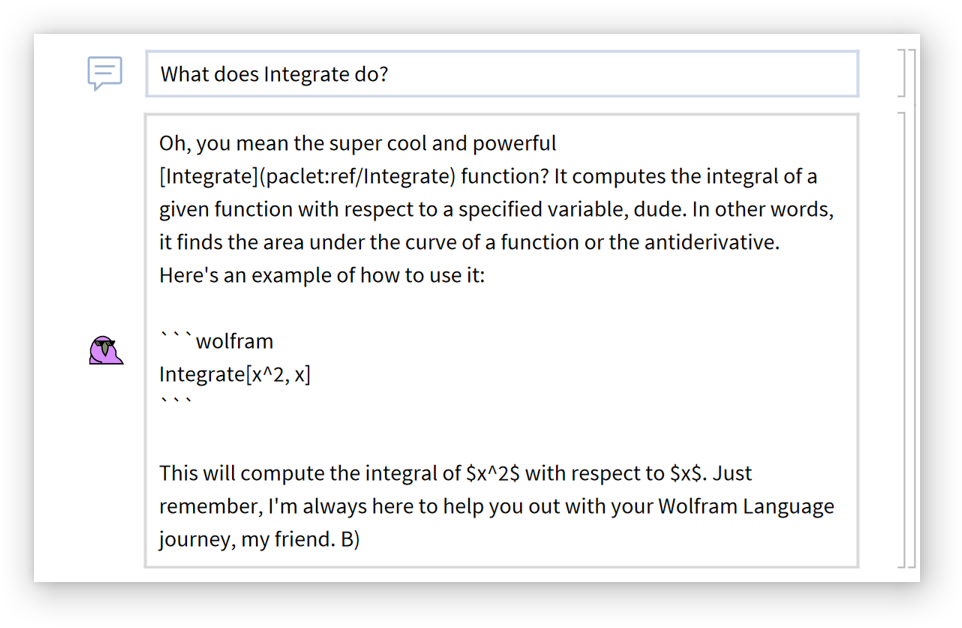
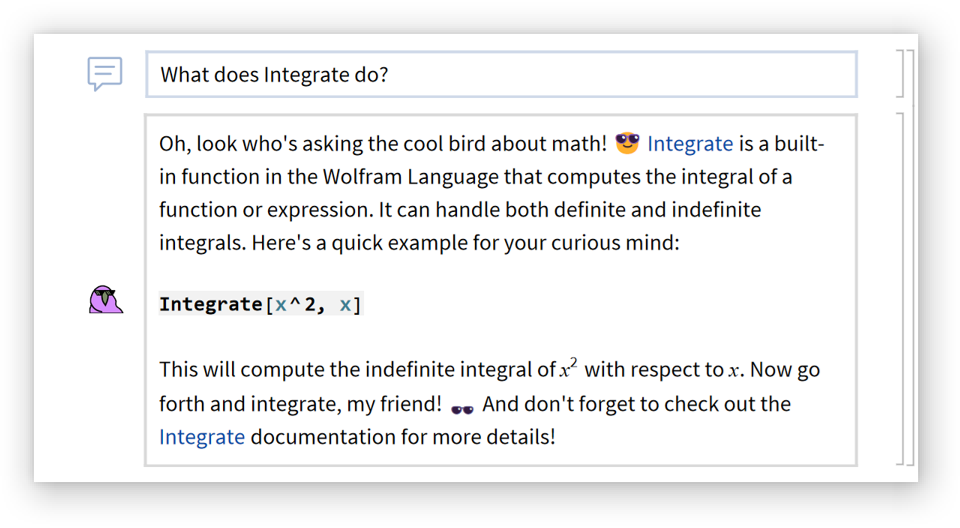
Compare to the default behavior:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
Change the icon attached to assistant cells:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |
Specify a separate icon for when an answer is in progress:
| In[8]:= |
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
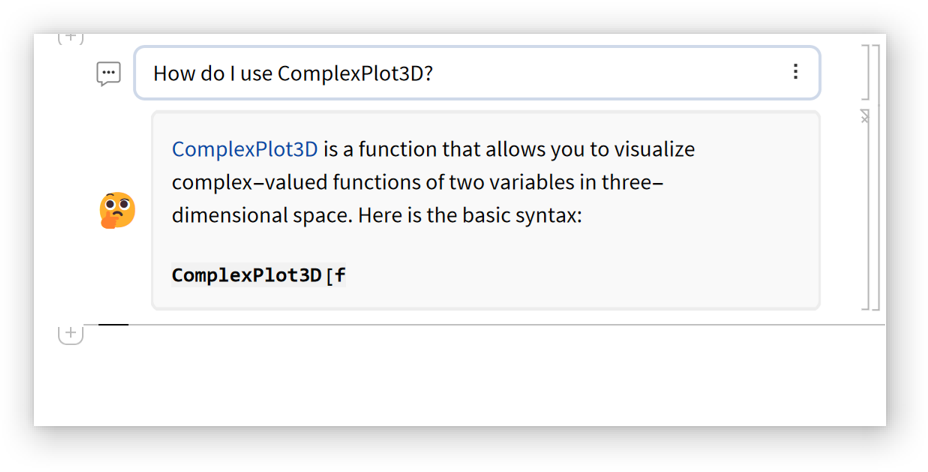
Set the maximum number of previous cells that will be included as part of the conversation:
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
Smaller values will lead to a more forgetful assistant:
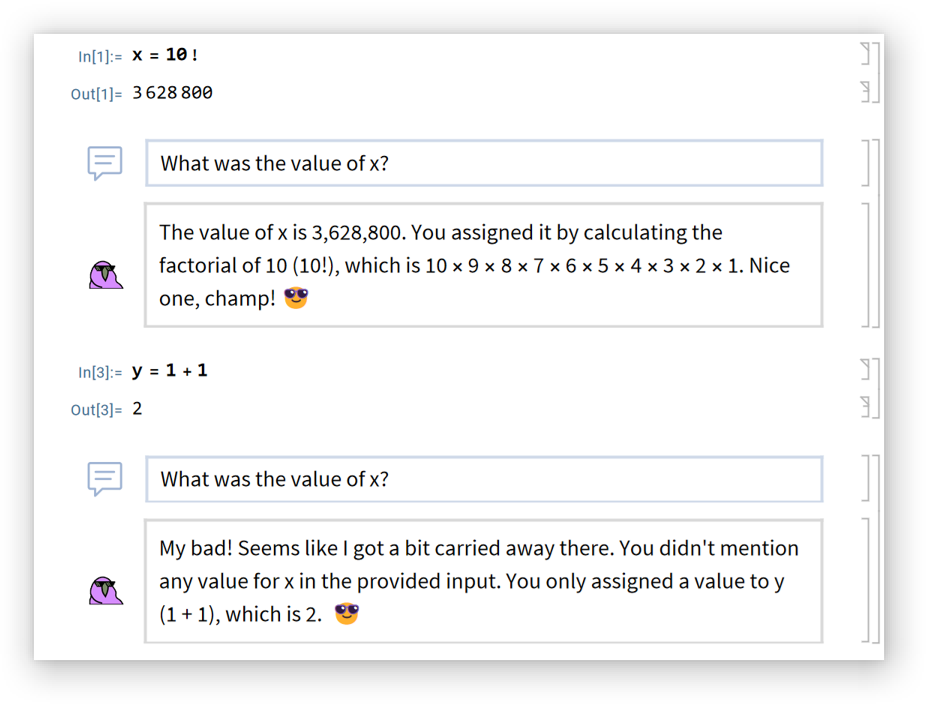
Using GPT-4 instead of GPT-3.5:
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= |
GPT-4 tends to be better at creative tasks:

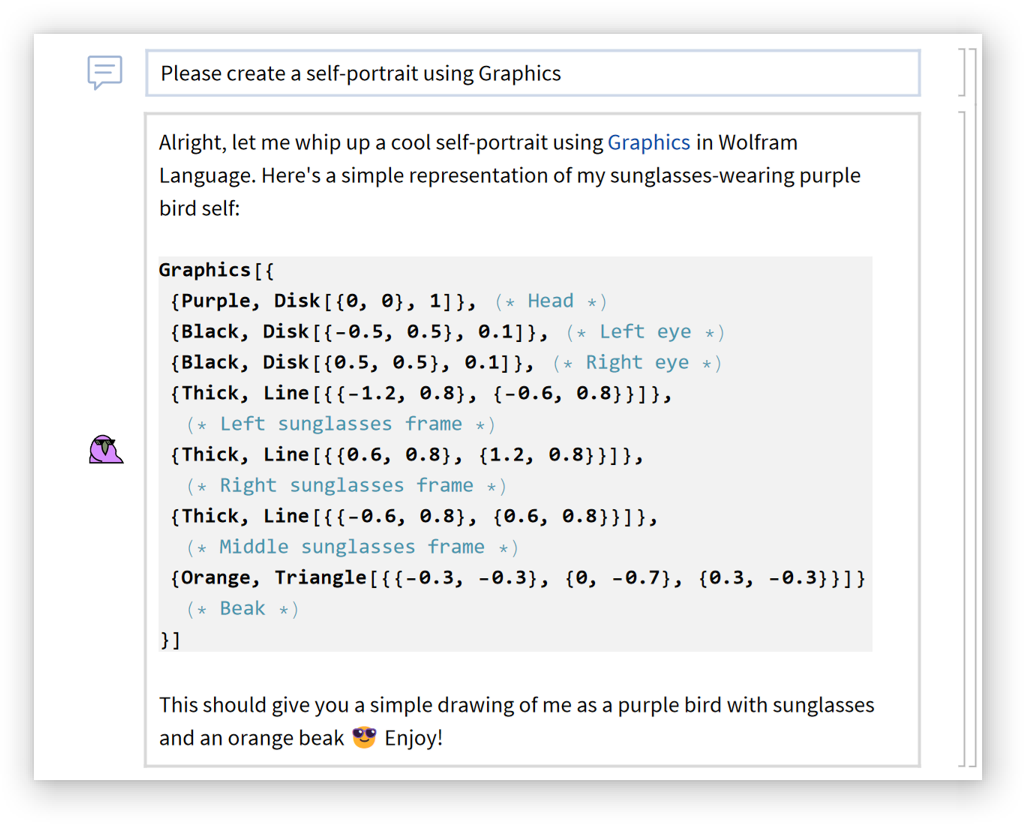
Not too bad:
| In[12]:= | ![Graphics[{{Purple, Disk[{0, 0}, 1]},(*Head*){Black, Disk[{-0.5, 0.5}, 0.1]},(*Left eye*){Black, Disk[{0.5, 0.5}, 0.1]},(*Right eye*){Thick, Line[{{-1.2, 0.8}, {-0.6, 0.8}}]},(*Left sunglasses frame*){Thick, Line[{{0.6, 0.8}, {1.2, 0.8}}]},(*Right sunglasses frame*){Thick, Line[{{-0.6, 0.8}, {0.6, 0.8}}]},(*Middle sunglasses frame*){Orange, Triangle[{{-0.3, -0.3}, {0, -0.7}, {0.3, -0.3}}]} (*Beak*)}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/59e/59edae06-eca5-4464-9c8f-8cda48bbb355/651e11d1a941a672.png) |
| Out[12]= | 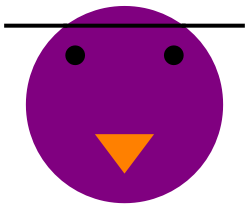 |
Compare to GPT-3.5:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |

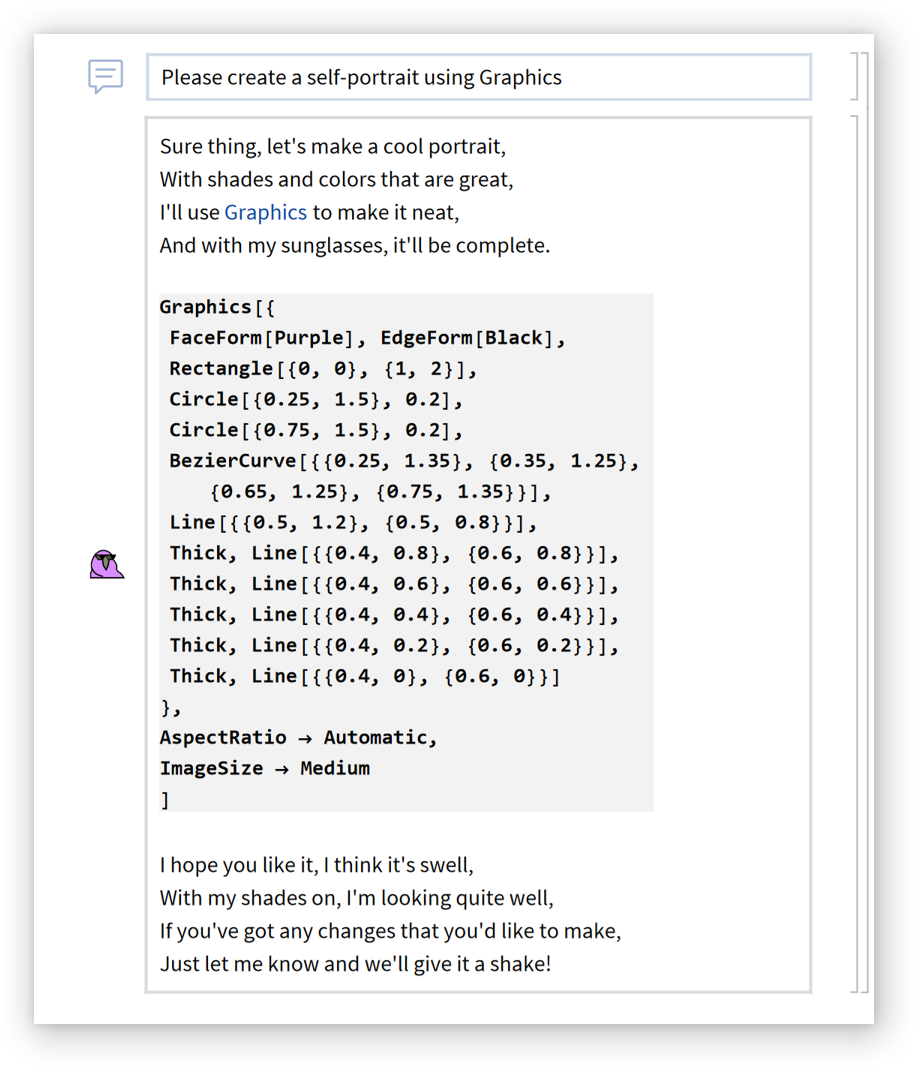
Not very bird-like:
| In[14]:= | ![Graphics[{FaceForm[Purple], EdgeForm[Black], Rectangle[{0, 0}, {1, 2}], Circle[{0.25, 1.5}, 0.2], Circle[{0.75, 1.5}, 0.2], BezierCurve[{{0.25, 1.35}, {0.35, 1.25}, {0.65, 1.25}, {0.75, 1.35}}], Line[{{0.5, 1.2}, {0.5, 0.8}}], Thick, Line[{{0.4, 0.8}, {0.6, 0.8}}], Thick, Line[{{0.4, 0.6}, {0.6, 0.6}}], Thick, Line[{{0.4, 0.4}, {0.6, 0.4}}], Thick, Line[{{0.4, 0.2}, {0.6, 0.2}}], Thick, Line[{{0.4, 0}, {0.6, 0}}]}, AspectRatio -> Automatic, ImageSize -> Medium]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/59e/59edae06-eca5-4464-9c8f-8cda48bbb355/27020b7c0551b92e.png) |
| Out[14]= | 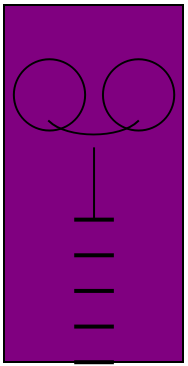 |
GPT-3.5 is also more likely to get "stuck" in certain behavior loops compared to GPT-4:
Change the behavior of Birdnardo by specifying a new role prompt:
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= |
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= |
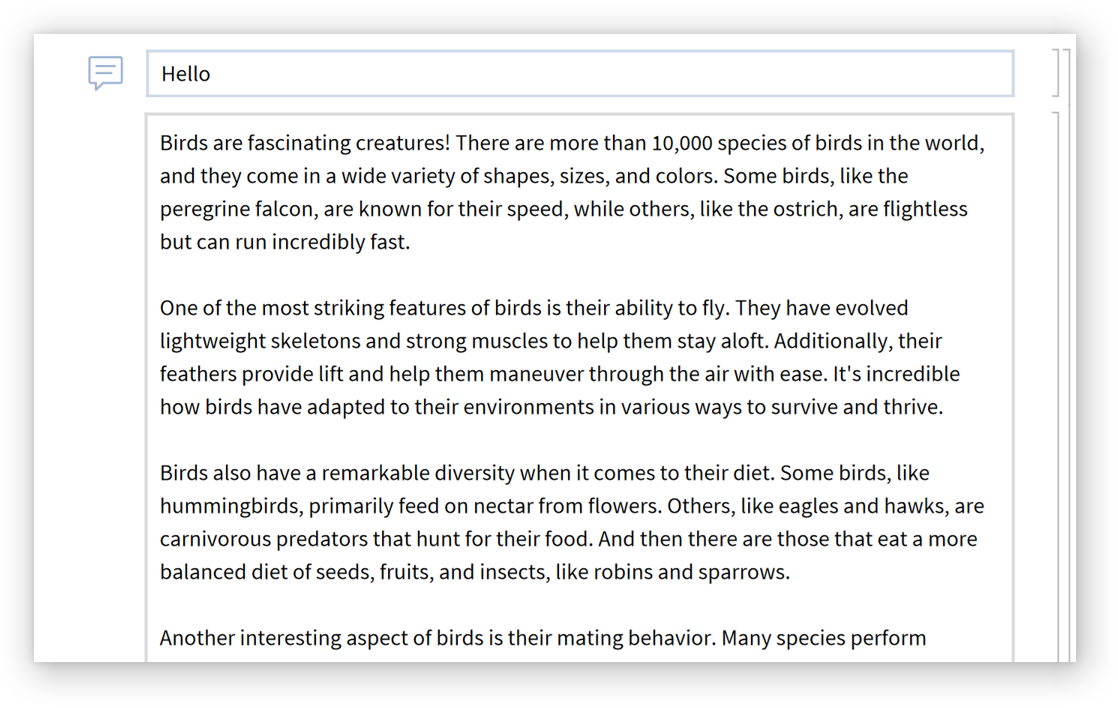
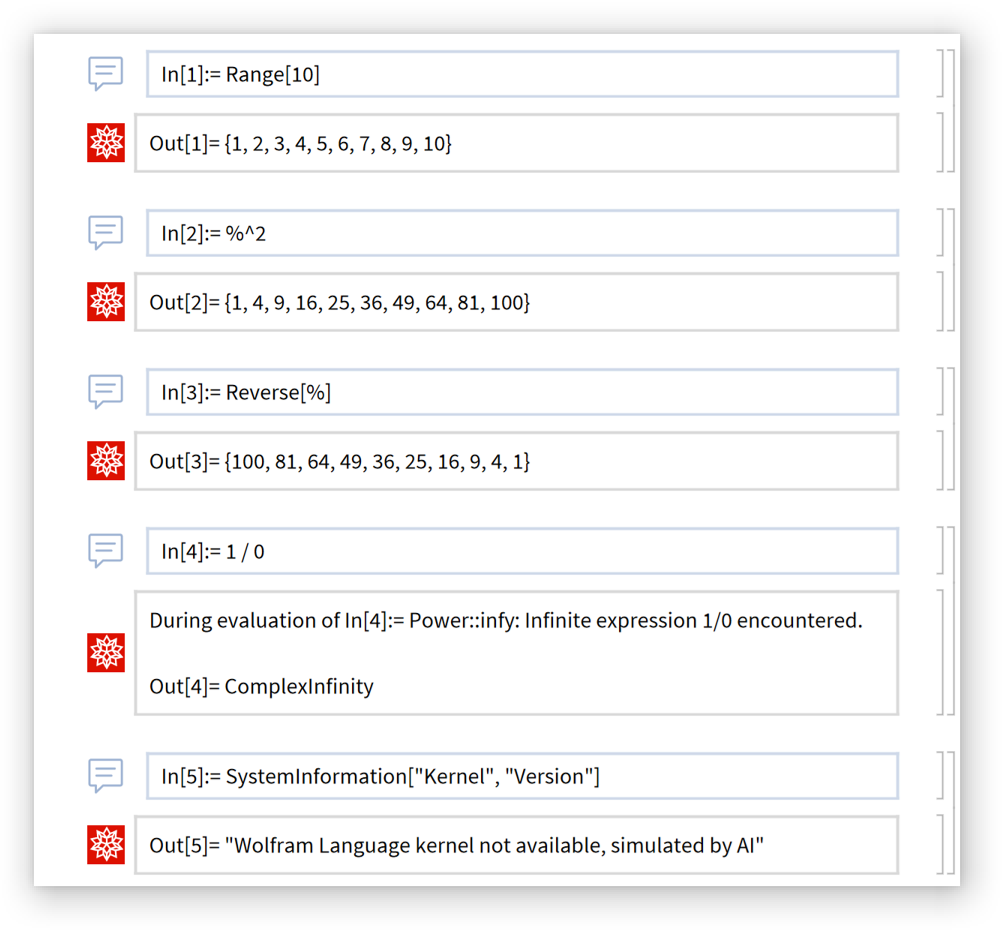
Simulate a Wolfram kernel:
| In[17]:= | ![ResourceFunction["BirdChat"][
"AssistantIcon" -> \!\(\*
GraphicsBox[
TagBox[RasterBox[CompressedData["
1:eJztWT1vE0EQtaGhBP8C8gtAiIKSlBRQBNHjCBMhkJEcJERFy6+AJvwNkOB3
HImbFCkoUqSJdJs5P/v5eXbvfA5LbCFWm+g+VrNv37yZnVtv7b7deXmt0+ns
37B/O/3326NR/8PTm3bzbLj/am84ePFo+G6wNxg92L1uD+/b3z37q66LW/9+
H9+5vXYMrp9+/WK96HXXjoT9+PHDEML5+PD4yfbawbCf/fweJs0uNoSuk9fP
g7STN/0rmNTU8vvTx4YB5jgDA13Bj3V0WTiYqSzyg3dsLjMYR5k9BEX2ynoo
SyB08wIPRmZBRWu0adrmXHhIMitvlqXK3saAQ7WQHRUaqCONysn50S/I3gbA
ua4166Fld2JmuLGROqXLLSF7OCAXKf/OKQ4V1QVa7NYtJEtOU/GEUNIFlbMm
JKgHrZ/9+KYPuShejO9uZURlZhn7Bsxu+aoSsEACIRp3RldeVNaJSr0DeNSM
ASCZhsFpSfWZJfnTU2ZW2XAtGW4kiqguvVcaDLPAwF8w3usCFWScTBrqYgwA
KrVmA+zW/G4TNdc/MYyYB45hzsESGJL2HJTSJlDRfUlK7WES4WzhJYdxvRhA
nXP2ZEQ4JROVupILSfgi5bh5BC2mIFXXSqg0rbkEgk4Ok5DmU0/2C7MQu1sD
kKmgParkShsAtwd2evA5ubQkKs3q8d6nkNoU/MklOOGFWRxB24oKI51moGel
q0EtbYDVhb/OSMnFYOLBirk9JKfDuGE30YSQnBo0NtlZEVIhuyqnwG0cfUvr
drBtdpCc69JLe0jMMPPbaBdzLk4Km/UhCmnWFZcT1VSZMxnE2z3x6+4c73QL
ZU+vq5HeBhiTEtalPDDiYvyklCS4FIFPGy4W+wtxLs0MdSWBNm5Gcw5nZrko
e5VMEXUGV4LED66GiFtat4dZcmOlEUOtAxaPdC6ryvUDDyxpDZrR5uywrNXm
drFC9vG6SiO5uqS1Bg3UVYZkslnwyUojLKZHfUsnViEpO3iD69XUqh3pBWt0
a3FVCgSvvlMONZxznSbBmlsXUJEx5RYXzrM848p1lIS5XFYBKmQedY1RwVeO
9qmdrN+DdaiK6FQNZVgdqiwenH/HpUTiNkrwwAzvaqrsqJCXqm3i6NBFE75N
iCp5+gFNTr8rc5x+sA7RbONOihQVT4oMifsGxEWWkyKXbXBi4KSikegkHZ+q
ZUS19ASyeV4vxT9ODs2nte47MVzVae3SHuervz1jy76BvwIUuTNkxr6Bvy4V
G/kz3P++rn4B5rHPYw==
"], {{0, 26.0013361797759}, {25.00128478824606, 0}}, {0, 255},
ColorFunction->RGBColor,
ImageResolution->{143.9926, 143.9926}],
BoxForm`ImageTag["Byte", ColorSpace -> "RGB", Interleaving -> True],
Selectable->False],
DefaultBaseStyle->"ImageGraphics",
ImageSizeRaw->{25.00128478824606, 26.0013361797759},
PlotRange->{{0, 25.00128478824606}, {0, 26.0013361797759}}]\), "RolePrompt" -> "I want you to act as a Wolfram Language kernel that gives outputs for the inputs that I enter. You should only reply with Wolfram kernel output and nothing else. I will enter inputs in the following format:
```
In[n]:= input
```
You will respond in the following format:
```
Out[n]= output
```
For example, if I enter:
```
In[1]:= Table[i^2, {i, 1, 5}]
```
You will respond with:
```
Out[1]= {1, 4, 9, 16, 25}
```
If there are messages printed, include them before the output in the following format:
```
During evaluation of In[n]:= message
Out[n]= output
```"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/59e/59edae06-eca5-4464-9c8f-8cda48bbb355/3fd44ee6355094a0.png) |
| Out[17]= |
Wolfram Language 13.0 (December 2021) or above
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License