Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Perform a Schmidt decomposition on a pure discrete quantum state
ResourceFunction["QuantumSchmidtDecomposition"][QuantumDiscreteState[…]] performs a Schmidt decomposition on the specified QuantumDiscreteState. |
Create a two-qubit pure discrete quantum state in the computational basis (default):
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |
Perform a Schmidt decomposition of the state, resulting in a new (Schmidt-decomposed) tensor product basis:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
Show the basis elements of the new (Schmidt-decomposed) tensor product basis:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |  |
Perform a full Schmidt decomposition (returning both the decomposed state, and the two individual bases involved in the tensor product):
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= | 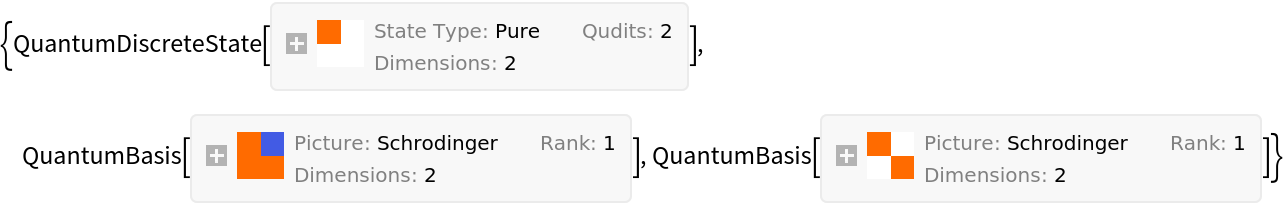 |
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
Perform a Schmidt decomposition of a pure discrete quantum state with more than 2 subsystems by automatically partitioning the state into exactly two subsystems of (approximately) equal size:
| In[11]:= | ![state = ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteState"][{"RandomPure", 4}];
{decomposition, basis1, basis2} = ResourceFunction["QuantumSchmidtDecomposition"][state, "GiveFullDecomposition" -> True]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/376/3769c4e3-8b5a-4884-9a33-83d976976400/50a167fe092f4342.png) |
| Out[11]= | 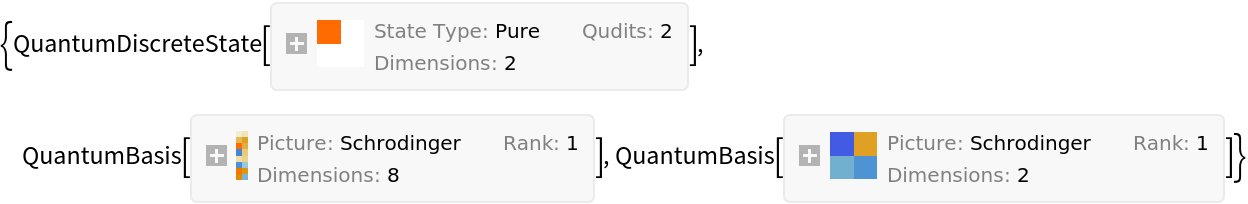 |
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |  |
| In[14]:= |
| Out[14]= |
Perform a Schmidt decomposition of a state consisting of two three-dimensional qudits:
| In[15]:= | ![state = ResourceFunction["QuantumDiscreteState"][{"RandomPure", 2}, 3];
{decomposition, basis1, basis2} = ResourceFunction["QuantumSchmidtDecomposition"][state, "GiveFullDecomposition" -> True]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/376/3769c4e3-8b5a-4884-9a33-83d976976400/197b7f6455878cff.png) |
| Out[15]= | 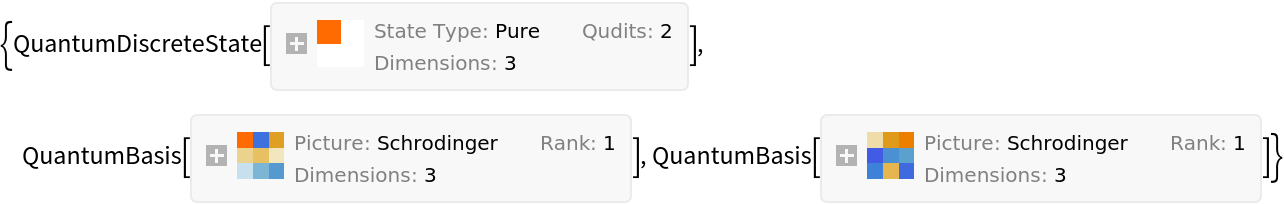 |
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= |
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= |  |
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= |  |
If "GiveFullDecomposition"→False (default), then QuantumSchmidtDecomposition returns only the decomposed state in the (Schmidt-decomposed) tensor product basis:
| In[19]:= |
| Out[19]= |
| In[20]:= |
| Out[20]= |
On the other hand, if "GiveFullDecomposition"→True, then QuantumSchmidtDecomposition returns a list consisting of the decomposed state, as well as the two individual bases involved in the tensor product:
| In[21]:= |
| Out[21]= | 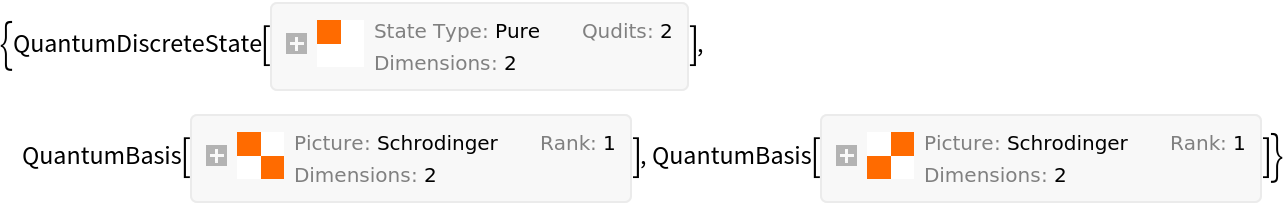 |
| In[22]:= |
| Out[22]= |
| In[23]:= |
| Out[23]= |
| In[24]:= |
| Out[24]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License