Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Bin data into hexagon tiles
ResourceFunction["HextileBins"][mat,r] bins a numerical full 2D array mat into hexagon grid tiles with radius r. | |
ResourceFunction["HextileBins"][cv,r] bins coordinates-to-value rules cv. |
Create a list of random 2D points:
| In[1]:= |
Bin the points:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 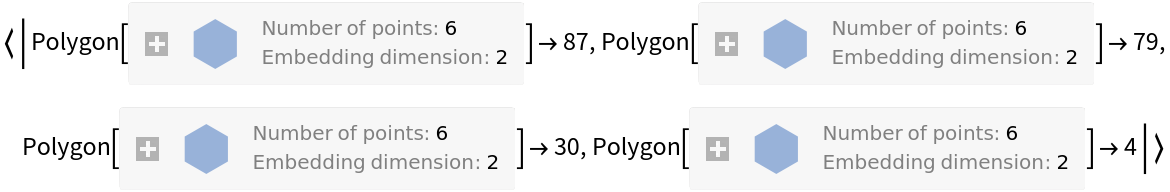 |
Bin the points and get the hex-tile centers as keys:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |
Plot the points and the hexagon bins:
| In[4]:= | ![Graphics[{EdgeForm[Black], FaceForm[Opacity[0.3]], Keys@ResourceFunction["HextileBins"][data, 10], Red, Point[data]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/287/287aac6d-cddc-4162-9aa3-07367ac1fbe7/3ea31cc3873f2b99.png) |
| Out[4]= | 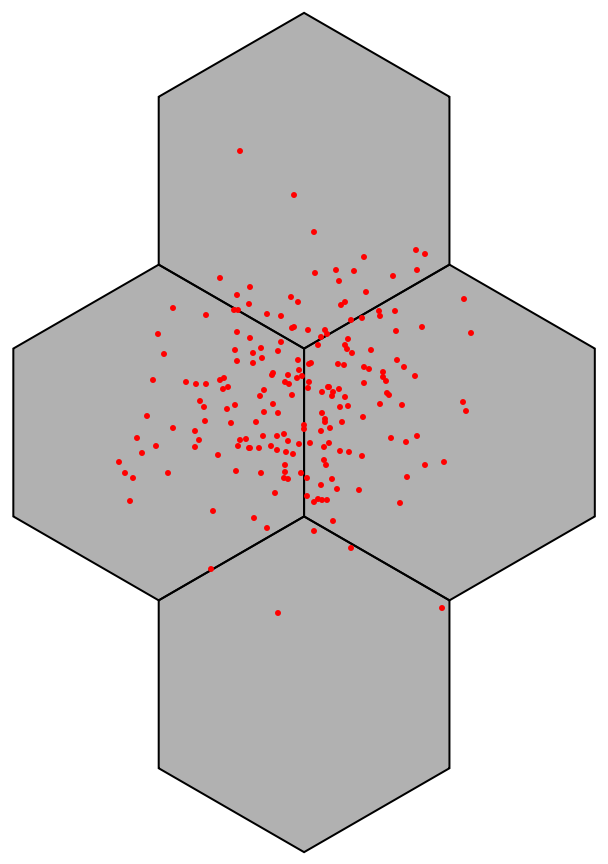 |
Associate random values to 2D data:
| In[5]:= | ![SeedRandom[113];
data = RandomVariate[
MultinormalDistribution[{10, 10}, 7*IdentityMatrix[2]], 200]; dataRules = AssociationThread[data, RandomReal[{0, 1}, Length[data]]];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/287/287aac6d-cddc-4162-9aa3-07367ac1fbe7/0fe452abb45e7b69.png) |
Bin the data rules:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= | 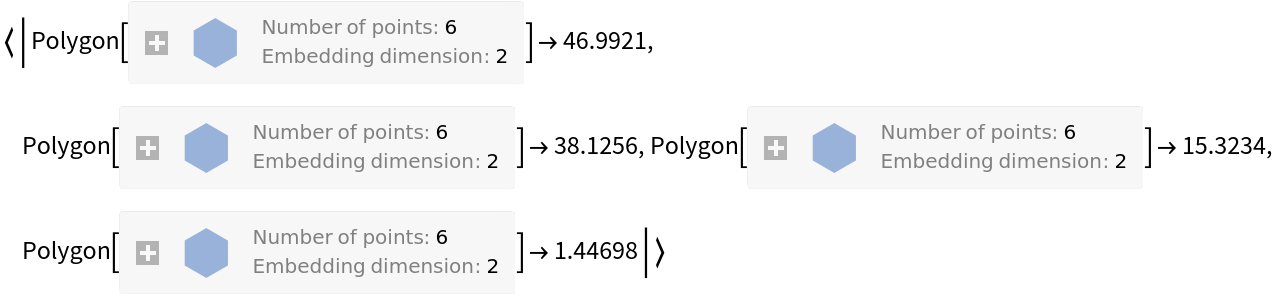 |
Bin the keys of the data rules:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= | 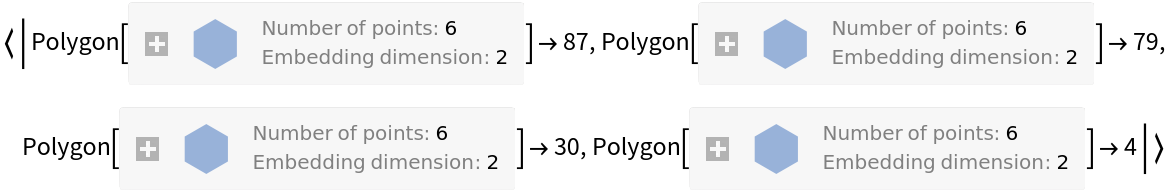 |
Check the equivalence:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
Bin the data rules and compute average values on each tile:
| In[9]:= | ![SeedRandom[113];
data = RandomVariate[
MultinormalDistribution[{10, 10}, 7*IdentityMatrix[2]], 200]; dataRules = AssociationThread[data, RandomReal[{0, 1}, Length[data]]];
ResourceFunction["HextileBins"][dataRules, 6, "AggregationFunction" -> Mean]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/287/287aac6d-cddc-4162-9aa3-07367ac1fbe7/03ef94fe39d8d726.png) |
| Out[6]= |  |
Compare with the default option value Total:
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |  |
Instead of polygons as keys, you can get the centers of the polygons:
| In[11]:= | ![SeedRandom[113];
data = RandomVariate[
MultinormalDistribution[{10, 10}, 7*IdentityMatrix[2]], 200]; dataRules = AssociationThread[data, RandomReal[{0, 1}, Length[data]]]; ResourceFunction[
"HextileBins"][dataRules, 10, "PolygonKeys" -> False]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/287/287aac6d-cddc-4162-9aa3-07367ac1fbe7/31bb7c9932a2c2c8.png) |
| Out[12]= |
Generate data rules:
| In[13]:= | ![SeedRandom[113];
data2 = RandomVariate[
MultinormalDistribution[{10, 10}, 7*IdentityMatrix[2]], 300]; dataRules2 = AssociationThread[data2, RandomReal[{0, 100}, Length[data2]]];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/287/287aac6d-cddc-4162-9aa3-07367ac1fbe7/1c81698d01d8fe6c.png) |
Here we bin the data:
| In[14]:= |
Plot points and hexagon bins by coloring each hexagon according to its aggregated value:
| In[15]:= | ![Graphics[{KeyValueMap[{FaceForm[
Opacity[Rescale[#2, MinMax[Values[res2]], {0, 1}], Blue]], #1} &, res2], Red, Point[Keys[dataRules2]]}, Frame -> True]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/287/287aac6d-cddc-4162-9aa3-07367ac1fbe7/1c920051f23a0466.png) |
| Out[15]= | 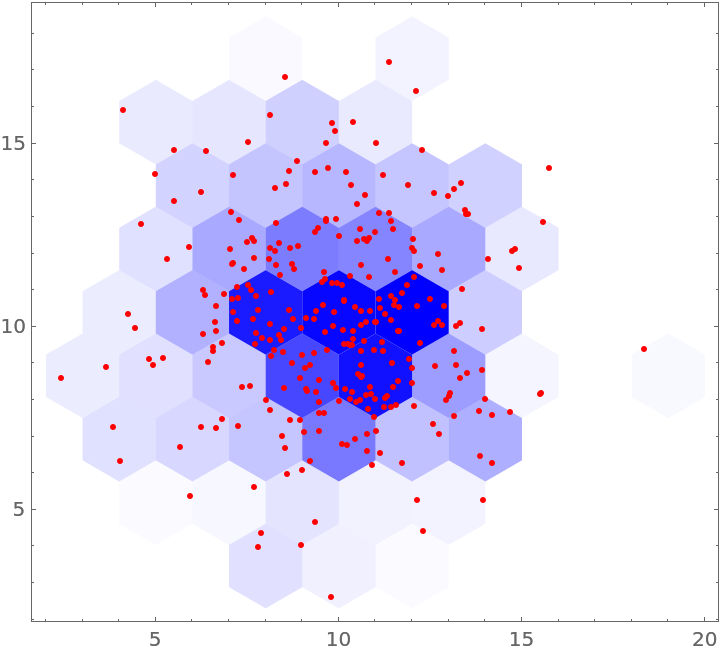 |
You can make hexagonal grids:
| In[16]:= |
| Out[17]= | 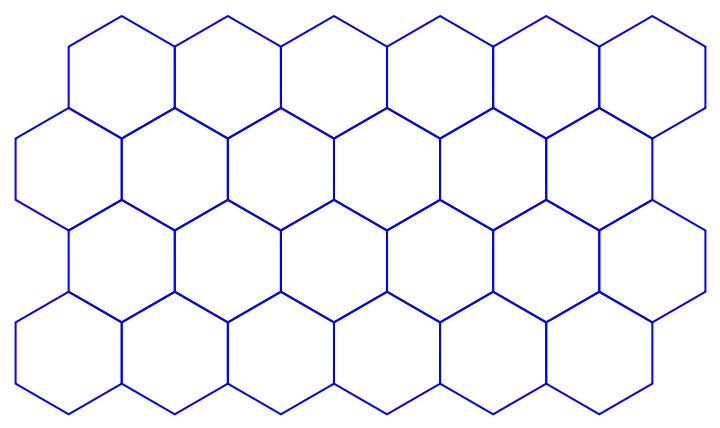 |
The coordinates of the polygons can be retrieved and transformed further:
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= |  |
The function GeoHistogram produces similar plots (in Version 12.1):
| In[19]:= |
| In[20]:= |
| In[21]:= | ![geoRes = ResourceFunction["HextileBins"][Reverse[#[[1]]] & /@ geoData,
0.8];
gr2 = Graphics[{KeyValueMap[{FaceForm[
Blend[{Lighter[Lighter[Yellow]], Brown}, Rescale[#2, MinMax[Values[geoRes]], {0, 1}]]], #1} &, geoRes]}, Frame -> True, Prolog -> {LightBlue, Rectangle[Scaled[{0, 0}], Scaled[{1, 1}]]},
PlotLabel -> "HextileBins", ImageSize -> 250];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/287/287aac6d-cddc-4162-9aa3-07367ac1fbe7/6579ae7eed27ab67.png) |
| In[22]:= |
| Out[22]= | 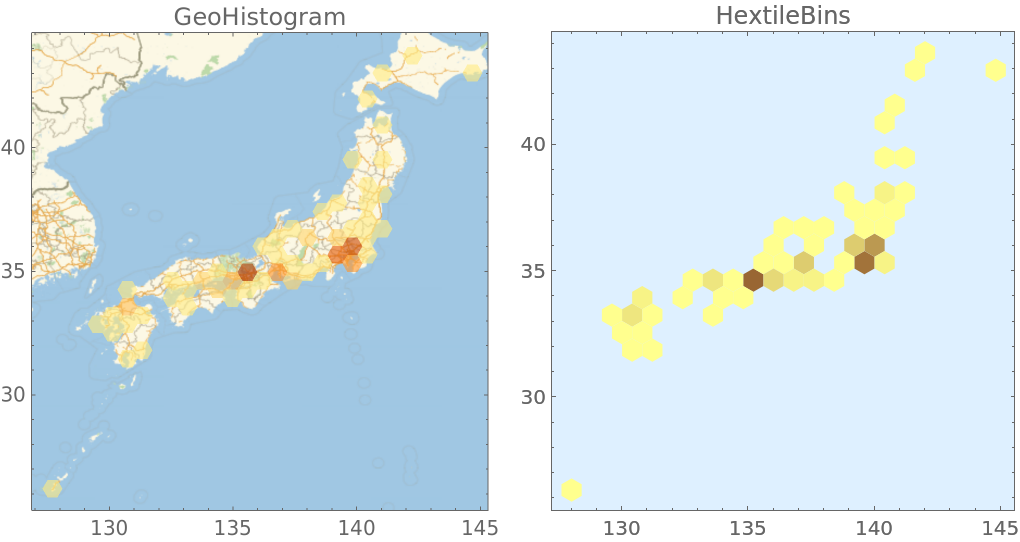 |
The resource function HexagonalGridGraph can be also used to make hexagonal grids:
| In[23]:= |
| Out[23]= | 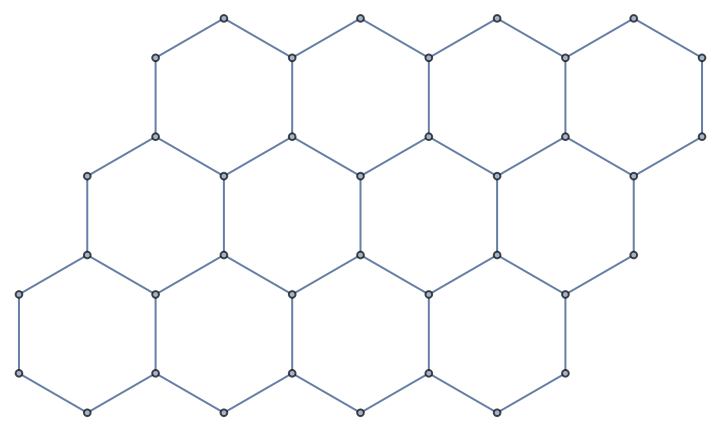 |
Here are the corresponding coordinates:
| In[24]:= |
| Out[24]= | 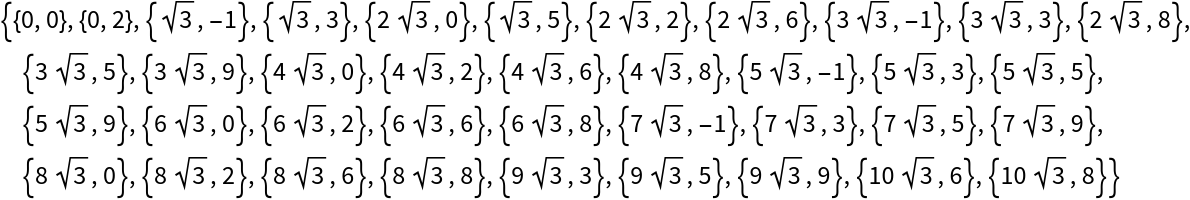 |
Here are the corresponding polygons:
| In[25]:= | ![grHexPolygons = Map[Polygon@(List @@@ #)[[All, 1]] &, FindCycle[grHex, {6, 6}, All]] /. v_Integer :> lsVCoords[[v]];
Graphics[{EdgeForm[Blue], FaceForm[Opacity[0.2]], grHexPolygons}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/287/287aac6d-cddc-4162-9aa3-07367ac1fbe7/56f8c7fa29080795.png) |
| Out[15]= | 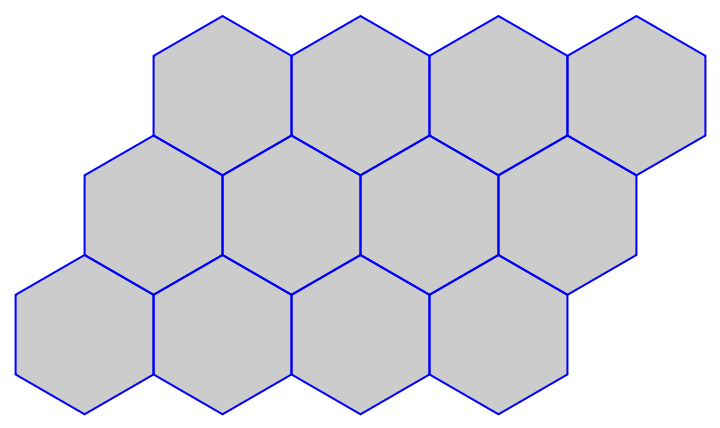 |
Make a similar grid with HextileBins:
| In[26]:= |
| Out[27]= | 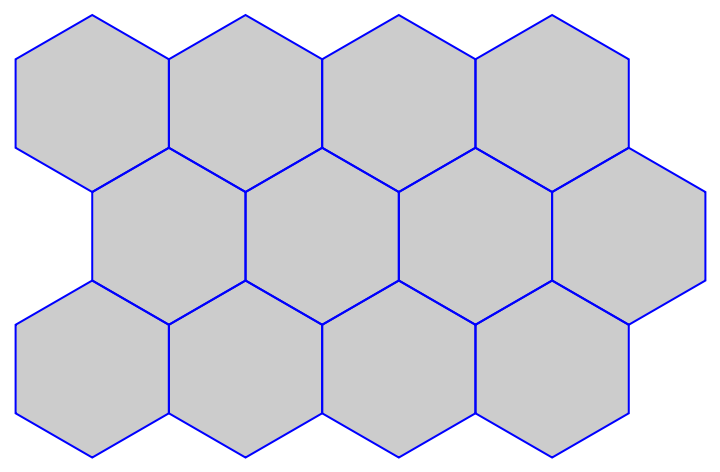 |
Here are the corresponding coordinates:
| In[28]:= |
| Out[28]= |  |
The resource function TileBins has similar design and implementation as HextileBins. Here are comparable examples:
| In[29]:= | ![GraphicsGrid[{{Graphics[{EdgeForm[Black], FaceForm[Opacity[0.3]], Keys@ResourceFunction["HextileBins"][data, 5], Red, Point[data]},
PlotLabel -> "HextileBins"], Graphics[{EdgeForm[Black], FaceForm[Opacity[0.3]], Keys@ResourceFunction["TileBins"][data, 5], Red, Point[data]}, PlotLabel -> "TileBins"]}}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/287/287aac6d-cddc-4162-9aa3-07367ac1fbe7/4cbf2d571c28172b.png) |
| Out[29]= | 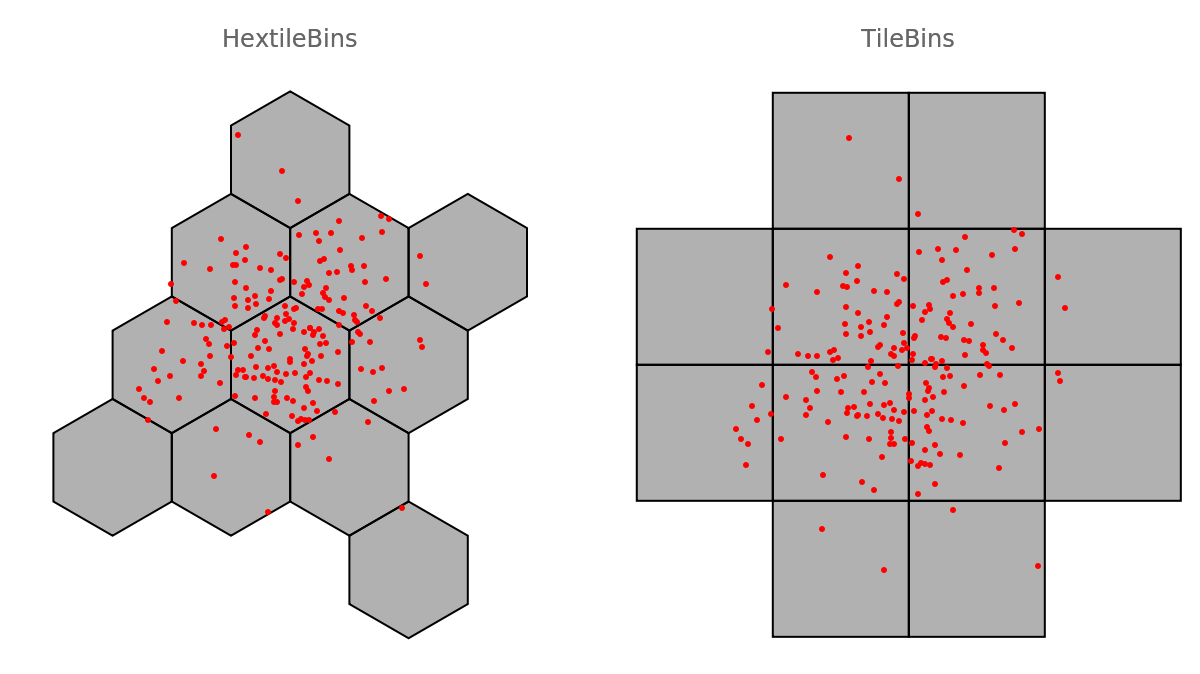 |
Bin data and summarize the values associated with bin centers:
| In[30]:= | ![SeedRandom[113];
data3 = RandomVariate[
MultinormalDistribution[{10, 10}, {1, 1.7}*IdentityMatrix[2]], 300]; dataRules3 = AssociationThread[data3, RandomReal[{0, 100}, Length[data3]]];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/287/287aac6d-cddc-4162-9aa3-07367ac1fbe7/26d2d4a4b8292768.png) |
| In[31]:= |
| Out[31]= |  |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License