Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Compute the normal surface of a curve
ResourceFunction["NormalSurface"][c,t,{u,v}] gives the normal surface of a curve c with parameter t using u and v to parametrize the result. |
Define and plot a Viviani’s curve:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 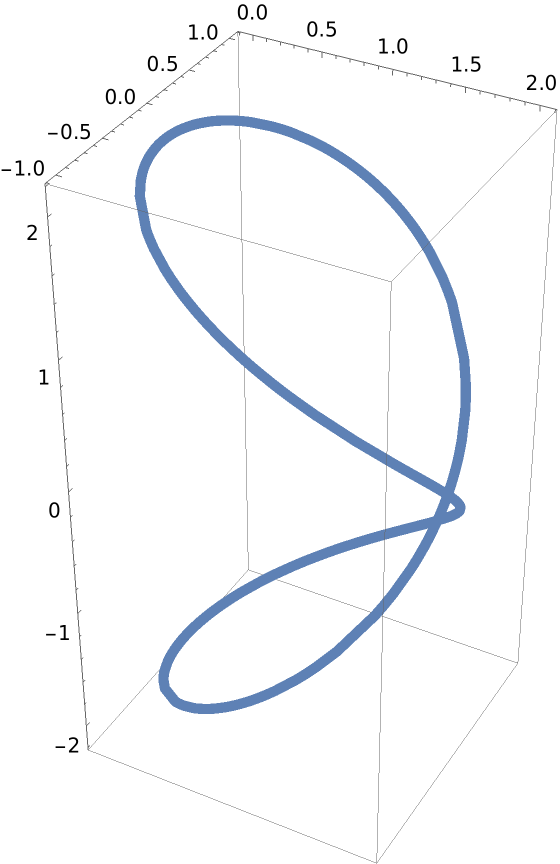 |
Compute the normal surface of Viviani’s curve:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= | 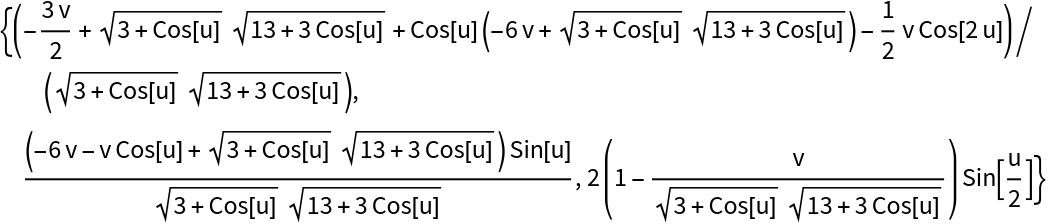 |
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= | 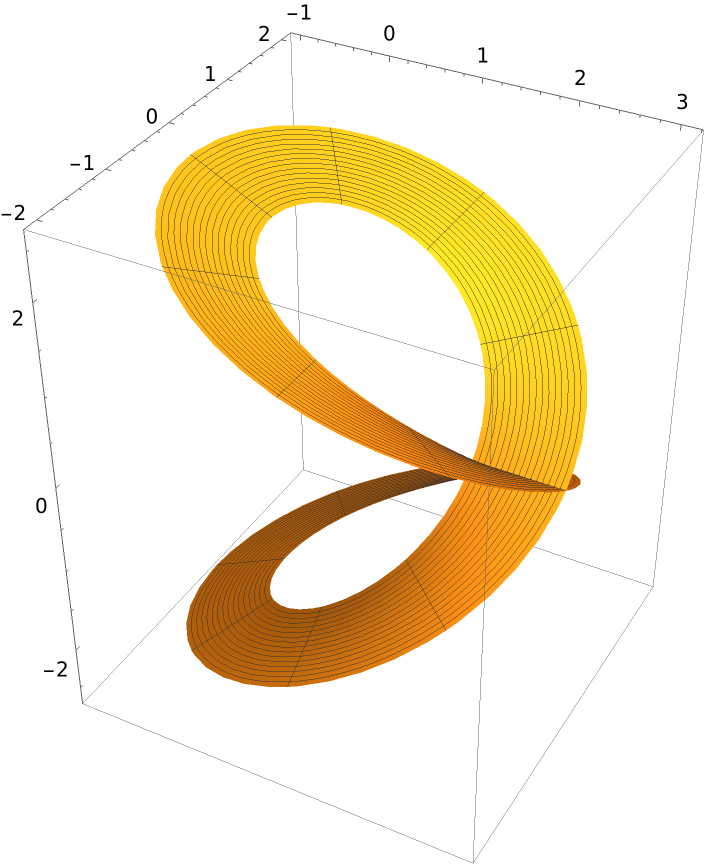 |
Compute the binormal surface of Viviani’s curve with the resource function BiormalSurface and plot the result:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= | 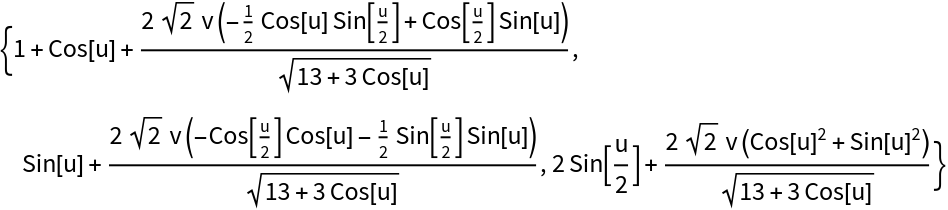 |
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= | 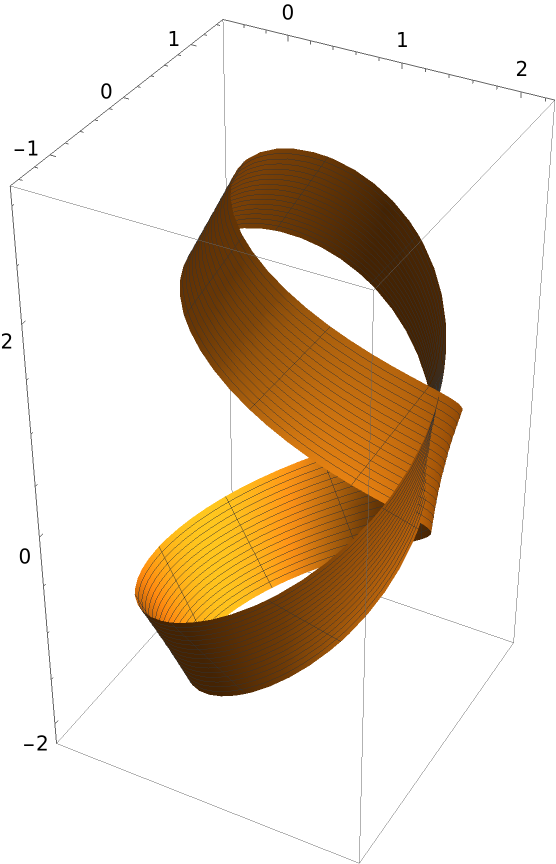 |
Show both surfaces along with Viviani’s curve:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= | 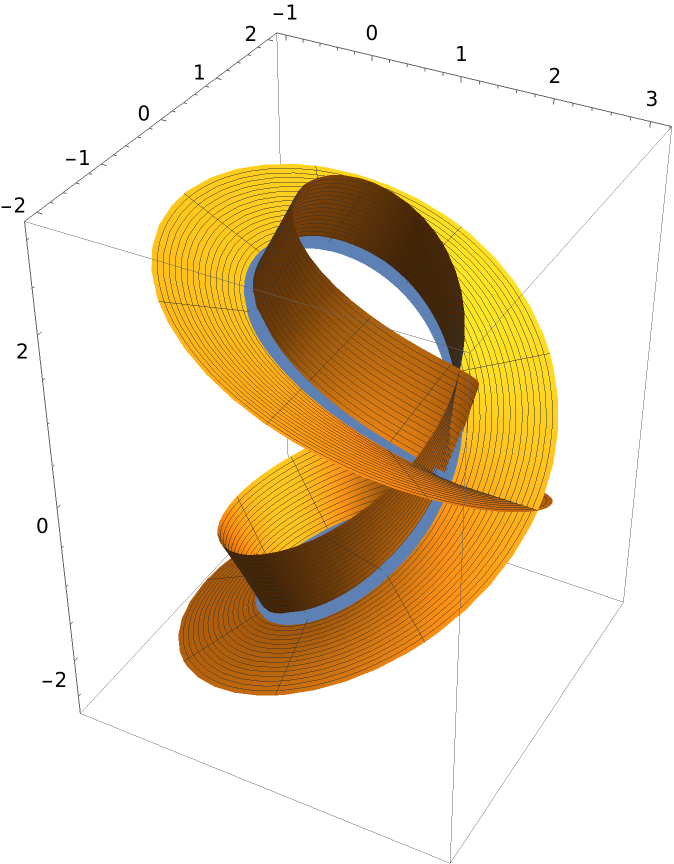 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License