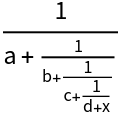Basic Examples (6)
Perform a right fold on a list:
Perform another right fold:
Use a right fold to form a power tower:
Use the last element of the list as the starting value:
Use the operator form of FoldRight on one argument:
Use the operator form of FoldRight on two arguments:
Scope (1)
Perform a chain of cross products:
Generalizations and Extensions (2)
The head need not be List:
Fold to the left:
Or equivalently:
Applications (5)
Form an alternating sum:
Form a continued fraction:
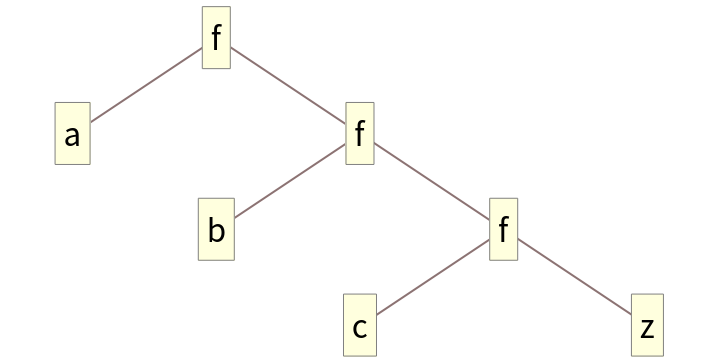
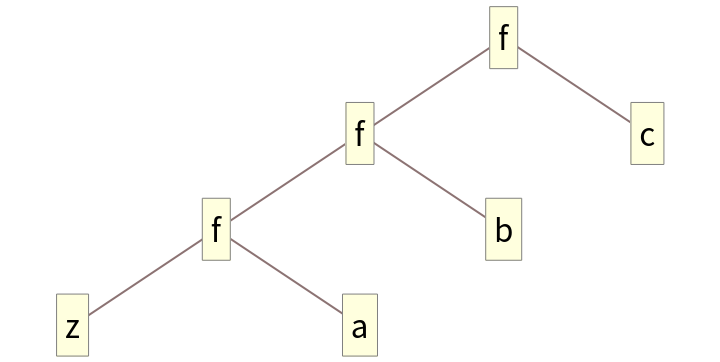
Form a binary tree:
FoldRight can be used to perform composition:
Or equivalently:
Similarly, Fold can be used to form a right composition:
Form a composition of subvalues:
Properties and Relations (5)
Folding with an empty list does not apply the function at all:
Functions that ignore their first argument give the same result as Nest:
Compare FoldRight to Fold structurally:
The order of arguments passed to f are reversed compared to Fold:
FoldRight takes elements starting on the right of the given list:
Compare to Fold:
Possible Issues (2)
An empty list cannot be folded:
Elements are taken in reverse order:
Compare to a typical recursive definition of foldr:
This implementation allows FoldRight to be tail recursive, which is far more efficient with respect to stack size:
Without tail recursion, the stack size would grow with respect to the size of the list: