Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Compute the normal curvature of a curve on a surface
ResourceFunction["NormalCurvature"][s,c,{u,v},t] computes the normal curvature of the plane curve c with respect to variable t over the surface s parameterized by u and v. |
A sphere:
| In[1]:= |
|
Normal curvature of the sphere:
| In[2]:= |
|
| In[3]:= |
|
A hyperbolic paraboloid:
| In[4]:= |
|
A normal section of the hyperbolic paraboloid:
| In[5]:= |
|
Plot of the normal sections of the hyperbolic paraboloid:
| In[6]:= |
![ParametricPlot3D[hp, {u, -2 \[Pi], 2 \[Pi]}, {v, -2 \[Pi], 2 \[Pi]}, BoxRatios -> {1, 1, 1}, Mesh -> 3, PlotPoints -> 50, MeshStyle -> {{Blue, Thickness[.005]}}, MaxRecursion -> 3, MeshFunctions -> {Cos[ArcTan[#1, #2]] &, Sin[ArcTan[#1, #2]] &}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/cb3/cb37a512-171c-4681-8e6c-7bd0c4583f73/4e4f9cd4e738b96b.png)
|
| Out[6]= |
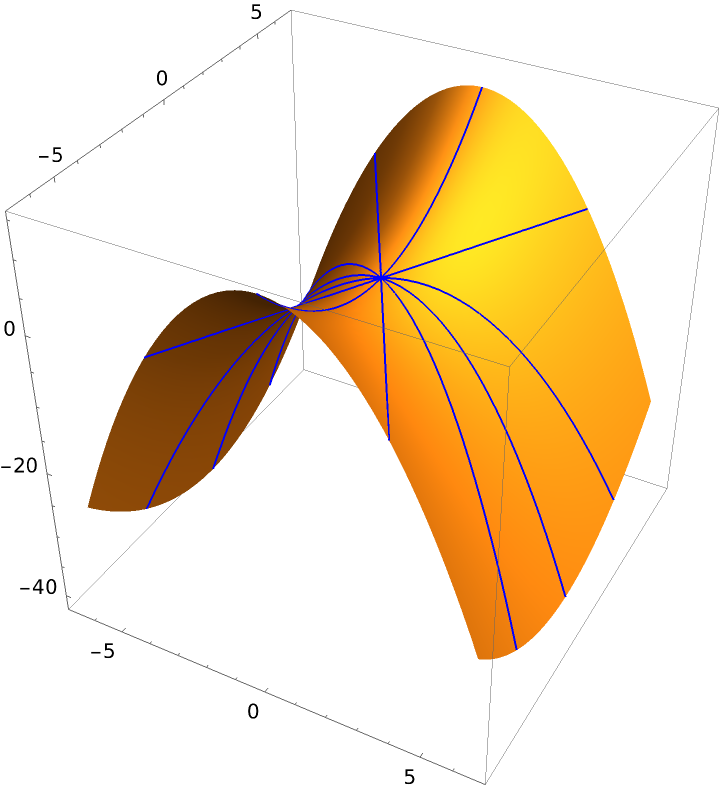
|
The normal curvature:
| In[7]:= |
|
| Out[7]= |
|
The change in direction happens when the curvature crosses zero:
| In[8]:= |
![Reduce[-((18 (1 + 2 Cos[2 \[CurlyPhi]]))/(Sqrt[
9 + 20 t^2 + 16 t^2 Cos[2 \[CurlyPhi]]] (9 + 12 t^2 + 16 t^2 Cos[2 \[CurlyPhi]] + 8 t^2 Cos[4 \[CurlyPhi]]))) == 0, \[CurlyPhi]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/cb3/cb37a512-171c-4681-8e6c-7bd0c4583f73/70bea7587f625648.png)
|
| Out[8]= |
|
Choose c1 to get zeros in the interval (0,π):
| In[9]:= |
|
| Out[9]= |
|
The principal curvatures:
| In[10]:= |
|
| Out[10]= |
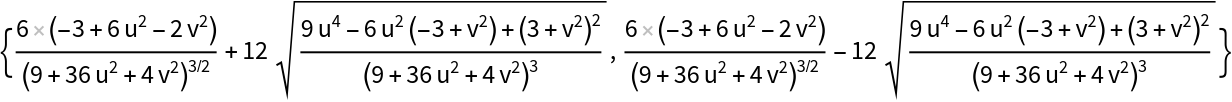
|
The maximum and minimum values of the normal curvature are the principal curvatures:
| In[11]:= |
|
| Out[11]= |
|
The normal curvature when t=0:
| In[12]:= |
|
| Out[12]= |
|
The normal curvature varying φ (principal curvatures have opposite signs in a hyperbolic point):
| In[13]:= |
![Manipulate[
Plot[-(2/3) (1 + 2 Cos[2 \[CurlyPhi]]), {\[CurlyPhi], 0, \[Pi]}, Epilog -> {Arrow[{{t, 0}, {t, -(2/3) (1 + 2 Cos[2 t])}}], Red, PointSize[.02], Point[{#, 0} & /@ zeroes], Blue, Point[{{0, -2}, {\[Pi]/2, 2/3}}], Text[Style["\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\(\[Kappa]\), \(2\)]\)", 16], {.1, -2.1}], Text[Style["\!\(\*SubscriptBox[
StyleBox[\"\[Kappa]\", \"TR\"], \(1\)]\)", 16], {1.6, .9}]}, AxesLabel -> {\[CurlyPhi], "\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\(\[Kappa]\), \(n\)]\)(\[CurlyPhi])"}, PlotRange -> {{-.1, \[Pi]}, {-2.3, 1}}], {t, 0, \[Pi]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/cb3/cb37a512-171c-4681-8e6c-7bd0c4583f73/2e5ce96f8aa1b546.png)
|
| Out[13]= |
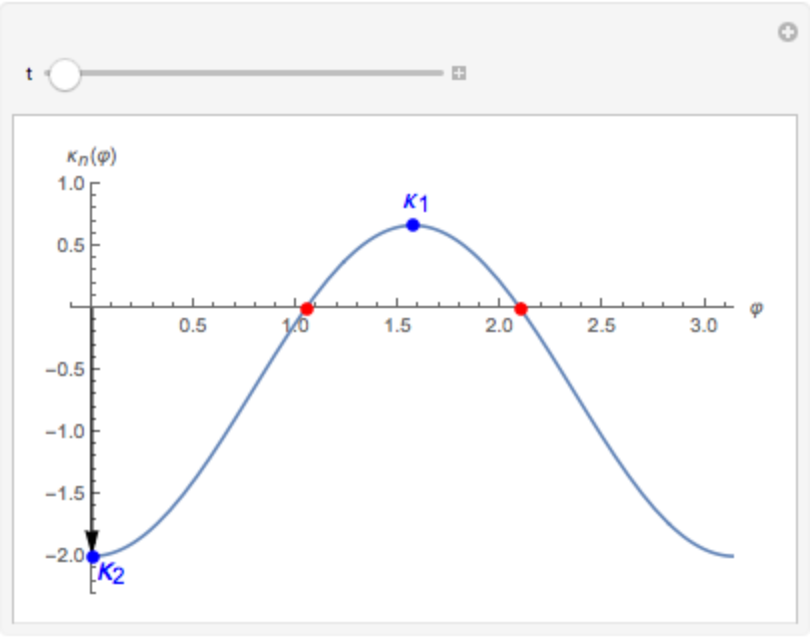
|
The asymptotic directions correspond to the angles for the zeros:
| In[14]:= |
|
| Out[14]= |
|
In these directions, the normal curvature vanishes:
| In[15]:= |
|
| Out[15]= |
|
Plot the principal directions and the principal curves:
| In[16]:= |
![Show[ParametricPlot3D[{u, v, -u^2 + v^2/3}, {u, -2 \[Pi], 2 \[Pi]}, {v, -2 \[Pi], 2 \[Pi]}, BoxRatios -> {1, 1, 1}, Mesh -> None], Graphics3D[{Opacity[.5], Rotate[Polygon[
4.5 {{\[Pi]/2, 0, -6}, {-\[Pi]/2, 0, -6}, {-\[Pi]/2, 0, 6}, {\[Pi]/2, 0, 6}}], \[Pi]/3, {0, 0, 1}], Rotate[Polygon[
4.5 {{\[Pi]/2, 0, -8}, {-\[Pi]/2, 0, -8}, {-\[Pi]/2, 0, 8}, {\[Pi]/2, 0, 8}}], 2 \[Pi]/3, {0, 0, 1}], Polygon[{{6, -6, 0}, {-6, -6, 0}, {-6, 6, 0}, {6, 6, 0}}]}], ParametricPlot3D[{{-t, Sqrt[3] t, 0}, {t, Sqrt[3] t, 0}}, {t, -3.6, 3.6}]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/cb3/cb37a512-171c-4681-8e6c-7bd0c4583f73/7d59ee141de7f7d5.png)
|
| Out[16]= |
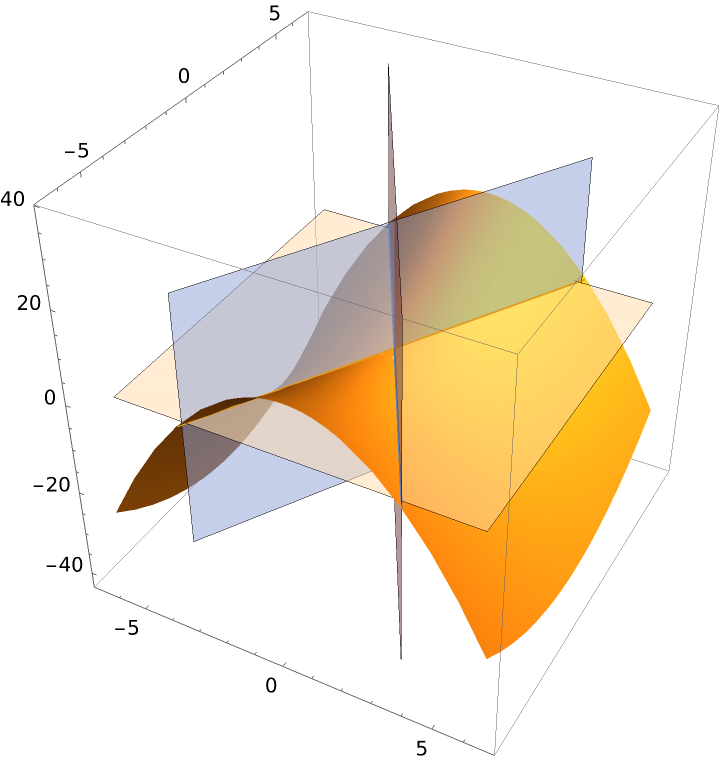
|
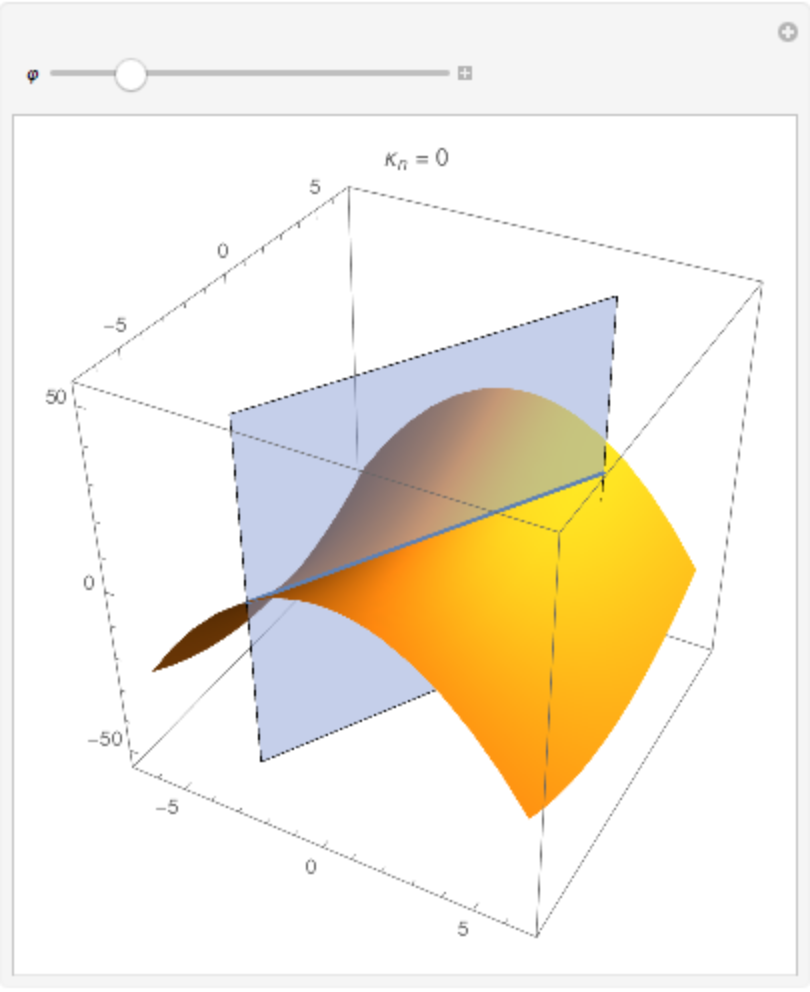
The normal sections and the normal curvature:
| In[17]:= |
![Manipulate[
Show[ParametricPlot3D[
hp, {u, -2 \[Pi], 2 \[Pi]}, {v, -2 \[Pi], 2 \[Pi]}, BoxRatios -> {1, 1, 1}, Mesh -> None, PlotLabel -> Row[{Subscript[\[Kappa], n], NumberForm[-(2/3) (1 + 2 Cos[2 \[CurlyPhi]]), {3, 2}]}, "="]], Graphics3D[{Opacity[.5], Rotate[Polygon[
2 \[Pi] {{1, 0, -8}, {-1, 0, -8}, {-1, 0, 8}, {1, 0, 8}}], \[CurlyPhi], {0, 0, 1}]}], ParametricPlot3D[{u Cos[\[CurlyPhi]], v Sin[\[CurlyPhi]], -(u Cos[\[CurlyPhi]])^2 + (v Sin[\[CurlyPhi]])^2/3} /. {u -> t, v -> t}, {t, -2 \[Pi], 2 \[Pi]}]], {{\[CurlyPhi], \[Pi]/3}, 0., 2 \[Pi]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/cb3/cb37a512-171c-4681-8e6c-7bd0c4583f73/494d97387a95df11.png)
|
| Out[17]= |
|
A cylinder:
| In[18]:= |
|
| Out[18]= |
|
The normal curvature:
| In[19]:= |
|
| Out[19]= |
|
Computing the normal curvature manually, first find the derivatives:
| In[20]:= |
|
| Out[20]= |
|
Derive again when t=0:
| In[21]:= |
|
| Out[21]= |
|
The dot product with the unit normal gives:
| In[22]:= |
|
| Out[22]= |
|
Another way to compute the normal curvature using the principal curvatures:
| In[23]:= |
|
| Out[23]= |
|
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License