Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
An operator that joins in front of its arguments the sequence of lists it is provided
ResourceFunction["JoinMost"][list] an operator that will join the sequence of lists it encounters with list. |
JoinMost uses Join to join its argument {3,4} with whatever else it encounters, which one may think of as "Most" of the Join:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
When used with an Association as its argument, JoinMost will override key-value pairs from the sequence of lists it encounters if any of them have the same key:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
The operator created by JoinMost using an association can accept sequence of associations and will override key-value pairs if and only it encounters any association in the sequence with the same key:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |
If JoinMost has no argument, it operates as an identity on the data it is given:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |
If JoinMost has a sequence of associations as its argument, it will use the last value for a key it confronts in that sequence to perform the override:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
JoinMost can be right-composed with Counts to create an Association that coerces an answer for certain anticipated values:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
JoinMost works similarly to Merge with a Last combiner function:
| In[7]:= | ![With[{data = {"a", "b", "a", "b", "a", "a", "a", "b"}, default = <|"a" -> 0|>}, SameQ[Query[Counts/*ResourceFunction["JoinMost"][default]][data], Merge[{Query[Counts][data], default}, Last]
]
]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/bed/bedc25a1-2dd7-485f-a8c0-118b76c32fe8/05f28ac66632ecea.png) |
| Out[7]= |
JoinMost is very similar to the resource function JoinRest. In JoinMost, its argument is placed last in the Join; in the resource function JoinRest, its argument is placed first in the Join.
JoinMost, like Join, will fail to evaluate if the heads of the expressions to be joined differ from one another:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
Why you should read code carefully before trusting the results:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= | 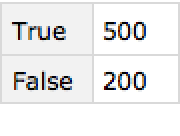 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License