Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Compute the Weingarten matrix of a surface
ResourceFunction["WeingartenMatrix"][s,{u,v}] is the matrix of the shape operator of surface s with respect to variables u and v. |
Define the monkey saddle:
| In[1]:= |
|
| Out[1]= |
|
Compute the Weingarten matrix:
| In[2]:= |
|
| Out[2]= |
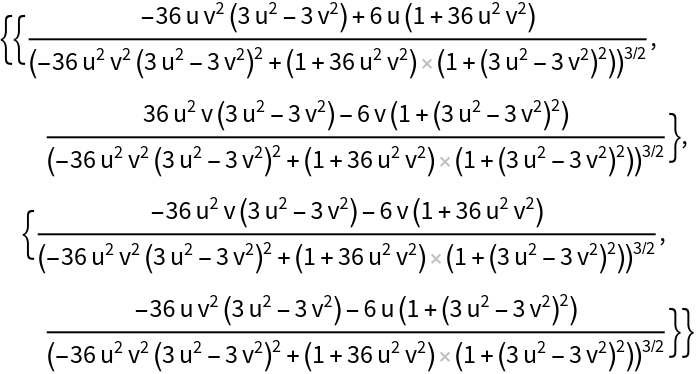
|
A paraboloid:
| In[3]:= |
|
| In[4]:= |
|
The Weingarten matrix can be computed using the shape operator:
| In[5]:= |
|
| Out[5]= |
|
Compute the shape operator of the paraboloid:
| In[6]:= |
|
| Out[6]= |
|
The product with the inverse metric:
| In[7]:= |
|
| Out[7]= |
|
The Weingarten matrix:
| In[8]:= |
|
| Out[8]= |
|
We will be comparing with the derivatives of the unit normals:
| In[9]:= |
|
| Out[9]= |
|
Derivatives of the unit normal:
| In[10]:= |
|
| Out[10]= |
|
The Gaussian and the mean curvature:
| In[11]:= |
|
| Out[11]= |
|
The Gaussian and mean curvatures can be computed from the Weingarten matrix. The Gaussian curvature is equal to the determinant of the Weingarten matrix:
| In[12]:= |
|
| Out[12]= |
|
The mean curvature is equal to half the trace of the Weingarten matrix:
| In[13]:= |
|
| Out[13]= |
|
| In[14]:= |
|
| Out[14]= |
|
The principal curvatures are minus the eigenvalues of the Weingarten matrix:
| In[15]:= |
|
| Out[15]= |
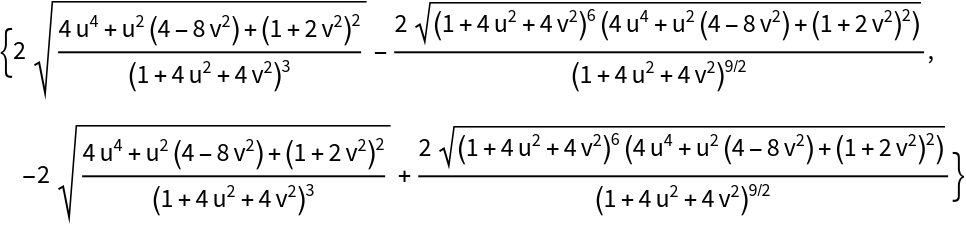
|
| In[16]:= |
|
| Out[16]= |
|
A Monge patch:
| In[17]:= |
|
The Weingarten matrix:
| In[18]:= |
|
| Out[18]= |
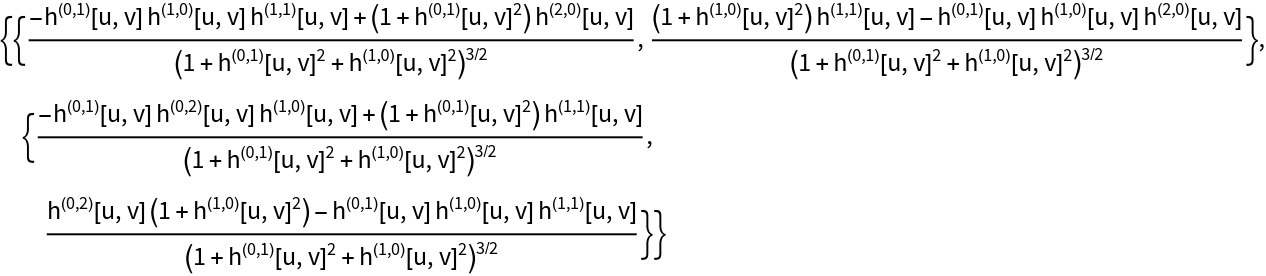
|
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License