Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Convert all nth roots in an expression, where n is an odd integer, to their real-valued nth roots
ResourceFunction["UseRealRoots"][expr] converts all nth roots in expr, where n is an odd integer, to their real-valued nth roots. Otherwise, it uses the principal roots in expr. |
UseRealRoots converts an odd integer root in an expression to an expression using Surd:
| In[1]:= |
|
| Out[1]= |
|
Unlike Surd, UseRealRoots evaluates even roots of negative real numbers:
| In[2]:= |
|
| Out[2]= |
|
| In[3]:= |
|
| Out[3]= |
|
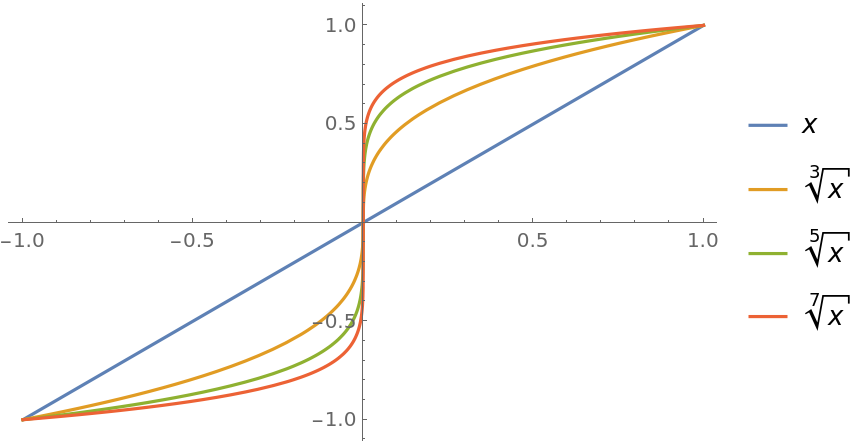
Plot over a subset of the reals (compare this with the corresponding example on the Surd documentation page):
| In[4]:= |
|
| Out[4]= |
|
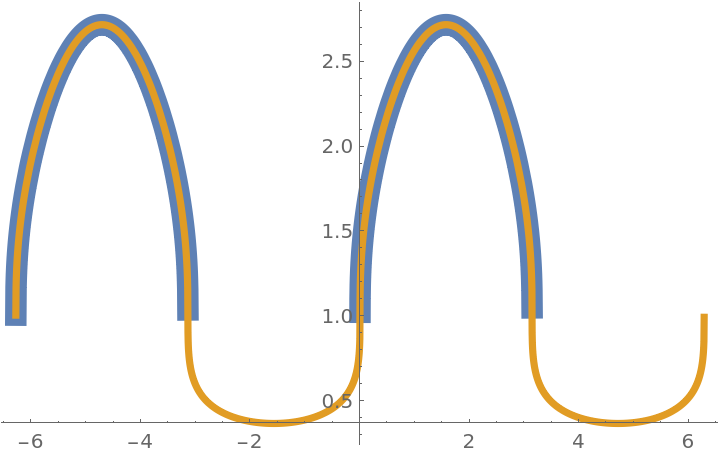
Compare a plot of the function f(x) with UseRealRoots[f(x)]:
| In[5]:= |
![Plot[{Exp[Sin[x]^(1/3)], ResourceFunction["UseRealRoots"][Exp[Sin[x]^(1/3)]]}, {x, -2 \[Pi], 2 \[Pi]}, PlotStyle -> {Thickness[.03], Thickness[.01]}, PlotRange -> All]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/8ff/8ffbc520-7f28-43ea-a317-304d8c65cc12/6ae63471447bc8a9.png)
|
| Out[5]= |
|
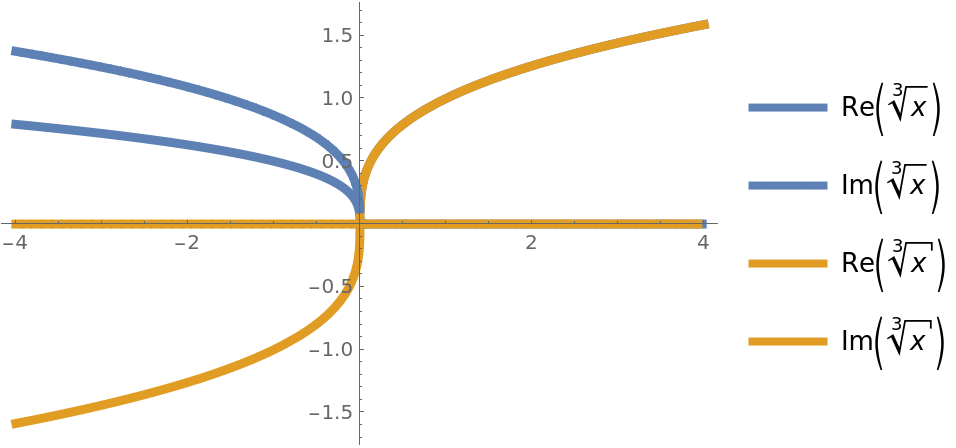
Compare the real and imaginary parts of ![]() and UseRealRoots[
and UseRealRoots[![]() ] over the reals (compare this with the corresponding example on the Surd documentation page):
] over the reals (compare this with the corresponding example on the Surd documentation page):
| In[6]:= |
![ReImPlot[{Power[x, (3)^-1], ResourceFunction["UseRealRoots"][Power[x, (3)^-1]]} // Evaluate, {x, -4, 4}, PlotStyle -> Thickness[.0125], PlotLegends -> Automatic]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/8ff/8ffbc520-7f28-43ea-a317-304d8c65cc12/01903f9dc3b485bd.png)
|
| Out[6]= |
|
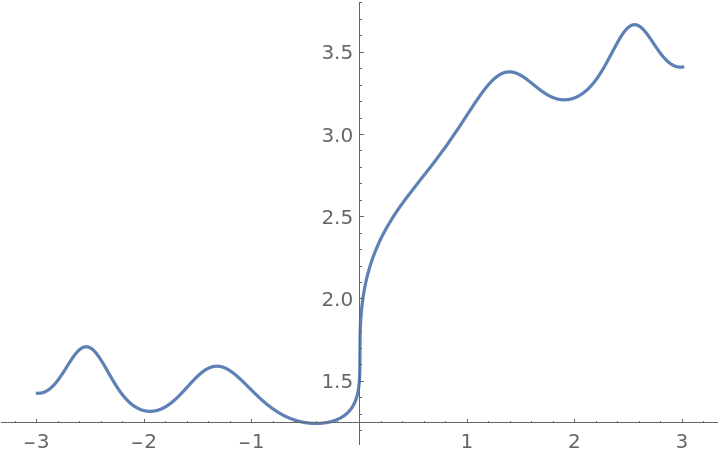
EnhancedPlot automatically incorporates UseRealRoots:
| In[7]:= |
|
| Out[7]= |
|
Compare with Plot:
| In[8]:= |
|
| Out[8]= |
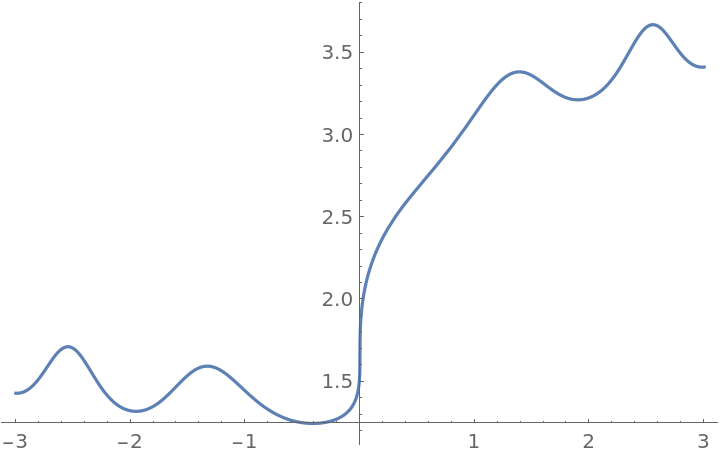
|
UseRealRoots can be used on any expression and it threads elementwise over lists and matrices:
| In[9]:= |
|
| Out[9]= |
|
| In[10]:= |
|
| Out[10]= |
|
| In[11]:= |
|
| Out[11]= |
|
Use UseRealRoots with FindRoot:
| In[12]:= |
|
| Out[12]= |
|
Check:
| In[13]:= |
|
| Out[13]= |
|
UseRealRoots[x1/n] and Surd[x,n] are both defined for all real values when n is an odd positive integer:
| In[14]:= |
|
| Out[14]= |
|
Compare with Power:
| In[15]:= |
|
| Out[15]= |
|
For positive even integers n, UseRealRoots[x1/n] and Surd[x,n] are both real-valued for non-negative x:
| In[16]:= |
|
| Out[16]= |
|
For negative n, UseRealRoots[x1/n] and Surd[x,n] are both defined for all positive x:
| In[17]:= |
|
| Out[17]= |
|
UseRealRoots[x1/n] and Surd[x,n] both assume all real values when n is an odd positive integer:
| In[18]:= |
|
| Out[18]= |
|
For positive even integers n, the range of both UseRealRoots[x1/n] and Surd[x,n] is the set of non-negative real numbers:
| In[19]:= |
|
| Out[19]= |
|
For negative odd n, 0 is removed from the range:
| In[20]:= |
|
| Out[20]= |
|
The first derivative with respect to x:
| In[21]:= |
|
| Out[21]= |
|
Higher derivatives of an even root with respect to x using UseRealRoots:
| In[22]:= |
|
| Out[22]= |
|
Higher derivatives of an odd root with respect to x using UseRealRoots:
| In[23]:= |
|
| Out[23]= |
|
Using Surd:
| In[24]:= |
|
| Out[24]= |
|
Plot the higher derivatives computed using UseRealRoots:
| In[25]:= |
|
| Out[25]= |
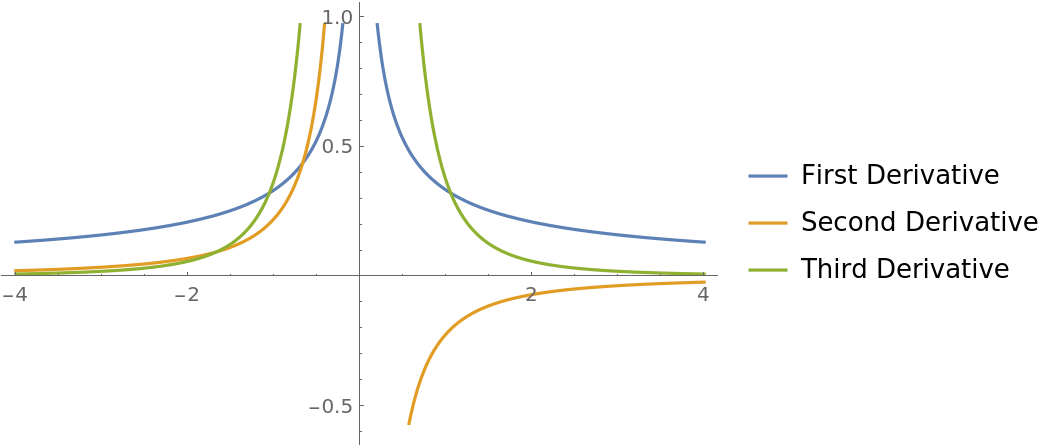
|
Plot the higher derivatives computed using Surd:
| In[26]:= |
|
| Out[26]= |
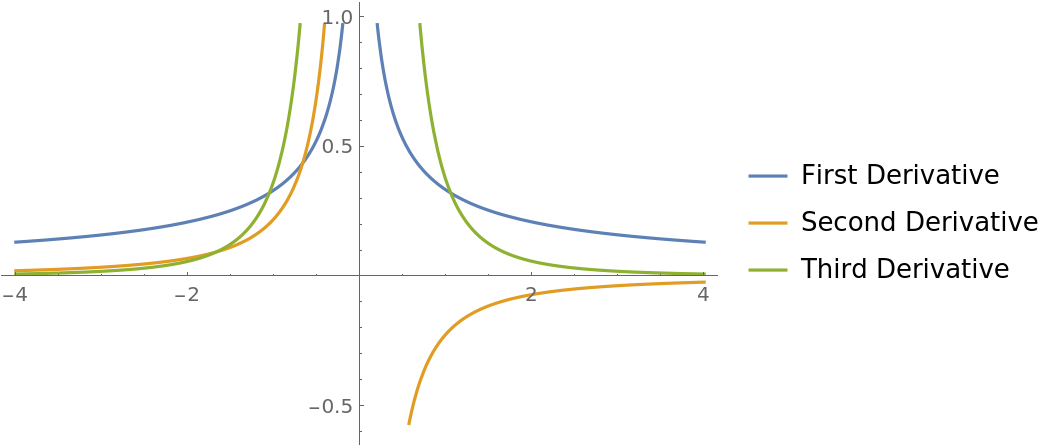
|
Compute the indefinite integral:
| In[27]:= |
|
| Out[27]= |
|
Verify by differentiating:
| In[28]:= |
|
| Out[28]= |
|
Definite integral:
| In[29]:= |
|
| Out[29]= |
|
An improper integral:
| In[30]:= |
|
| Out[30]= |
|
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License