Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Represent a stress-energy tensor (field) over a Riemannian or pseudo-Riemannian manifold
ResourceFunction["StressEnergyTensor"]["name",…] represents a named stress-energy tensor "name". | |
ResourceFunction["StressEnergyTensor"][{"name",…},…] represents a named parameterized stress-energy tensor "name", with additional parameter(s) specified within a list. | |
ResourceFunction["StressEnergyTensor"][d,…] represents a generic d-dimensional (symmetric) stress-energy tensor. | |
ResourceFunction["StressEnergyTensor"][ResourceFunction["StressEnergyTensor"][…],coords] transforms a specified ResourceFunction["StressEnergyTensor"] into the new coordinate system coords. | |
ResourceFunction["StressEnergyTensor"][ResourceFunction["StressEnergyTensor"][…],i1,i2] transforms a specified ResourceFunction["StressEnergyTensor"] into one with new indices i1 and i2 (with True representing a covariant index and False representing a contravariant one), raising and lowering existing indices as necessary. | |
ResourceFunction["StressEnergyTensor"][ResourceFunction["StressEnergyTensor"][…],coords,i1,i2] transforms a specified ResourceFunction["StressEnergyTensor"] into one with new coordinate system coords and new indices i1 and i2 (with True representing a covariant index and False representing a contravariant one), raising and lowering existing indices as necessary. |
| "Symmetric" | a generic 4-dimensional symmetric stress-energy tensor (whose matrix representation is populated with constants of the form Tij=Tji) |
| {"Symmetric",d} | a generic d-dimensional symmetric stress-energy tensor (whose matrix representation is populated with constants of the form Tij=Tji) |
| "SymmetricField" | a generic 4-dimensional symmetric stress-energy tensor field (whose matrix representation is populated with functions of the chosen spacetime coordinates of the form Tij=Tji) |
| {"SymmetricField",d} | a generic d-dimensional symmetric stress-energy tensor field (whose matrix representation is populated with functions of the chosen spacetime coordinates of the form Tij=Tji) |
| "Asymmetric" | a generic 4-dimensional asymmetric stress-energy tensor (whose matrix representation is populated with constants of the form Tij≠Tji) |
| {"Asymmetric",d} | a generic d-dimensional asymmetric stress-energy tensor (whose matrix representation is populated with constants of the form Tij≠Tji) |
| "AsymmetricField" | a generic 4-dimensional asymmetric stress-energy tensor field (whose matrix representation is populated with functions of the chosen spacetime coordinates of the form Tij≠Tji) |
| {"AsymmetricField",d} | a generic d-dimensional asymmetric stress-energy tensor field (whose matrix representation is populated with functions of the chosen spacetime coordinates of the form Tij≠Tji) |
| "PerfectFluid" | the stress-energy tensor describing a static perfect fluid distribution in thermal equilibrium (i.e. an idealized fluid with no heat conduction, viscosity or shear stresses), with purely symbolic spacetime velocity "u", purely symbolic mass-energy density "" and purely symbolic hydrostatic pressure "P" |
| {"PerfectFluid",uμ} | the stress-energy tensor describing a static perfect fluid distribution in thermal equilibrium (i.e. an idealized fluid with no heat conduction, viscosity or shear stresses), with numerical spacetime velocity uμ, purely symbolic mass-energy density "" and purely symbolic hydrostatic pressure "P" |
| {"PerfectFluid",uμ,ρ} | the stress-energy tensor describing a static perfect fluid distribution in thermal equilibrium (i.e. an idealized fluid with no heat conduction, viscosity or shear stresses), with numerical spacetime velocity uμ, numerical mass-energy density ρ and purely symbolic hydrostatic pressure "P" |
| {"PerfectFluid",uμ,ρ,P} | the stress-energy tensor describing a static perfect fluid distribution in thermal equilibrium (i.e. an idealized fluid with no heat conduction, viscosity or shear stresses), with numerical spacetime velocity uμ, numerical mass-energy density ρ and numerical hydrostatic pressure P |
| "PerfectFluidField" | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic perfect fluid distribution in thermal equilibrium (i.e. an idealized fluid with no heat conduction, viscosity or shear stresses), with purely symbolic spacetime velocity function "u", purely symbolic mass-energy density function "" and purely symbolic hydrostatic pressure function "P" (with all three being functions of the chosen spacetime coordinates) |
| {"PerfectFluidField",uμ} | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic perfect fluid distribution in thermal equilibrium (i.e. an idealized fluid with no heat conduction, viscosity or shear stresses), with numerical spacetime velocity function uμ, purely symbolic mass-energy density function "" and purely symbolic hydrostatic pressure function "P" (with all three being functions of the chosen spacetime coordinates) |
| {"PerfectFluidField",uμ,ρ} | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic perfect fluid distribution in thermal equilibrium (i.e. an idealized fluid with no heat conduction, viscosity or shear stresses), with numerical spacetime velocity function uμ, numerical mass-energy density function ρ and purely symbolic hydrostatic pressure function "P" (with all three being functions of the chosen spacetime coordinates) |
| {"PerfectFluidField",uμ,ρ,P} | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic perfect fluid distribution in thermal equilibrium (i.e. an idealized fluid with no heat conduction, viscosity or shear stresses), with numerical spacetime velocity function uμ, numerical mass-energy density function ρ and numerical hydrostatic pressure function P (with all three being functions of the chosen spacetime coordinates) |
| "Dust" | the stress-energy tensor describing a static distribution of idealized dust particles (i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid with vanishing hydrostatic pressure), with purely symbolic spacetime velocity "u" and purely symbolic mass-energy density "" |
| {"Dust",uμ} | the stress-energy tensor describing a static distribution of idealized dust particles (i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid with vanishing hydrostatic pressure), with numerical spacetime velocity uμ and purely symbolic mass-energy density "" |
| {"Dust",uμ,ρ} | the stress-energy tensor describing a static distribution of idealized dust particles (i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid with vanishing hydrostatic pressure), with numerical spacetime velocity uμ and numerical mass-energy density ρ |
| "DustField" | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic distribution of idealized dust particles (i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid with vanishing hydrostatic pressure), with purely symbolic spacetime velocity function "u" and purely symbolic mass-energy density function "" |
| {"DustField",uμ} | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic distribution of idealized dust particles (i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid with vanishing hydrostatic pressure), with numerical spacetime velocity function uμ and purely symbolic mass-energy density function "" |
| {"DustField",uμ,ρ} | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic distribution of idealized dust particles (i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid with vanishing hydrostatic pressure), with numerical spacetime velocity function uμ and numerical mass-energy density function ρ |
| "Radiation" | the stress-energy tensor describing a static distribution of idealized radiation (i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid whose mass-energy density is equal to the number of spatial dimensions multiplied by the radiation pressure), with purely symbolic spacetime velocity "u" and purely symbolic radiation pressure "P" |
| {"Radiation",uμ} | the stress-energy tensor describing a static distribution of idealized radiation (i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid whose mass-energy density is equal to the number of spatial dimensions multiplied by the radiation pressure), with numerical spacetime velocity uμ and purely symbolic radiation pressure "P" |
| {"Radiation",uμ,P} | the stress-energy tensor describing a static distribution of idealized radiation (i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid whose mass-energy density is equal to the number of spatial dimensions multiplied by the radiation pressure), with numerical spacetime velocity uμ and numerical radiation pressure P |
| "RadiationField" | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic distribution of idealized radiation (i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid whose mass-energy density is equal to the number of spatial dimensions multiplied by the radiation pressure), with purely symbolic spacetime velocity function "u" and purely symbolic radiation pressure function "P" |
| {"RadiationField",uμ} | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic distribution of idealized radiation (i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid whose mass-energy density is equal to the number of spatial dimensions multiplied by the radiation pressure), with numerical spacetime velocity function uμ and purely symbolic radiation pressure function "P" |
| {"RadiationField",uμ,P} | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic distribution of idealized radiation (i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid whose mass-energy density is equal to the number of spatial dimensions multiplied by the radiation pressure), with numerical spacetime velocity function uμ and numerical radiation pressure function P |
| "ElectromagneticField" | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic, source-free electromagnetic field, with purely symbolic spacetime electromagnetic potential "A" (combining both the symbolic electric scalar potential “" and the symbolic magnetic vector potential "Ai") and purely symbolic vacuum magnetic permeability constant "0" |
| {"ElectromagneticField",Aμ} | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic, source-free electromagnetic field, with numerical spacetime electromagnetic potential Aμ (combining both the numerical electric scalar potential Φ and the numerical magnetic vector potential Ai) and purely symbolic vacuum magnetic permeability constant "0" |
| {"ElectromagneticField",Aμ,μ0} | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic, source-free electromagnetic field, with numerical spacetime electromagnetic potential Aμ (combining both the numerical electric scalar potential Φ and the numerical magnetic vector potential Ai) and numerical vacuum magnetic permeability constant μ0 |
| "MassiveScalarField" | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic, complex scalar field satisfying the massive Klein-Gordon equation, with purely symbolic mass "m" and purely symbolic scalar function "" |
| {"MassiveScalarField",m} | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic, complex scalar field satisfying the massive Klein-Gordon equation, with numerical mass m and purely symbolic scalar function "" |
| {"MassiveScalarField",m,ψ} | the stress-energy tensor field describing a dynamic, complex scalar field satisfying the massive Klein-Gordon equation, with numerical mass m and numerical scalar function ψ |
| "MatrixRepresentation" | stress-energy tensor represented in explicit matrix form |
| "ReducedMatrixRepresentation" | stress-energy tensor represented in explicit matrix form, modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "Trace" | trace of the stress-energy tensor |
| "ReducedTrace" | trace of the stress-energy tensor, modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "MetricTensor" | underlying metric tensor associated to the stress-energy tensor |
| "Coordinates" | list of coordinate symbols for the stress-energy tensor |
| "CoordinateOneForms" | list of differential 1-form symbols for the coordinates of the stress-energy tensor |
| "Indices" | list of booleans specifying whether each index of the stress-energy tensor is lowered/covariant (True) or raised/contravariant (False) |
| "CovariantQ" | whether the stress-energy tensor is covariant (i.e. both indices are lowered/covariant) |
| "ContravariantQ" | whether the stress-energy tensor is contravariant (i.e. both indices are raised/contravariant) |
| "MixedQ" | whether the stress-energy tensor is mixed (i.e. one index is lowered/covariant and one index is raised/contravariant) |
| "Symbol" | symbolic representation of the stress-energy tensor with approriately raised/lowered indices |
| "EnergyDensity" | relativistic mass-energy density (i.e. the time-time component of the stress-energy tensor in contravariant/raised-index form) |
| "ReducedEnergyDensity" | relativistic mass-energy density (i.e. the time-time component of the stress-energy tensor in contravariant/raised-index form), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "MomentumDensity" | relativistic spatial momentum density (i.e. the time-space/space-time components of the stress-energy tensor in contravariant/raised-index form) |
| "ReducedMomentumDensity" | relativistic spatial momentum density (i.e. the time-space/space-time components of the stress-energy tensor in contravariant/raised-index form), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "SpacetimeMomentumDensity" | relativistic spacetime momentum density (i.e. the time-time component plus the time-space/space-time components of the stress energy tensor in contravariant/raised-index form) |
| "ReducedSpacetimeMomentumDensity" | relativistic spacetime momentum density (i.e. the time-time component plus the time-space/space-time components of the stress-energy tensor in contravariant/raised-index form), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "Pressure" | relativistic pressure (i.e. the directional average of the trace part of the space-space components of the stress-energy tensor in contravariant/raised-index form) |
| "ReducedPressure" | relativistic pressure (i.e. the directional average of the trace part of the space-space components of the stress-energy tensor in contravariant/raised-index form), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "StressTensor" | relativistic Cauchy stress tensor (i.e. the space-space components of the stress-energy tensor in contravariant/raised-index form) |
| "ReducedStressTensor" | relativistic Cauchy stress tensor (i.e. the space-space components of the stress-energy tensor in contravariant/raised-index form), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "ShearStressTensor" | relativistic shear stress tensor (i.e. the trace-free part of the space-space components of the stress-energy tensor in contravariant/raised-index form) |
| "ReducedShearStressTensor" | relativistic shear stress tensor (i.e. the trace-free part of the space-space components of the stress-energy tensor in contravariant/raised-index form), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "CovariantDerivatives" | association of covariant derivatives (i.e. derivatives along tangent vectors of the underlying manifold) of the stress-energy tensor |
| "ReducedCovariantDerivatives" | association of covariant derviatives (i.e. derivatives along tangent vectors of the underlying manifold) of the stress-energy tensor, modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "SymbolicCovariantDerivatives" | association of covariant derivatives (i.e. derivatives along tangent vectors of the underlying manifold) of the stress-energy tensor, with purely symbolic partial derivative operators |
| "ContinuityEquations" | list of continuity equations asserting that the covariant divergence of the stress-energy tensor vanishes (i.e. energy and momentum are conserved) |
| "ReducedContinuityEquations" | list of continuity equations asserting that the covariant divergence of the stress-energy tensor vanishes (i.e. energy and momentum are conserved), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "SymbolicContinuityEquations" | list of continuity equations asserting that the covariant divergence of the stress-energy tensor vanishes (i.e. energy and momentum are conserved), with purely symbolic partial derivative operators |
| "Dimensions" | number of dimensions of the underlying manifold/spacetime associated to the stress-energy tensor |
| "SymmetricQ" | whether the stress-energy tensor is symmetric (i.e. is represented by a symmetric matrix in contravariant form) |
| "DiagonalQ" | whether the stress-energy tensor is diagonal (i.e. is represented by a diagonal matrix in contravariant form) |
| "Signature" | list of +1s and -1s designating the signature of the underlying manifold described by the stress-energy tensor (+1 for each positive eigenvalue of the metric, -1 for each negative eigenvalue of the metric) |
| "RiemannianQ" | whether the underlying manifold described by the stress-energy tensor is Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues of the metric have the same sign) |
| "PseudoRiemannianQ" | whether the underlying manifold described by the stress-energy tensor is pseudo-Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues of the metric are non-zero, but not all have the same sign) |
| "LorentzianQ" | whether the underlying manifold described by the stress-energy tensor is Lorentzian (i.e. all eigenvalues of the metric have the same sign, except for one eigenvalue which has the opposite sign) |
| "RiemannianConditions" | list of conditions required to guarantee that the underlying manifold described by the stress-energy tensor is Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues of the metric are positive) |
| "PseudoRiemannianConditions" | list of conditions required to guarantee that the underlying manifold described by the stress-energy tensor is pseudo-Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues of the metric are non-zero) |
| "LorentzianConditions" | list of conditions required to guarantee that the underlying manifold described by the stress-energy tensor is Lorentzian (i.e. the "time" eigenvalue of the metric is negative and all other eigenvalues are positive) |
| "StressEnergySingularities" | list of possible coordinate values that cause the stress-energy tensor (in contravariant/raised-index form) to become singular |
| "TraceSingularities" | list of possible coordinate values that cause the trace of the stress-energy tensor to become singular |
| "Determinant" | determinant of the stress-energy tensor (represented in contravariant matrix form) |
| "ReducedDeterminant" | determinant of the stress-energy tensor (represented in contravariant matrix form), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "Eigenvalues" | eigenvalues of the stress-energy tensor (represented in contravariant matrix form) |
| "ReducedEigenvalues" | eigenvalues of the stress-energy tensor (represented in contravariant matrix form), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "Eigenvectors" | eigenvectors of the stress-energy tensor (represented in contravariant matrix form) |
| "ReducedEigenvectors" | eigenvectors of the stress-energy tensor (represented in contravariant matrix form), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "CovariantStressEnergyTensor" | covariant form of the stress-energy tensor (i.e. both indices are lowered/covariant) |
| "ContravariantStressEnergyTensor" | contravariant form of the stress-energy tensor (i.e. both indices are raised/contravariant) |
| "NullEnergyCondition" | null energy condition for the stress-energy tensor (i.e. the condition that all observers following a future-pointing, null vector field always observe a non-negative mass-energy density) |
| "ReducedNullEnergyCondition" | null energy condition for the stress-energy tensor (i.e. the condition that all observers following a future-pointing, null vector field always observe a non-negative mass-energy density), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "WeakEnergyCondition" | weak energy condition for the stress-energy tensor (i.e. the condition that all observers following a timelike vector field always observe a non-negative mass-energy density) |
| "ReducedWeakEnergyCondition" | weak energy condition for the stress-energy tensor (i.e. the condition that all observers following a timelike vector field always observe a non-negative mass-energy density), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "DominantEnergyCondition" | dominant energy condition for the stress-energy tensor (i.e. the condition that, in addition to the weak energy condition, all observers following a future-pointing, causal vector field always observe mass-energy to be flowing no faster than light) |
| "ReducedDominantEnergyCondition" | dominant energy condition for the stress-energy tensor (i.e. the condition that, in addition to the weak energy condition, all observers following a future-pointing, causal vector field always observe mass-energy to be flowing no faster than light), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "StrongEnergyCondition" | strong energy condition for the stress-energy tensor (i.e. the condition that all observers following a timelike vector field always observe the tidal tensor/electrogravitic tensor to have a non-negative trace) |
| "ReducedStrongEnergyCondition" | strong energy condition for the stress-energy tensor (i.e. the condition that all observers following a timelike vector field always observe the tidal tensor/electrogravitic tensor to have a non-negative trace), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "Properties" | list of properties |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic fluid (with symbolic 4-velocity "u", symbolic density "" and symbolic pressure "P") in the default 4-dimensional flat/Minkowski spacetime:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 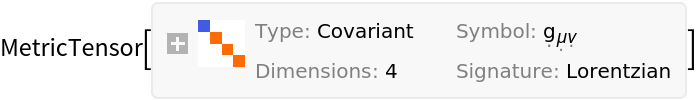 |
Show the stress-energy tensor for a perfect relativistic fluid in 4-dimensional Minkowski space in explicit (contravariant) matrix form:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= | 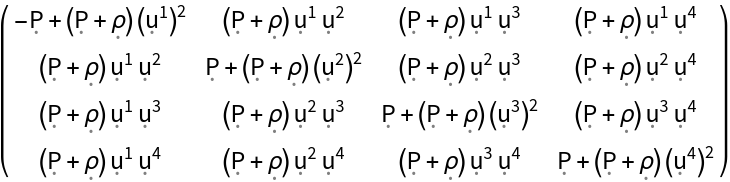 |
Show the covariant matrix form instead:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= | 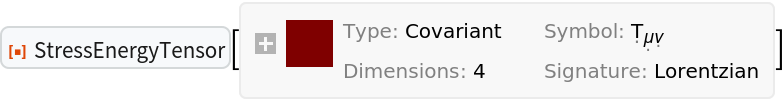 |
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= | 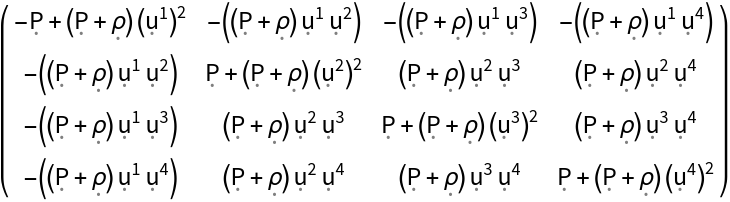 |
Show the mass-energy density of a perfect relativistic fluid in 4-dimensional Minkowski space:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
Show the pressure of a perfect relativistic fluid in 4-dimensional Minkowski space:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |
Show the pressure of a perfect relativistic fluid in 4-dimensional Minkowski space, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for the same perfect and static relativistic fluid in the Schwarzschild geometry (e.g. for an uncharged, non-rotating black hole with symbolic mass "M") in standard spherical polar coordinates, and with both indices lowered/covariant:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |  |
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |  |
Show the explicit (covariant) matrix form:
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= | 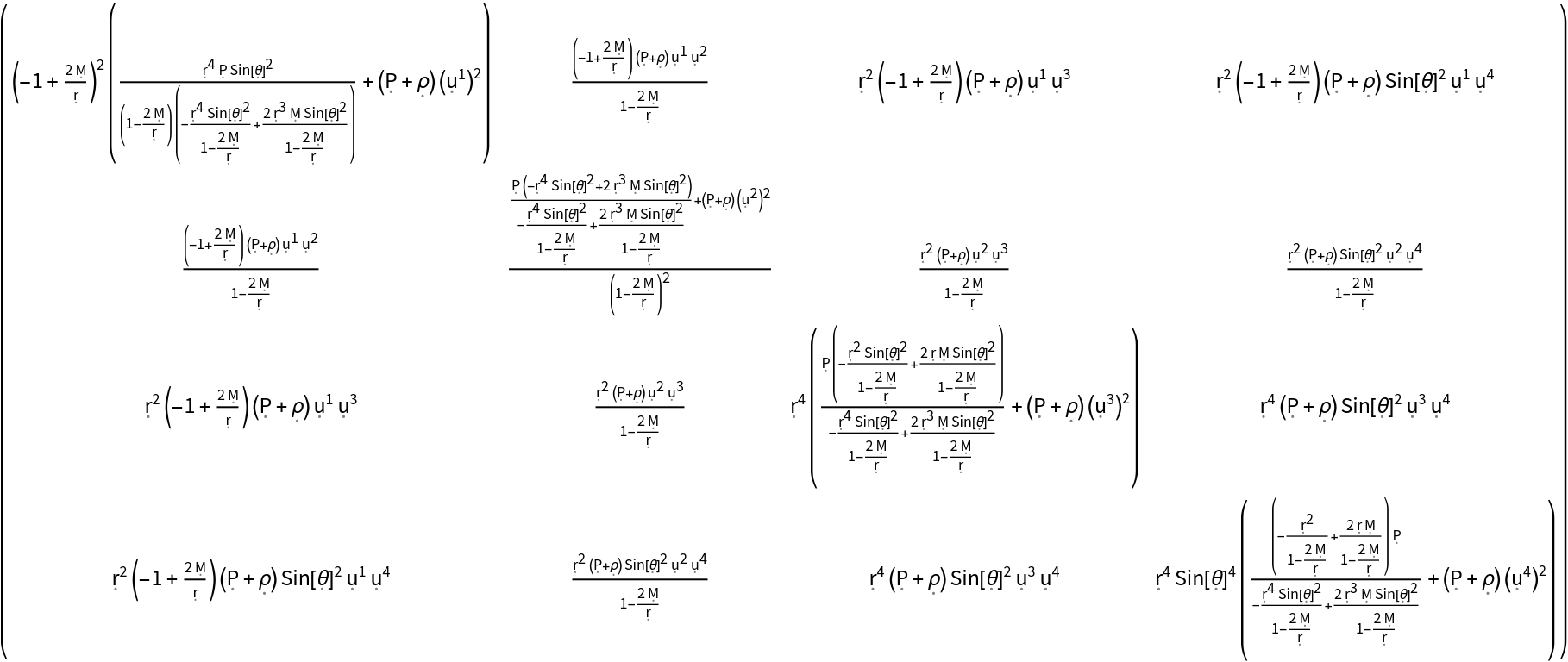 |
Show the explicit (covariant) matrix form, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= | 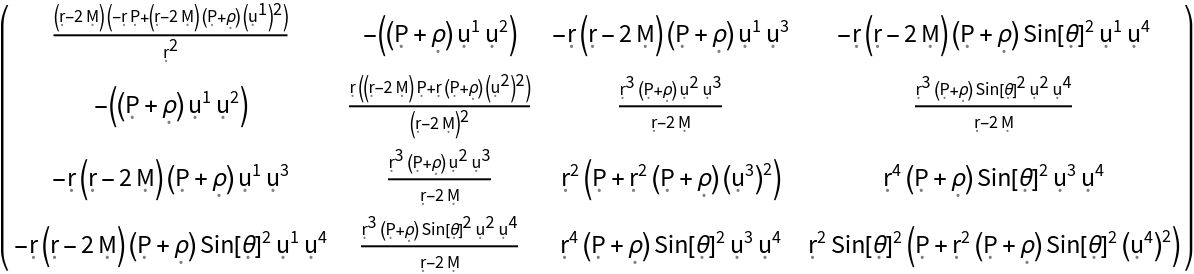 |
Show the mass-energy density and pressure of a perfect relativistic fluid in the Schwarzschild geometry, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |
| In[14]:= |
| Out[14]= |
Show the momentum density, Cauchy stress tensor and shear stress tensor of a perfect relativistic fluid in the Schwarzschild geometry, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= |
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= | 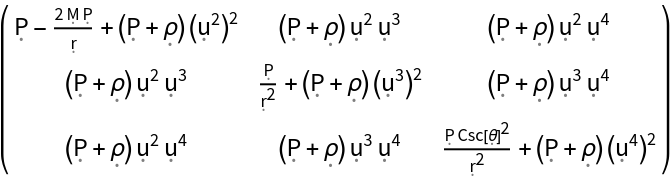 |
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= | 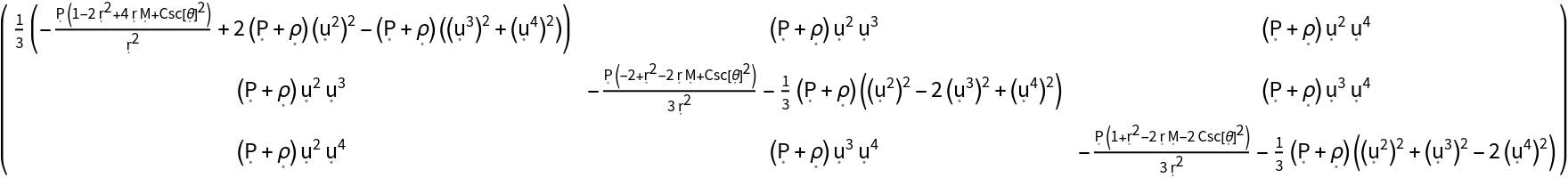 |
Show the null energy condition for a perfect relativistic fluid in the Schwarzschild geometry:
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= | 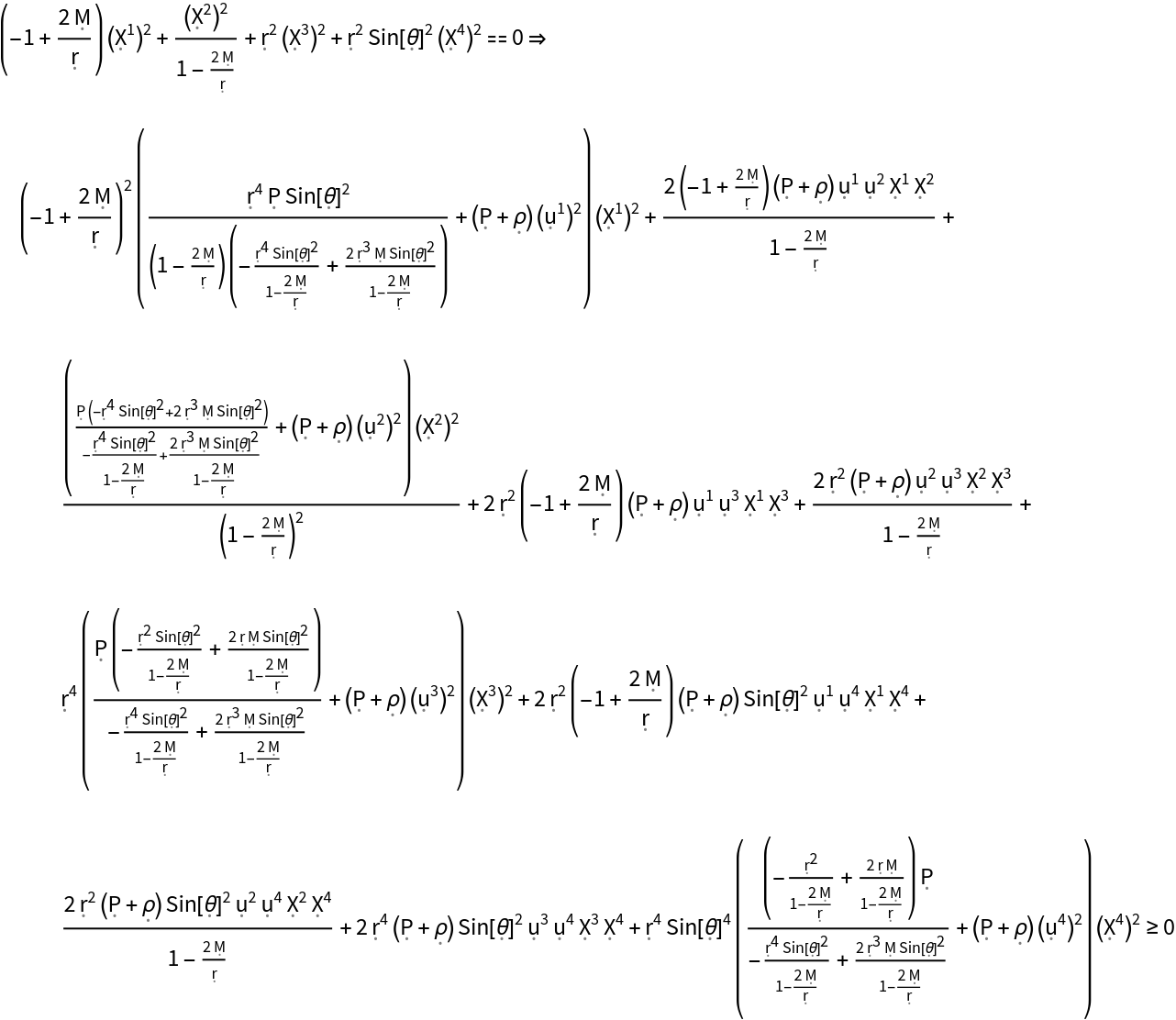 |
Show the null energy condition with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[19]:= |
| Out[19]= | 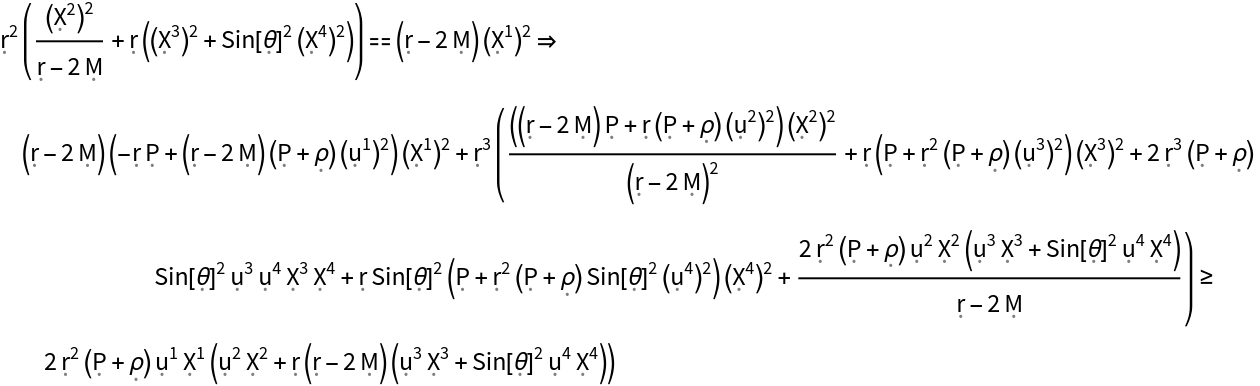 |
Show the weak energy condition for a perfect relativistic fluid in the Schwarzschild geometry:
| In[20]:= |
| Out[20]= | 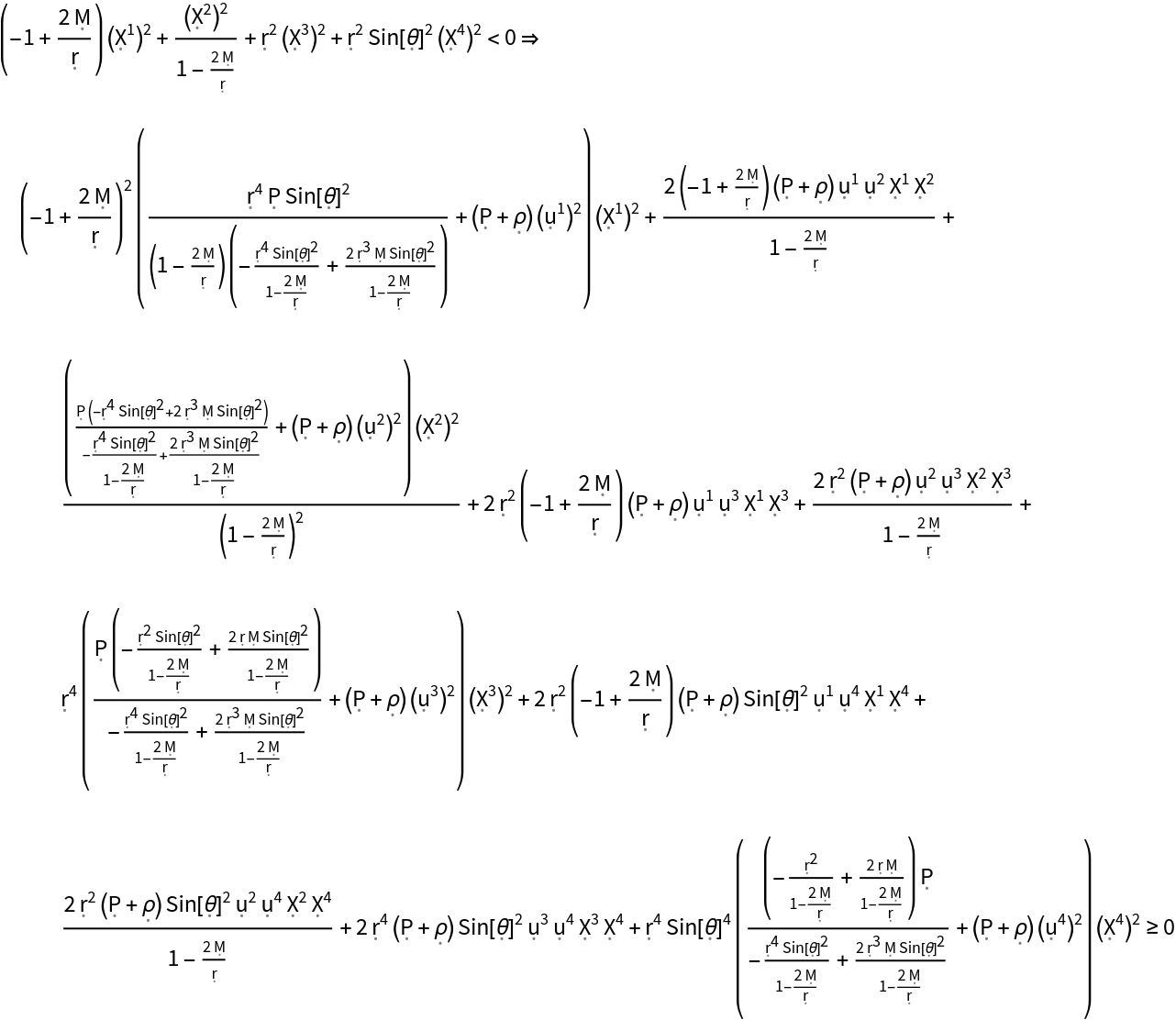 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic fluid in the same Schwarzschild geometry as above, but with numerical 4-velocity {-1,0,0,0}, numerical density 1/2 and numerical pressure 1/3:
| In[21]:= |
| Out[21]= |
| In[22]:= |
| Out[22]= | 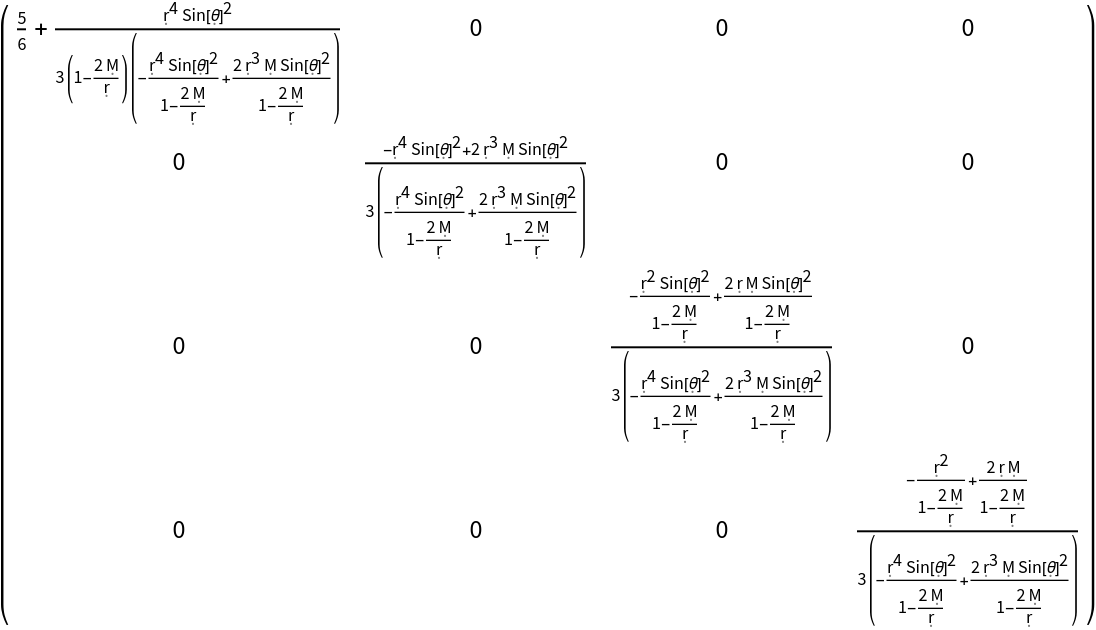 |
| In[23]:= |
| Out[23]= | 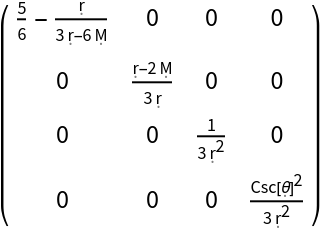 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a perfect and dynamic relativistic fluid (with symbolic 4-velocity function "u", symbolic density function "" and symbolic pressure function "P") in the same Schwarzschild geometry as above:
| In[24]:= |
| Out[24]= |
| In[25]:= |
| Out[25]= | 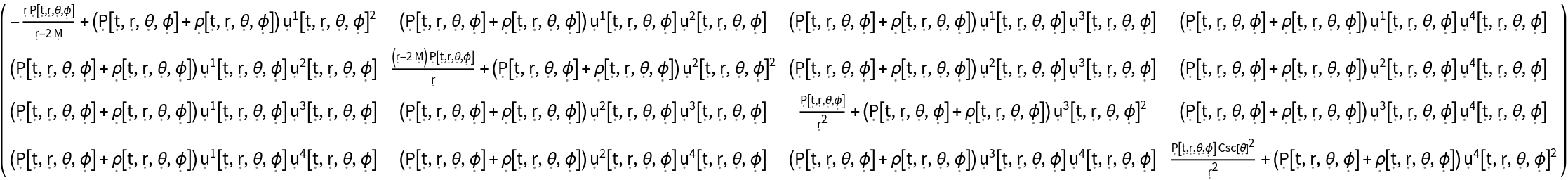 |
Show the association of all covariant derivatives of the stress-energy tensor field for a perfect and dynamic relativistic fluid in the Schwarzschild geometry:
| In[26]:= |
| Out[26]= | 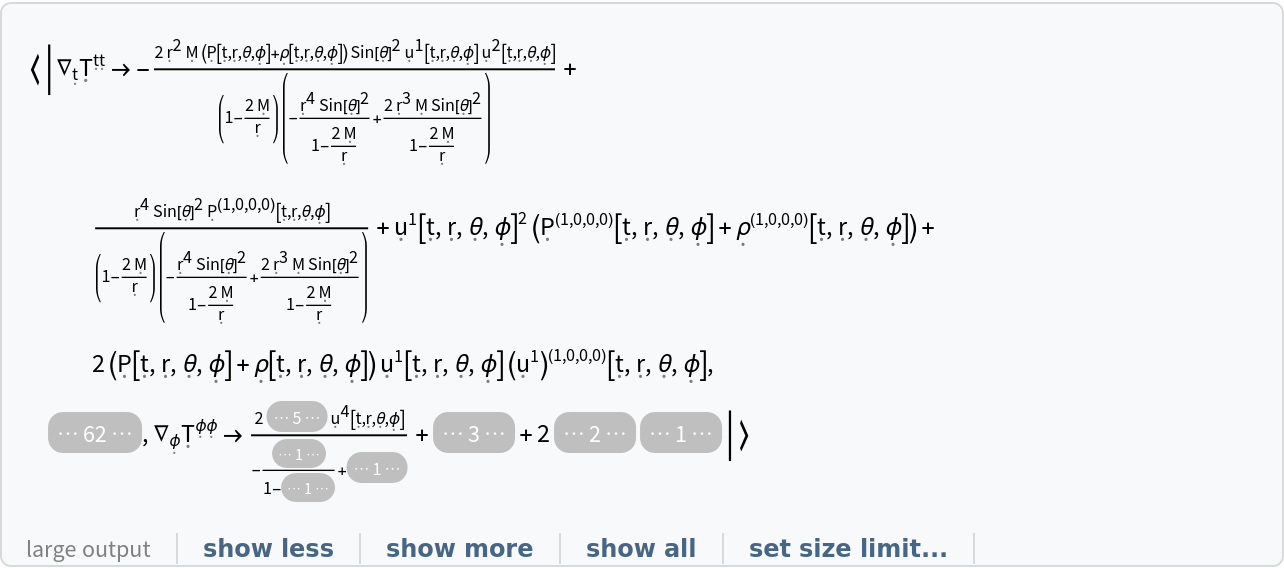 |
Show the association of all covariant derivatives, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[27]:= |
| Out[27]= |  |
Show the association of all covariant derivatives of the stress-energy tensor in covariant form instead, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[28]:= |
| Out[28]= | 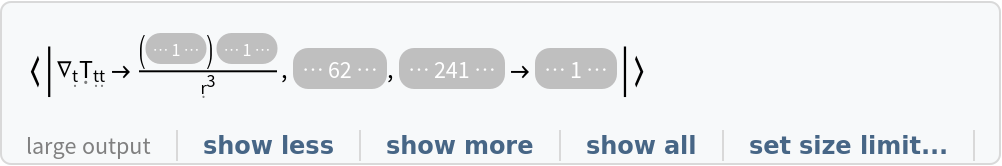 |
Show the list of all continuity equations for the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and dynamic relativistic fluid in the Schwarzschild geometry, asserting that energy and momentum are conserved (i.e. the covariant divergence of the stress-energy tensor vanishes), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[29]:= |
| Out[29]= | 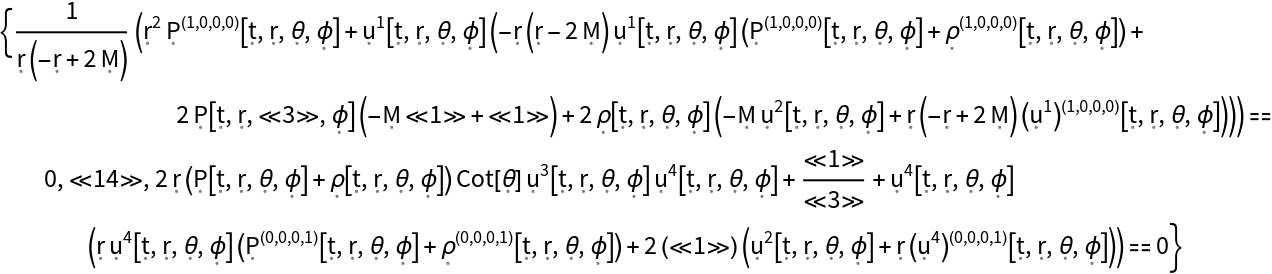 |
Construct stress-energy tensors for a static relativistic dust (i.e. a static perfect fluid with vanishing pressure) and a static relativistic radiation distribution (i.e. a static perfect fluid whose density is equal to three times its pressure) in the default 4-dimensional flat/Minkowski spacetime:
| In[30]:= |
| Out[30]= |
| In[31]:= |
| Out[31]= | 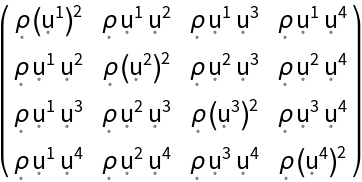 |
| In[32]:= |
| Out[32]= |
| In[33]:= |
| Out[33]= | 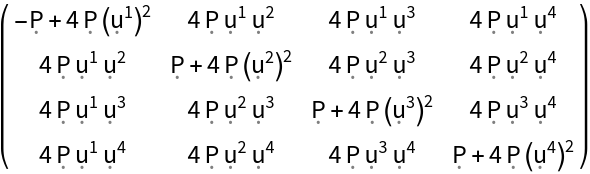 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a dynamic, source-free electromagnetic field (with purely symbolic spacetime electromagnetic potential "A" and purely symbolic vacuum magnetic permeability constant "0") in the default 4-dimensional flat/Minkowski spacetime:
| In[34]:= |
| Out[34]= |
| In[35]:= |
| Out[35]= | 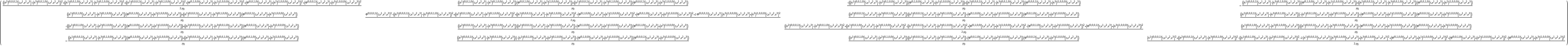 |
Show the list of all continuity equations for the stress-energy tensor for a dynamic, source-free electromagnetic field in 4-dimensional Minkowski space (i.e. special relativistic Maxwell equations), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[36]:= |
| Out[36]= | 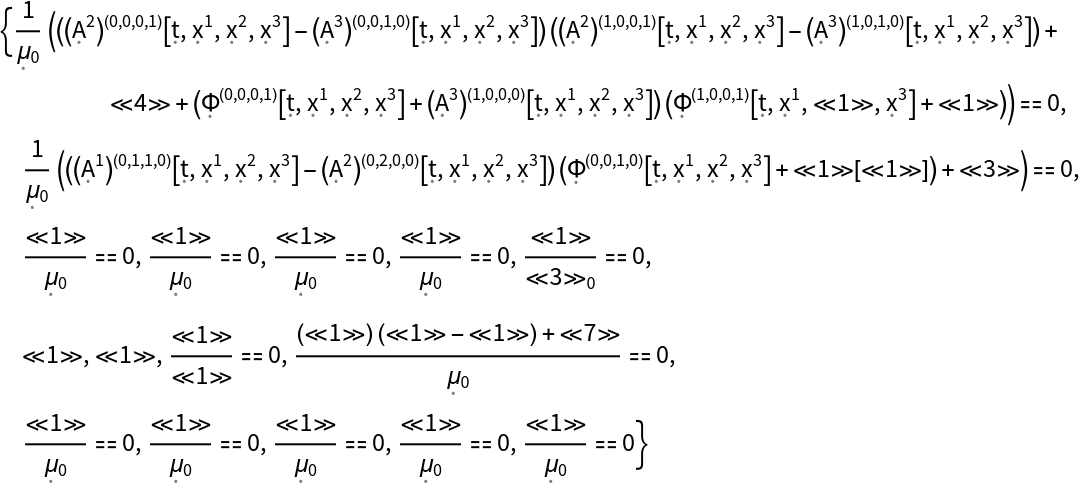 |
Show that the stress-energy tensor for a dynamic, source-free electromagnetic field in 4-dimensional Minkowski space has a vanishing trace:
| In[37]:= |
| Out[37]= |
Show the pressure and the stress tensor of a dynamic, source-free electromagnetic field in 4-dimensional Minkowski space (i.e. the magnetic pressure and the Maxwell stress tensor, respectively), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[38]:= |
| Out[38]= | 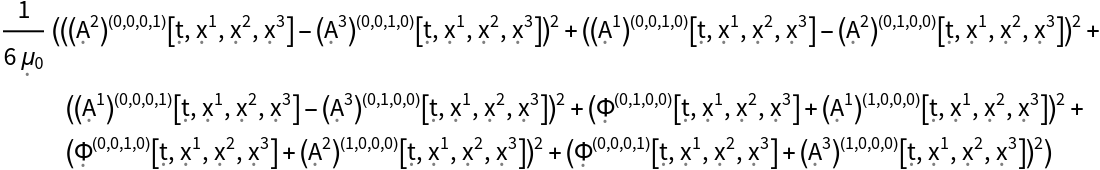 |
| In[39]:= |
| Out[39]= | 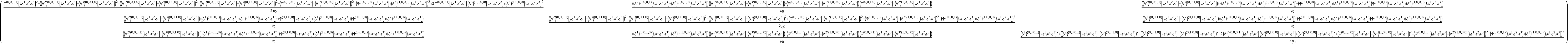 |
Show the momentum density of a dynamic, source free-electromagnetic field in 4-dimensional Minkowski space (i.e. the Poynting vector), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[40]:= |
| Out[40]= | 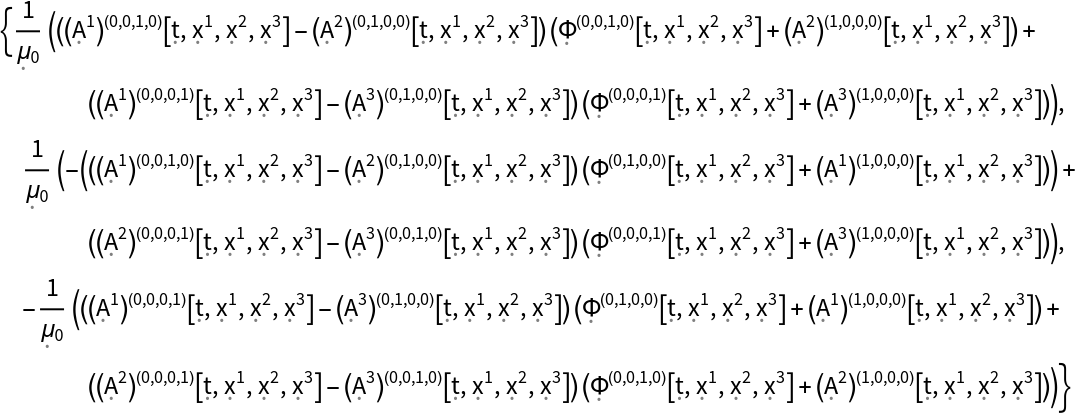 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for the same dynamic, source-free electromagnetic field in the Reissner-Nordström geometry (e.g. for a charged, non-rotating black hole with symbolic mass "M" and symbolic electric charge "Q") in standard spherical polar coordinates:
| In[41]:= |
| Out[41]= | 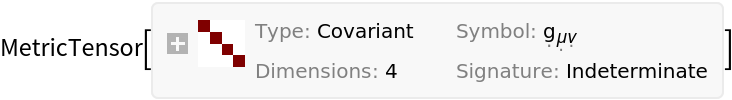 |
| In[42]:= |
| Out[42]= |
| In[43]:= |
| Out[43]= | 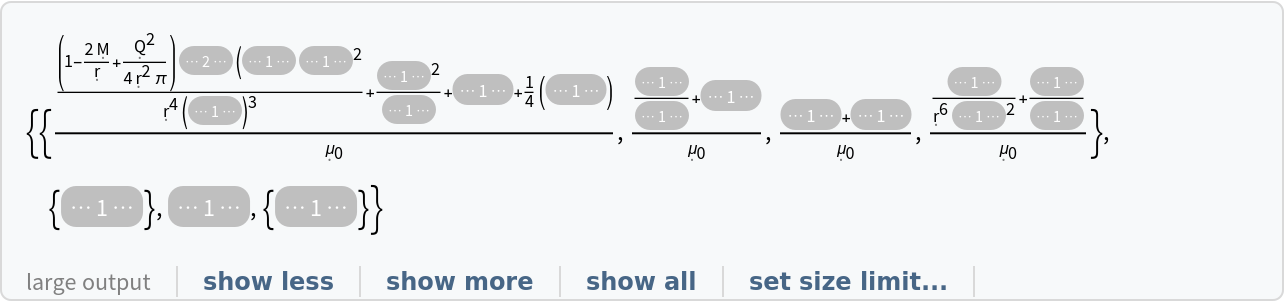 |
Show that the electromagnetic stress-energy tensor for the Reissner-Nordström geometry is still trace-free:
| In[44]:= |
| Out[44]= |
Show the list of continuity equations for the stress-energy tensor for a dynamic, source-free electromagnetic field in the Reissner-Nordström geometry (i.e. general relativistic Maxwell equations):
| In[45]:= |
| Out[45]= | 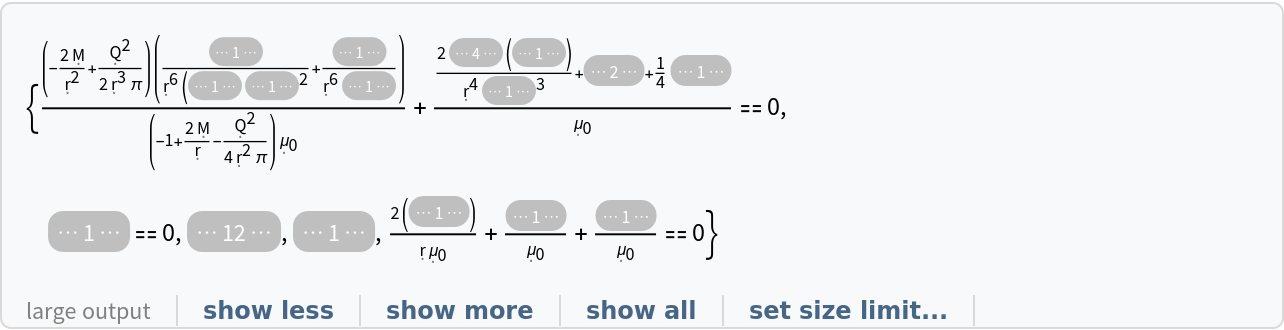 |
Show the mass-energy density of a dynamic, source-free electromagnetic field in the Reissner-Nordström geometry:
| In[46]:= |
| Out[46]= | 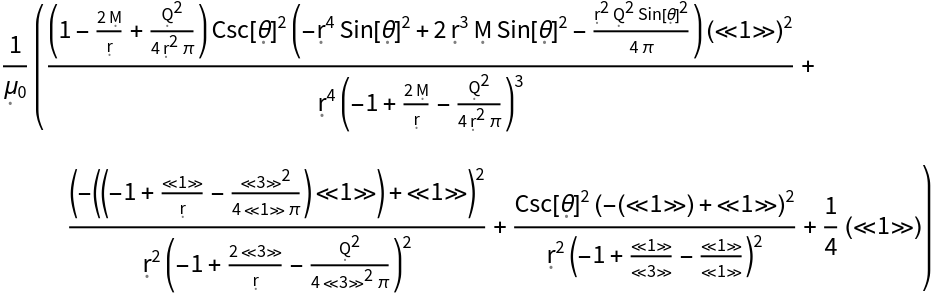 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a dynamic, complex scalar field obeying the massive Klein-Gordon equation (with purely symbolic mass "m" and purely symbolic scalar function "") in the default 4-dimensional flat/Minkowski spacetime, and with both indices lowered/covariant:
| In[47]:= |
| Out[47]= |  |
| In[48]:= |
| Out[48]= |  |
Extract the time-time component of the stress-energy tensor for a dynamic, complex scalar field obeying the massive Klein-Gordon equation in 4-dimensional Minkowski space:
| In[49]:= |
| Out[49]= | 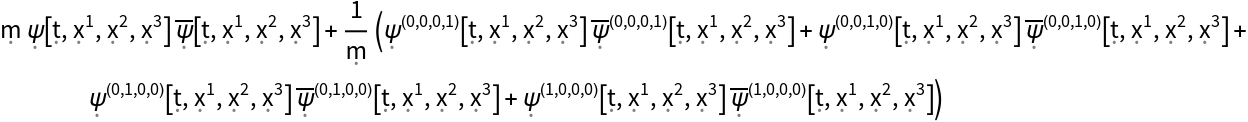 |
Extract the first row of the stress-energy tensor for a dynamic, complex scalar field obeying the massive Klein-Gordon equation in 4-dimensional Minkowski space:
| In[50]:= |
| Out[50]= | 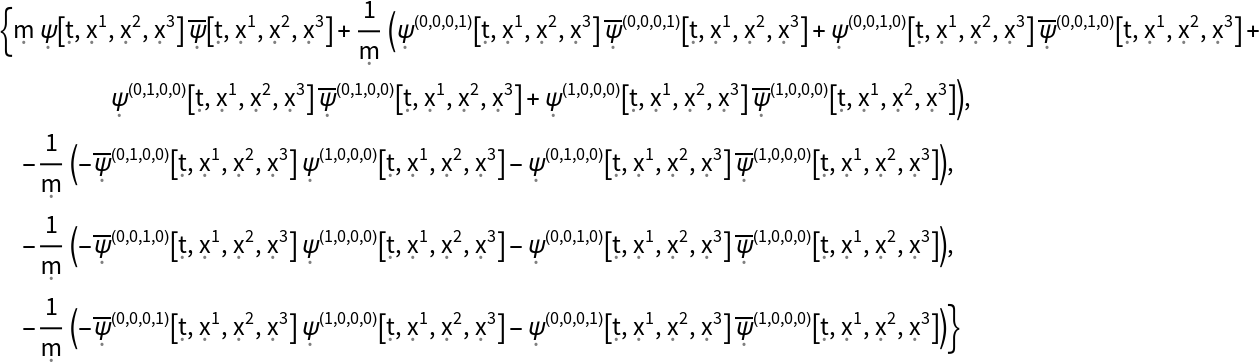 |
Extract the first column of the stress-energy tensor for a dynamic, complex scalar field obeying the massive Klein-Gordon equation in 4-dimensional Minkowski space:
| In[51]:= |
| Out[51]= | 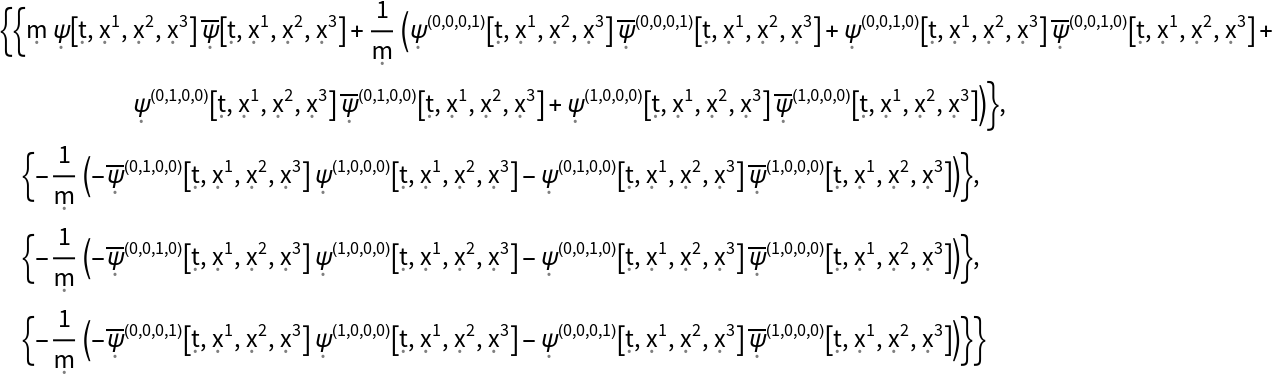 |
Transform to use the new coordinate symbols T, x, y and z:
| In[52]:= |
| Out[52]= |  |
| In[53]:= |
| Out[53]= | 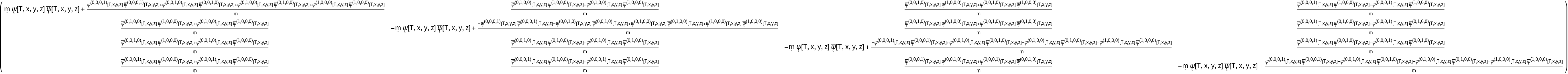 |
Transform to use the new coordinate symbols T, x, y and z, and raise one index, simultaneously:
| In[54]:= |
| Out[54]= | 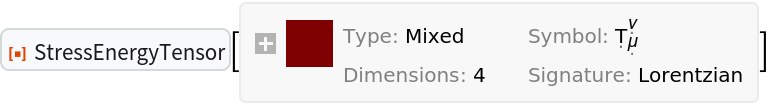 |
| In[55]:= |
| Out[55]= | 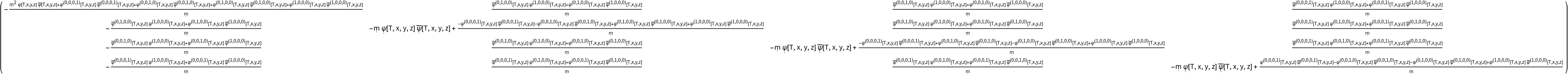 |
Stress-energy tensors can be constructed directly from a matrix representation:
| In[56]:= |
| Out[56]= |
| In[57]:= |
| Out[57]= |
Additional arguments can be used to specify the underlying metric tensor (otherwise the flat spacetime/Minkowski metric will be chosen automatically):
| In[58]:= |
| Out[58]= |
| In[59]:= |
| Out[59]= | 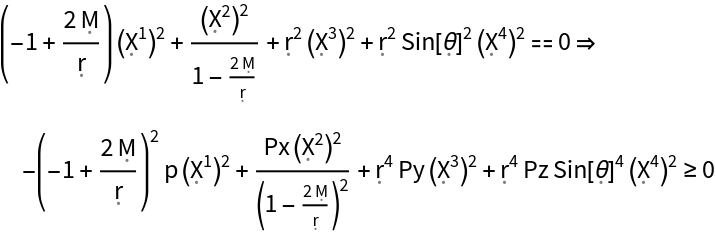 |
Or the indices (True for lowered/covariant and False for raised/contravariant - otherwise both indices will be set as lowered/covariant by default):
| In[60]:= |
| Out[60]= | 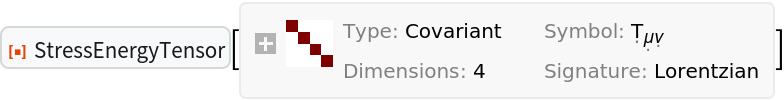 |
| In[61]:= |
| Out[61]= |
Or both simultaneously:
| In[62]:= |
| Out[62]= | 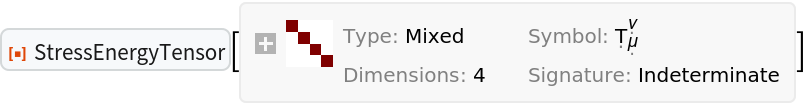 |
| In[63]:= |
| Out[63]= |  |
| In[64]:= |
| Out[64]= |
Common stress-energy tensors can also be constructed using an in-built name:
| In[65]:= |
| Out[65]= |
| In[66]:= |
| Out[66]= | 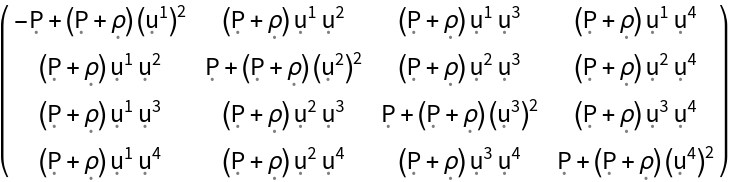 |
When an in-built/named stress-energy tensor has one or more parameters, those parameters can be left unspecified (in which case they are filled with purely symbolic defaults, such as "" in the above), or can be specified explicitly in list form:
| In[67]:= |
| Out[67]= |
| In[68]:= |
| Out[68]= |  |
If only some parameters are explicitly specified, then the remainder are filled with symbolic defaults (e.g. if one specifies only a numerical 4-velocity for the perfect fluid stress-energy tensor, then StressEnergyTensor will use a purely symbolic density and a purely symbolic pressure, namely "" and "P", respectively):
| In[69]:= |
| Out[69]= |
| In[70]:= |
| Out[70]= | 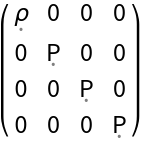 |
Metric and index information can also be specified for in-built/named stress-energy tensors:
| In[71]:= |
| Out[71]= |  |
| In[72]:= |
| Out[72]= | 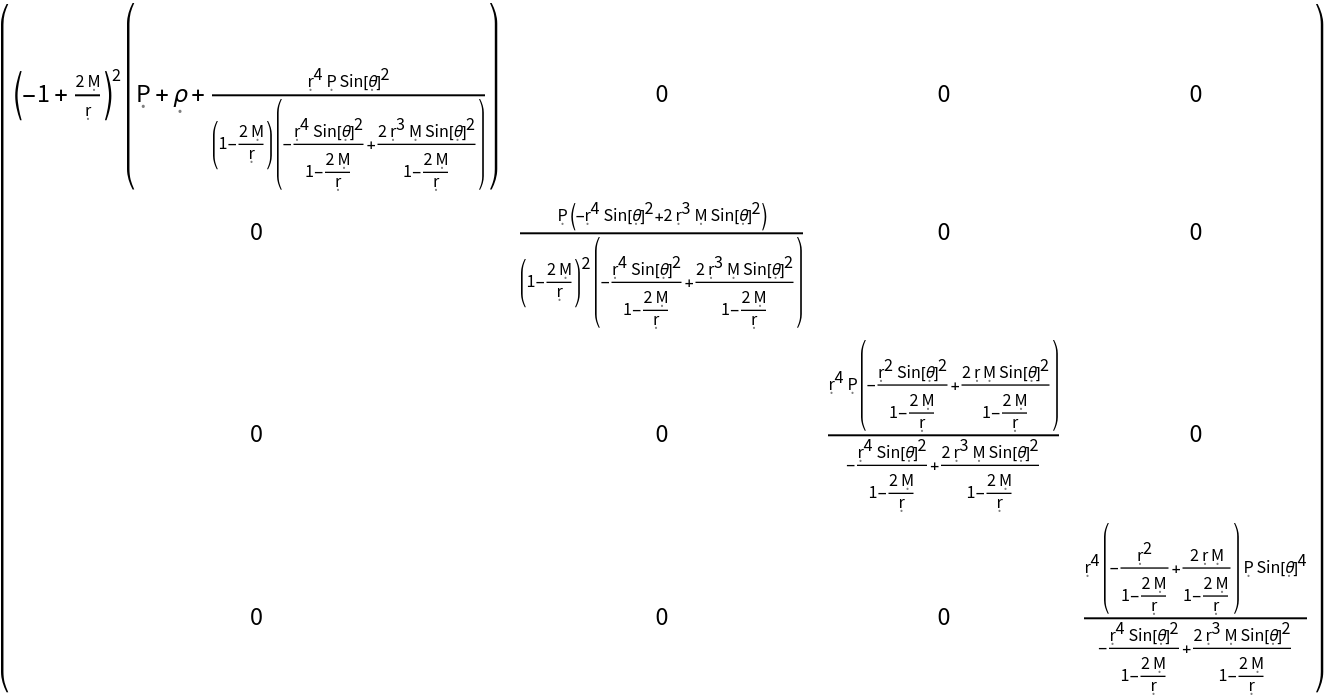 |
| In[73]:= |
| Out[73]= | 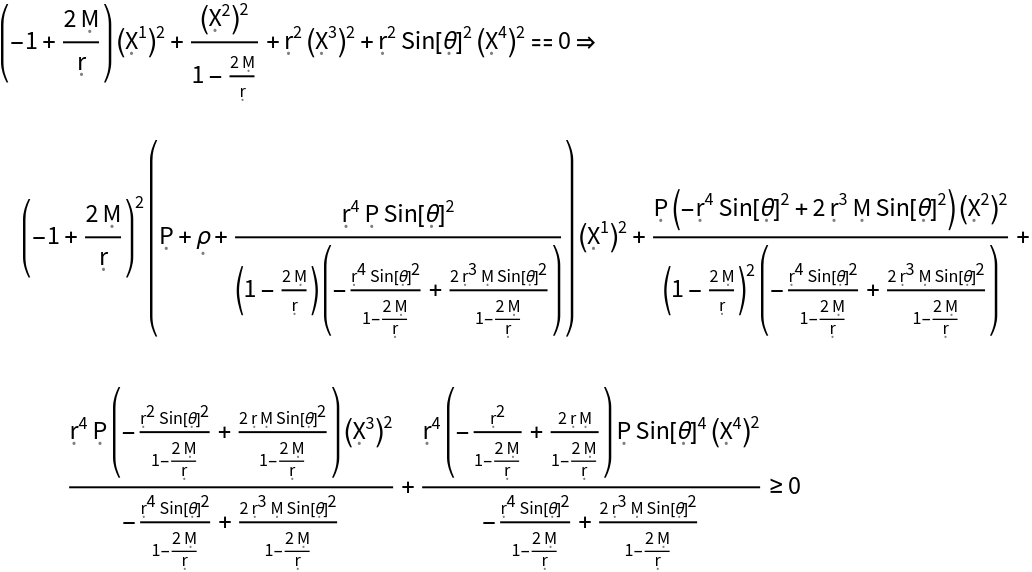 |
All named/in-built metric tensors can be generalized to arbitrary numbers of spacetime dimensions, as necessary:
| In[74]:= |
| Out[74]= |
| In[75]:= |
| Out[75]= | 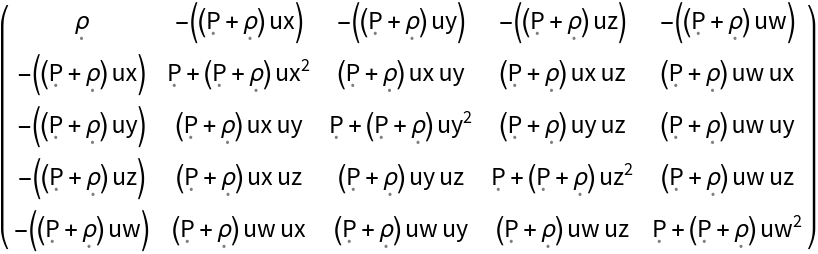 |
New coordinate symbols can be specified for any stress-energy tensor:
| In[76]:= |
| Out[76]= |
| In[77]:= |
| Out[77]= |
| In[78]:= |
| Out[78]= |
| In[79]:= |
| Out[79]= |
Indices can also be raised and lowered on any stress-energy tensor:
| In[80]:= |
| Out[80]= | 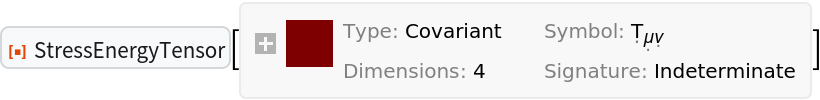 |
| In[81]:= |
| Out[81]= |
New coordinate symbols and new index positions can also be specified simultaneously:
| In[82]:= |
| Out[82]= | 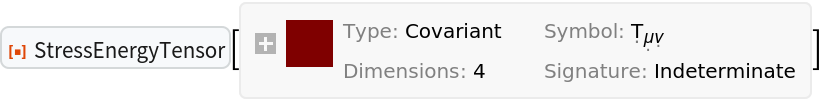 |
| In[83]:= |
| Out[83]= |
| In[84]:= |
| Out[84]= |
Show the list of all in-built/named stress-energy tensors:
| In[85]:= |
| Out[85]= |
Construct a generic 4-dimensional symmetric stress-energy tensor (default):
| In[86]:= |
| Out[86]= | 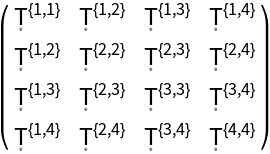 |
Construct a generic 5-dimensional symmetric stress-energy tensor:
| In[87]:= |
| Out[87]= |  |
Calling StressEnergyTensor[d] is a shorthand version, equivalent to calling StressEnergyTensor[{"Symmetric",d}]:
| In[88]:= |
| Out[88]= |  |
Construct a generic 4-dimensional symmetric stress-energy tensor field (default):
| In[89]:= |
| Out[89]= | 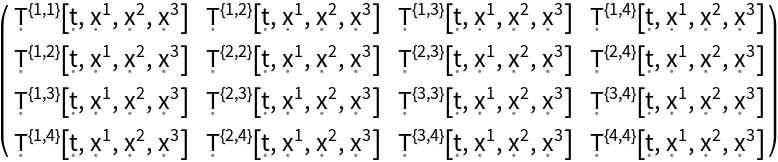 |
Construct a generic 5-dimensional symmetric stress-energy tensor field:
| In[90]:= |
| Out[90]= | 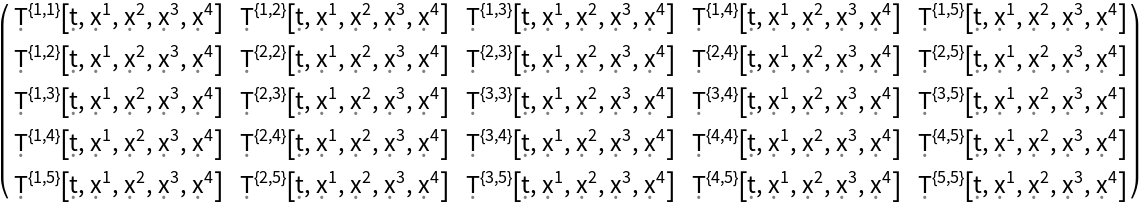 |
Construct a generic 4-dimensional asymmetric stress-energy tensor (default):
| In[91]:= |
| Out[91]= | 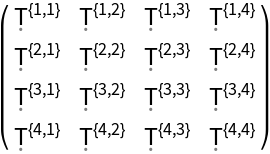 |
Construct a generic 5-dimensional asymmetric stress-energy tensor:
| In[92]:= |
| Out[92]= |  |
Construct a generic 4-dimensional asymmetric stress-energy tensor field (default):
| In[93]:= |
| Out[93]= | 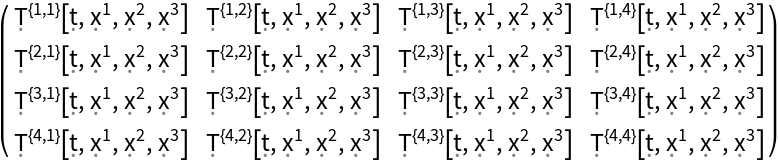 |
Construct a generic 5-dimensional asymmetric stress-energy tensor field:
| In[94]:= |
| Out[94]= | 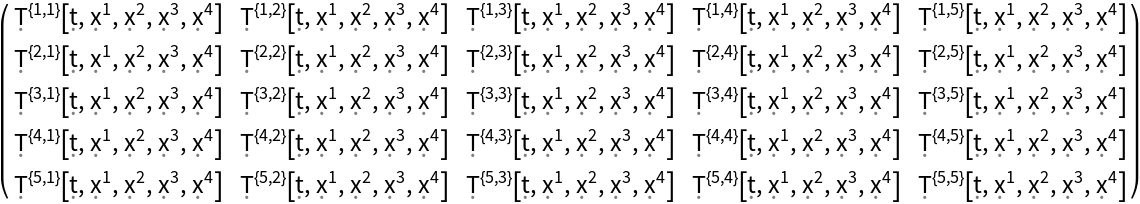 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic fluid, i.e. an idealized fluid distribution with vanishing conductivity, viscosity and shear stress, with symbolic spacetime velocity "u", symbolic mass-energy density "" and symbolic hydrostatic pressure "P" (default):
| In[95]:= |
| Out[95]= | 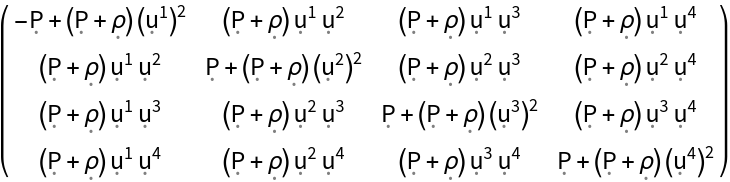 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic fluid with numerical spacetime velocity {-1,1/2,1/2,1/3}, symbolic mass-energy density "" and symbolic hydrostatic pressure "P":
| In[96]:= |
| Out[96]= | 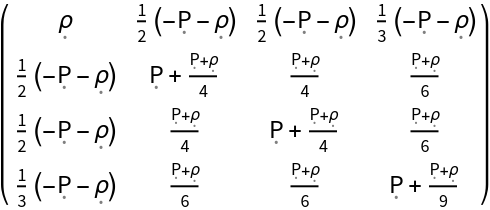 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic fluid with numerical spacetime velocity {-1,1/2,1/2,1/3}, numerical mass-energy density 1 and symbolic hydrostatic pressure "P":
| In[97]:= |
| Out[97]= | 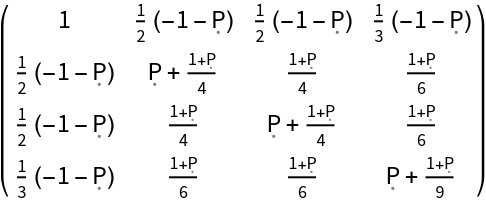 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic fluid with numerical spacetime velocity {-1,1/2,1/2,1/3}, numerical mass-energy density 1 and numerical hydrostatic pressure 2:
| In[98]:= |
| Out[98]= |  |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a perfect and dynamic relativistic fluid, i.e. an idealized fluid distribution with vanishing conductivity, viscosity and shear stress, with symbolic spacetime velocity function "u", symbolic mass-energy density function "" and symbolic hydrostatic pressure function "P" (default):
| In[99]:= |
| Out[99]= | 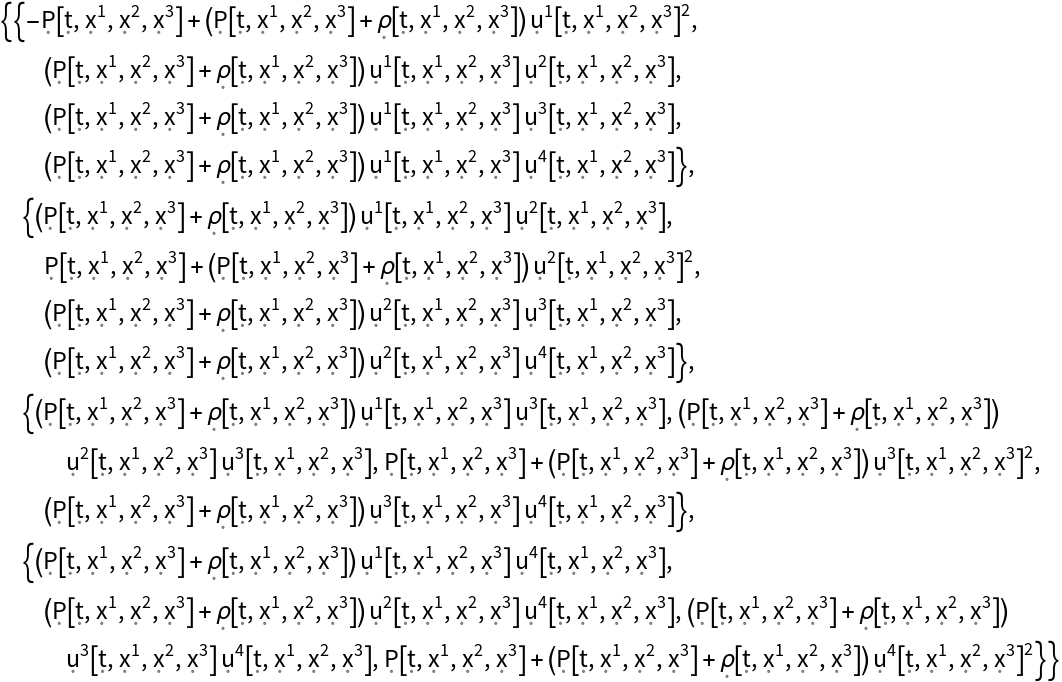 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a perfect and dynamic relativistic fluid with numerical spacetime velocity function {(-#1)&,(#2/2)&,(#3/2)&,(#4/3)&}, symbolic mass-energy density function "" and symbolic hydrostatic pressure function "P":
| In[100]:= |
| Out[100]= | 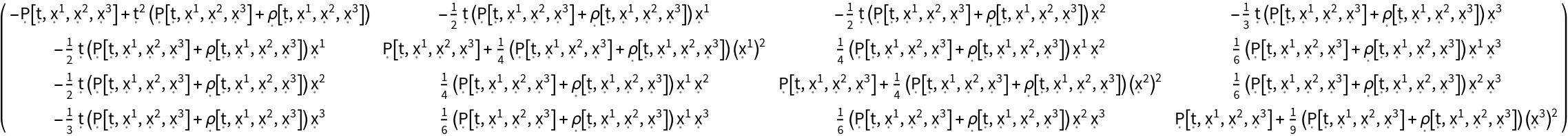 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a perfect and dynamic relativistic fluid with numerical spacetime velocity function {(-#1)&,(#2/2)&,(#3/2)&,(#4/3)&}, numerical mass-energy density function (#1^2)& and symbolic hydrostatic pressure function "P":
| In[101]:= |
| Out[101]= | 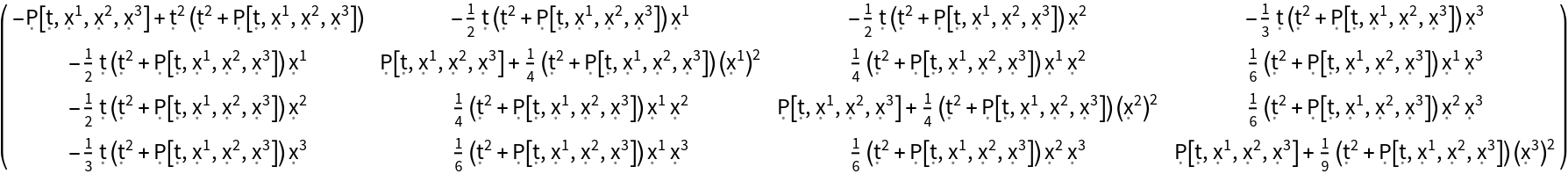 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a perfect and dynamic relativistic fluid with numerical spacetime velocity function {(-#1)&,(#2/2)&,(#3/2)&,(#4/3)&}, numerical mass-energy density function (#1^2)& and numerical hydrostatic pressure function (#4^3)&:
| In[102]:= |
| Out[102]= | 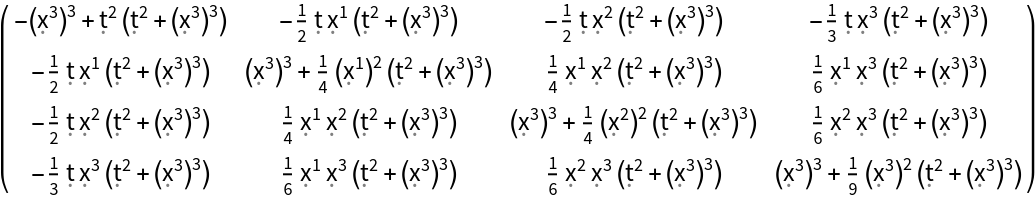 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic dust, i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid with vanishing hydrostatic pressure, with symbolic spacetime velocity "u" and symbolic mass-energy density "":
| In[103]:= |
| Out[103]= | 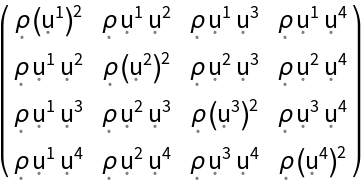 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic dust with numerical spacetime velocity {-1,1/2,1/2,1/3} and symbolic mass-energy density "":
| In[104]:= |
| Out[104]= | 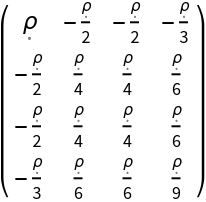 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic dust with numerical spacetime velocity {-1,1/2,1/2,1/3} and numerical mass energy-density 1:
| In[105]:= |
| Out[105]= | 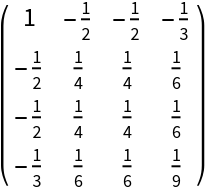 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a perfect and dynamic relativistic dust, i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid with vanishing hydrostatic pressure, with symbolic spacetime velocity function "u" and symbolic mass-energy density function "":
| In[106]:= |
| Out[106]= | 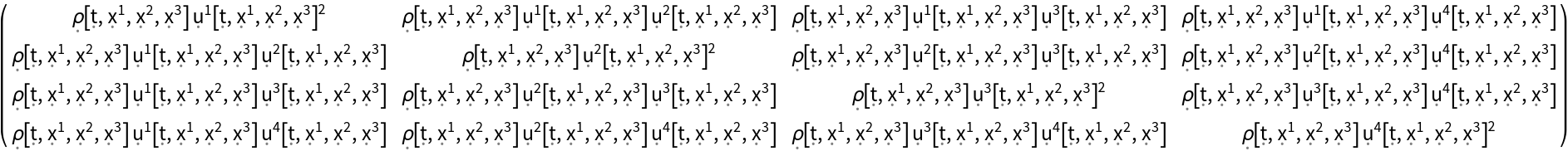 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a perfect and dynamic relativistic dust with numerical spacetime velocity function {(-#1)&,(#2/2)&,(#3/2)&,(#4/3)&} and symbolic mass-energy density function "":
| In[107]:= |
| Out[107]= | 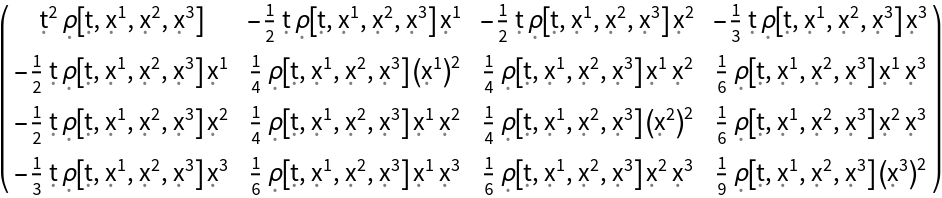 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a perfect and dynamic relativistic dust with numerical spacetime velocity function {(-#1)&,(#2/2)&,(#3/2)&,(#4/3)&} and numerical mass-energy density function (#1^2)&:
| In[108]:= |
| Out[108]= | 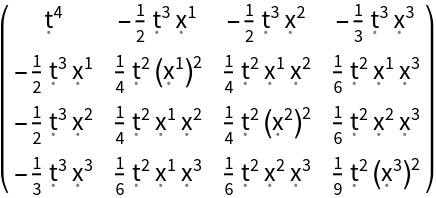 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic radiation distribution, i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid whose mass-energy density is equal to the number of spatial dimensions multiplied by the radiation pressure, with symbolic spacetime velocity "u" and symbolic radiation pressure "P" (default):
| In[109]:= |
| Out[109]= |  |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic radiation distribution with numerical spacetime velocity {-1,1/2,1/2,1/3} and symbolic radiation pressure "P":
| In[110]:= |
| Out[110]= |  |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic radiation distribution with numerical spacetime velocity {-1,1/2,1/2,1/3} and numerical radiation pressure 2:
| In[111]:= |
| Out[111]= | 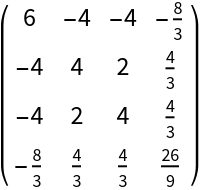 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a perfect and dynamic relativistic radiation distribution, i.e. a perfect relativistic fluid whose mass-energy density is equal to the number of spatial dimensions multiplied by the radiation pressure, with symbolic spacetime velocity function "u" and symbolic radiation pressure function "P" (default):
| In[112]:= |
| Out[112]= | 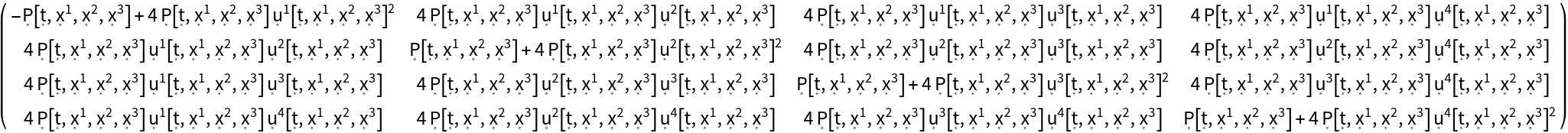 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a perfect and dynamic relativistic radiation distribution with numerical spacetime velocity function {(-#1)&,(#2/2)&,(#3/2)&,(#4/3)&} and symbolic radiation pressure function "P":
| In[113]:= |
| Out[113]= | 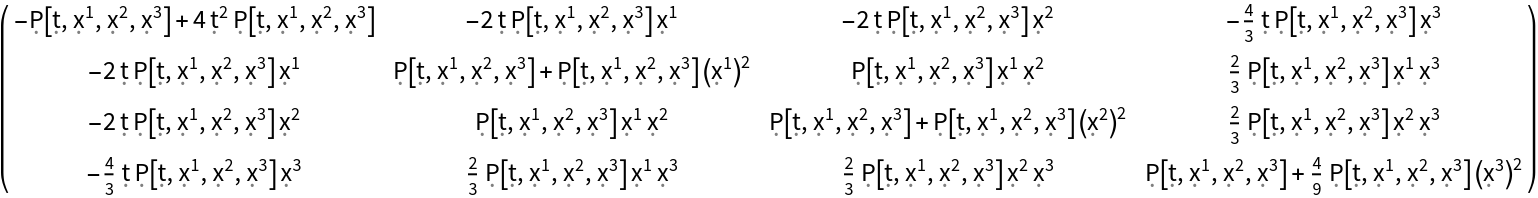 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a perfect and dynamic relativistic radiation distribution with numerical spacetime velocity function {(-#1)&,(#2/2)&,(#3/2)&,(#4/3)&} and numerical radiation pressure function (#4^3)&:
| In[114]:= |
| Out[114]= | 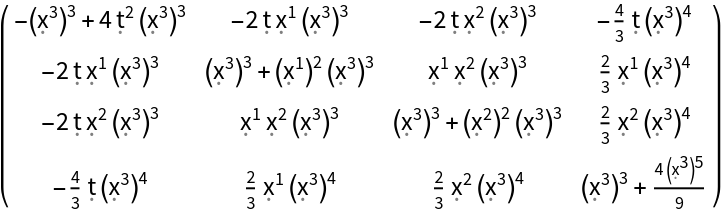 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a source-free and dynamic electromagnetic field with symbolic spacetime electromagnetic potential "A" (combining the symbolic electric scalar potential "" and the symbolic magnetic vector potential "Ai") and symbolic vacuum magnetic permeability constant "0" (default):
| In[115]:= |
| Out[115]= | 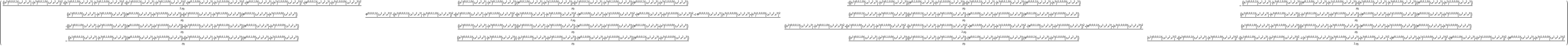 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a source-free and dynamic electromagnetic field with numerical spacetime electromagnetic potential {(#4)&,(#3/2)&,(#2/2)&,(#1/3)&} (combining the numerical electric scalar potential (#4)& with the numerical magnetic vector potential {(#3/2)&,(#2/2)&,(#1/3)&}) and symbolic magnetic permeability constant "0":
| In[116]:= |
| Out[116]= |  |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a source-free and dynamic electromagnetic field with numerical spacetime electromagnetic potential {(#4)&,(#3/2)&,(#2/2)&,(#1/3)&} (combining the numerical electric scalar potential (#4)& with the numerical magnetic vector potential {(#3/2)&,(#2/2)&,(#1/3)&}) and numerical magnetic permeability constant 4*Pi:
| In[117]:= |
| Out[117]= | 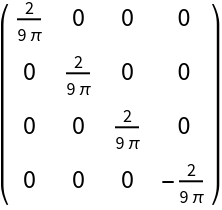 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a massive, dynamic, complex scalar field, i.e. a complex scalar function obeying the massive Klein-Gordon equation, with symbolic mass "m" and symbolic scalar function "" (default):
| In[118]:= |
| Out[118]= | 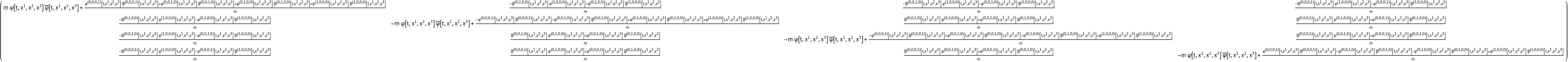 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a massive, dynamic, complex scalar field with numerical mass 1 and symbolic scalar function "":
| In[119]:= |
| Out[119]= | 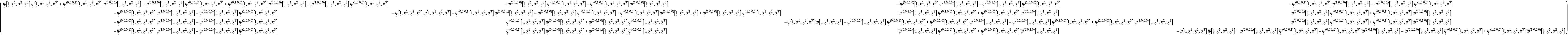 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor field for a massive, dynamic, complex scalar field with numerical mass 1 and numerical scalar function {(-#1)&,(I*#2/2)&,(-I*#3/2)&,(#4/3)&}:
| In[120]:= |
| Out[120]= | 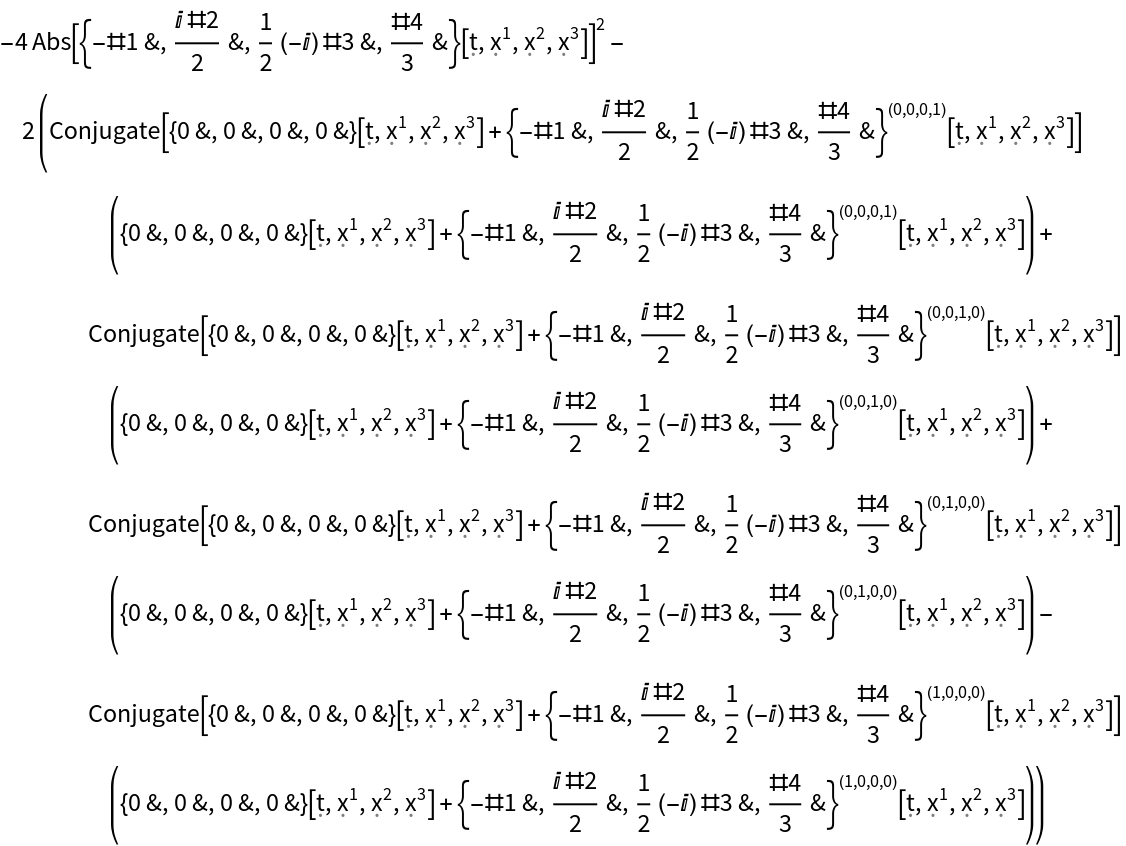 |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic fluid (with symbolic 4-velocity "u", symbolic density "" and symbolic pressure "P") in the Schwarzschild metric, with symbolic mass "M":
| In[121]:= |
| Out[121]= |
Show the list of properties:
| In[122]:= |
| Out[122]= | 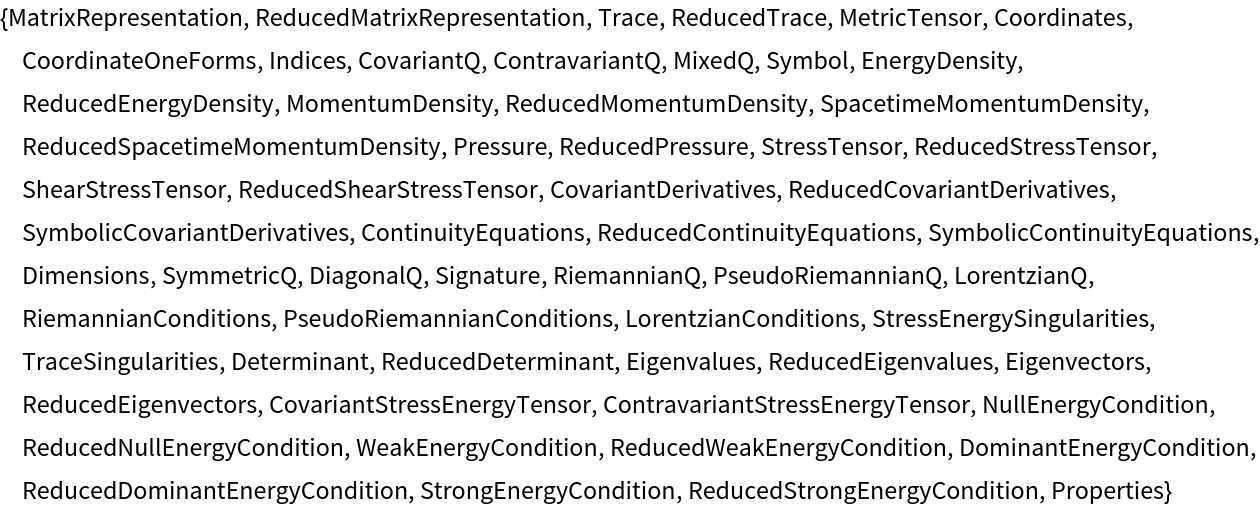 |
Show the explicit matrix representation of the stress-energy tensor:
| In[123]:= |
| Out[123]= | 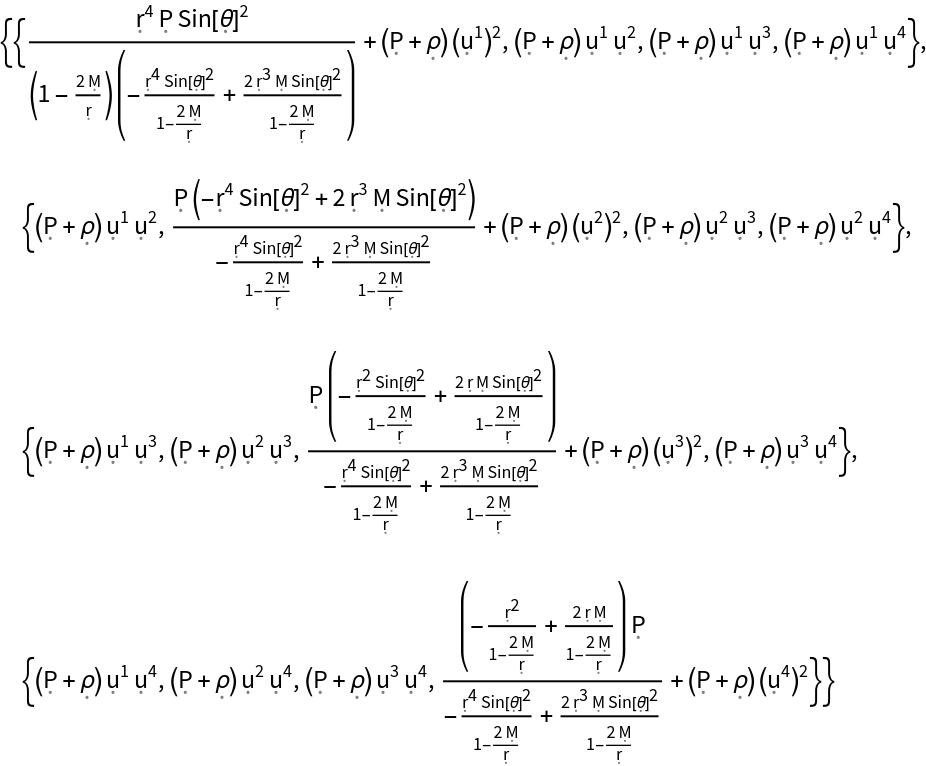 |
Show the explicit matrix representation of the stress-energy tensor, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[124]:= |
| Out[124]= | 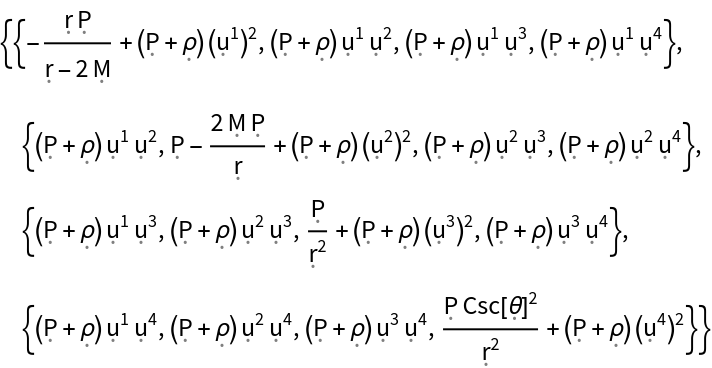 |
Show the trace of the stress-energy tensor:
| In[125]:= |
| Out[125]= | 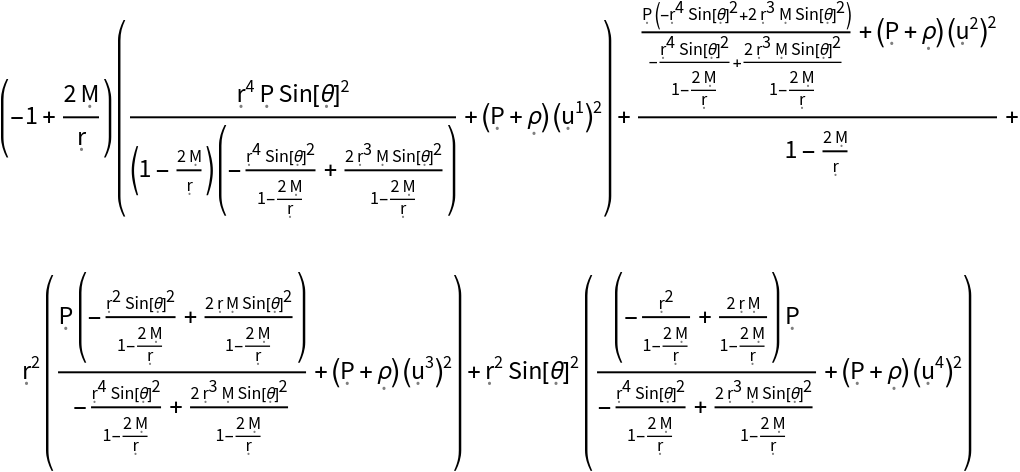 |
Show the trace of the stress-energy tensor, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[126]:= |
| Out[126]= |
Show the metric tensor for the underlying manifold associated to the stress-energy tensor:
| In[127]:= |
| Out[127]= | 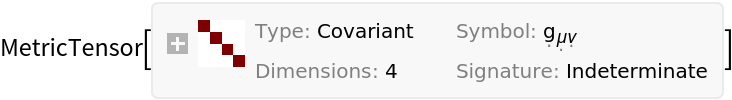 |
Show the list of coordinate symbols for the stress-energy tensor:
| In[128]:= |
| Out[128]= |
Show the list of differential 1-form symbols for the coordinates of the stress-energy tensor:
| In[129]:= |
| Out[129]= |
Show the list of booleans specifying the positions of the indices of the stress-energy tensor (True for lowered/covariant and False for raised/contravariant):
| In[130]:= |
| Out[130]= |
Determine whether the stress-energy tensor is covariant (i.e. both indices are lowered/covariant):
| In[131]:= |
| Out[131]= |
Determine whether the stress-energy tensor is contravariant (i.e. both indices are raised/contravariant):
| In[132]:= |
| Out[132]= |
Determine whether the stress-energy tensor is mixed (i.e. one index is lowered/covariant and one index is raised/contravariant):
| In[133]:= |
| Out[133]= |
Show a symbolic representation of the stress-energy tensor with appropriately raised/lowered indices:
| In[134]:= |
| Out[134]= |
Show the relativistic mass-energy density (i.e. the time-time component of the contravariant stress-energy tensor):
| In[135]:= |
| Out[135]= | 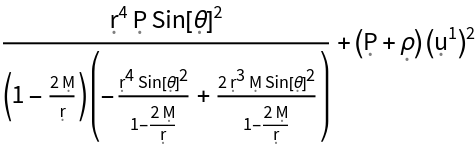 |
Show the relativistic mass-energy density (i.e. the time-time component of the contravariant stress-energy tensor), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[136]:= |
| Out[136]= |
Show the relativistic spatial momentum density (i.e. the time-space/space-time components of the contravariant stress-energy tensor):
| In[137]:= |
| Out[137]= |
Show the relativistic spatial momentum density (i.e. the time-space/space-time components of the contravariant stress-energy tensor), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[138]:= |
| Out[138]= |
Show the relativistic spacetime momentum density (i.e. the time-time component plus the time-space/space-time components of the contravariant stress-energy tensor):
| In[139]:= |
| Out[139]= | 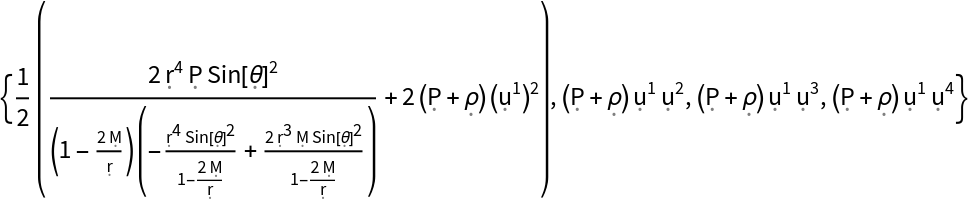 |
Show the relativistic spacetime momentum density (i.e. the time-time component plus the time-space/space-time components of the contravariant stress-energy tensor), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[140]:= |
| Out[140]= |
Show the relativistic pressure (i.e. the directional average of the trace part of the space-space components of the contravariant stress-energy tensor):
| In[141]:= |
| Out[141]= | 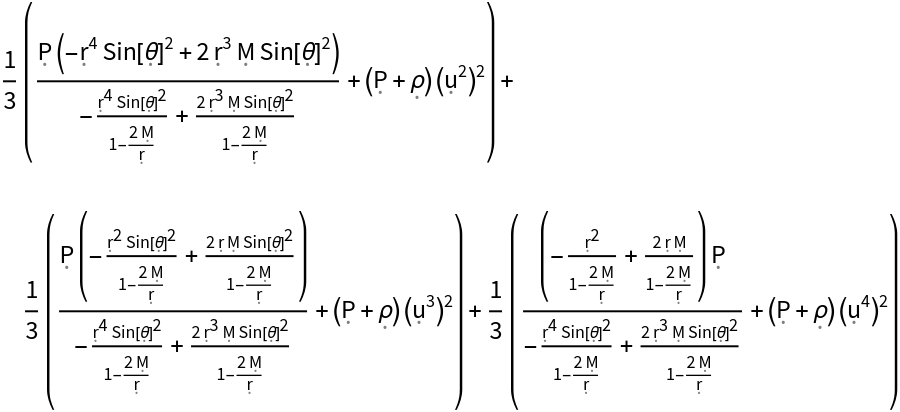 |
Show the relativistic pressure (i.e. the directional average of the trace part of the space-space components of the contravariant stress-energy tensor), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[142]:= |
| Out[142]= |
Show the relativistic Cauchy stress tensor (i.e. the space-space components of the contravariant stress-energy tensor):
| In[143]:= |
| Out[143]= | 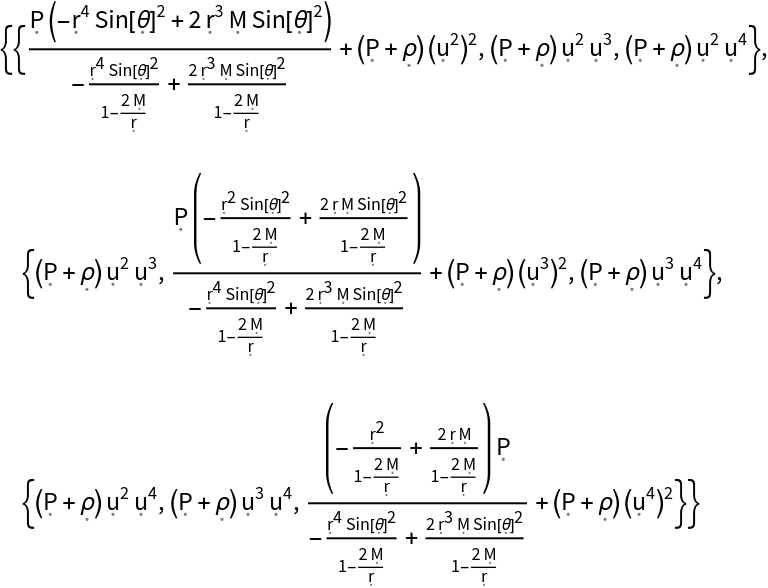 |
Show the relativistic Cauchy stress tensor (i.e. the space-space components of the contravariant stress-energy tensor), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[144]:= |
| Out[144]= | 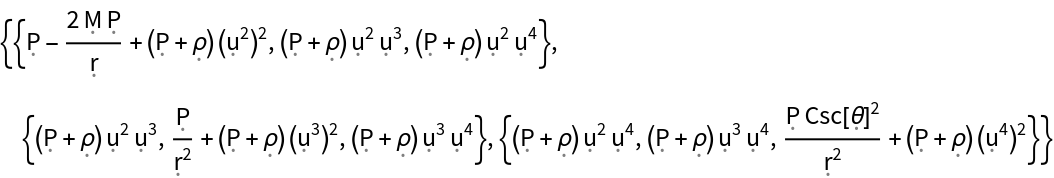 |
Show the relativistic shear stress tensor (i.e. the trace-free part of the space-space components of the contravariant stress-energy tensor):
| In[145]:= |
| Out[145]= | 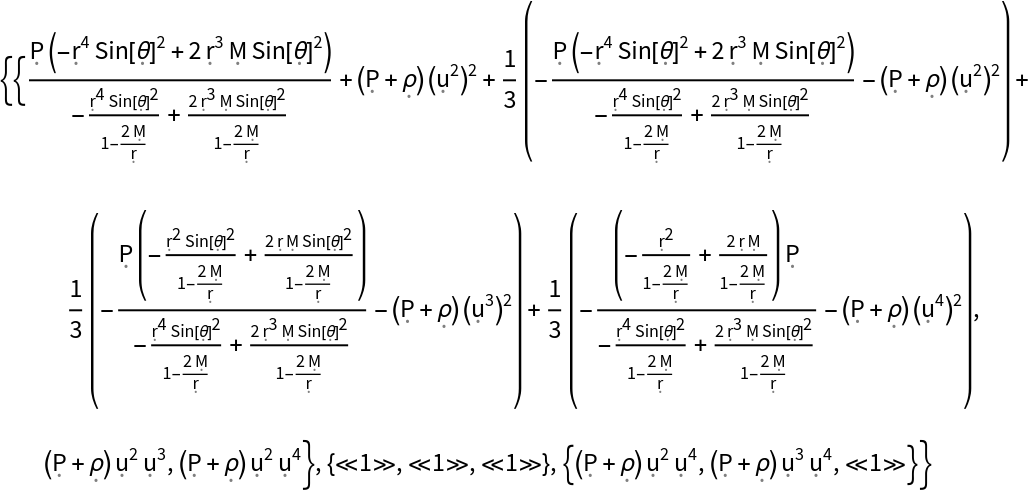 |
Show the relativistic shear stress tensor (i.e. the trace-free part of the space-space components of the contravariant stress-energy tensor), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[146]:= |
| Out[146]= | 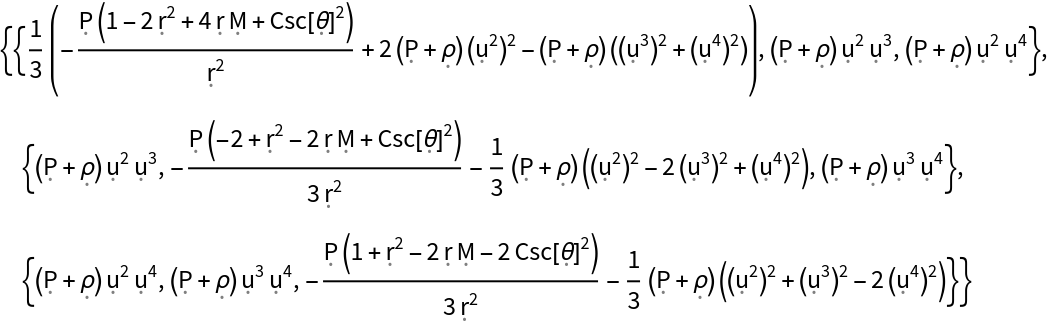 |
Show the association of all covariant derivatives (i.e. all derivatives along tangent vectors of the underlying manifold) of the stress-energy tensor:
| In[147]:= |
| Out[147]= | 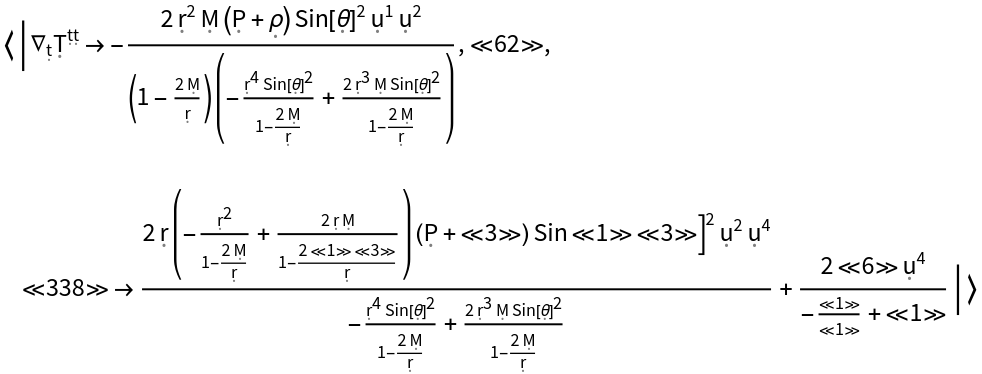 |
Show the association of all covariant derivatives (i.e. all derivatives along tangent vectors of the underlying manifold) of the stress-energy tensor, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[148]:= |
| Out[148]= | 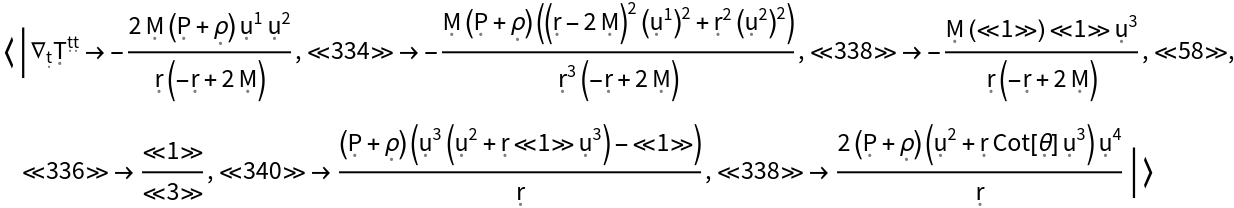 |
Show the association of all covariant derivatives (i.e. all derivatives along tangent vectors of the underlying manifold) of the stress-energy tensor, with all partial derivative operators left purely symbolic:
| In[149]:= |
| Out[149]= | 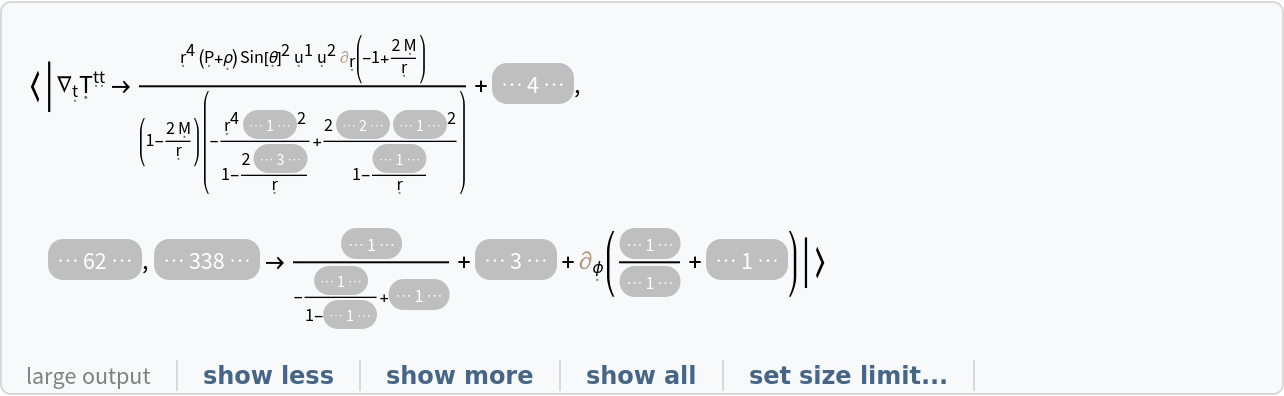 |
Show the list of all continuity equations asserting that the covariant divergence of the stress-energy tensor must vanish (i.e. energy and momentum are conserved):
| In[150]:= |
| Out[150]= | 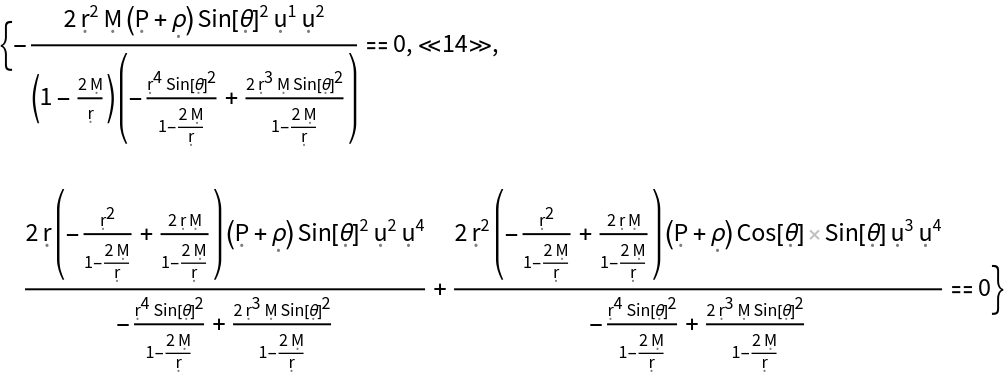 |
Show the list of all continuity equations asserting that the covariant divergence of the stress-energy tensor must vanish (i.e. energy and momentum are conserved), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[151]:= |
| Out[151]= | 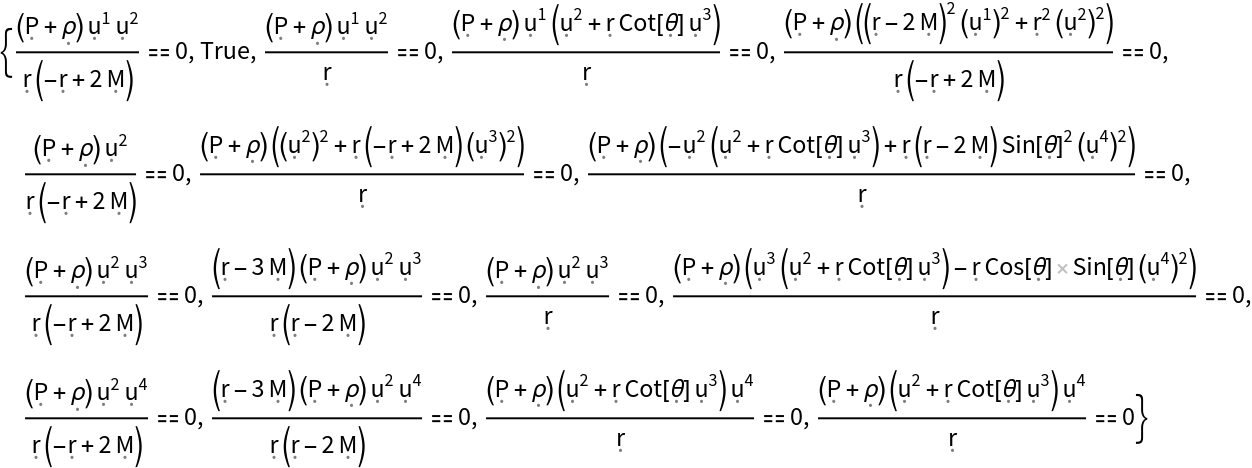 |
Show the list of all continuity equations asserting that the covariant divergence of the stress-energy tensor must vanish (i.e. energy and momentum are conserved), with all partial derivative operators left purely symbolic:
| In[152]:= |
| Out[152]= |  |
Show the number of dimensions of the underlying manifold associated to the stress-energy tensor:
| In[153]:= |
| Out[153]= |
Determine whether the stress-energy tensor is symmetric (in explicit, contravariant matrix form):
| In[154]:= |
| Out[154]= |
Determine whether the stress-energy tensor is diagonal (in explicit, contravariant matrix form):
| In[155]:= |
| Out[155]= |
Show the signature of the underlying manifold associated to the stress-energy tensor (with +1s representing positive eigenvalues and -1s representing negative eigenvalues of the metric tensor):
| In[156]:= |
| Out[156]= |
Determine whether the underlying manifold associated to the stress-energy tensor is Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues of the metric tensor have the same sign):
| In[157]:= |
| Out[157]= |
Determine whether the underlying manifold associated to the stress-energy tensor is pseudo-Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues are non-zero, but not all have the same sign):
| In[158]:= |
| Out[158]= |
Determine whether the underlying manifold associated to the stress-energy tensor is Lorentzian (i.e. all eigenvalues of the metric tensor have the same sign, except for one eigenvalue which has the opposite sign):
| In[159]:= |
| Out[159]= |
Show the list of conditions on the coordinates required to guarantee that the underlying manifold associated to the stress-energy tensor is Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues of the metric tensor are positive):
| In[160]:= |
| Out[160]= |
Show the list of conditions on the coordinates required to guarantee that the underlying manifold associated to the stress-energy tensor is pseudo-Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues of the metric tensor are non-zero):
| In[161]:= |
| Out[161]= |
Show the list of conditions on the coordinates required to guarantee that the underlying manifold associated to the stress-energy tensor is Lorentzian (i.e. the "time" eigenvalue is negative, and all other eigenvalues are positive):
| In[162]:= |
| Out[162]= |
Show the list of coordinate values that cause the stress-energy tensor to become singular:
| In[163]:= |
| Out[163]= |
Show the list of coordinate values that cause the trace of the stress-energy tensor to become singular:
| In[164]:= |
| Out[164]= |
Construct the stress-energy tensor for a perfect and static relativistic fluid (with symbolic 4-velocity "u", symbolic density "" and symbolic pressure "P") in the default 4-dimensional flat/Minkowski spacetime:
| In[165]:= |
| Out[165]= |
Show the determinant of the stress-energy tensor (when represented as a contravariant matrix):
| In[166]:= |
| Out[166]= |
Show the determinant of the stress-energy tensor (when represented as a contravariant matrix), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[167]:= |
| Out[167]= |
Show the eigenvalues of the stress-energy tensor (when represented as a contravariant matrix):
| In[168]:= |
| Out[168]= | 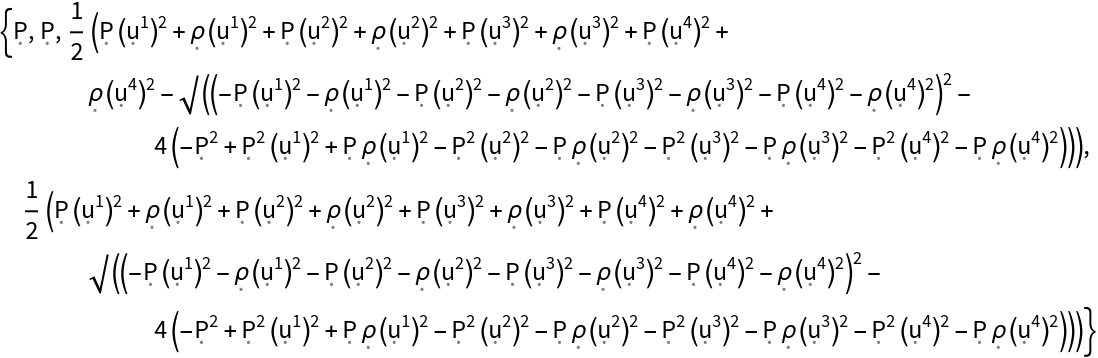 |
Show the eigenvalues of the stress-energy tensor (when represented as a contravariant matrix), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[169]:= |
| Out[169]= | 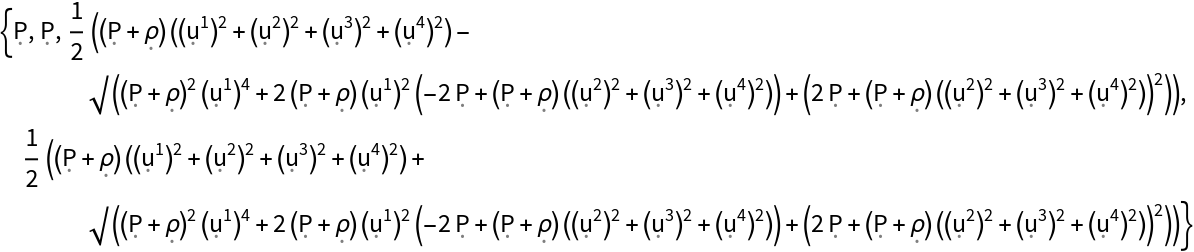 |
Show the eigenvectors of the stress-energy tensor (when represented as a contravariant matrix):
| In[170]:= |
| Out[170]= | 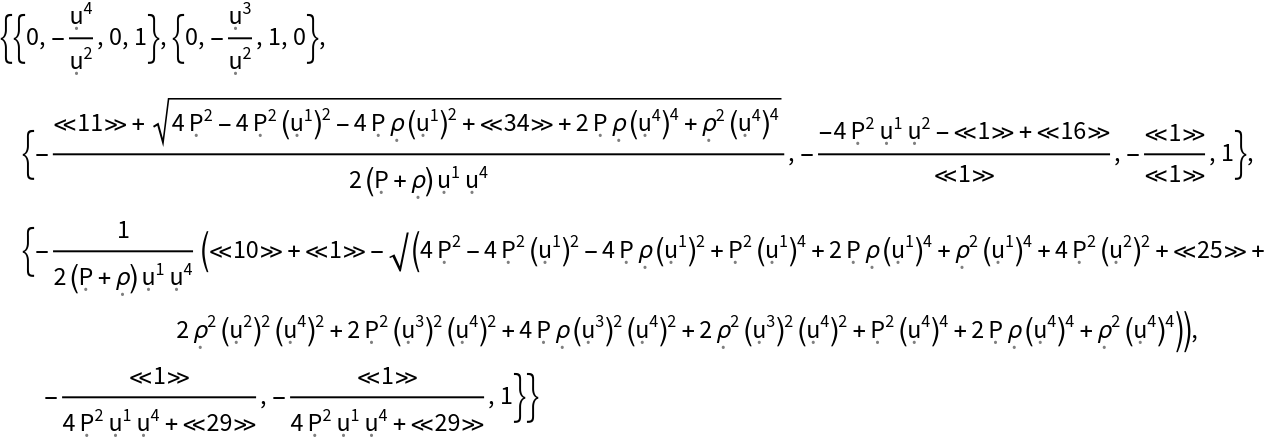 |
Show the eigenvectors of the stress-energy tensor (when represented as a contravariant matrix), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[171]:= |
| Out[171]= | 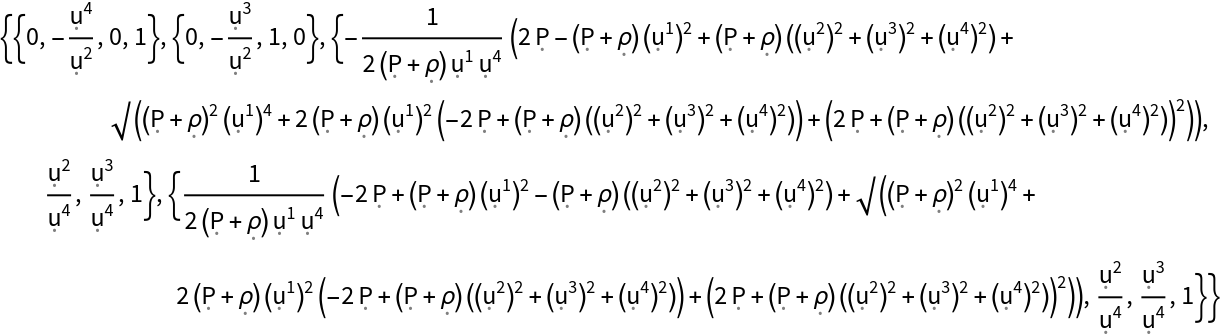 |
Compute the covariant form of the stress-energy tensor (with both indices lowered/covariant):
| In[172]:= |
| Out[172]= |  |
Compute the contravariant form of the stress-energy tensor (with both indices raised/contravariant):
| In[173]:= |
| Out[173]= |
Show the null energy condition (i.e. all observers following future-pointing, null vector fields always observe a non-negative mass-energy density) for the stress-energy tensor:
| In[174]:= |
| Out[174]= | 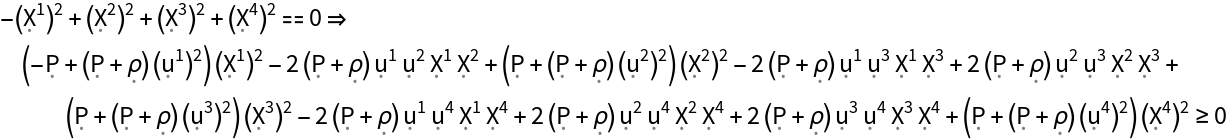 |
Show the null energy condition (i.e. all observers following future-pointing, null vector fields always observe a non-negative mass-energy density) for the stress-energy tensor, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[175]:= |
| Out[175]= |
Show the weak energy condition (i.e. all observers following timelike vector fields always observe a non-negative mass-energy density) for the stress-energy tensor:
| In[176]:= |
| Out[176]= | 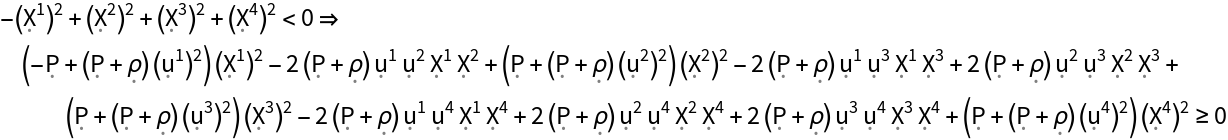 |
Show the weak energy condition (i.e. all observers following timelike vector fields always observe a non-negative mass-energy density) for the stress-energy tensor, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[177]:= |
| Out[177]= |
Show the dominant energy condition (i.e. the weak energy condition, plus all observers following future-pointing, causal vector fields always observe mass-energy to be flowing no faster than light) for the stress-energy tensor:
| In[178]:= |
| Out[178]= | 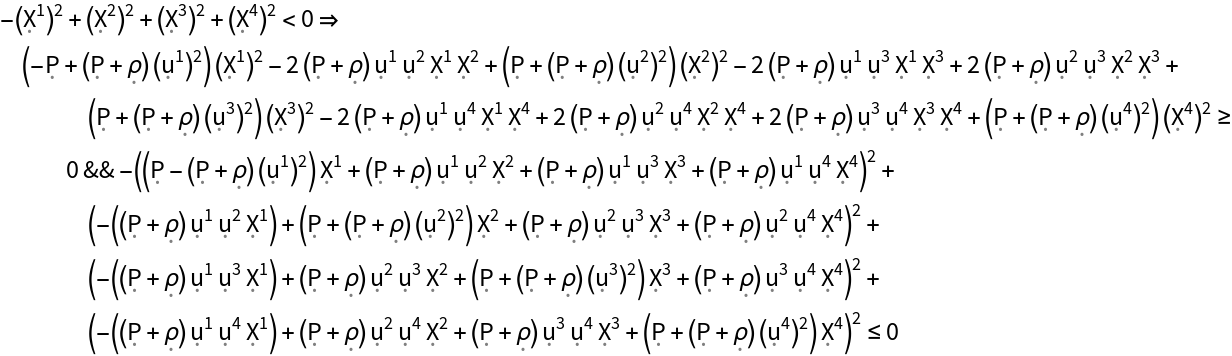 |
Show the dominant energy condition (i.e. the weak energy condition, plus all observers following future-pointing, causal vector fields always observe mass-energy to be flowing no faster than light) for the stress-energy tensor, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[179]:= |
| Out[179]= | 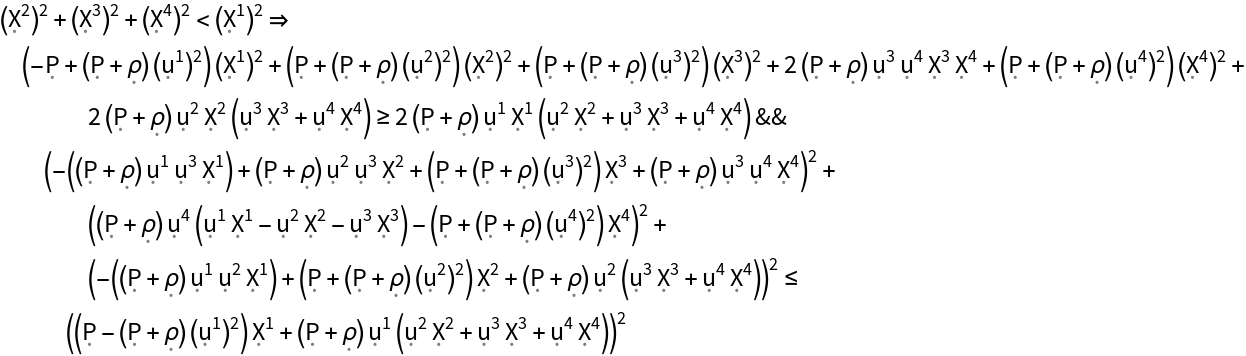 |
Show the strong energy condition (i.e. all observers following timelike vector fields always observe the tidal tensor to have a non-negative trace) for the stress energy tensor:
| In[180]:= |
| Out[180]= | 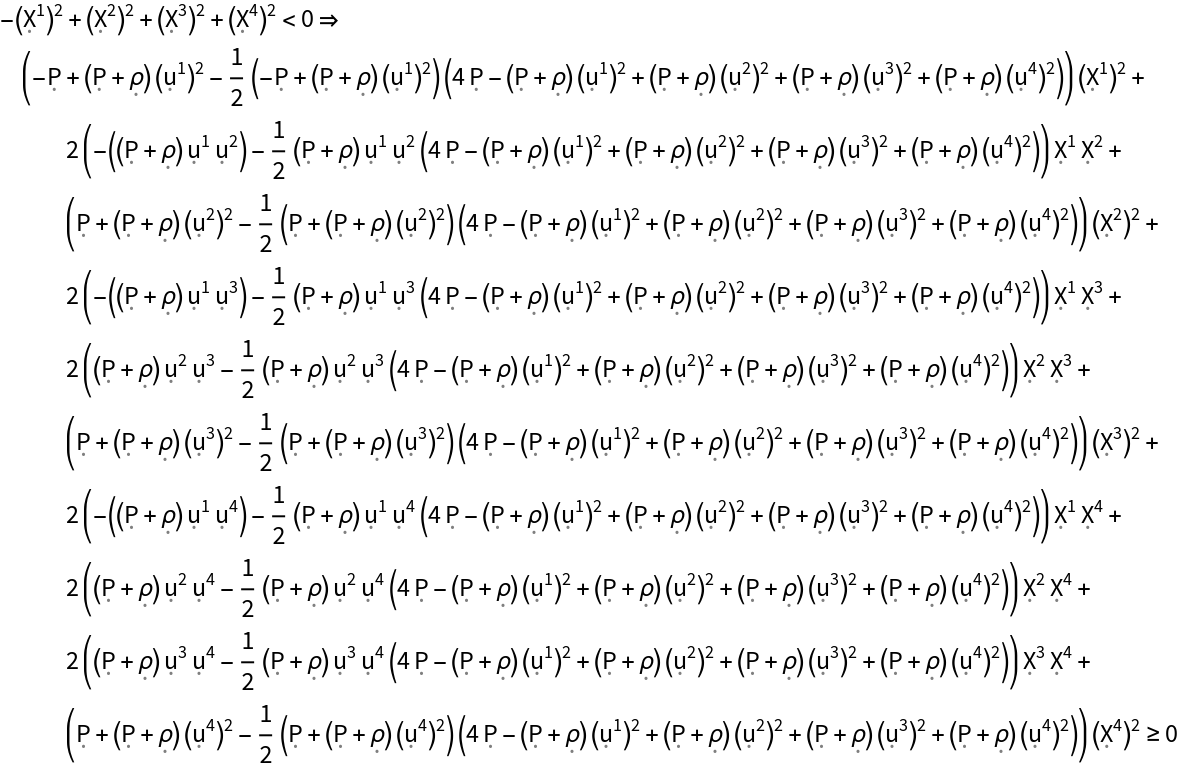 |
Show the strong energy condition (i.e. all observers following timelike vector fields always observe the tidal tensor to have a non-negative trace) for the stress-energy tensor, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[181]:= |
| Out[181]= | 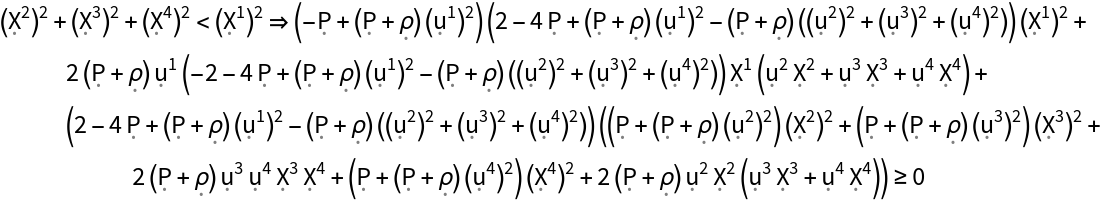 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License