Details and Options
A shuffle is a permuation of elements in a list.
Shuffle handles lists of arbitrary elements, although the most common application is shuffling a deck of cards.
ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][], ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][n], ResourceFunction["Shuffle"]["type"] and ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][n,"type"] represent operator forms of ResourceFunction["Shuffle"] that can be applied to a list.
The specification "type" can be one of:
| "Out" | perfect out shuffle |
| "In" | perfect in shuffle |
| "ReverseOut" | reverse out shuffle |
| "ReverseIn" | reverse in shuffle |
| "DownUnder" | down under shuffle |
| "Monge" | Monge shuffle |
| "DownMonge" | down Monge shuffle |
| "Milk" | milk shuffle |
| "RandomSample" | random permutation |
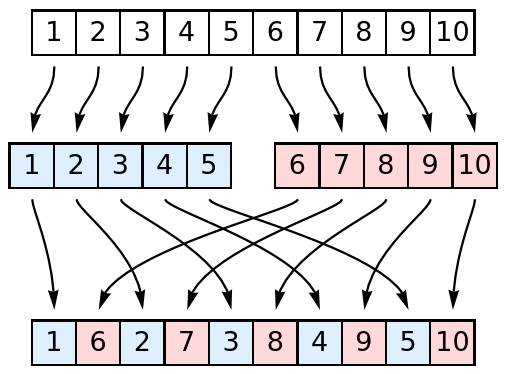
An out shuffle is defined as follows: (1) split the list in two halves; and (2) interweave each half of the list starting with the first half, such that every other element comes from the same half of the list.
Here is an example of a list with 10 items:
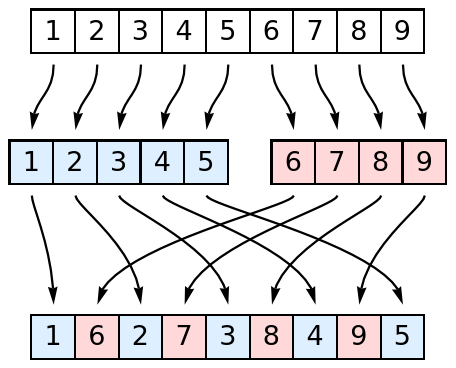
When the list has an odd length n, the first "half" will be (n+1)/2 long and the second "half" will be (n-1)/2 long:
The out shuffle keeps the top card on top and the bottom card on bottom of the deck.
An in shuffle is similar to the out shuffle, only the order of the interleaving halves is reversed so the top card in the original deck ends up in the second position from the top.
Perfect shuffles (in and out) are also known as Faro shuffles, weave shuffles or dovetail shuffles.
Reverse perfect shuffles pick every second card in a separate pile and then join the halves, placing the separate pile on top of (for the reverse in shuffle) or under (for the reverse out shuffle) the remaining cards.
In a down under shuffle, one places the top card down on another pile, then places the second card under the bottom of the remaining deck and repeats the procedure until just one card remains.
The down under shuffle is also called the Australian shuffle, in a reference to Australia.
A Monge shuffle is defined as taking the cards from a deck and shuffling them by forming a new deck, alternating between putting the cards from the old deck on the top and bottom of the new deck.
There are two types of Monge shuffles, depending on how the deck is held in the hand—face up or face down— or, equivalently, whether the cards are numbered from top to bottom or from bottom to top.
The down Monge shuffle is equivalent to perforing the Monge shuffle and then reversing the deck.
The Monge shuffle is also known as an over Monge shuffle, Mongean shuffle and Monge's shuffle.
In a milk shuffle, the deck of cards is "milked" by taking a card off the top and bottom and putting them aside, then repeating the milking, adding the milked cards on top of the pile aside.
The milk shuffle is also known as the Klondike shuffle.
ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][list] is the same as
ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][list,"Out"]. ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][…][list] is equiavalent to ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][list,…].
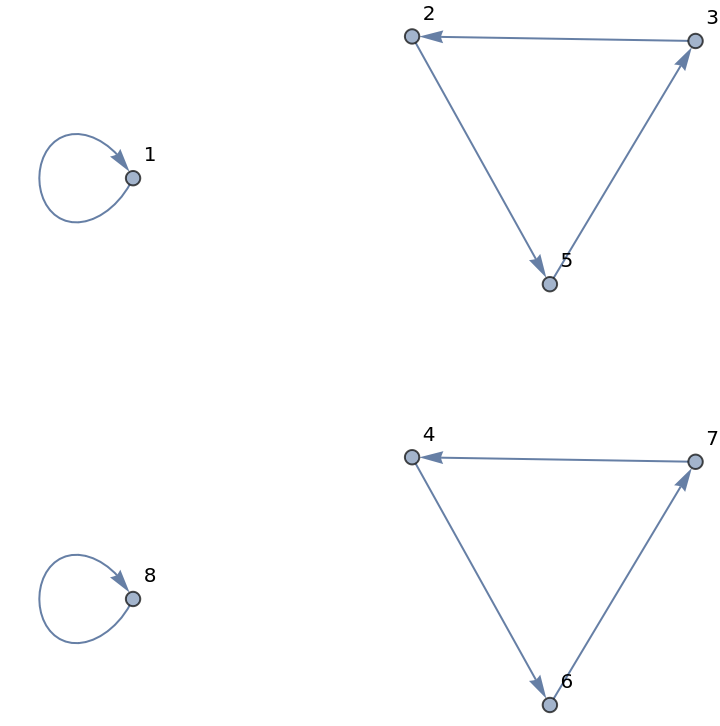
![ResourceFunction["PermutationCyclesGraph"][
ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][Range[12], "Out"], VertexLabels -> "Name"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/6c6/6c6e1d1b-ee3c-41f3-a57e-8c7e5d796671/1029b3cd58dcd799.png)
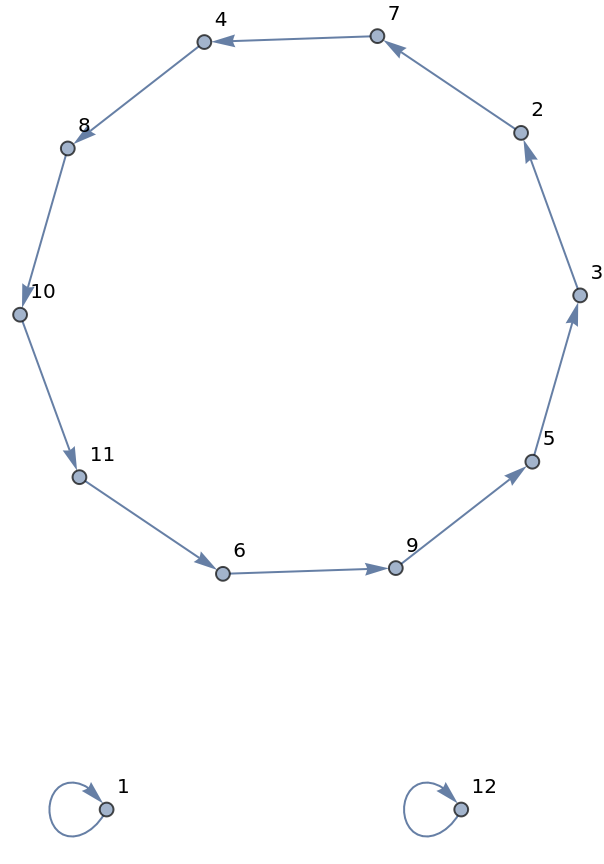
![ResourceFunction["PermutationCyclesGraph"][
ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][Range[#], "Out"], VertexLabels -> "Name"] & /@ {7, 8}](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/6c6/6c6e1d1b-ee3c-41f3-a57e-8c7e5d796671/54366132a0327585.png)
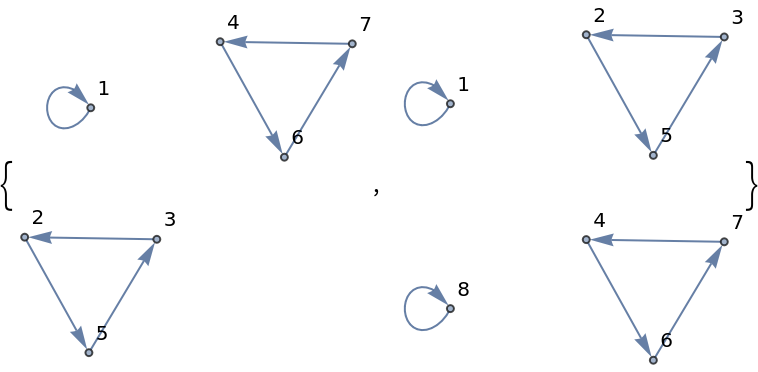
![Grid[Partition[
Labeled[ResourceFunction["PermutationCyclesGraph"][
ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][Range[#], "In"], VertexLabels -> "Name"], #, Top] & /@ Range[5, 8], 2], Frame -> All]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/6c6/6c6e1d1b-ee3c-41f3-a57e-8c7e5d796671/431bb0630a6480ac.png)
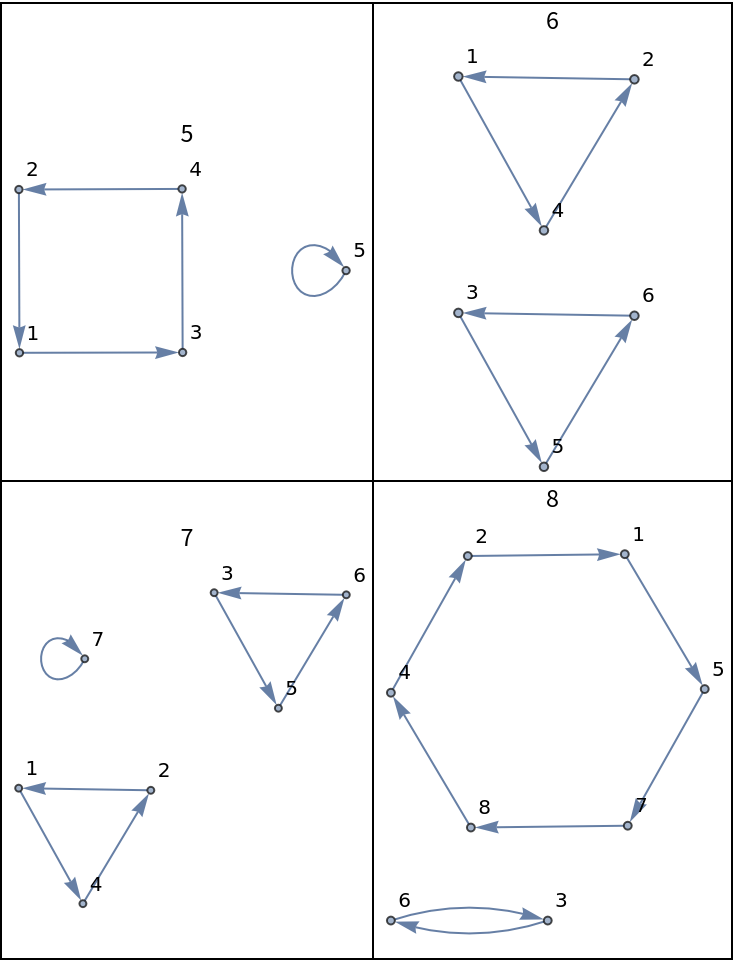
![Grid[Partition[
Labeled[ResourceFunction["PermutationCyclesGraph"][
ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][Range[#], "Monge"], VertexLabels -> "Name"], #, Top] & /@ Range[5, 8], 2], Frame -> All]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/6c6/6c6e1d1b-ee3c-41f3-a57e-8c7e5d796671/09a53a9813edd32c.png)
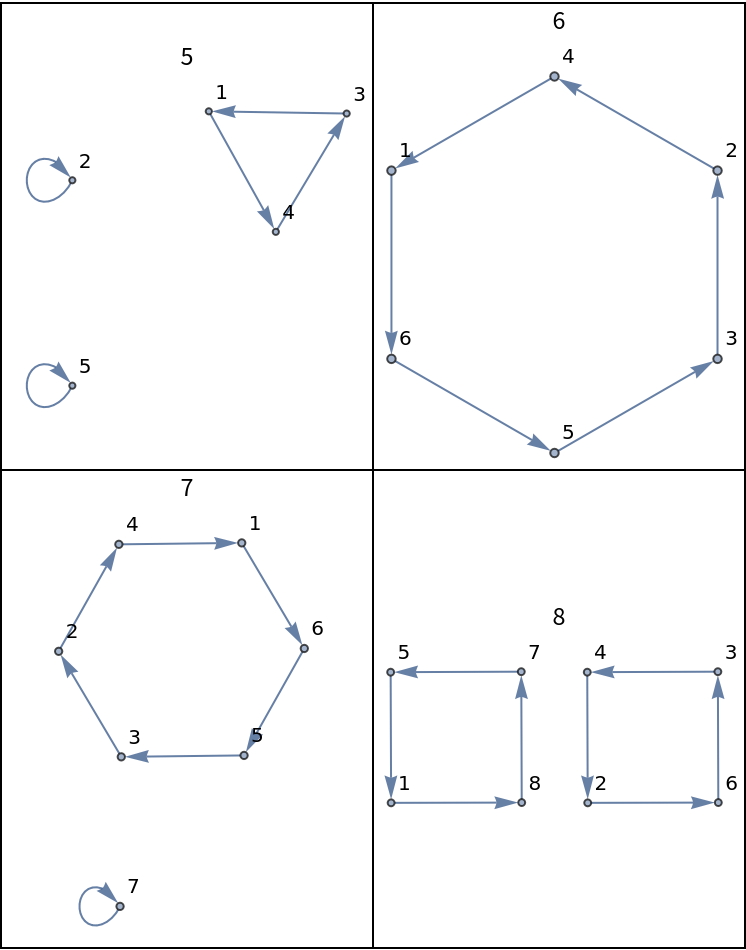
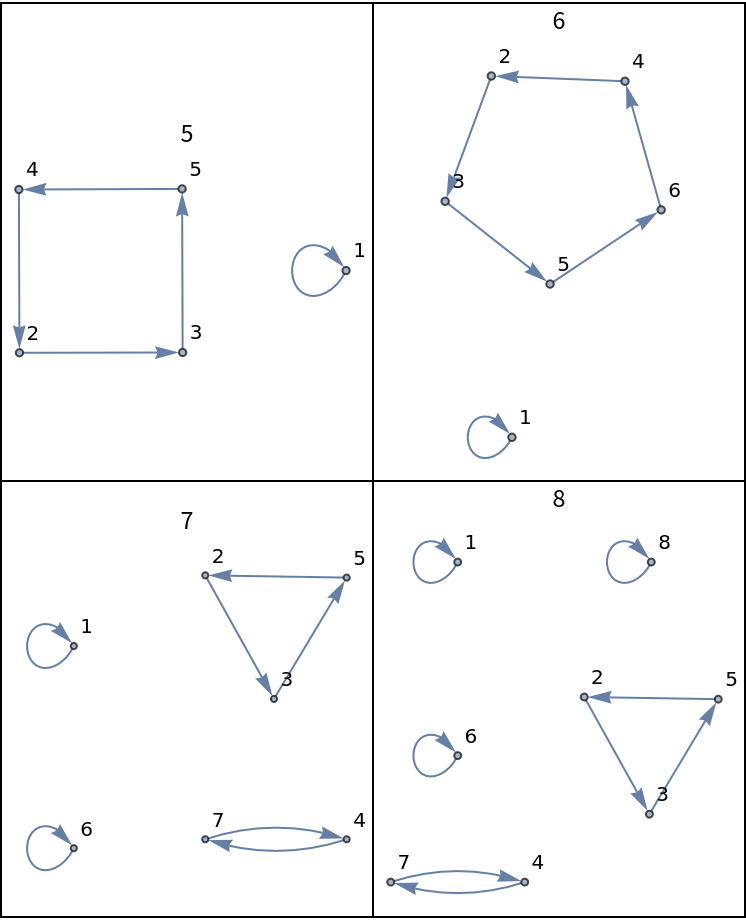
![Grid[Partition[
Labeled[ResourceFunction["PermutationCyclesGraph"][
ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][Range[#], "DownMonge"], VertexLabels -> "Name"], #, Top] & /@ Range[5, 8], 2], Frame -> All]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/6c6/6c6e1d1b-ee3c-41f3-a57e-8c7e5d796671/001266fb159ed253.png)
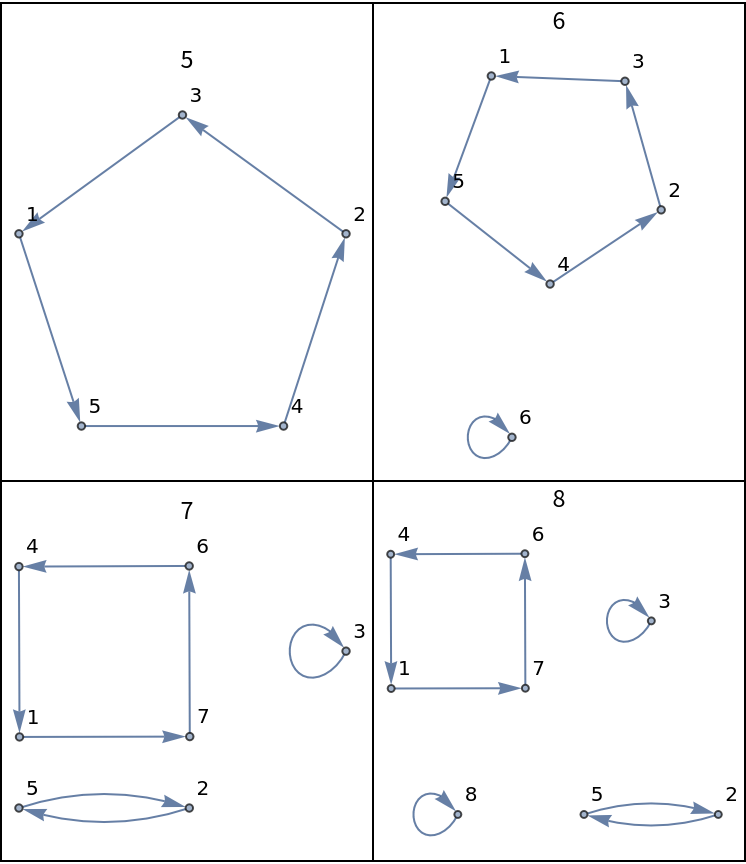
![Grid[Partition[
Labeled[ResourceFunction["PermutationCyclesGraph"][
ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][Range[#], "DownUnder"], VertexLabels -> "Name"], #, Top] & /@ Range[5, 8], 2], Frame -> All]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/6c6/6c6e1d1b-ee3c-41f3-a57e-8c7e5d796671/67d1ab7137fb6c0d.png)
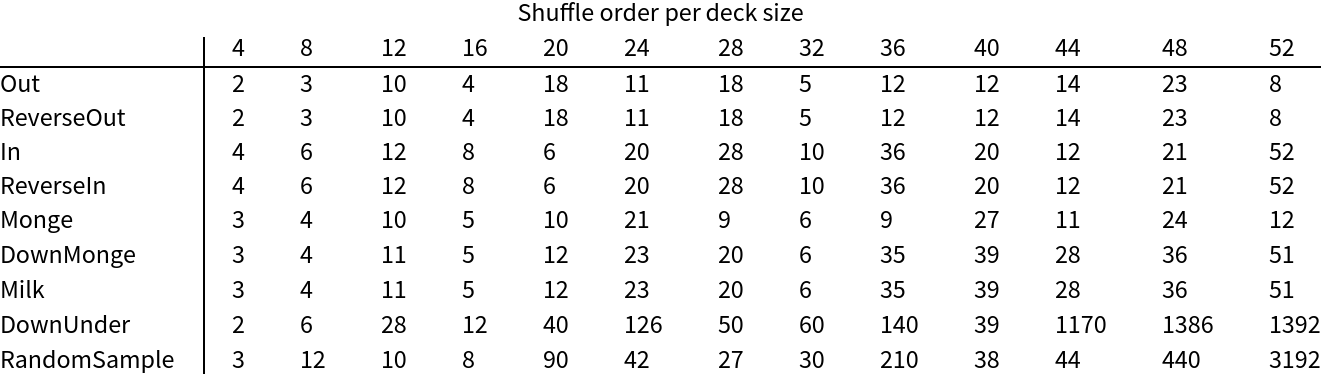
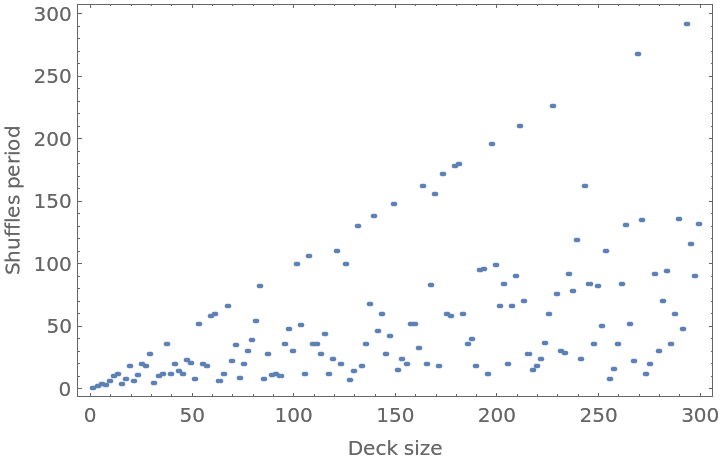
![Labeled[TableForm[
Table[ResourceFunction["ShuffleOrder"][
ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][type], #] & /@ range, {type, ResourceFunction["Shuffle"]["Types"]}], TableHeadings -> {ResourceFunction["Shuffle"]["Types"], range}], "Shuffle order per deck size", Top]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/6c6/6c6e1d1b-ee3c-41f3-a57e-8c7e5d796671/2dcc1e782821789e.png)
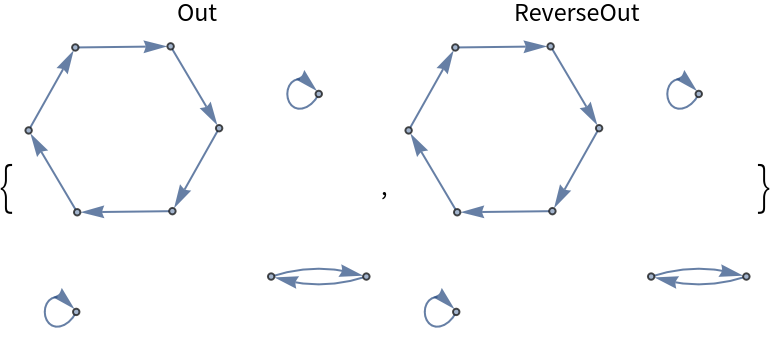
![Labeled[ResourceFunction["PermutationCyclesGraph"][
ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][Range[10], #]], #, Top] & /@ {"Out", "ReverseOut"}](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/6c6/6c6e1d1b-ee3c-41f3-a57e-8c7e5d796671/0d3cf04e2933e507.png)


![Table[ListPlot[
Callout /@ ResourceFunction["Shuffle"][Range[10], n, "Monge"], PlotLabel -> ToString[n] <> "-shuffle"], {n, 1, 6}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/6c6/6c6e1d1b-ee3c-41f3-a57e-8c7e5d796671/7074fd4cd1b92f48.png)
