Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Represent an array as polyomino regions
ResourceFunction["PolyominoPlot"][mat] for matrix mat, aggregates adjacent identical values and plots the result as a configuration of polyominoes. |
Plot a chair tromino next to a monomino:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |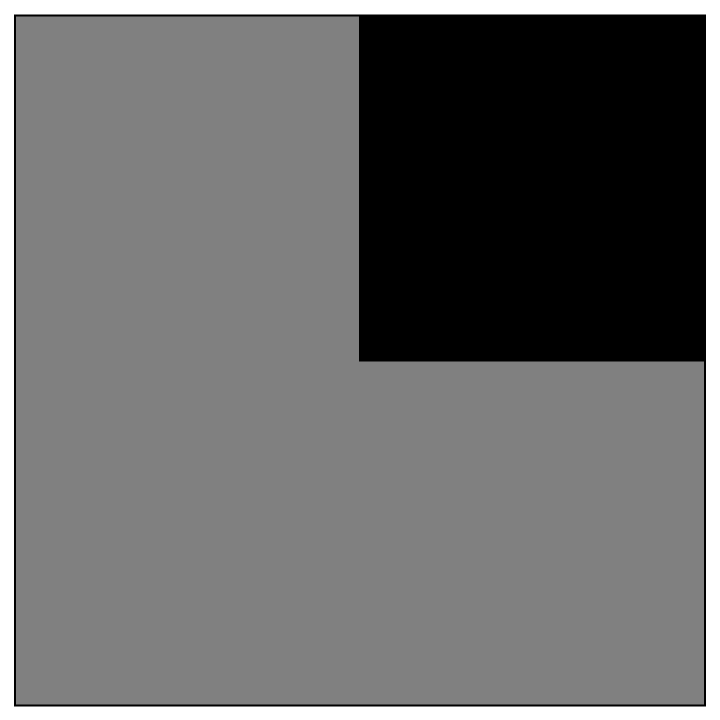  |
Plot two chair trominoes next to three monominoes:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 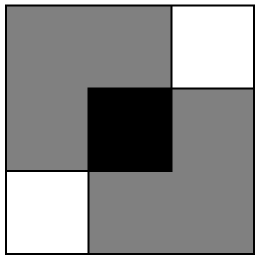 |
A random polyomino plot over four values:
| In[3]:= | ![With[{seed = SeedRandom[123]},
ResourceFunction["PolyominoPlot"][RandomInteger[{1, 4}, {5, 10}]]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/09a/09acd48d-13f8-4b3c-8853-77887c594dd9/4494bff63b5a61ac.png) |
| Out[3]= |  |
Add color by setting ColorRules:
| In[4]:= | ![With[{seed = SeedRandom[123]},
ResourceFunction["PolyominoPlot"][RandomInteger[3, {5, 10}],
ColorRules -> {0 -> Yellow, 1 -> Red, 2 -> Darker[Green, .3], 3 -> Blue}
]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/09a/09acd48d-13f8-4b3c-8853-77887c594dd9/4fdb8c308dec0d06.png) |
| Out[4]= | 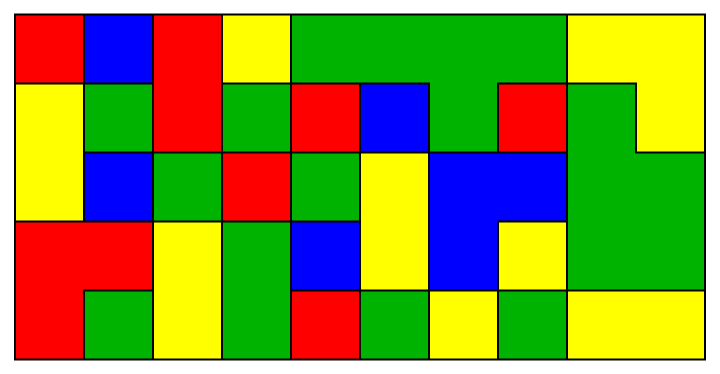 |
Colors can also be added by setting ColorFunction:
| In[5]:= | ![With[{seed = SeedRandom[123]},
ResourceFunction["PolyominoPlot"][RandomInteger[3, {5, 10}],
ColorFunction -> Function[Hue[#/4]]
]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/09a/09acd48d-13f8-4b3c-8853-77887c594dd9/123e5f9ed54f684c.png) |
| Out[5]= | 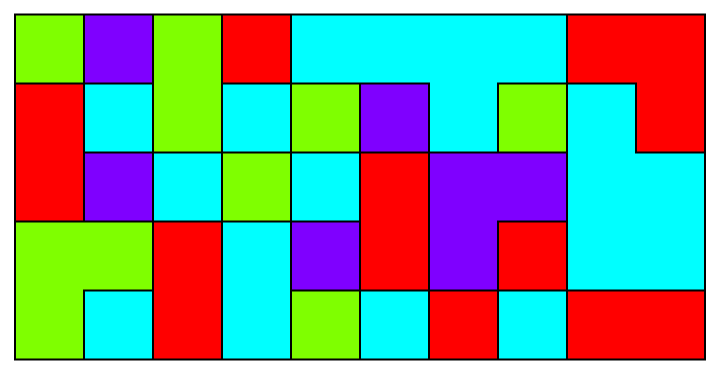 |
Override the edge style interior to Graphics:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= | 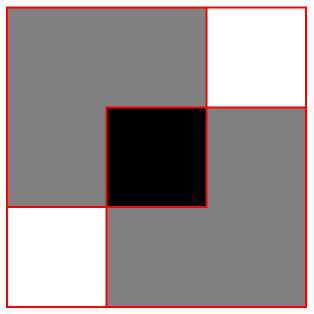 |
PolyominoPlot differs from ArrayPlot in its ability to draw region boundaries:
| In[7]:= | ![With[{seed = SeedRandom[123]},
#[RandomInteger[3, {5, 10}],
ColorRules -> {0 -> Yellow, 1 -> Red, 2 -> Darker[Green, .3], 3 -> Blue},
Apply[Sequence, If[SameQ[#, ArrayPlot],
{Mesh -> All, MeshStyle -> Black}, {}]]
]] & /@ {ResourceFunction["PolyominoPlot"], ArrayPlot}](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/09a/09acd48d-13f8-4b3c-8853-77887c594dd9/33ef7b01f407687c.png) |
| Out[7]= | 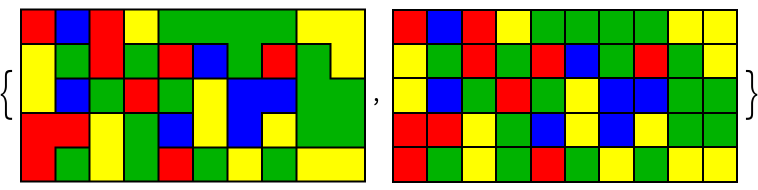 |
Unlike ArrayPlot, colors are not strictly necessary:
| In[8]:= | ![With[{seed = SeedRandom[123]},
#[RandomInteger[3, {5, 10}],
ColorFunction -> Function[null, White]
]] & /@ {ResourceFunction["PolyominoPlot"], ArrayPlot}](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/09a/09acd48d-13f8-4b3c-8853-77887c594dd9/33164ec05941982a.png) |
| Out[8]= | 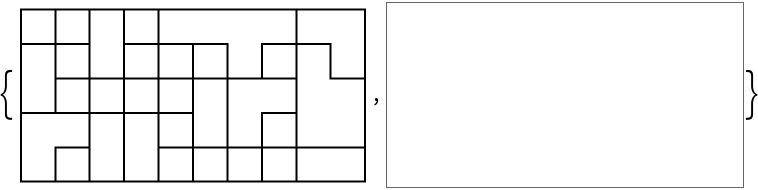 |
PolyominoPlot can achieve finer results than ArrayMesh:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= | 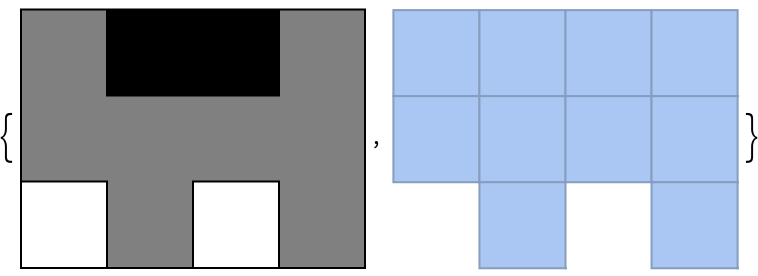 |
Plot a solution to Scott's pentomino problem:
| In[10]:= | ![With[{sol = {{3, 3, 2, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4}, {3, 2, 2, 2, 5, 5, 5, 6}, {3, 3, 2, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6}, {7, 7, 8, 0, 0, 13, 13, 6}, {7, 7, 8, 0, 0,
11, 13, 13}, {9, 7, 8, 11, 11, 11, 12, 13}, {9, 8, 8, 11, 10, 12, 12, 12}, {9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 10, 10, 12}}},
ResourceFunction["PolyominoPlot"][sol, ColorFunction -> Function[
If[SameQ[#, 0], Gray, Lighter[Hue[#/16], 1/1.5]]],
"GraphicsStyle" -> Directive[Thick, EdgeForm[Gray]]
]
]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/09a/09acd48d-13f8-4b3c-8853-77887c594dd9/068061c3572cd527.png) |
| Out[10]= | 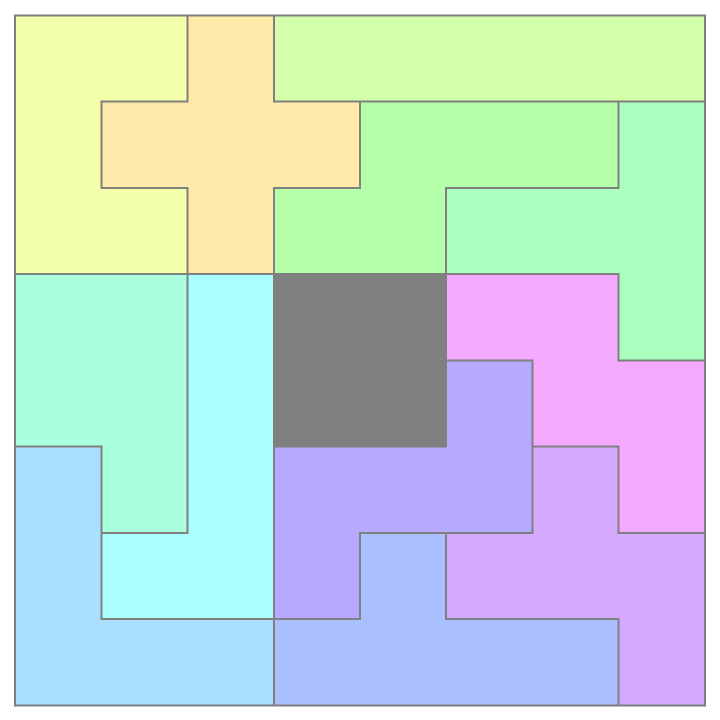 |
Plot a solution to the heart puzzle:
| In[11]:= | ![With[{sol = {{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 3, 5, 5, 5, 0, 0, 6, 6, 7, 7, 0, 0}, {0, 3, 3, 3, 11, 11, 11, 11, 6, 6, 9, 7, 8, 0}, {0, 4, 3, 12, 11, 10, 10, 10, 10, 9, 9, 9, 8, 0}, {0, 4, 12, 12, 14, 14, 14, 14, 2, 17, 17, 8, 8, 0}, {0, 0, 12, 13, 13, 14, 21, 20, 20, 20, 17, 17, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 13, 13, 13, 1, 21, 20, 18, 20, 19, 17, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 15, 15, 21, 21, 21, 18, 19, 19, 0,
0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 15, 22, 22, 22, 18, 19, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0,
0, 15, 15, 16, 22, 18, 19, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 16, 16, 22, 18, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 16, 16, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}}},
ResourceFunction["PolyominoPlot"][sol, ColorFunction -> Function[
If[SameQ[#, 0], White, Lighter[Hue[#/23], 1/1.5]]],
"GraphicsStyle" -> Directive[Thick, EdgeForm[Gray]]
]
]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/09a/09acd48d-13f8-4b3c-8853-77887c594dd9/7647cd3e7732f05f.png) |
| Out[11]= | 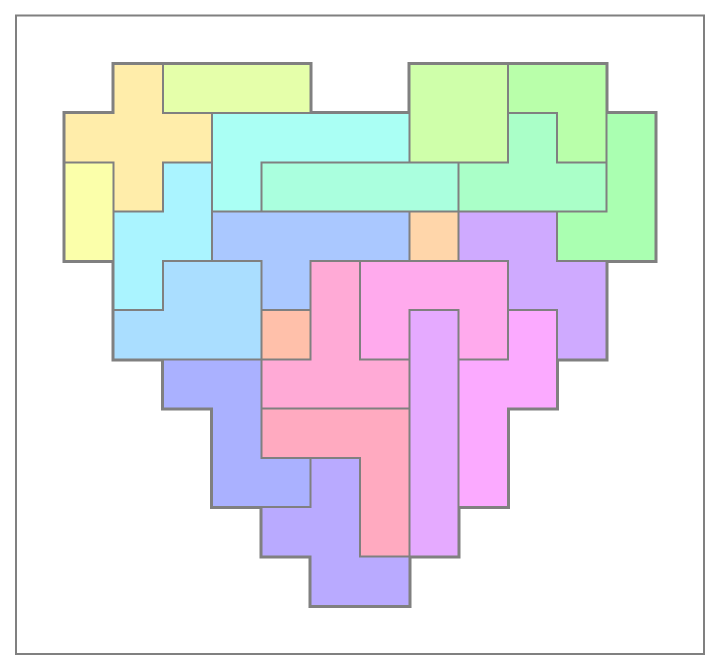 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License