Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Perform persistent homology on a point cloud dataset
ResourceFunction["PersistentHomology"][{e1,e2,…}] performs persistent homology on the ei and returns a PersistentHomologyObject that can be queried for results. | |
ResourceFunction["PersistentHomology"][{e1,e2,…},"Modulus"→p] performs persistent homology over the coefficient field ℤp. |
| "Distance" | "Maximal" | the maximal distance scale to perform homology |
| "Modulus" | 2 | the characteristic of the coefficient field used |
Perform persistent homology on random data:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |  |
Query the output for the barcode:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 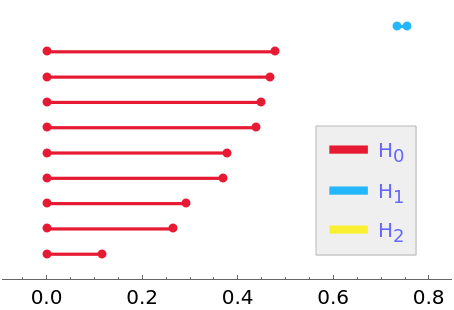 |
Visualize the MeshRegion for the H1 generator found:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= | 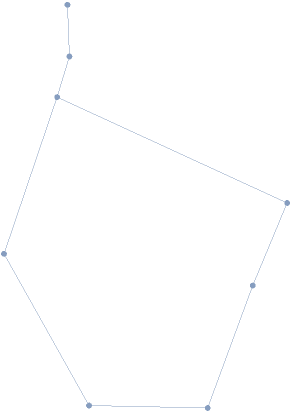 |
PersistentHomology can be performed for data of any dimension:
| In[4]:= |
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |  |
Evaluate the persistent homology of data with dimension 1000:
| In[6]:= |
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |  |
The maximum distance used in computations can be specified:
| In[8]:= |
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |  |
This will sometimes speed up computation times:
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= | 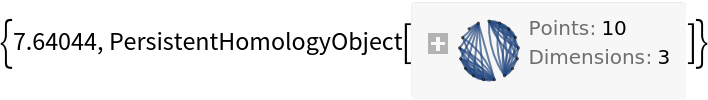 |
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= | 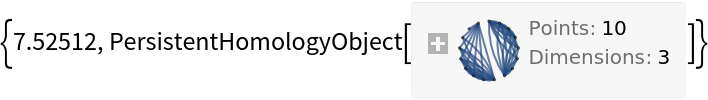 |
The finite field chosen for computations can be specified:
| In[12]:= |
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |  |
PersistentHomology is invariant under isometries:
| In[14]:= |
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= | 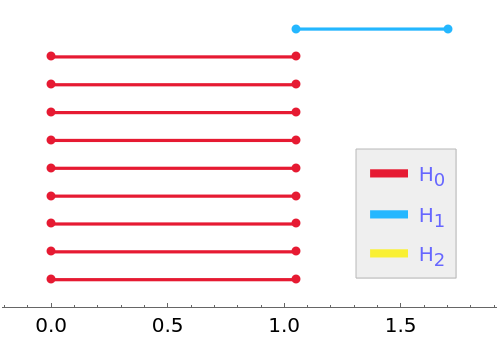 |
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= | 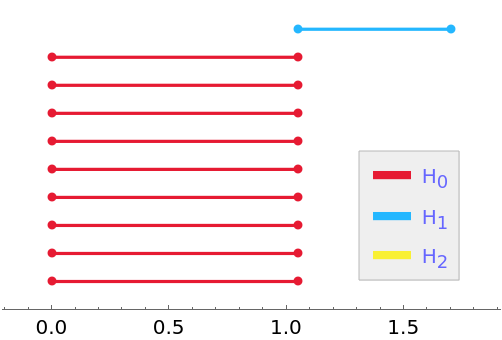 |
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= | 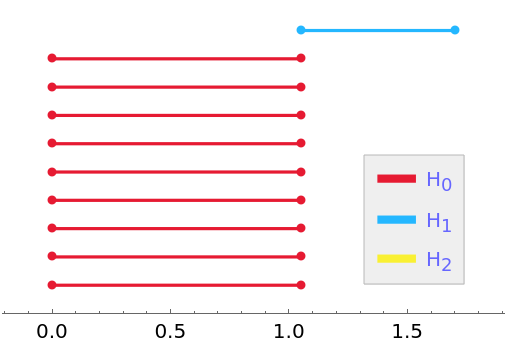 |
PersistentHomology computation times grow quickly in the number of data points:
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= | 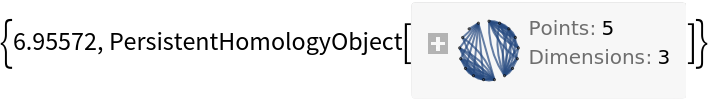 |
| In[19]:= |
| Out[19]= | 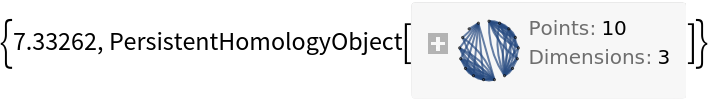 |
| In[20]:= |
| Out[20]= |  |
| In[21]:= |
| Out[21]= |  |
Draw some data in ![]() and perform PersistentHomology on it:
and perform PersistentHomology on it:
| In[22]:= | ![DynamicModule[{data = {}, phom = Graphics[{}]},
Column[{
Button["Compute", phom = ResourceFunction["PersistentHomology"][data]["Barcode"]],
Row@{ClickPane[
Framed@Dynamic[
ListPlot[data, PlotRange -> { {-1, 1}, {-1, 1} }, PlotStyle -> PointSize[Large], ImageSize -> 250, PlotLabel -> Length[data]], Initialization :> {introdata = {{-0.6276498538011699, 0.2755882642199108}, {-0.4923245614035091, 0.5533552010221645}, {-0.2955729166666671, 0.6799858764026732}, {-0.09562317251462027, 0.5479957591277764}, {-0.1305738304093571, 0.16936042970631437`}, {-0.3572505482456144, -0.12215624768016273`}, {-0.5747898391812869, 0.00902071289351639}, {
0.25758406432748493`, 0.46985879247442125`}, {
0.413788377192982, 0.7182412030281331}, {
0.7561220760233913, 0.6458332949515377}, {
0.7347176535087716, 0.19375513074283965`}, {
0.6180327119883036, -0.1418198551823316}, {
0.4325886330409352, -0.18868725050704988`}, {
0.20876736111111072`, -0.11716642246814621`}, {
0.19435307017543813`, 0.19434651743463421`}}}], AppendTo[data, #] &], Dynamic[Show[phom, ImageSize -> 250]]}
}, Alignment -> Left
]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/9c9/9c999c34-06e3-4e38-8f6b-7c01e218eac6/3d55470c9862078d.png) |
| Out[22]= | 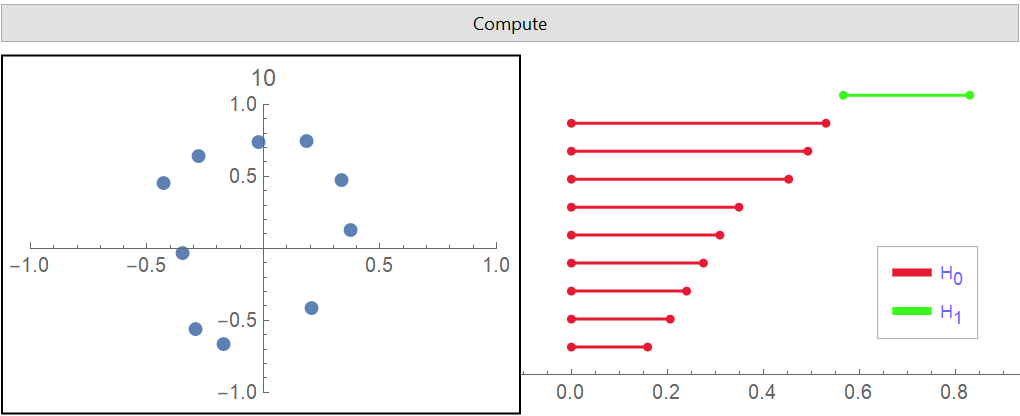 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License