Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Generate a periodic pattern
ResourceFunction["PeriodicPatternGenerator"][{n,{x,y},disp}] creates a periodic square array with a side length of x×y based on repeated x×y rectangles filled with the digits of integer n in base 2 with displacement disp on subsequent rows. | |
ResourceFunction["PeriodicPatternGenerator"][{n,{x,y},disp,b}] uses base b. |
Create a periodic pattern based on the binary expansion of 3::
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
Show a binary periodic pattern:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 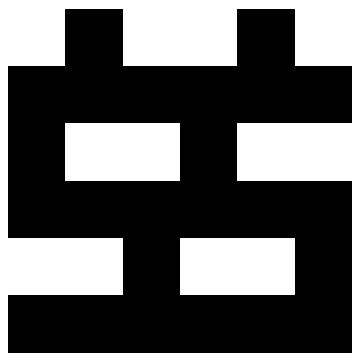 |
Show the order 2 binary periodic patterns (horizontal stripes, vertical stripes, checkerboard):
| In[3]:= | ![order2 = {{1, {1, 2}, 0}, {1, {2, 1}, 0}, {1, {2, 1}, 1}};
Row[Column[{#, ArrayPlot[ArrayFlatten[Table[
ResourceFunction["PeriodicPatternGenerator"][#], {4}, {4}]],
PixelConstrained -> 11, Mesh -> {7, 7}]}] & /@ order2, Spacer[10]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/68b/68b333da-867a-435f-9fae-278c431154e3/6d1bc14e3afe6633.png) |
| Out[4]= | 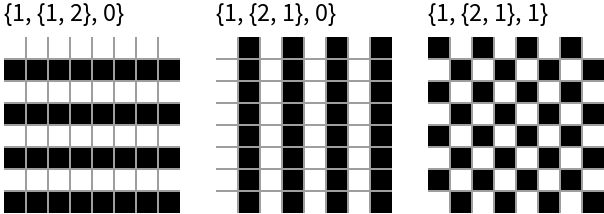 |
Show all eight order 3 binary periodic patterns:
| In[5]:= | ![order3 = {{1, {1, 3}, 0}, {1, {3, 1}, 0}, {1, {3, 1}, 1}, {1, {3, 1}, 2}, {3, {1, 3}, 0}, {3, {3, 1}, 0}, {3, {3, 1}, 1}, {3, {3, 1}, 2}};
Grid[Partition[Column[{#, ArrayPlot[ArrayFlatten[Table[
ResourceFunction["PeriodicPatternGenerator"][#], {3}, {3}]],
PixelConstrained -> 10, Mesh -> {8, 8}]}] & /@ order3, 4], Frame -> All]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/68b/68b333da-867a-435f-9fae-278c431154e3/3ec8df342c6b024a.png) |
| Out[6]= |  |
Show all twenty order 4 periodic patterns (with Tooltips):
| In[7]:= | ![Grid[Partition[Tooltip[ArrayPlot[ArrayFlatten[Table[
ResourceFunction["PeriodicPatternGenerator"][#], {3}, {3}]],
PixelConstrained -> 6, Mesh -> {11, 11}], #] & /@ {{1, {1, 4}, 0}, {1, {2, 2}, 0}, {1, {2, 2}, 1}, {1, {4, 1}, 0}, {1, {4, 1}, 1}, {1, {4, 1}, 2}, {1, {4, 1}, 3}, {3, {1, 4}, 0}, {3, {4, 1}, 0}, {3, {4, 1}, 1}, {3, {4, 1}, 2}, {3, {4, 1}, 3}, {5, {2, 2}, 1}, {7, {1, 4}, 0}, {7, {2, 2}, 0}, {7, {2, 2}, 1}, {7, {4, 1}, 0}, {7, {4, 1}, 1}, {7, {4, 1}, 2}, {7, {4, 1}, 3}}, 5], Frame -> All]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/68b/68b333da-867a-435f-9fae-278c431154e3/5a153859008f4028.png) |
| Out[7]= | 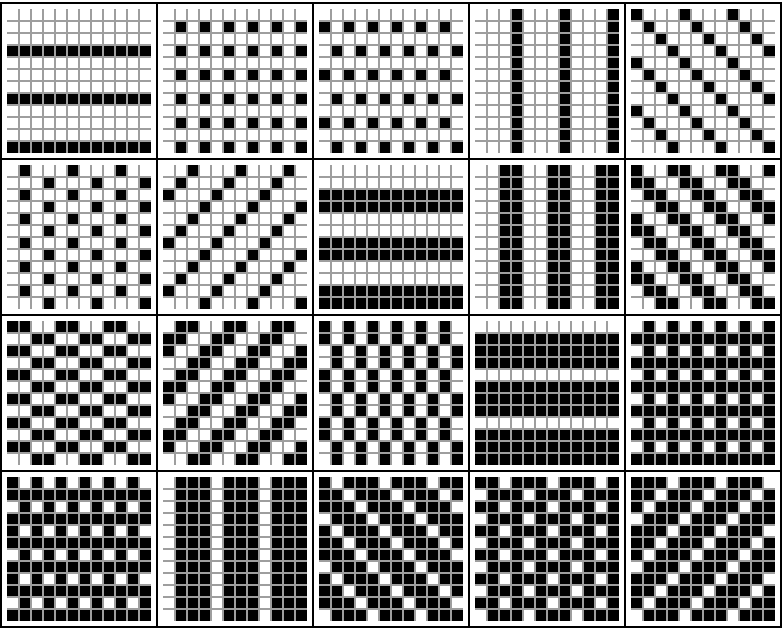 |
These periodic patterns are equivalent by displacement:
| In[8]:= | ![Table[ArrayPlot[
ArrayFlatten[
Table[ResourceFunction[
"PeriodicPatternGenerator"][{2^k, {2, 2}, 0}], {2}, {2}]], ImageSize -> Tiny], {k, 0, 3}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/68b/68b333da-867a-435f-9fae-278c431154e3/1612bff15c48dcda.png) |
| Out[8]= | 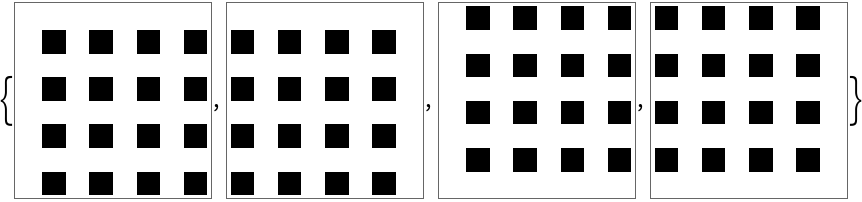 |
There are 8 order-3 ternary periodic patterns:
| In[9]:= | ![Grid[Partition[Tooltip[ArrayPlot[ArrayFlatten[Table[
ResourceFunction["PeriodicPatternGenerator"][#], {3}, {3}]],
PixelConstrained -> 6, Mesh -> {8, 8}], #] & /@ {{11, {1, 3}, 0,
3}, {11, {3, 1}, 0, 3}, {11, {3, 1}, 1, 3}, {11, {3, 1}, 2, 3}, {15, {1, 3}, 0, 3}, {15, {3, 1}, 0, 3}, {15, {3, 1}, 1, 3}, {15, {3, 1}, 2, 3}}, 4], Frame -> All]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/68b/68b333da-867a-435f-9fae-278c431154e3/3984fc9ee0b14848.png) |
| Out[9]= | 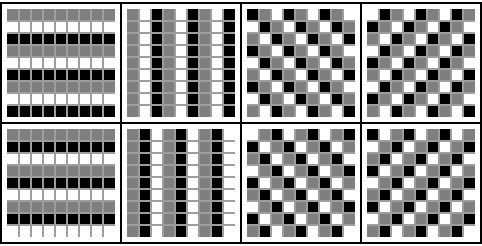 |
There are 65 order-4 ternary periodic patterns:
| In[10]:= | ![Grid[Partition[Tooltip[ArrayPlot[ArrayFlatten[Table[
ResourceFunction["PeriodicPatternGenerator"][#], {2}, {2}]],
PixelConstrained -> 6, Mesh -> {7, 7}], #] & /@ {{11, {1, 4}, 0,
3}, {11, {2, 2}, 0, 3}, {11, {2, 2}, 1, 3}, {11, {4, 1}, 0, 3}, {11, {4, 1}, 1, 3}, {11, {4, 1}, 2, 3}, {11, {4, 1}, 3, 3}, {15, {1, 4}, 0, 3}, {15, {2, 2}, 0, 3}, {15, {2, 2}, 1, 3}, {15, {4, 1}, 0, 3}, {15, {4, 1}, 1, 3}, {15, {4, 1}, 2, 3}, {15, {4, 1}, 3, 3}, {21, {1, 4}, 0, 3}, {21, {2, 2}, 0, 3}, {21, {4, 1}, 0, 3}, {21, {4, 1}, 1, 3}, {21, {4, 1}, 2, 3}, {21, {4, 1}, 3, 3}, {32, {1, 4}, 0, 3}, {32, {2, 2}, 0, 3}, {32, {2, 2}, 1, 3}, {32, {4, 1}, 0, 3}, {32, {4, 1}, 1, 3}, {32, {4, 1}, 2, 3}, {32, {4, 1}, 3, 3}, {34, {1, 4}, 0, 3}, {34, {2, 2}, 0, 3}, {34, {2, 2}, 1, 3}, {34, {4, 1}, 0, 3}, {34, {4, 1}, 1, 3}, {34, {4, 1}, 2, 3}, {34, {4, 1}, 3, 3}, {35, {1, 4}, 0, 3}, {35, {2, 2}, 0, 3}, {35, {2, 2}, 1, 3}, {35, {4, 1}, 0, 3}, {35, {4, 1}, 1, 3}, {35, {4, 1}, 2, 3}, {35, {4, 1}, 3, 3}, {38, {2, 2}, 0, 3}, {38, {2, 2}, 1, 3}, {42, {1, 4}, 0, 3}, {42, {4, 1}, 0, 3}, {42, {4, 1}, 1, 3}, {42, {4, 1}, 2, 3}, {42, {4, 1}, 3, 3}, {45, {2, 2}, 0, 3}, {45, {2, 2}, 1, 3}, {47, {1, 4}, 0, 3}, {47, {2, 2}, 0, 3}, {47, {2, 2}, 1, 3}, {47, {4, 1}, 0, 3}, {47, {4, 1}, 1, 3}, {47, {4, 1}, 2, 3}, {47, {4, 1}, 3, 3}, {51, {1, 4}, 0, 3}, {51, {2, 2}, 0, 3}, {51, {2, 2}, 1, 3}, {51, {4, 1}, 0, 3}, {51, {4, 1}, 1, 3}, {51, {4, 1}, 2, 3}, {51, {4, 1}, 3, 3}, {65, {2, 2}, 0, 3}}, UpTo[10]]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/68b/68b333da-867a-435f-9fae-278c431154e3/2366bdb0338e96b9.png) |
| Out[10]= | 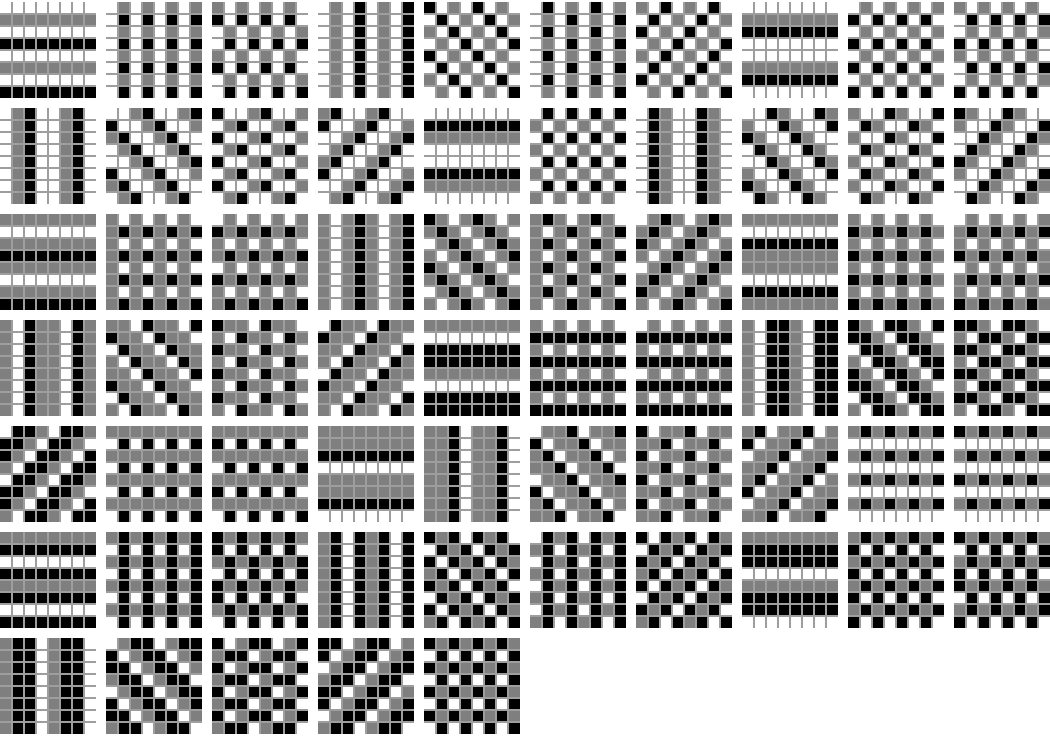 |
Boring patterns usually have a simpler representation:
| In[11]:= | ![ArrayPlot[
ArrayFlatten[
Table[ResourceFunction[
"PeriodicPatternGenerator"][{4095, {3, 4}, 2}], {2}, {2}]],
PixelConstrained -> 3, Frame -> False]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/68b/68b333da-867a-435f-9fae-278c431154e3/42d19e5723f58fa7.png) |
| Out[11]= |  |
| In[12]:= | ![ArrayPlot[
ArrayFlatten[
Table[ResourceFunction[
"PeriodicPatternGenerator"][{1, {1, 1}, 0}], {24}, {24}]],
PixelConstrained -> 3, Frame -> False]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/68b/68b333da-867a-435f-9fae-278c431154e3/4cce38c498fb7c0d.png) |
| Out[12]= |  |
Using PeriodicPatternGenerator, CanonicalListRotation and a brute force algorithm, we can find all displacement-distinct binary patterns up to order 9, given here as a convenience:
| In[13]:= |
Show all 180 order 5 ternary patterns:
| In[14]:= | ![Grid[Transpose[
Partition[
Tooltip[ArrayPlot[
ArrayFlatten[
Table[ResourceFunction[
"PeriodicPatternGenerator"][#], {2}, {2}]],
PixelConstrained -> 3, Frame -> False], #] & /@ {{11, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {11, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {11, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {11, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {11, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {11, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {15, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {15, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {15, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {15, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {15, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {15, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {19, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {19, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {19, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {19, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {19, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {19, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {21, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {21, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {21, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {21, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {21, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {21, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {32, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {32, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {32, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {32, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {32, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {32, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {34, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {34, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {34, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {34, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {34, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {34, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {35, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {35, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {35, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {35, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {35, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {35, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {38, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {38, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {38, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {38, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {38, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {38, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {42, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {42, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {42, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {42, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {42, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {42, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {47, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {47, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {47, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {47, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {47, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {47, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {48, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {48, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {48, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {48, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {48, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {48, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {51, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {51, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {51, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {51, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {51, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {51, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {61, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {61, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {61, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {61, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {61, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {61, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {66, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {66, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {66, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {66, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {66, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {66, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {69, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {69, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {69, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {69, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {69, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {69, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {75, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {75, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {75, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {75, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {75, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {75, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {95, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {95, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {95, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {95, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {95, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {95, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {97, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {97, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {97, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {97, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {97, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {97, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {98, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {98, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {98, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {98, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {98, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {98, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {103, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {103, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {103, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {103, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {103, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {103, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {104, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {104, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {104, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {104, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {104, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {104, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {106, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {106, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {106, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {106, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {106, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {106, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {107, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {107, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {107, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {107, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {107, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {107, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {123, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {123, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {123, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {123, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {123, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {123, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {128, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {128, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {128, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {128, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {128, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {128, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {132, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {132, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {132, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {132, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {132, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {132, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {140, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {140, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {140, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {140, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {140, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {140, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {143, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {143, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {143, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {143, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {143, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {143, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {155, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {155, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {155, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {155, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {155, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {155, {5, 1}, 4, 3}, {159, {1, 5}, 0, 3}, {159, {5, 1}, 0, 3}, {159, {5, 1}, 1, 3}, {159, {5, 1}, 2, 3}, {159, {5, 1}, 3, 3}, {159, {5, 1}, 4, 3}}, 12]], Frame -> All]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/68b/68b333da-867a-435f-9fae-278c431154e3/2ceb24e182115495.png) |
| Out[14]= | 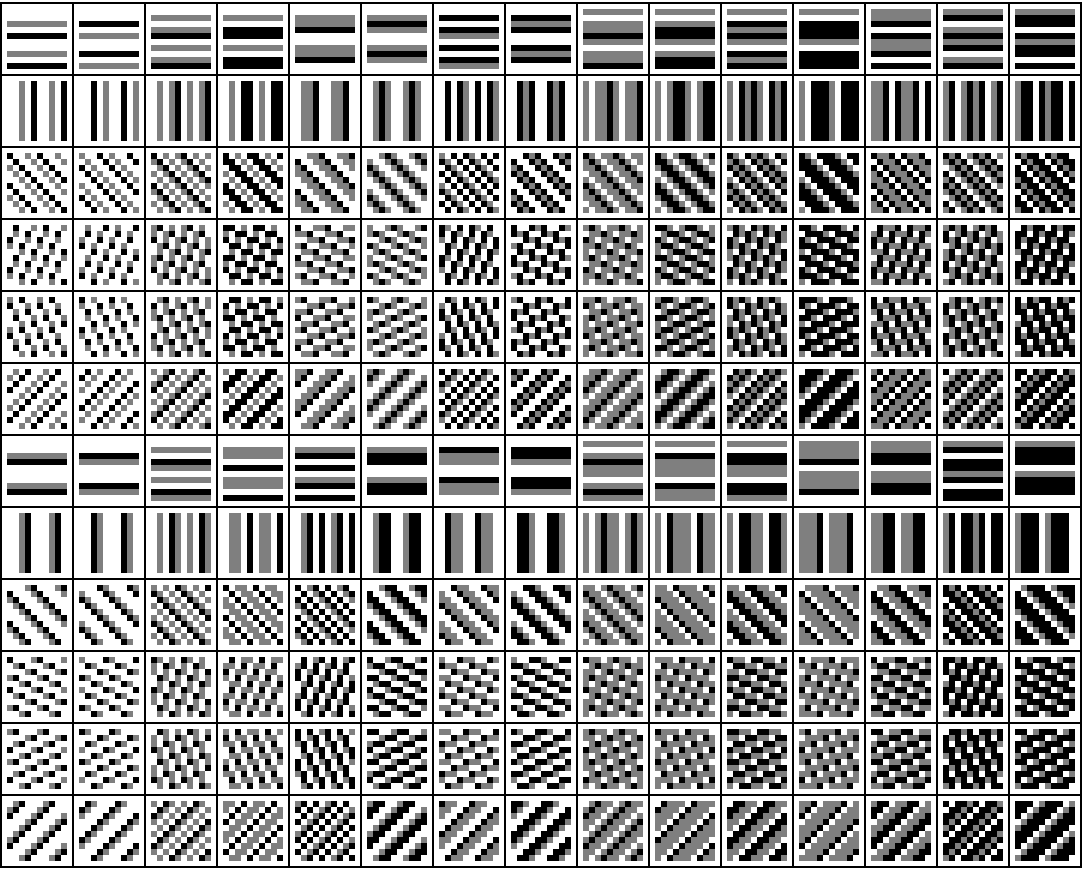 |
Show samples of the 129064 order 16 binary patterns:
| In[15]:= | ![Grid[Partition[
Tooltip[ArrayPlot[
ArrayFlatten[
Table[ResourceFunction[
"PeriodicPatternGenerator"][#], {2}, {2}]],
PixelConstrained -> 3, Frame -> False], #] & /@ {{499, {4, 4}, 2}, {1443, {16, 1}, 9}, {2773, {16, 1}, 8}, {3771, {16, 1}, 11}, {4447, {8, 2}, 6}, {4799, {16, 1}, 8}, {6037, {8, 2}, 3}, {6654, {8, 2}, 5}, {6783, {16, 1}, 2}, {6953, {16, 1}, 7}, {6969, {16, 1}, 7}, {7013, {8, 2}, 7}, {7423, {16, 1}, 8}, {7528, {4, 4}, 0}, {7757, {16, 1}, 4}, {9511, {16, 1}, 3}, {10107, {16, 1}, 15}, {10909, {8, 2}, 7}, {11707, {16, 1}, 15}, {11885, {16, 1}, 0}, {14325, {1, 16}, 0}, {14933, {4, 4}, 2}, {15317, {8, 2}, 6}, {16223, {16, 1}, 13}, {16346, {4, 4}, 2}},
5], Frame -> All]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/68b/68b333da-867a-435f-9fae-278c431154e3/23d4846614f02ae5.png) |
| Out[15]= | 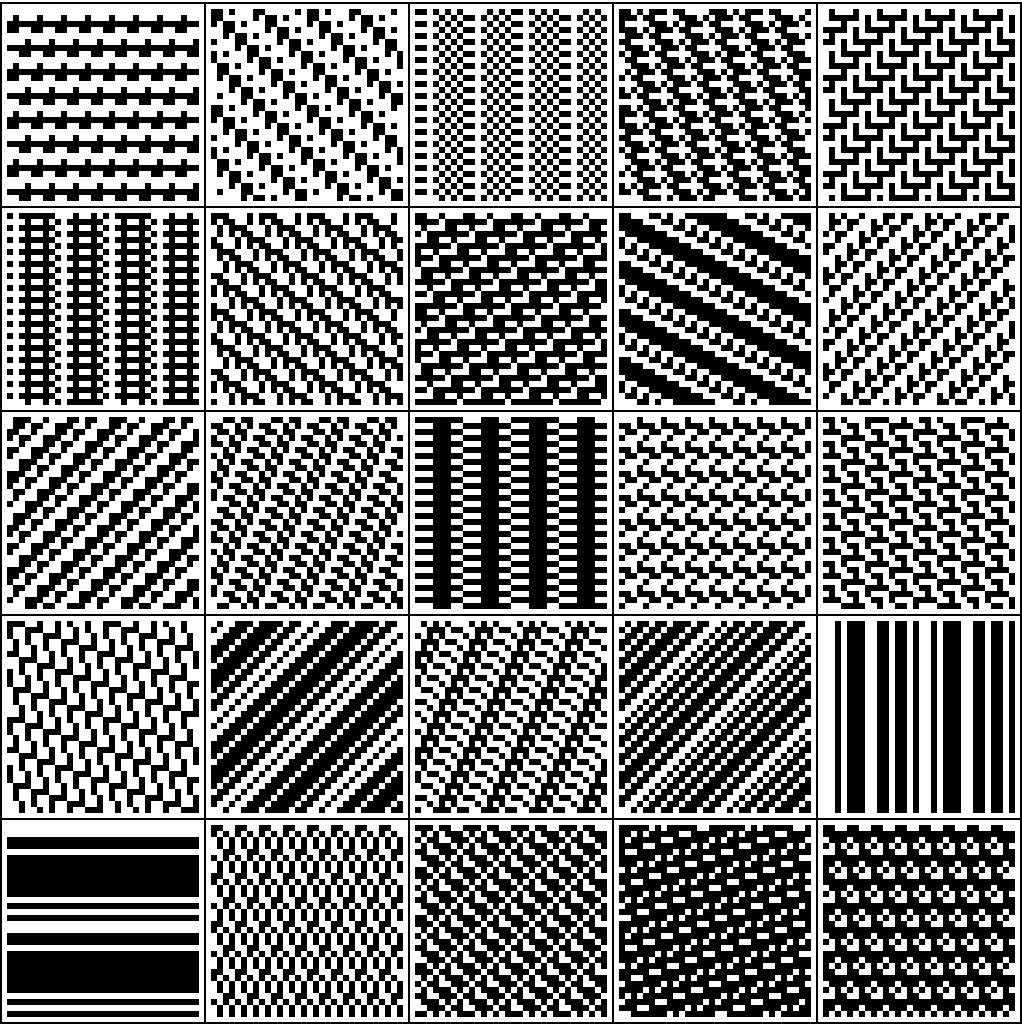 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License