Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Determine the value of an integral using a numerical method
ResourceFunction["NumericalIntegralApproximation"][f,{x,xmin,xmax},method] gives a numerical approximation to the integral |
| "Midpoint" | midpoint rule |
| "RightHand" | right Riemann sum |
| "LeftHand" | left Riemann sum |
| "Simpson" | Simpson's rule |
| "Trapezoidal" | trapezoidal rule |
| "Boole" | Boole's rule |
| "Intervals" | Automatic | the number of subintervals to divide the integral into |
| WorkingPrecision | MachinePrecision | the precision used in internal computations |
Integrate expressions using classic numerical methods such as Simpson’s rule:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
Compare left hand, right hand, and midpoint integrations:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |
Compute integrals with "Trapezoidal" or "Boole" rules:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
Increase accuracy by using multiple intervals:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |
Examine how increasing the number of intervals affects the result:
| In[8]:= | ![results = Table[ResourceFunction["NumericalIntegralApproximation"][
x^3 - x^2, {x, 1, 3}, "Midpoint", "Intervals" -> i], {i, 50}];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/e57/e57d8216-5c6b-4d21-9c07-d17b2731dbeb/4c1121f59c138459.png) |
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= | 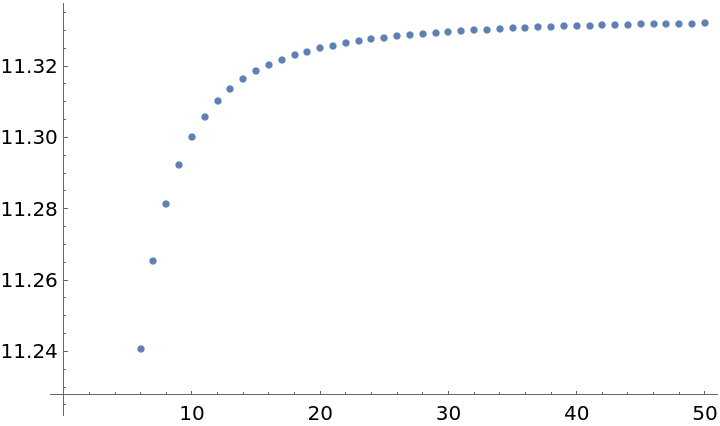 |
Compare the results to the exact answer:
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License