Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Fast numerical approximation to the PDF of the Voigt distribution with around 1.2% of maximum deviation
ResourceFunction["NPseudoVoigt"][x,b,σ] calculates the approximation at postions x of a Voigt distribution with CauchyDistribution parameter b and NormalDistribution parameter σ. |
NPseudoVoigt always returns numerical results, even for exact inputs:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
NPseudoVoigt compared to the analytic solution:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 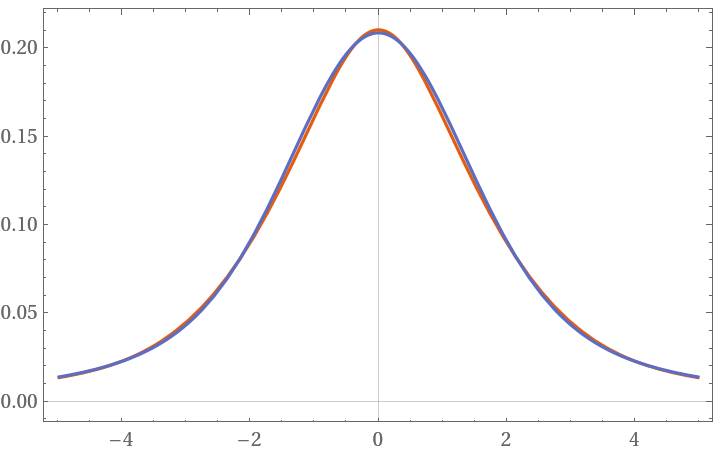 |
NPseudoVoigt automatically threads over lists:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |
NPseudoVoigt is approximately normed to 1 for b and σ greater than 0:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |
NPseudoVoigt's norm has four additional terms that cancel out for non-extreme values of b and σ:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
NPseudoVoigt's deviation to the analytic solution in the maximum is usually less than ±1% for every parameter combination b and σ:
| In[6]:= | ![PercentForm /@ MinMax[Table[(PDF[VoigtDistribution[b, \[Sigma]], 0] - ResourceFunction["NPseudoVoigt"][0, b, \[Sigma]])/
PDF[VoigtDistribution[b, \[Sigma]], 0], {b, 1/10, 3, 1/10}, {\[Sigma], 1/10, 3, 1/10}]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/558/55892d25-f133-44da-8df7-0a10d1a32781/7d87542eb294a67c.png) |
| Out[6]= |
NPseudoVoigt's relative deviation increases if b and σ approach one another:
| In[7]:= | ![Plot3D[(PDF[VoigtDistribution[b, \[Sigma]], 0] - ResourceFunction["NPseudoVoigt"][0, b, \[Sigma]])/
PDF[VoigtDistribution[b, \[Sigma]], 0], {b, 0.1, 3}, {\[Sigma], 0.1,
3}, PlotRange -> All]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/558/55892d25-f133-44da-8df7-0a10d1a32781/20ca6a985aa928c9.png) |
| Out[7]= | 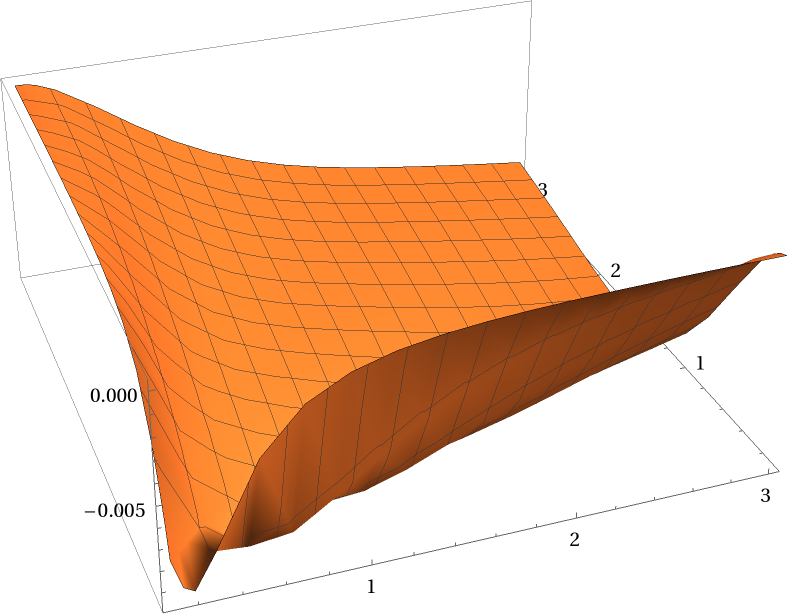 |
NPseudoVoigt is also stable against σ being 0:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
NPseudoVoigt can be compiled to obtain faster execution times:
| In[9]:= | ![data = Range[-5, 5, 0.0005];
Total[PDF[VoigtDistribution[1, 1], data]] // Timing (*analytical solution*)](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/558/55892d25-f133-44da-8df7-0a10d1a32781/4bc0420ecb0d5b25.png) |
| Out[3]= |
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
| In[11]:= | ![NPseudoVoigtC = Compile[{x, b, \[Sigma]}, Evaluate@
ResourceFunction["NPseudoVoigt"][x, b, \[Sigma]]]; (*compile*)
Total[NPseudoVoigtC[#, 1, 1] & /@ data] // Timing (*compiled [\[FilledSmallSquare]] NPseudoVoigt *)](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/558/55892d25-f133-44da-8df7-0a10d1a32781/4b1bf6c24a815c56.png) |
| Out[11]= |
Negative b parameters can produce imaginary values:
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |
Negative σ parameters do not yield symmetric values:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |
NPseudoVoigt can be used to approximate an atomic absorption spectrum efficiently:
| In[14]:= | ![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/0491b635-2333-4685-9024-5b7aae861c0e"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/558/55892d25-f133-44da-8df7-0a10d1a32781/04fd34fee436725c.png) |
| Out[15]= | 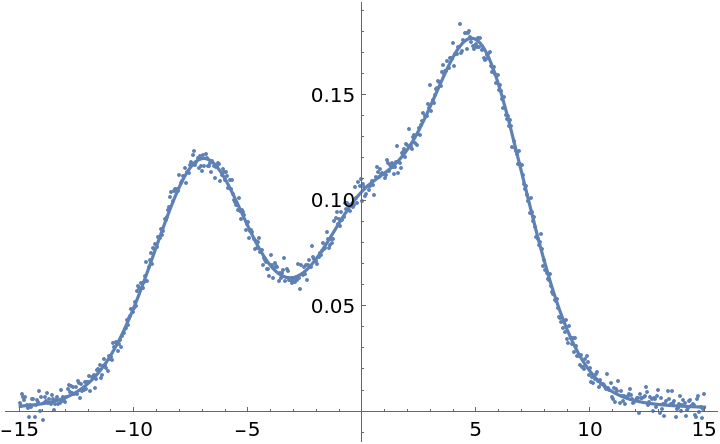 |
| Out[16]= |  |
NPseudoVoigt can be used to show that σ is negligible or even 0, whereas the VoigtDistribution could throw errors:
| In[17]:= | ![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/e6f1ac70-dd92-4c57-b5df-a43fc58904f8"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/558/55892d25-f133-44da-8df7-0a10d1a32781/368a7a33e46ae802.png) |
| Out[19]= |  |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License