Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Numerically evaluate the gradient of a function summed over the eigenvalues of a matrix, with respect to matrix parameters
ResourceFunction["NEigenvalueSumGradient"][f, m][x, y, …] finds the gradient of the function f summed over the eigenvalues of the matrix m[x,y,…]. |
Define a symmetric matrix function:
| In[1]:= | ![SeedRandom[49];
mat[x_, y_] = (# + Transpose[#]) &[
RandomInteger[10, {3, 3}] + RandomInteger[
10, {3, 3}] (RandomChoice[{x, y}, {3, 3}]^
RandomInteger[5, {3, 3}])];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d72/d72ef6e4-59b9-4c09-968b-62fd4f4fa122/6afc508b16b0d790.png) |
Find the gradient of the eigenvalue function #Log[#]& summed over the eigenvalues at x=1, y=1:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
Check:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[4]= |
A non-symmetric matrix:
| In[5]:= | ![SeedRandom[42];
mat[x_, y_] = RandomInteger[10, {3, 3, 2}] . {1, I} + RandomInteger[
10, {3, 3}] (RandomChoice[{x, y}, {3, 3}]^
RandomInteger[5, {3, 3}]);
mat[x, y] // MatrixForm](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d72/d72ef6e4-59b9-4c09-968b-62fd4f4fa122/754c570c2ecb7f74.png) |
| Out[7]= | 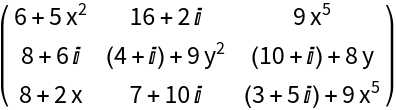 |
Find the gradient of the function Sin[#]Log[#]& summed over the eigenvalues at x=1, y=1:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
Check:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[10]= |
A somewhat large matrix with two parameters:
| In[11]:= | ![SeedRandom[1];
n = 10;
mat[x_, y_] = RandomReal[1, {n, n}] + RandomReal[
10, {n, n}] (RandomChoice[{x, y}, {n, n}]^
RandomInteger[5, {n, n}]);](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d72/d72ef6e4-59b9-4c09-968b-62fd4f4fa122/13e1680c31571cb4.png) |
Finding the eigenvalues of even a moderately large matrix with symbolic parameters is slow:
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |
Using NEigenvalueSumGradient is quick:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[14]= |
Check:
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= |
Very large matrix:
| In[16]:= | ![SeedRandom[1];
n = 1000;
mat[x_, y_] = RandomReal[1, {n, n}] + RandomReal[
1, {n, n}] (RandomChoice[{x, y}, {n, n}]^
RandomInteger[5, {n, n}]);](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d72/d72ef6e4-59b9-4c09-968b-62fd4f4fa122/6e1abd8dfb7ef04e.png) |
Using NEigenvalueSumGradient is reasonably quick:
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License