Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Represent a metric tensor (field) for a Riemannian or pseudo-Riemannian manifold
ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"]["name",…] represents a named metric tensor "name". | |
ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][{"name",…},…] represents a named parameterized metric tensor "name", with additional parameter(s) specified within a list. | |
ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][d,…] represents a generic d-dimensional (symmetric) metric tensor. | |
ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][…],coords] transforms a specified ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"] into the new coordinate system coords. | |
ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][…],i1,i2] transforms a specified ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"] into one with new indices i1 and i2 (with True representing a covariant index and False representing a contravariant one), raising and lowering existing indices as necessary. | |
ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][…],coords,i1,i2] transforms a specified ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"] into one with new coordinate system coords and new indices i1 and i2 (with True representing a covariant index and False representing a contravariant one), raising and lowering existing indices as necessary. |
| "Symmetric" | a generic 4-dimensional symmetric metric (whose matrix representation is populated with constants of the form gij=gji) |
| {"Symmetric",d} | a generic d-dimensional symmetric metric (whose matrix representation is populated with constants of the form gij=gji) |
| "SymmetricField" | a generic 4-dimensional symmetric metric tensor field (whose matrix representation is populated with functions of the chosen coordinates of the form gij=gji) |
| {"SymmetricField",d} | a generic d-dimensional symmetric metric tensor field (whose matrix representation is populated with functions of the chosen coordinates of the form gij=gji) |
| "Asymmetric" | a generic 4-dimensional asymmetric metric (whose matrix representation is populated with constants of the form gij≠gji) |
| {"Asymmetric",d} | a generic d-dimensional asymmetric metric (whose matrix representation is populated with constants of the form gij≠gji) |
| "AsymmetricField" | a generic 4-dimensional asymmetric metric tensor field (whose matrix representation is populated with functions of the chosen coordinates of the form gij≠gji) |
| {"AsymmetricField",d} | a generic d-dimensional asymmetric metric tensor field (whose matrix representation is populated with functions of the chosen coordinates of the form gij≠gji) |
| "Euclidean" | the metric for 3-dimensional flat/Euclidean space in Cartesian coordinates |
| {"Euclidean",d} | the metric for d-dimensional flat/Euclidean space in Cartesian coordinates |
| "Minkowski" | the metric for 4-dimensional (or 1+3-dimensional) flat/Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates |
| {"Minkowski",d} | the metric for d-dimensional (or 1+(d-1)-dimensional) flat/Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates |
| "Schwarzschild" | the metric describing the exterior spacetime geometry surrounding an uncharged, spherically-symmetric, non-rotating mass distribution (e.g. an uncharged, non-rotating black hole) in Schwarzschild/spherical polar coordinates, with purely symbolic mass "M" |
| {"Schwarzschild",M} | the metric describing the exterior spacetime geometry surrounding an uncharged, spherically-symmetric, non-rotating mass distribution (e.g. an uncharged, non-rotating black hole) in Schwarzschild/spherical polar coordinates, with numerical mass M |
| "IsotropicSchwarzschild" | the Schwarzschild metric represented in isotropic coordinates (i.e. the Cartesian-like coordinate system in which radial distances are defined such that light cones appear round), with purely symbolic mass "M" |
| {"IsotropicSchwarzschild",M} | the Schwarzschild metric represented in isotropic coordinates (i.e. the Cartesian-like coordinate system in which radial distances are defined such that light cones appear round), with numerical mass M |
| "EddingtonFinkelstein" | the Schwarzschild metric represented in Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system adapted to radial lightlike geodesics), with purely symbolic mass "M" |
| {"EddingtonFinkelstein",M} | the Schwarzschild metric represented in Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system adapted to radial lightlike geodesics), with numerical mass M |
| "IngoingEddingtonFinkelstein" | the Schwarzschild metric represented in ingoing Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system adapted to inward-traveling radial lightlike geodesics), with purely symbolic mass "M" |
| {"IngoingEddingtonFinkelstein",M} | the Schwarzschild metric represented in ingoing Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system adapted to inward-traveling radial lightlike geodesics), with numerical mass M |
| "OutgoingEddingtonFinkelstein" | the Schwarzschild metric represented in outgoing Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system adapted to outward-traveling radial lightlike geodesics), with purely symbolic mass "M" |
| {"OutgoingEddingtonFinkelstein",M} | the Schwarzschild metric represented in outgoing Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system adapted to outward-traveling radial lightlike geodesics), with numerical mass M |
| "GullstrandPainleve" | the Schwarzschild metric represented in Gullstrand-Painlevé coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system whose time coordinate follows the proper time of a free-falling observer from infinity), with purely symbolic mass "M" |
| {"GullstrandPainleve",M} | the Schwarzschild metric represented in Gullstrand-Painlevé coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system whose time coordinate follows the proper time of a free-falling observer from infinity), with numerical mass M |
| "IngoingGullstrandPainleve" | the Schwarzschild metric represented in ingoing Gullstrand-Painlevé coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system whose time coordinate follows the proper time of a free-falling observer, falling inwards from infinity), with purely symbolic mass "M" |
| {"IngoingGullstrandPainleve",M} | the Schwarzschild metric represented in ingoing Gullstrand-Painlevé coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system whose time coordinate follows the proper time of a free-falling observer, falling inwards from infinity), with numerical mass M |
| "OutgoingGullstrandPainleve" | the Schwarzschild metric represented in outgoing Gullstrand-Painlevé coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system whose time coordinate follows the proper time of a free-falling observer, falling outwards to infinity), with purely symbolic mass "M" |
| {"OutgoingGullstrandPainleve",M} | the Schwarzschild metric represented in outgoing Gullstrand-Painlevé coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system whose time coordinate follows the proper time of a free-falling observer, falling outwards to infinity), with numerical mass M |
| "KruskalSzekeres" | the Schwarzschild metric represented in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system that covers the entire spacetime manifold of the maximal analytic extension of the Schwarzschild solution), with purely symbolic mass "M" |
| {"KruskalSzekeres",M} | the Schwarzschild metric represented in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates (i.e. the coordinate system that covers the entire spacetime manifold of the maximal analytic extension of the Schwarzschild solution), with numerical mass M |
| "Kerr" | the metric describing the exterior spacetime geometry surrounding an uncharged, axially-symmetric, rotating mass distribution (e.g. an uncharged, spinning black hole) in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates, with purely symbolic mass "M" and purely symbolic angular momentum "J" |
| {"Kerr",M} | the metric describing the exterior spacetime geometry surrounding an uncharged, axially-symmetric, rotating mass distribution (e.g. an uncharged, spinning black hole) in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates, with numerical mass M and purely symbolic angular momentum "J" |
| {"Kerr",M,J} | the metric describing the exterior spacetime geometry surrounding an uncharged, axially-symmetric, rotating mass distribution (e.g. an uncharged, spinning black hole) in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates, with numerical mass M and numerical angular momentum J |
| "ReissnerNordstrom" | the metric describing the exterior spacetime geometry surrounding a charged, spherically-symmetric, non-rotating mass distribution (e.g. a charged, non-rotating black hole) in Schwarzschild/spherical polar coordinates, with purely symbolic (total) mass "M" and purely symbolic electric charge "Q" |
| {"ReissnerNordstrom",M} | the metric describing the exterior spacetime geometry surrounding a charged, spherically-symmetric, non-rotating mass distribution (e.g. a charged, non-rotating black hole) in Schwarzschild/spherical polar coordinates, with numerical (total) mass M and purely symbolic electric charge "Q" |
| {"ReissnerNordstrom",M,Q} | the metric describing the exterior spacetime geometry surrounding a charged, spherically-symmetric, non-rotating mass distribution (e.g. a charged, non-rotating black hole) in Schwarzschild/spherical polar coordinates, with numerical (total) mass M and numerical electric charge Q |
| "KerrNewman" | the metric describing the exterior spacetime geometry surrounding a charged, axially-symmetric, rotating mass distribution (e.g. a charged, spinning black hole) in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates, with purely symbolic (total) mass "M", purely symbolic angular momentum "J" and purely symbolic electric charge "Q" |
| {"KerrNewman",M} | the metric describing the exterior spacetime geometry surrounding a charged, axially-symmetric, rotating mass distribution (e.g. a charged, spinning black hole) in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates, with numerical (total) mass M, purely symbolic angular momentum "J" and purely symbolic electric charge "Q" |
| {"KerrNewman",M,J} | the metric describing the exterior spacetime geometry surrounding a charged, axially-symmetric, rotating mass distribution (e.g. a charged, spinning black hole) in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates, with numerical (total) mass M, numerical angular momentum J and purely symbolic electric charge "Q" |
| {"KerrNewman",M,J,Q} | the metric describing the exterior spacetime geometry surrounding a charged, axially-symmetric, rotating mass distribution (e.g. a charged, spinning black hole) in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates, with numerical (total) mass M, numerical angular momentum J and numerical electric charge Q |
| "Godel" | the metric describing the spacetime geometry of a rotating, dust-filled universe in Gödel's Cartesian-like coordinates, with purely symbolic angular velocity "" |
| {"Godel",ω} | the metric describing the spacetime geometry of a rotating, dust-filled universe in Gödel's Cartesian-like coordinates, with numerical angular velocity ω |
| "FLRW" | the metric describing the spacetime geometry of a homogeneous, isotropic universe which is either contracting or expanding in spherical polar coordinates, with purely symbolic global curvature "k" and purely symbolic scale factor "a" (treated as a function of coordinate time) |
| {"FLRW",k} | the metric describing the spacetime geometry of a homogeneous, isotropic universe which is either contracting or expanding in spherical polar coordinates, with numerical global curvature k and purely symbolic scale factor "a" (treated as a function of coordinate time) |
| {"FLRW",k,a} | the metric describing the spacetime geometry of a homogeneous, isotropic universe which is either contracting or expanding in spherical polar coordinates, with numerical global curvature k and numerical scale factor a (treated as a function of coordinate time) |
| "MatrixRepresentation" | metric tensor represented in explicit matrix form |
| "ReducedMatrixRepresentation" | metric tensor represented in explicit matrix form, modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "Coordinates" | list of coordinate symbols for the metric tensor |
| "CoordinateOneForms" | list of differential 1-form symbols for the coordinates of the metric tensor |
| "Indices" | list of booleans specifying whether each index is lowered/covariant (True) or raised/contravariant (False) |
| "CovariantQ" | whether the metric tensor is covariant (i.e. both indices are lowered/covariant) |
| "ContravariantQ" | whether the metric tensor is contravariant (i.e. both indices are raised/contravariant) |
| "MixedQ" | whether the metric tensor is mixed (i.e. one index is lowered/covariant and one index is raised/contravariant) |
| "Symbol" | symbolic representation of the metric tensor with appropriately raised/lowered indices |
| "Dimensions" | number of dimensions of the manifold/spacetime represented by the metric tensor |
| "SymmetricQ" | whether the metric tensor is symmetric (i.e. is represented by a symmetric matrix in covariant form) |
| "DiagonalQ" | whether the metric tensor is diagonal (i.e. is represented by a diagonal matrix in covariant form) |
| "Signature" | list of +1s and -1s designating the signature of the metric tensor (+1 for each positive eigenvalue, -1 for each negative eigenvalue) |
| "RiemannianQ" | whether the metric tensor describes a Riemannian manifold (i.e. all eigenvalues have the same sign) |
| "PseudoRiemannianQ" | whether the metric tensor describes a pseudo-Riemannian manifold (i.e. all eigenvalues are non-zero, but not all have the same sign) |
| "LorentzianQ" | whether the metric tensor describes a Lorentzian manifold (i.e. all eigenvalues have the same sign, except for one eigenvalue which has the opposite sign) |
| "RiemannianConditions" | list of conditions required to guarantee that the manifold described by the metric tensor is Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues are positive) |
| "PseudoRiemannianConditions" | list of conditions required to guarantee that the manifold described by the metric tensor is pseudo-Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues are non-zero) |
| "LorentzianConditions" | list of conditions required to guarantee that the manifold described by the metric tensor is Lorentzian (i.e. the "time" eigenvalue is negative and all other eigenvalues are positive) |
| "MetricSingularities" | list of possible coordinate values that cause the metric tensor to become singular |
| "Determinant" | determinant of the metric tensor (represented in covariant matrix form) |
| "ReducedDeterminant" | determinant of the metric tensor (represented in covariant matrix form), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "Trace" | trace of the metric tensor |
| "ReducedTrace" | trace of the metric tensor, modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "Eigenvalues" | eigenvalues of the metric tensor (represented in covariant matrix form) |
| "ReducedEigenvalues" | eigenvalues of the metric tensor (represented in covariant matrix form), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "Eigenvectors" | eigenvectors of the metric tensor (represented in covariant matrix form) |
| "ReducedEigenvectors" | eigenvectors of the metric tensor (represented in covariant matrix form), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "MetricTensor" | covariant form of the metric tensor (i.e. both indices are lowered/covariant) |
| "InverseMetricTensor" | contravariant form of the metric tensor (i.e. both indices are raised/contravariant) |
| "LineElement" | metric tensor represented as a line element (i.e. an algebraic relationship between "ds" and the differential 1-form symbols for the coordinates) |
| "ReducedLineElement" | metric tensor represented as a line element (i.e. an algebraic relationship between "ds" and the differential 1-form symbols for the coordinates), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "VolumeForm" | volume form on the manifold (i.e. an algebraic relationship between "dV" and the determinant of the metric tensor) |
| "ReducedVolumeForm" | volume form on the manifold (i.e. an algebraic relationship between "dV" and the determinant of the metric tensor), modulo all tensor equivalences |
| "TimelikeQ" | pure function to determine whether a given tangent vector is timelike (i.e. lies strictly on the interior of a light cone), for a pseudo-Riemannian metric tensor |
| "LightlikeQ" | pure function to determine whether a given tangent vector is lightlike (i.e. lies on the boundary of a light cone), for a pseudo-Riemannian metric tensor |
| "SpacelikeQ" | pure function to determine whether a given tangent vector is spacelike (i.e. lies strictly on the exterior of a light cone), for a pseudo-Riemannian metric tensor |
| "LengthPureFunction" | pure function to determine the length of a given tangent vector, for an arbitrary metric tensor |
| "AnglePureFunction" | pure function to determine the angle between two given tangent vectors, for an arbitrary metric tensor |
| "Properties" | list of properties |
Construct a Schwarzschild metric (e.g. for an uncharged, non-rotating black hole with symbolic mass "M") in standard spherical polar coordinates:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= | 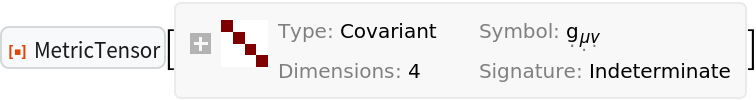 |
Show the Schwarzschild metric in explicit matrix form:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 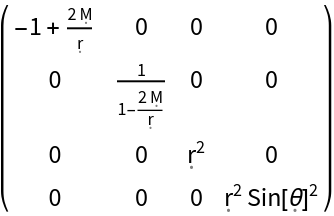 |
Show the spacetime line element for the Schwarzschild metric:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= | 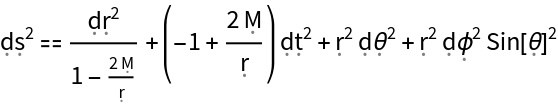 |
Show the volume form for the Schwarzschild metric:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= | 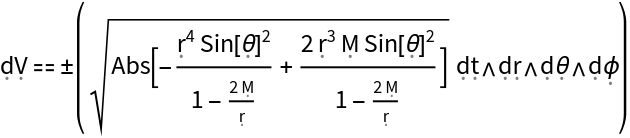 |
Show the reduced volume form for the Schwarzschild metric, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
Show the list of Schwarzschild coordinate symbols:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
Show the list of differential 1-form symbols for each of the Schwarzschild coordinates:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |
Show the list of coordinate values that cause the Schwarzschild metric to become singular:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
Show the list of coordinate conditions that must hold for the Schwarzschild metric to be Lorentzian:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
Construct the same (Schwarzschild) metric in spherical polar coordinates, but with numerical mass 1, coordinate symbols t, r, a1 and a2, and both indices raised/contravariant:
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
Show the explicit matrix form:
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= | 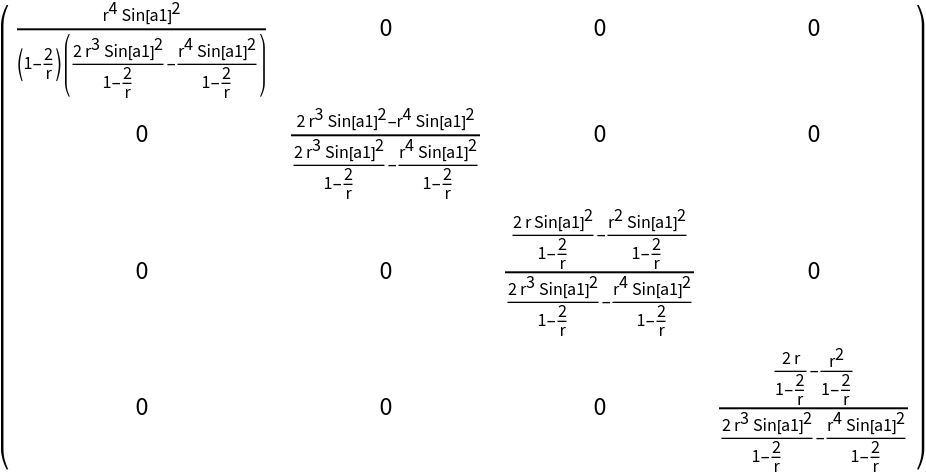 |
Show the reduced explicit matrix form, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |  |
Show the spacetime line element:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |
Show the reduced spacetime line element, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[14]:= |
| Out[14]= |
Construct the same (Schwarzschild) metric in isotropic coordinates, in which all light cones appear round:
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= | 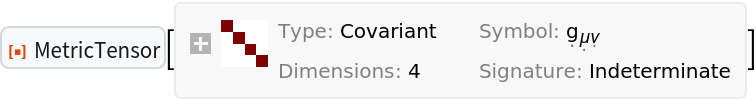 |
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= | 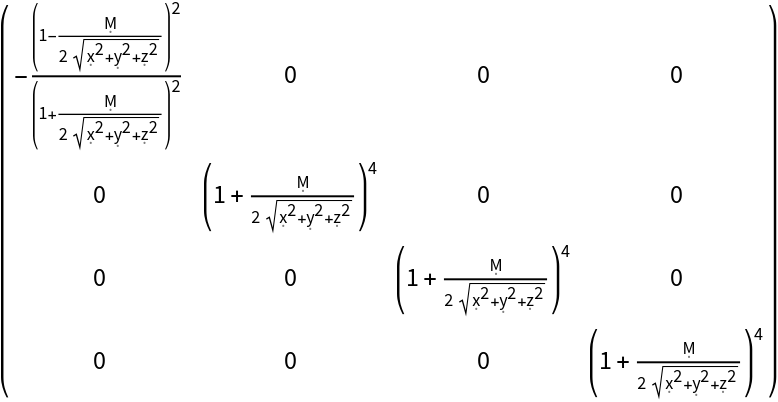 |
Show the list of metric singularities:
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= |
Show that the coordinate singularity at the event horizon disappears when using Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates:
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= | 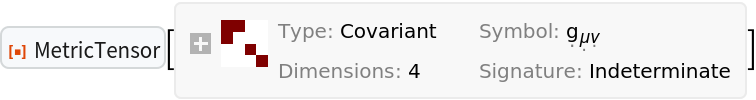 |
| In[19]:= |
| Out[19]= |  |
| In[20]:= |
| Out[20]= |
Or Gullstrand-Painlevé coordinates:
| In[21]:= |
| Out[21]= |  |
| In[22]:= |
| Out[22]= | 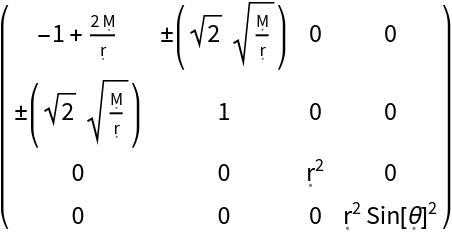 |
| In[23]:= |
| Out[23]= |
Construct a Kerr-Newman metric (e.g. for a charged, spinning black hole with symbolic mass "M", symbolic angular momentum "J" and symbolic electric charge "Q") in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates:
| In[24]:= |
| Out[24]= |  |
| In[25]:= |
| Out[25]= | 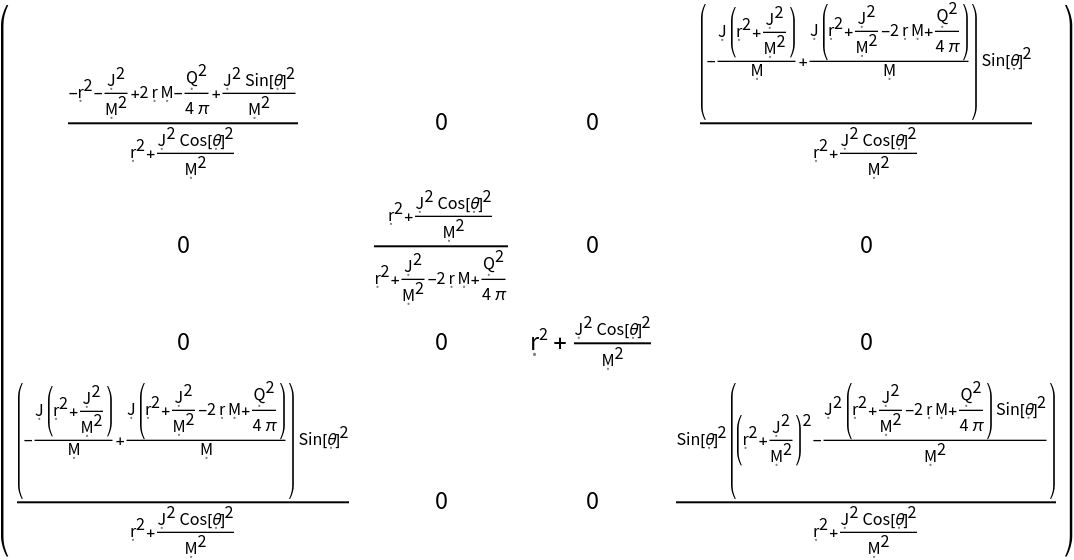 |
Show the explicit matrix form, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[26]:= |
| Out[26]= | 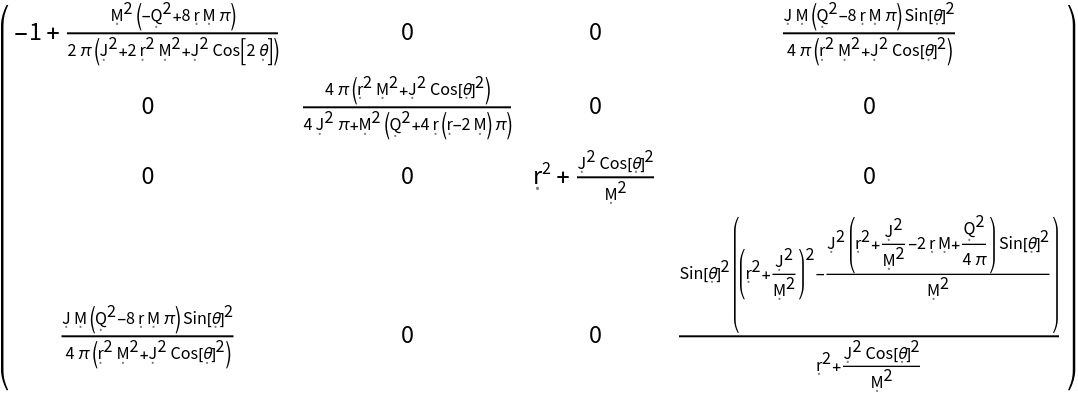 |
Extract the time-time component of the Kerr-Newman metric:
| In[27]:= |
| Out[27]= | 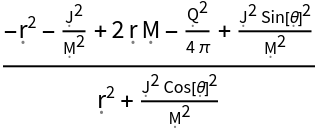 |
Extract the first row of the Kerr-Newman metric in matrix form:
| In[28]:= |
| Out[28]= | 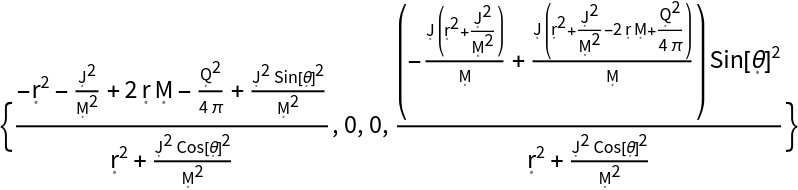 |
Extract the first column of the Kerr-Newman metric in matrix form:
| In[29]:= |
| Out[29]= | 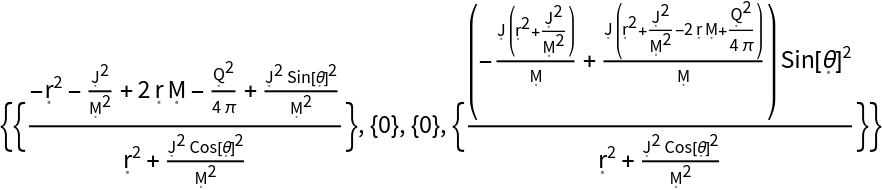 |
Show the list of metric singularities:
| In[30]:= |
| Out[30]= | 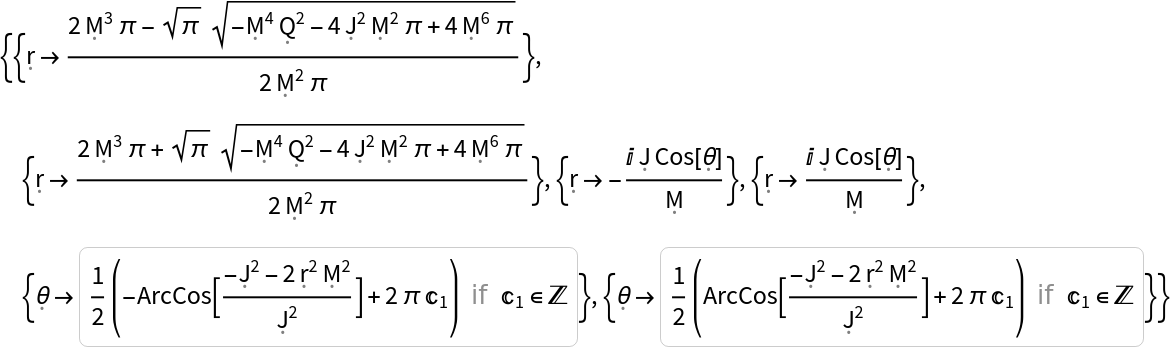 |
Compute the length of the 4-vector {-1,1,0,0} in the Kerr-Newman geometry:
| In[31]:= |
| Out[31]= | 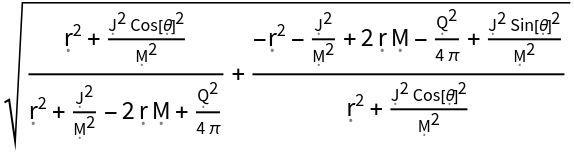 |
Compute the angle between the 4-vectors {-1,1,0,0} and {-1/2,1/2,1/2,0} in the Kerr-Newman geometry:
| In[32]:= |
| Out[32]= | 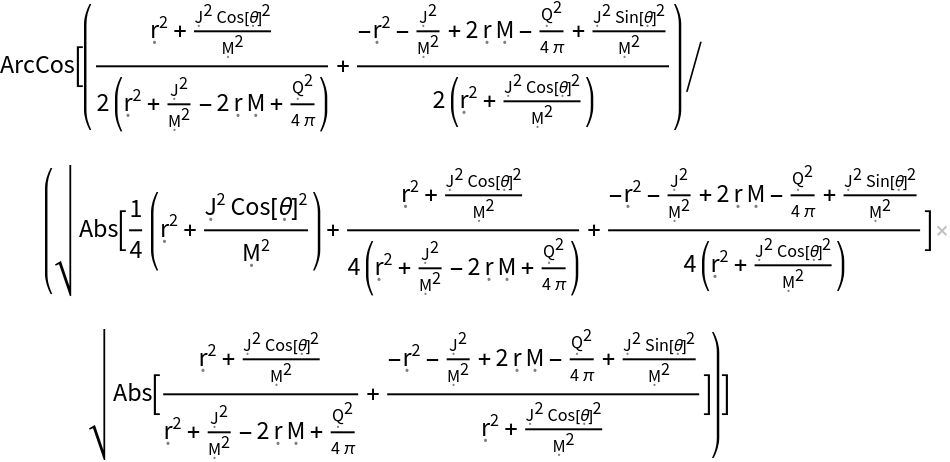 |
Show the pure function for determining lengths of 4-vectors in the Kerr-Newman geometry:
| In[33]:= |
| Out[33]= | 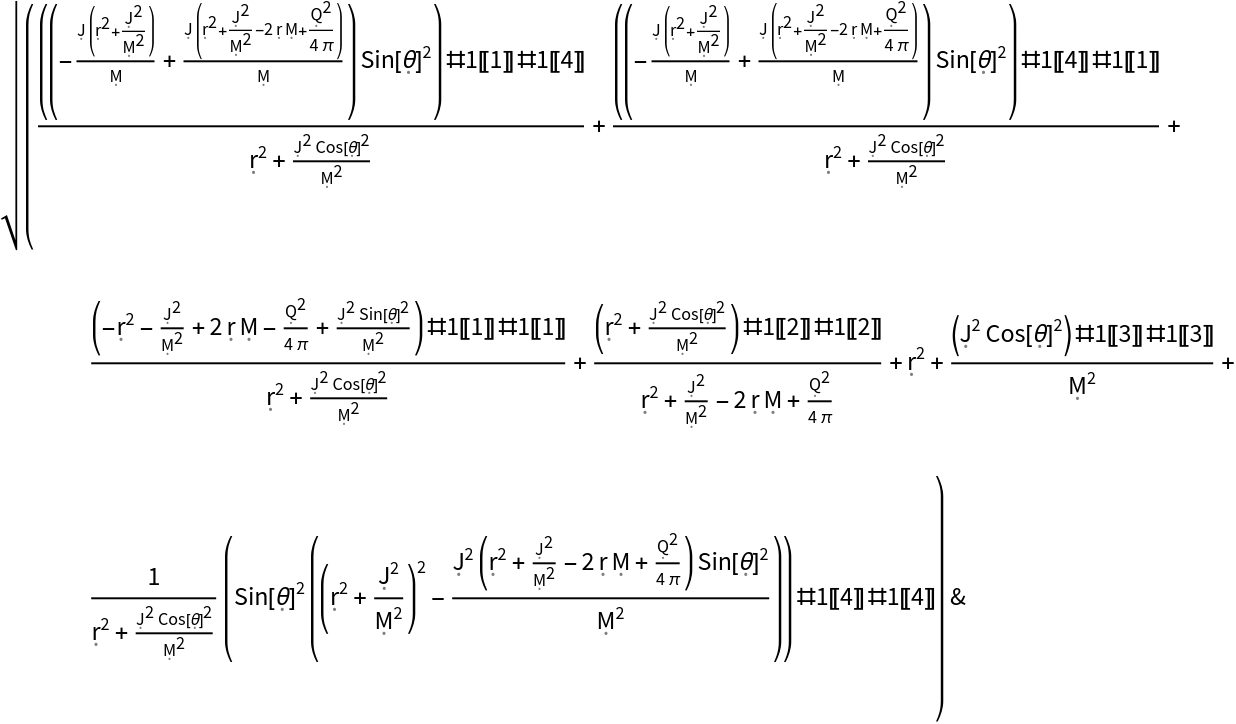 |
Show the pure function for determining angles between 4-vectors in the Kerr-Newman geometry:
| In[34]:= |
| Out[34]= |  |
Applying this pure function directly to the same pair of 4-vectors as above gives the same result:
| In[35]:= |
| Out[35]= | 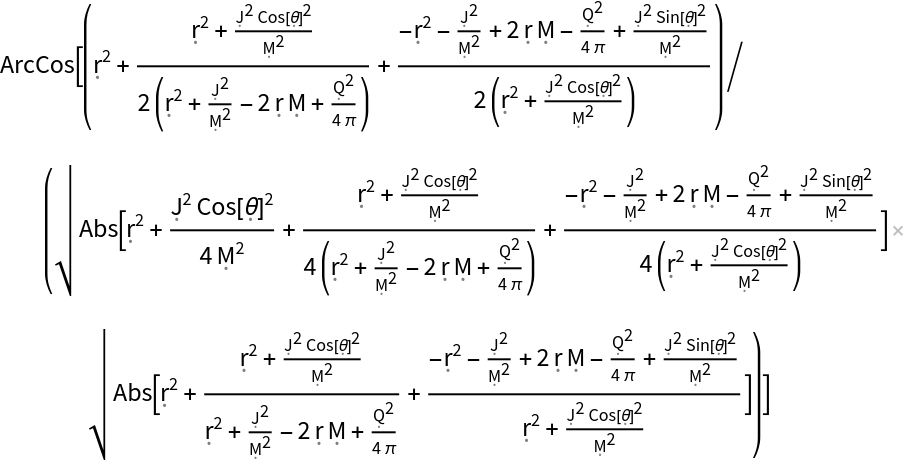 |
Show the pure function for determining whether a 4-vector is timelike (i.e. lies strictly on the interior of a light cone):
| In[36]:= |
| Out[36]= | 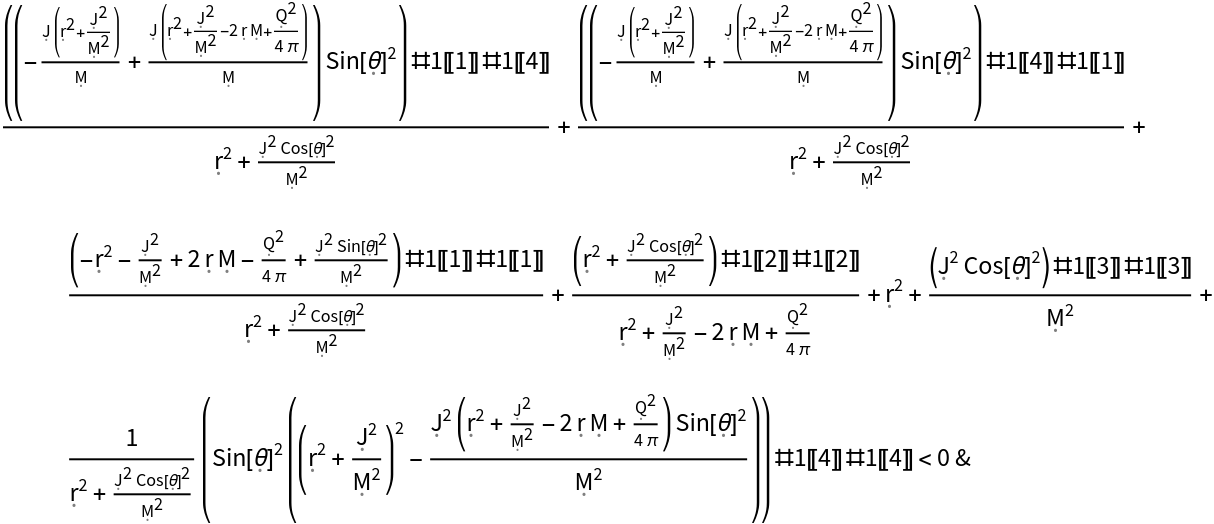 |
Determine the conditions under which the 4-vector {-1,1,0,0} is spacelike:
| In[37]:= |
| Out[37]= | 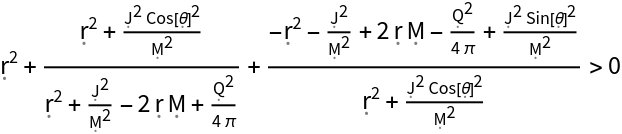 |
Show that, in the limit as the angular momentum parameter goes to zero, the Kerr-Newman metric becomes equivalent to the Reissner-Nordström metric (e.g. for a charged, non-rotating black hole):
| In[38]:= | ![FullSimplify[
ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][{"KerrNewman", M, 0, Q}][
"ReducedMatrixRepresentation"] == ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][{"ReissnerNordstrom", M, Q}][
"ReducedMatrixRepresentation"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/c6c/c6c98873-a3bc-43e4-a1a4-ed6e5dbbaa32/50a6127cde11684d.png) |
| Out[38]= |
Show that, in the limit as the electric charge parameter goes to zero, the Kerr-Newman metric becomes equivalent to the Kerr metric (e.g. for an uncharged, spinning black hole):
| In[39]:= | ![FullSimplify[
ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][{"KerrNewman", M, J, 0}][
"ReducedMatrixRepresentation"] == ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][{"Kerr", M, J}][
"ReducedMatrixRepresentation"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/c6c/c6c98873-a3bc-43e4-a1a4-ed6e5dbbaa32/00b5bf18897d174c.png) |
| Out[39]= |
Show that, in the limit as the angular momentum and electric charge parameters both go to zero, the Kerr-Newman metric becomes equivalent to the Schwarzschild metric:
| In[40]:= | ![FullSimplify[
ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][{"KerrNewman", M, 0, 0}][
"ReducedMatrixRepresentation"] == ResourceFunction["MetricTensor"][{"Schwarzschild", M}][
"ReducedMatrixRepresentation"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/c6c/c6c98873-a3bc-43e4-a1a4-ed6e5dbbaa32/5b76eb4632df0e4c.png) |
| Out[40]= |
Construct a metric tensor from a random symmetric matrix:
| In[41]:= | ![randomMatrix = RandomReal[{-1, 1}, {8, 8}];
randomSymmetric = randomMatrix + Transpose[randomMatrix];
randomSymmetric // MatrixForm](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/c6c/c6c98873-a3bc-43e4-a1a4-ed6e5dbbaa32/480c5ec3e2f62641.png) |
| Out[43]= | 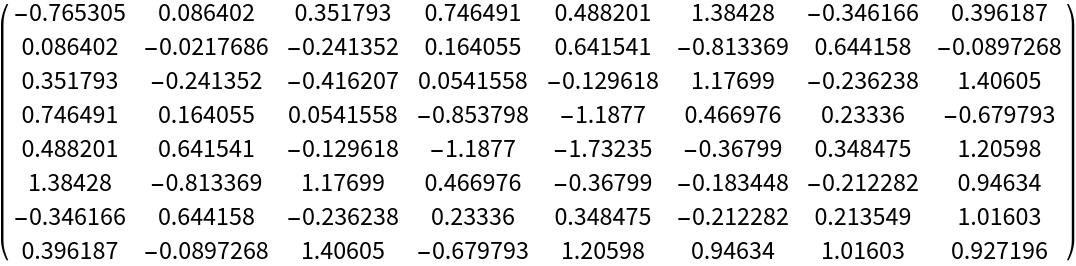 |
| In[44]:= |
| Out[44]= |  |
Determine whether the metric is Lorentzian:
| In[45]:= |
| Out[45]= |
Determine whether the metric is Riemannian:
| In[46]:= |
| Out[46]= |
Determine whether the metric is pseudo-Riemannian:
| In[47]:= |
| Out[47]= |
Construct a metric tensor for 8-dimensional (i.e. 1+7-dimensional) Minkowski space in Cartesian coordinates:
| In[48]:= |
| Out[48]= | 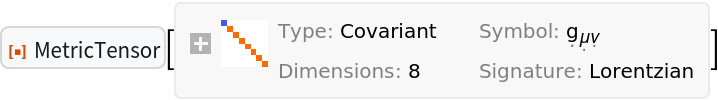 |
| In[49]:= |
| Out[49]= |  |
Show that the Minkowski metric is Lorentzian:
| In[50]:= |
| Out[50]= |
Construct the most general 5-dimensional (symmetric) metric tensor:
| In[51]:= |
| Out[51]= | 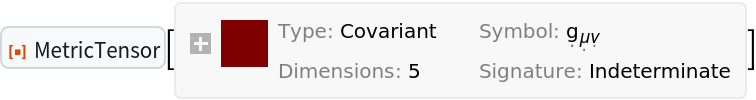 |
| In[52]:= |
| Out[52]= |  |
| In[53]:= |
| Out[53]= |
Construct the most general 5-dimensional (asymmetric) metric tensor:
| In[54]:= |
| Out[54]= | 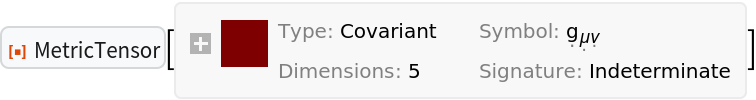 |
| In[55]:= |
| Out[55]= |  |
| In[56]:= |
| Out[56]= |
Construct the most general 5-dimensional (asymmetric) metric tensor field:
| In[57]:= |
| Out[57]= | 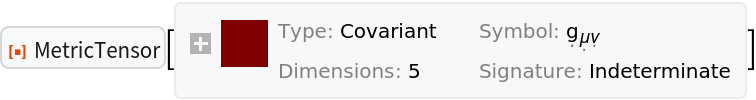 |
| In[58]:= |
| Out[58]= | 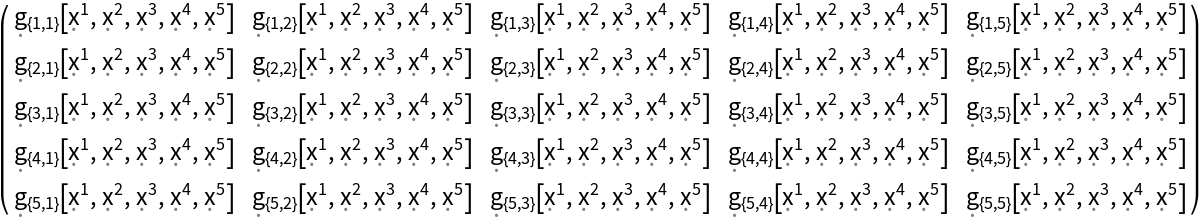 |
| In[59]:= |
| Out[59]= |
Construct a Friedmann-Lemaître-Robertson-Walker (FLRW) metric for a homogeneous, isotropic and uniformly-expanding/contracting universe, with symbolic curvature parameter "k" and symbolic scale factor "a", in standard spherical polar coordinates:
| In[60]:= |
| Out[60]= |  |
| In[61]:= |
| Out[61]= | 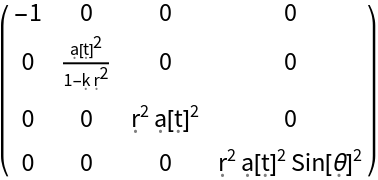 |
Compute the inverse metric tensor (with both indices raised/contravariant):
| In[62]:= |
| Out[62]= |
| In[63]:= |
| Out[63]= | 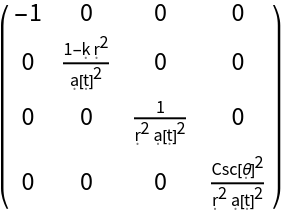 |
| In[64]:= |
| Out[64]= |
| In[65]:= |
| Out[65]= |
Show that having one index raised/contravariant and one index lowered/covariant yields the identity tensor:
| In[66]:= |
| Out[66]= | 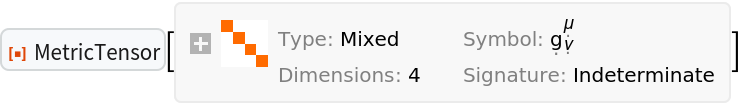 |
| In[67]:= |
| Out[67]= | 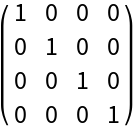 |
| In[68]:= |
| Out[68]= |
| In[69]:= |
| Out[69]= |
Transform to use the new coordinate symbols t, r, a1 and a2:
| In[70]:= |
| Out[70]= |  |
| In[71]:= |
| Out[71]= | 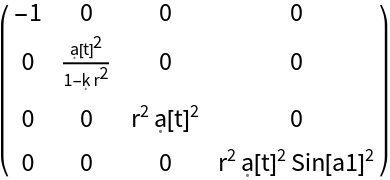 |
Transform to use the new coordinate symbols t, r, a1 and a2, and raise both indices, simultaneously:
| In[72]:= |
| Out[72]= |
| In[73]:= |
| Out[73]= | 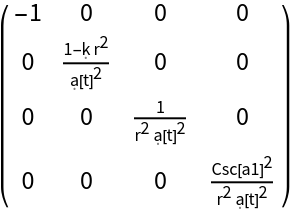 |
Metric tensors can be constructed directly from a matrix representation:
| In[74]:= |
| Out[74]= |  |
| In[75]:= |
| Out[75]= |
Additional arguments can be used to specify the coordinate names (otherwise default symbols will be chosen automatically):
| In[76]:= |
| Out[76]= |  |
| In[77]:= |
| Out[77]= |
Or the indices (True for lowered/covariant and False for raised/contravariant - otherwise both indices will be set as lowered/covariant by default):
| In[78]:= |
| Out[78]= |
| In[79]:= |
| Out[79]= |
Or both simultaneously:
| In[80]:= |
| Out[80]= |  |
| In[81]:= |
| Out[81]= |
| In[82]:= |
| Out[82]= |
Common metric tensors can also be constructed using an in-built name:
| In[83]:= |
| Out[83]= |  |
| In[84]:= |
| Out[84]= |  |
When an in-built/named metric has one or more parameters, those parameters can be left unspecified (in which case they are filled with purely symbolic defaults, such as "M"):
| In[85]:= |
| Out[85]= |  |
| In[86]:= |
| Out[86]= | 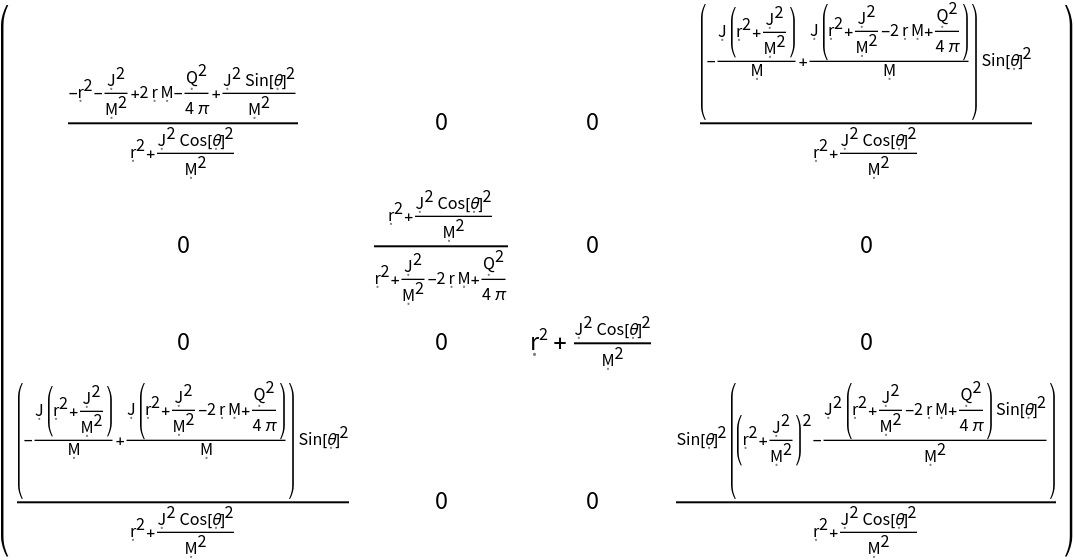 |
Otherwise, they can be specified explicitly in list form:
| In[87]:= |
| Out[87]= |  |
| In[88]:= |
| Out[88]= | 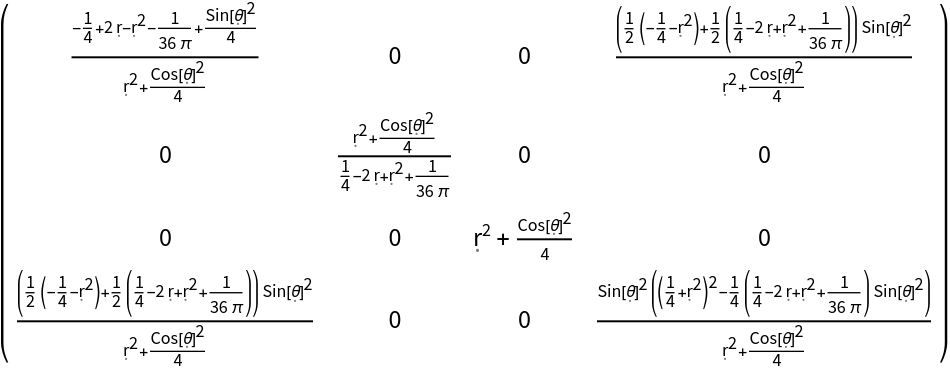 |
If only some parameters are explicitly specified, then the remainder are filled with symbolic defaults (e.g. if one specifies only a numerical mass and a numerical angular momentum for the Kerr-Newman metric, then MetricTensor will use a purely symbolic electric charge, namely "Q"):
| In[89]:= |
| Out[89]= |  |
| In[90]:= |
| Out[90]= | 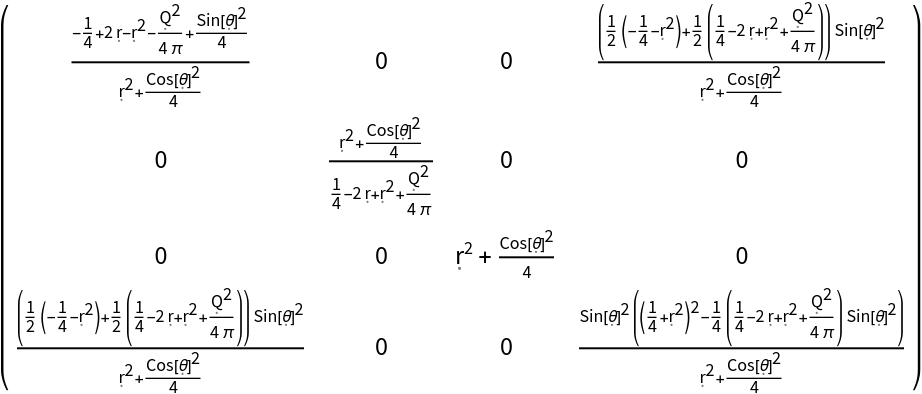 |
Coordinate and index information can also be specified for in-built/named metrics:
| In[91]:= |
| Out[91]= |
| In[92]:= |
| Out[92]= | 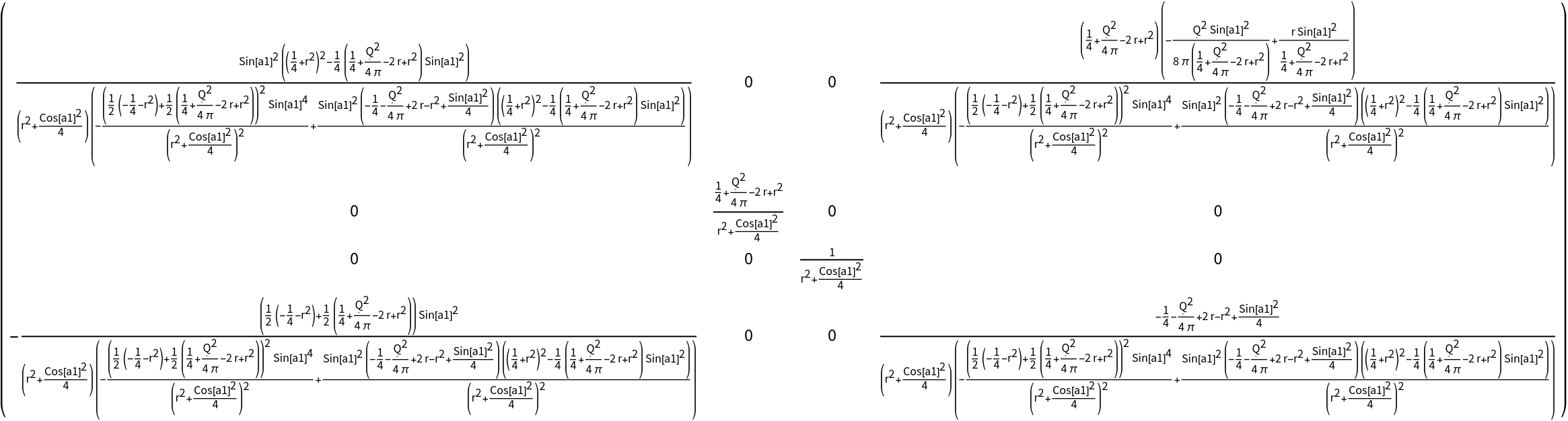 |
| In[93]:= |
| Out[93]= |  |
New coordinate symbols can be specified for any metric tensor:
| In[94]:= |
| Out[94]= | 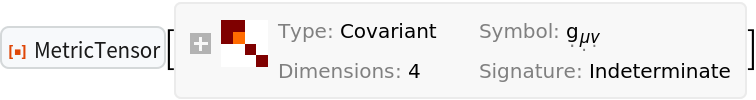 |
| In[95]:= |
| Out[95]= |
| In[96]:= |
| Out[96]= | 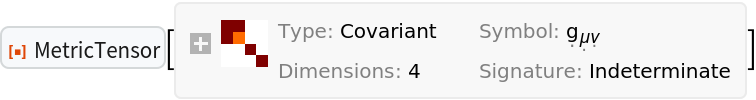 |
| In[97]:= |
| Out[97]= |
Indices can also be raised and lowered on any metric tensor:
| In[98]:= |
| Out[98]= |
| In[99]:= |
| Out[99]= |
| In[100]:= |
| Out[100]= | 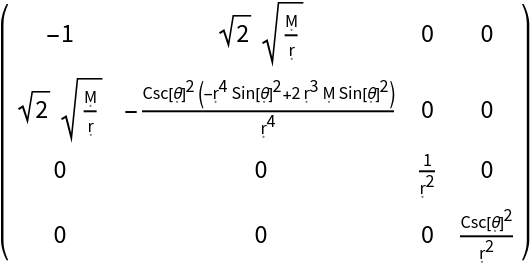 |
| In[101]:= |
| Out[101]= |
New coordinate symbols and new index positions can also be specified simultaneously:
| In[102]:= |
| Out[102]= |
| In[103]:= |
| Out[103]= |
| In[104]:= |
| Out[104]= |
Show the list of all in-built/named metric tensors:
| In[105]:= |
| Out[105]= |  |
Construct a generic 4-dimensional symmetric metric (default):
| In[106]:= |
| Out[106]= |  |
Construct a generic 5-dimensional symmetric metric:
| In[107]:= |
| Out[107]= |  |
CallingMetricTensor[d] is a shorthand version, equivalent to calling MetricTensor[{"Symmetric",d}]:
| In[108]:= |
| Out[108]= |  |
Construct a generic 4-dimensional symmetric metric tensor field (default):
| In[109]:= |
| Out[109]= | 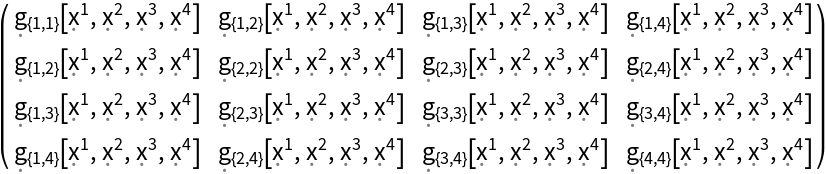 |
Construct a generic 5-dimensional symmetric metric tensor field:
| In[110]:= |
| Out[110]= | 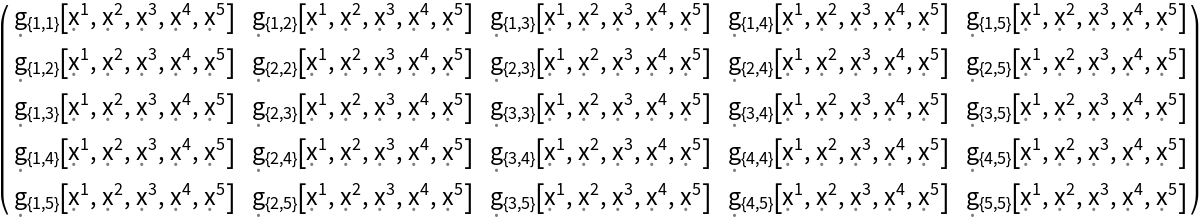 |
Construct a generic 4-dimensional asymmetric metric (default):
| In[111]:= |
| Out[111]= |  |
Construct a generic 5-dimensional asymmetric metric:
| In[112]:= |
| Out[112]= |  |
Construct a generic 4-dimensional asymmetric metric tensor field (default):
| In[113]:= |
| Out[113]= | 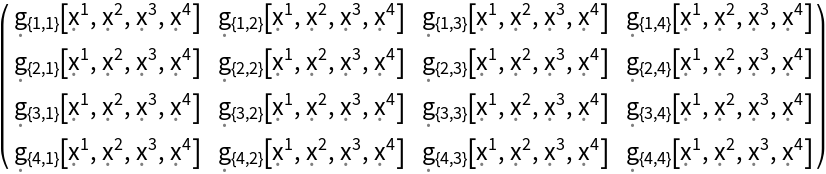 |
Construct a generic 5-dimensional asymmetric metric tensor field:
| In[114]:= |
| Out[114]= | 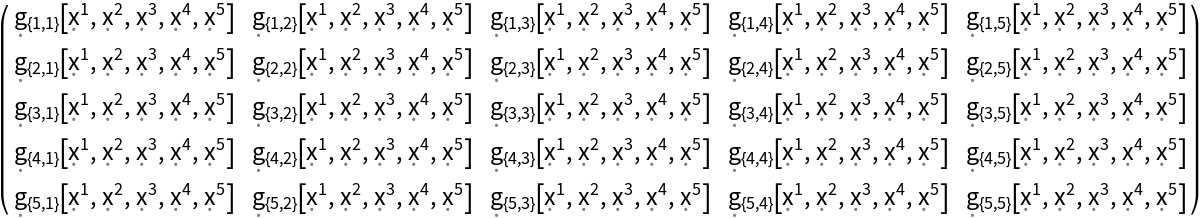 |
Construct the metric for 3-dimensional flat/Euclidean space (default) in Cartesian coordinates:
| In[115]:= |
| Out[115]= |
Construct the metric for 7-dimensional flat/Euclidean space in Cartesian coordinates:
| In[116]:= |
| Out[116]= | 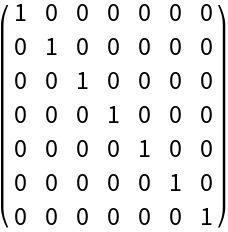 |
Construct the metric for 4-dimensional (i.e. 1+3-dimensional) Minkowski space (default) in Cartesian coordinates:
| In[117]:= |
| Out[117]= |  |
Construct the metric for 7-dimensional (i.e. 1+6-dimensional) Minkowski space in Cartesian coordinates:
| In[118]:= |
| Out[118]= |  |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry, e.g. the exterior spacetime of an uncharged, non-rotating black hole, with symbolic mass "M" (default) in spherical polar coordinates:
| In[119]:= |
| Out[119]= | 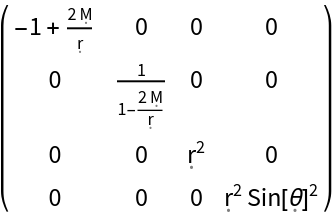 |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with numerical mass 1 in spherical polar coordinates:
| In[120]:= |
| Out[120]= | 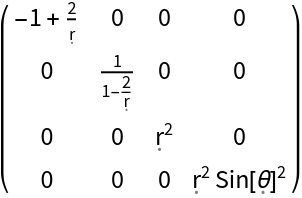 |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with symbolic mass "M" (default) in Cartesian-like/isotropic coordinates, in which all light cones appear round:
| In[121]:= |
| Out[121]= | 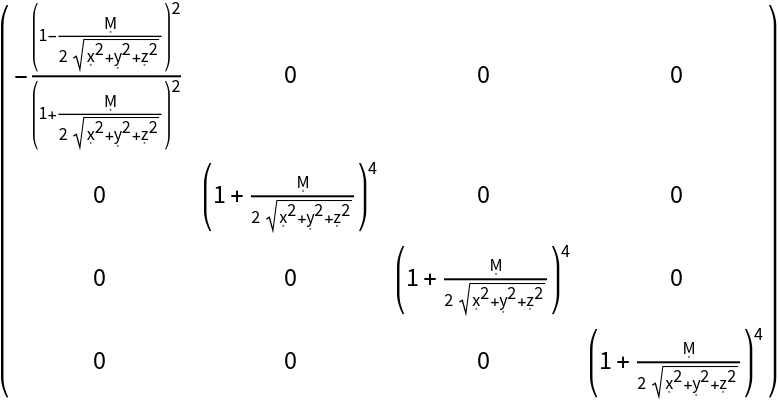 |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with numerical mass 1 in Cartesian-like/isotropic coordinates:
| In[122]:= |
| Out[122]= | 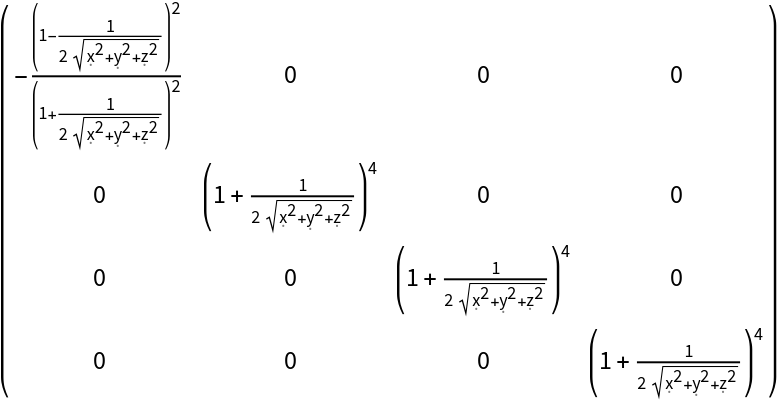 |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with symbolic mass "M" (default) in Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates, adapted to radial lightlike geodesics:
| In[123]:= |
| Out[123]= |  |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with numerical mass 1 in Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates:
| In[124]:= |
| Out[124]= | 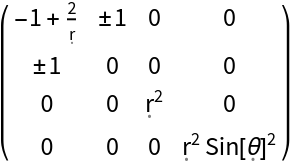 |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with symbolic mass "M" (default) in ingoing Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates, adapted to inward-traveling radial lightlike geodesics:
| In[125]:= |
| Out[125]= | 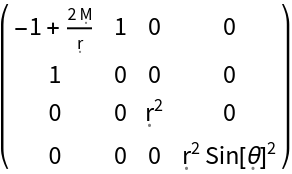 |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with numerical mass 1 in ingoing Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates:
| In[126]:= |
| Out[126]= | 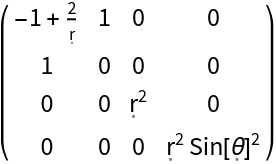 |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with symbolic mass "M" (default) in outgoing Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates, adapted to outward-traveling radial lightlike geodesics:
| In[127]:= |
| Out[127]= |  |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with numerical mass 1 in outgoing Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates:
| In[128]:= |
| Out[128]= |  |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with symbolic mass "M" (default) in Gullstrand-Painlevé coordinates, in which coordinate time is the proper time experienced by a free-falling observer from infinity:
| In[129]:= |
| Out[129]= | 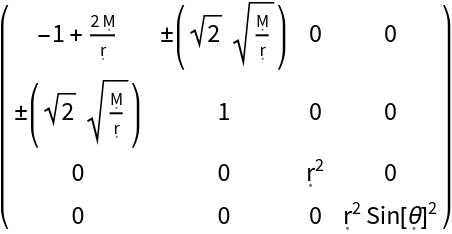 |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with numerical mass 1 in Gullstrand-Painlevé coordinates:
| In[130]:= |
| Out[130]= | 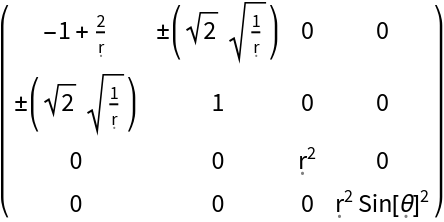 |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with symbolic mass "M" (default) in ingoing Gullstrand-Painlevé coordinates, in which coordinate time is the proper time experienced by a free-falling observer, falling inwards from infinity:
| In[131]:= |
| Out[131]= | 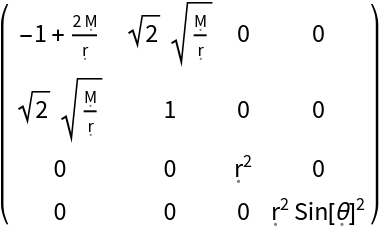 |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with numerical mass 1 in ingoing Gullstrand-Painlevé coordinates:
| In[132]:= |
| Out[132]= | 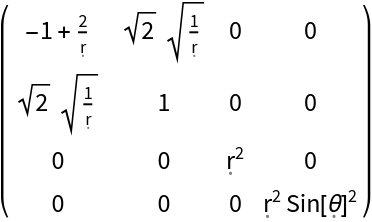 |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with symbolic mass "M" (default) in outgoing Gullstrand-Painlevé coordinates, in which coordinate time is the proper time experienced by a free-falling observer, falling outwards to infinity:
| In[133]:= |
| Out[133]= | 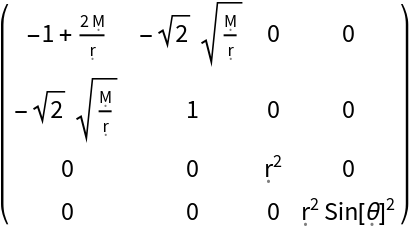 |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with numerical mass 1 in outgoing Gullstrand-Painlevé coordinates:
| In[134]:= |
| Out[134]= |  |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with symbolic mass "M" (default) in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates, which cover the complete spacetime manifold for the maximal analytic extension of the Schwarzschild metric:
| In[135]:= |
| Out[135]= | 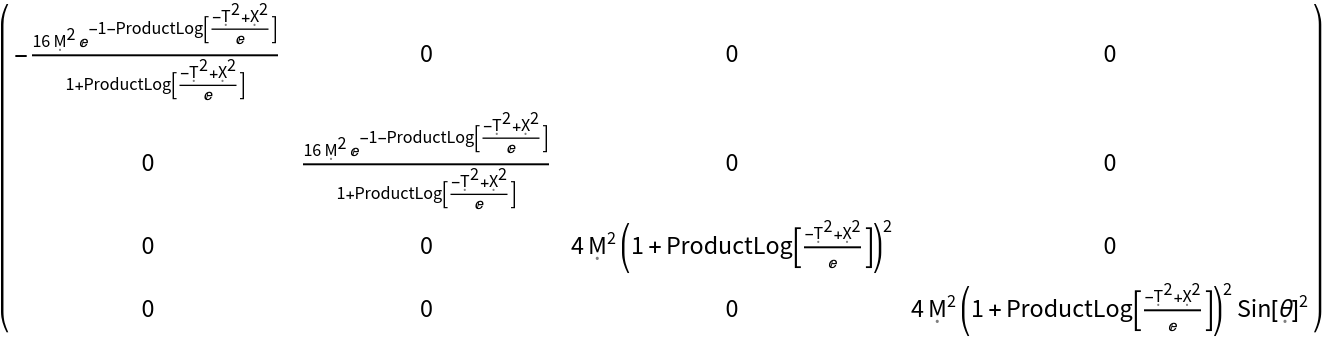 |
Construct the metric for the Schwarzschild geometry with numerical mass 1 in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates:
| In[136]:= |
| Out[136]= | 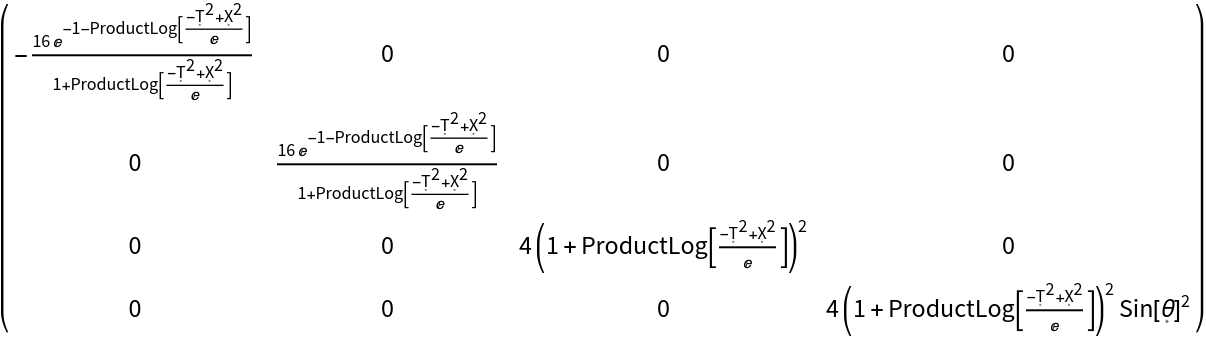 |
Construct the metric for the Kerr geometry, e.g. the exterior spacetime of an uncharged, spinning black hole, with symbolic mass "M" and symbolic angular momentum "J" (default) in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates:
| In[137]:= |
| Out[137]= | 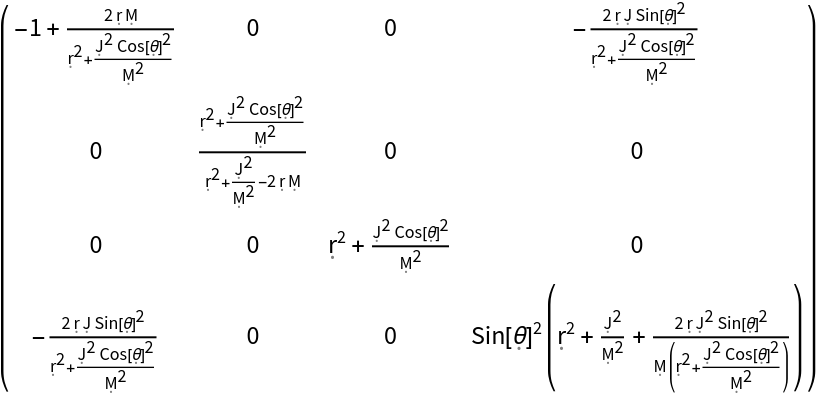 |
Construct the metric for the Kerr geometry with numerical mass 1 and symbolic angular momentum "J" in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates:
| In[138]:= |
| Out[138]= | 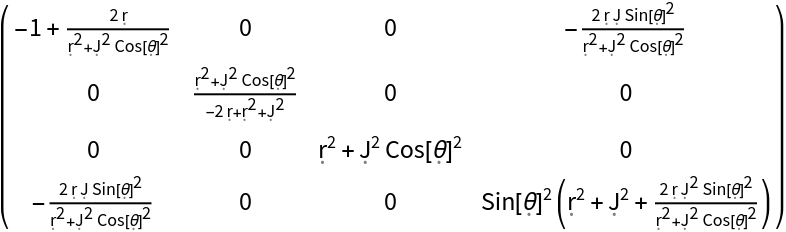 |
Construct the metric for the Kerr geometry with numerical mass 1 and numerical angular momentum 1/2 in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates:
| In[139]:= |
| Out[139]= | 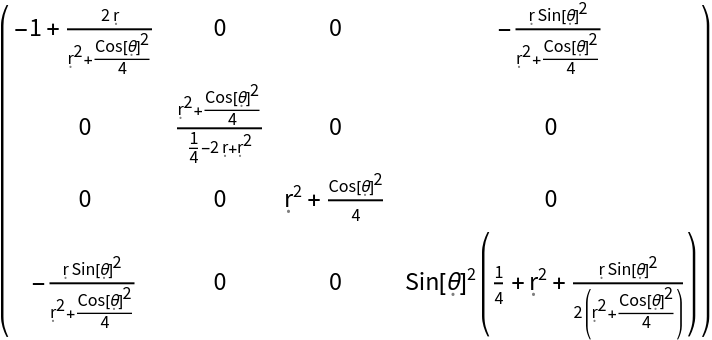 |
Construct the metric for the Reissner-Nordström geometry, e.g. the exterior spacetime of a charged, non-rotating black hole, with symbolic mass "M" and symbolic electric charge "Q" (default) in spherical polar coordinates:
| In[140]:= |
| Out[140]= | 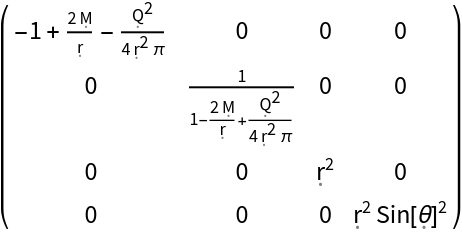 |
Construct the metric for the Reissner-Nordström geometry with numerical mass 1 and symbolic electric charge "Q" in spherical polar coordinates:
| In[141]:= |
| Out[141]= | 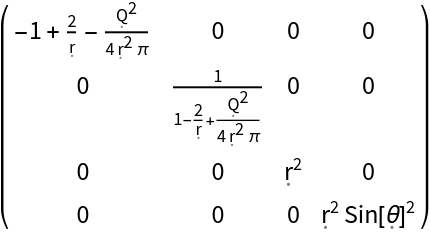 |
Construct the metric for the Reissner-Nordström geometry with numerical mass 1 and numerical electric charge 1/3 in spherical polar coordinates:
| In[142]:= |
| Out[142]= | 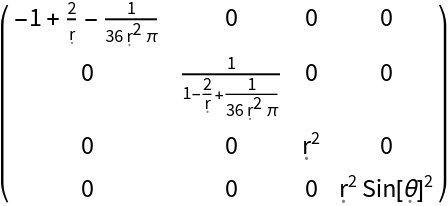 |
Construct the metric for the Kerr-Newman geometry, e.g. the exterior spacetime of a charged, spinning black hole, with symbolic mass "M", symbolic angular momentum "J" and symbolic electric charge "Q" (default) in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates:
| In[143]:= |
| Out[143]= | 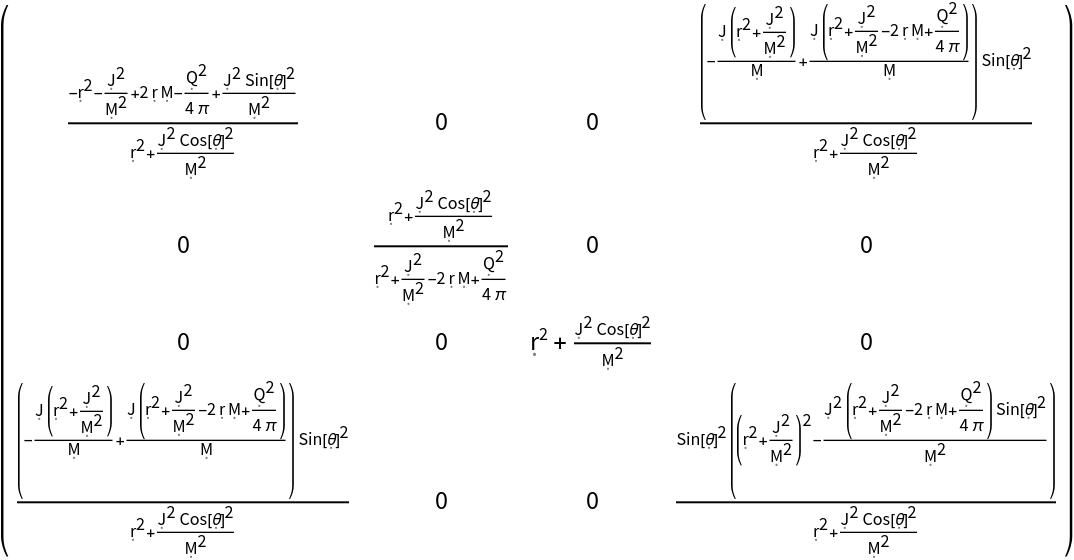 |
Construct the metric for the Kerr-Newman geometry with numerical mass 1, symbolic angular momentum "J" and symbolic electric charge "Q" in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates:
| In[144]:= |
| Out[144]= |  |
Construct the metric for the Kerr-Newman geometry with numerical mass 1, numerical angular momentum 1/2 and symbolic electric charge "Q" in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates:
| In[145]:= |
| Out[145]= | 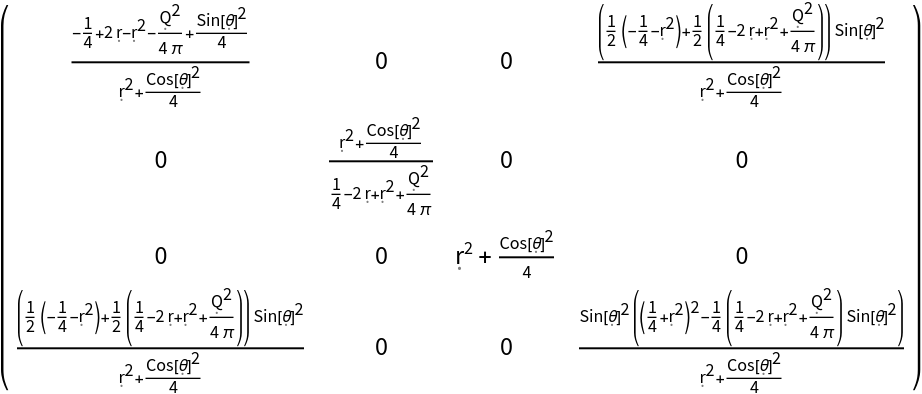 |
Construct the metric for the Kerr-Newman geometry with numerical mass 1, numerical angular momentum 1/2 and numerical electric charge 1/3 in Boyer-Lindquist/oblate spheroidal coordinates:
| In[146]:= |
| Out[146]= | 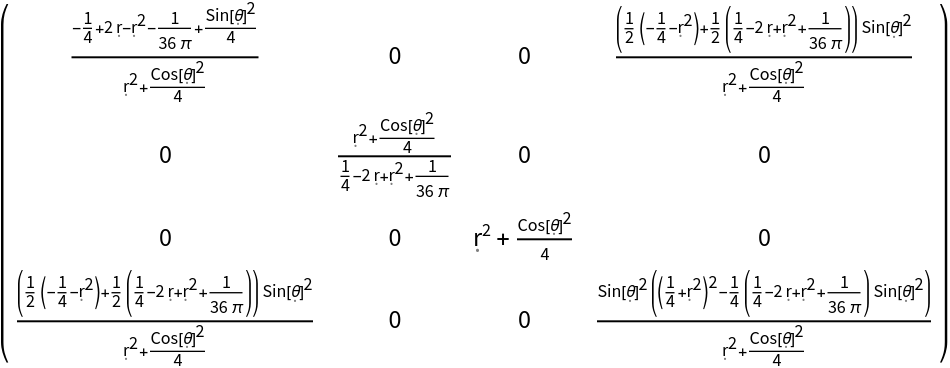 |
Construct the Gödel metric, i.e. the metric for a rotating, dust-filled universe, with symbolic angular velocity "" (default) in Gödel's Cartesian-like coordinates:
| In[147]:= |
| Out[147]= |  |
Construct the Gödel metric with numerical angular velocity 1/2 in Gödel's Cartesian-like coordinates:
| In[148]:= |
| Out[148]= | 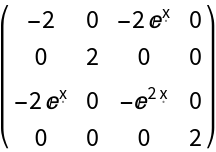 |
Construct the Friedmann-Lemaître-Robertson-Walker/FLRW metric, i.e. the metric for a homogeneous, isotropic and uniformly expanding/contracting universe, with symbolic global curvature "k" and symbolic scale function "a" (default) in spherical polar coordinates:
| In[149]:= |
| Out[149]= | 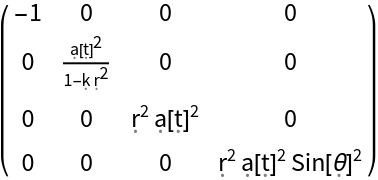 |
Construct the FLRW metric with numerical global curvature -1 and symbolic scale function "a" in spherical polar coordinates:
| In[150]:= |
| Out[150]= | 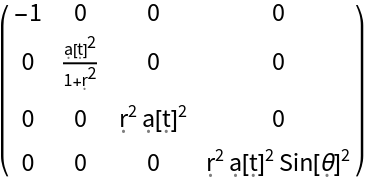 |
Construct the FLRW metric with numerical global curvature -1 and numerical scale function (#*3)& in spherical polar coordinates:
| In[151]:= |
| Out[151]= | 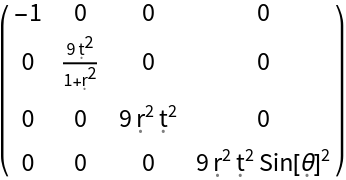 |
Construct a Schwarzschild metric, with symbolic mass "M":
| In[152]:= |
| Out[152]= | 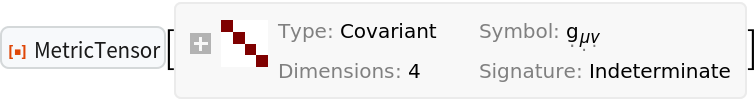 |
Show the list of properties:
| In[153]:= |
| Out[153]= |  |
Show the explicit matrix representation of the metric tensor:
| In[154]:= |
| Out[154]= | 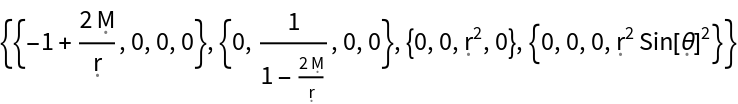 |
Show the explicit matrix representation of the metric tensor, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[155]:= |
| Out[155]= |
Show the list of coordinate symbols for the metric tensor:
| In[156]:= |
| Out[156]= |
Show the list of differential 1-form symbols for the coordinates of the metric tensor:
| In[157]:= |
| Out[157]= |
Show the list of booleans specifying the positions of the indices of the metric tensor (True for lowered/covariant and False for raised/contravariant):
| In[158]:= |
| Out[158]= |
Determine whether the metric tensor is covariant (i.e. both indices are lowered/covariant):
| In[159]:= |
| Out[159]= |
Determine whether the metric tensor is contravariant (i.e. both indices are raised/contravariant):
| In[160]:= |
| Out[160]= |
Determine whether the metric tensor is mixed (i.e. one index is lowered/covariant and one index is raised/contravariant):
| In[161]:= |
| Out[161]= |
Show a symbolic representation of the metric tensor with appropriately raised/lowered indices:
| In[162]:= |
| Out[162]= |
Show the number of dimensions of the underlying manifold represented by the metric tensor:
| In[163]:= |
| Out[163]= |
Determine whether the metric tensor is symmetric (in explicit, covariant matrix form):
| In[164]:= |
| Out[164]= |
Determine whether the metric tensor is diagonal (in explicit, covariant matrix form):
| In[165]:= |
| Out[165]= |
Show the signature of the metric tensor (with +1s representing positive eigenvalues and -1s representing negative eigenvalues):
| In[166]:= |
| Out[166]= |
Determine whether the metric tensor is Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues have the same sign):
| In[167]:= |
| Out[167]= |
Determine whether the metric tensor is pseudo-Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues are non-zero, but not all have the same sign):
| In[168]:= |
| Out[168]= |
Determine whether the metric tensor is Lorentzian (i.e. all eigenvalues have the same sign, except for one eigenvalue which has the opposite sign):
| In[169]:= |
| Out[169]= |
Show the list of conditions on the coordinates required to guarantee that the metric tensor is Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues are positive):
| In[170]:= |
| Out[170]= |
Show the list of conditions on the coordinates required to guarantee that the metric tensor is pseudo-Riemannian (i.e. all eigenvalues are non-zero):
| In[171]:= |
| Out[171]= |
Show the list of conditions on the coordinates required to guarantee that the metric tensor is Lorentzian (i.e. the "time" eigenvalue is negative, and all other eigenvalues are positive):
| In[172]:= |
| Out[172]= |
Show the list of coordinate values that cause the metric tensor to become singular:
| In[173]:= |
| Out[173]= |
Show the determinant of the metric tensor (when represented as a covariant matrix):
| In[174]:= |
| Out[174]= | 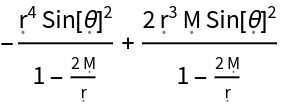 |
Show the determinant of the metric tensor (when represented as a covariant matrix), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[175]:= |
| Out[175]= |
Show the trace of the metric tensor:
| In[176]:= |
| Out[176]= | 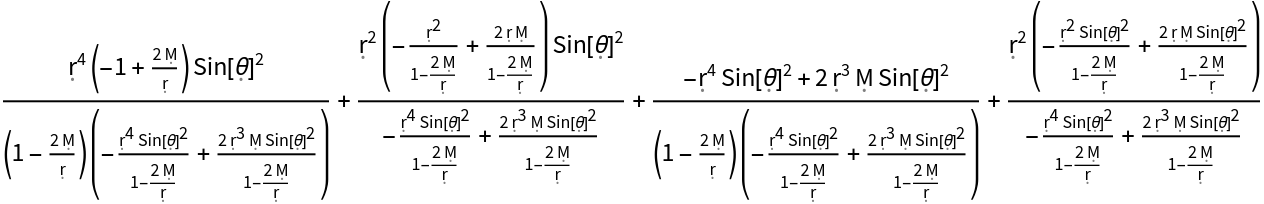 |
Show the trace of the metric tensor, with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[177]:= |
| Out[177]= |
Show the eigenvalues of the metric tensor (when represented as a covariant matrix):
| In[178]:= |
| Out[178]= | 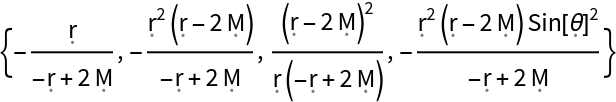 |
Show the eigenvalues of the metric tensor (when represented as a covariant matrix), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[179]:= |
| Out[179]= |
Show the eigenvectors of the metric tensor (when represented as a covariant matrix):
| In[180]:= |
| Out[180]= |
Show the eigenvectors of the metric tensor (when represented as a covariant matrix), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[181]:= |
| Out[181]= |
Compute the covariant form of the metric tensor (with both indices lowered/covariant):
| In[182]:= |
| Out[182]= | 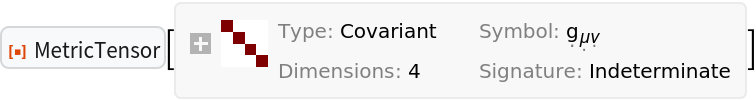 |
Compute the contravariant form of the metric tensor (with both indices raised/contravariant), otherwise known as the inverse metric tensor:
| In[183]:= |
| Out[183]= |
Show the spacetime line element for the metric tensor (i.e. the algebraic relationship between "ds" and the differential 1-form symbols for the coordinates):
| In[184]:= |
| Out[184]= | 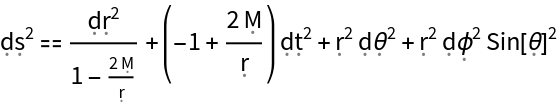 |
Show the spacetime line element for the metric tensor (i.e. the algebraic relationship between "ds" and the differential 1-form symbols for the coordinates), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[185]:= |
| Out[185]= |
Show the volume form (i.e. the algebraic relationship between "dV" and the determinant of the metric tensor):
| In[186]:= |
| Out[186]= | 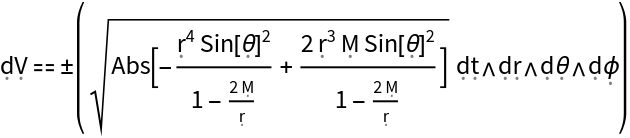 |
Show the volume form (i.e. the algebraic relationship between "dV" and the determinant of the metric tensor), with all algebraic equivalences imposed:
| In[187]:= |
| Out[187]= |
Show the pure function for determining whether tangent vectors are timelike (i.e. whether they lie strictly on the interiors of light cones) for a pseudo-Riemannian metric tensor:
| In[188]:= |
| Out[188]= | 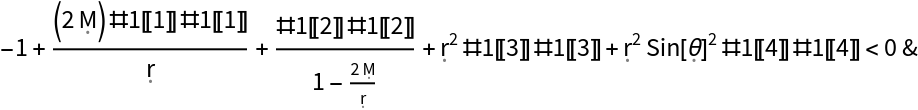 |
Show the pure function for determining whether tangent vectors are lightlike (i.e. whether they lie on the boundaries of light cones) for a pseudo-Riemannian metric tensor:
| In[189]:= |
| Out[189]= |  |
Show the pure function for determining whether tangent vectors are spacelike (i.e. whether they lie strictly on the exteriors of light cones) for a pseudo-Riemannian metric tensor:
| In[190]:= |
| Out[190]= | 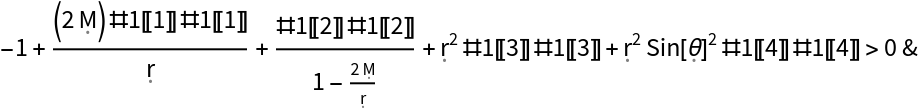 |
Show the pure function for determining the lengths of tangent vectors for an arbitrary metric tensor:
| In[191]:= |
| Out[191]= | 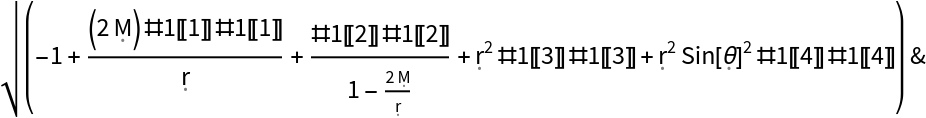 |
Show the pure function for determining the angles between pairs of tangent vectors for an arbitrary metric tensor:
| In[192]:= |
| Out[192]= | 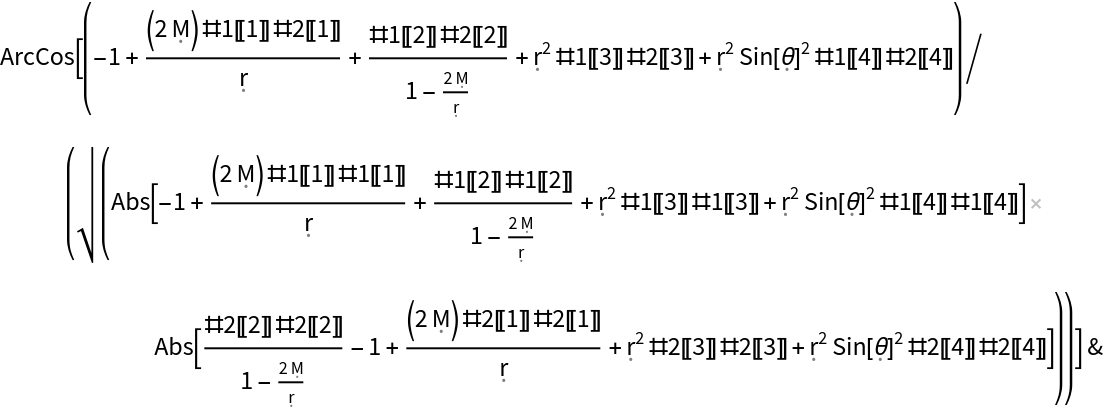 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License