Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Evaluate a matrix polynomial
ResourceFunction["MatrixPolynomial"][p,m] gives the matrix generated by the polynomial function p at the matrix argument m. | |
ResourceFunction["MatrixPolynomial"][p,m,v] gives the matrix generated by the polynomial function p at the matrix argument m, applied to the vector v. |
Compute a matrix polynomial, specifying the polynomial as a pure function:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
Evaluate a matrix polynomial with a machine-precision matrix:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
The polynomial can be specified as a list of coefficients:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |
Evaluate a matrix polynomial with a complex matrix:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |
Evaluate a matrix polynomial with an arbitrary-precision matrix:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
Evaluating a matrix polynomial with a large machine-precision matrix is efficient:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[7]= |
Directly applying the matrix polynomial to a single vector is even more efficient:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[9]= |
Compute a matrix polynomial applied to a vector for a sparse matrix:
| In[10]:= | ![ma = SparseArray[{{i_, i_} -> -2., {i_, j_} /; Abs[i - j] == 1 -> 1.}, {10, 10}];
ve = RandomReal[1, 10];
ResourceFunction["MatrixPolynomial"][
x |-> NorlundB[11, 1/2, x], ma, ve]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/435/4358088a-30c5-4a2c-8ab1-fd72012b13e5/045997d9c46a4ee1.png) |
| Out[12]= |
Evaluate a matrix rational function:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= | 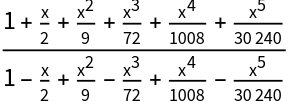 |
| In[14]:= | ![num[x_] = Numerator[rat[x]];
den[x_] = Denominator[rat[x]];
ma = RandomReal[1, {4, 4}, WorkingPrecision -> 20];
LinearSolve[ResourceFunction["MatrixPolynomial"][den, ma], ResourceFunction["MatrixPolynomial"][num, ma]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/435/4358088a-30c5-4a2c-8ab1-fd72012b13e5/42db80ebe374f222.png) |
| Out[17]= |  |
Compare with the result of MatrixFunction:
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= |
MatrixPolynomial is more efficient than MatrixFunction:
| In[19]:= |
| Out[19]= |
| In[20]:= |
| Out[20]= |
If m is diagonalizable with m=v.d.v-1 and the eigenvectors are well conditioned, then p(m)=v.p(d).v-1:
| In[21]:= | ![poly[x_] = LaguerreL[11, 5/2, x];
ma = RandomReal[1, {4, 4}];
{d, vt} = Eigensystem[ma]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/435/4358088a-30c5-4a2c-8ab1-fd72012b13e5/0453abbc6e6bbafb.png) |
| Out[23]= |  |
| In[24]:= |
| Out[24]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License