Examples
Basic Examples (1)
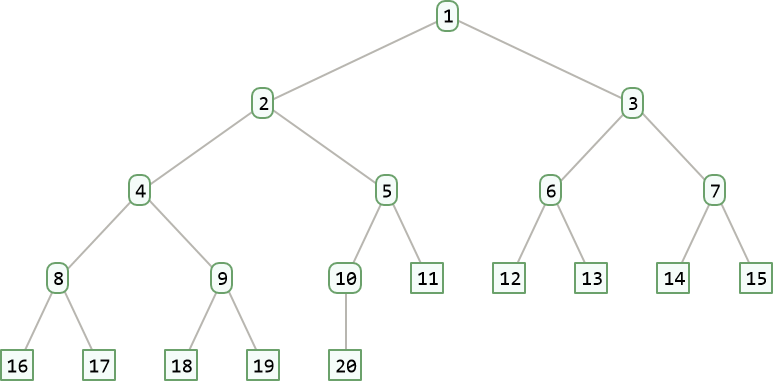
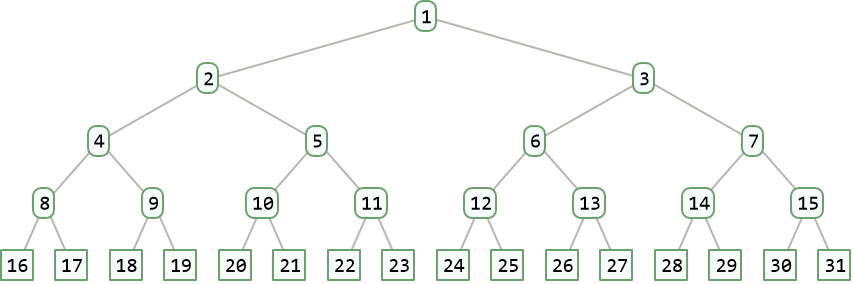
Arrange 20 elements on a complete binary tree:
Options (2)
ListToBinaryTree accepts the same options as Tree:
ListToBinaryTree accepts multiple options:
Properties and Relations (2)
A complete binary tree of height h has at least 2h nodes and at most 2h+1-1 nodes. For instance when h=4:
The height of the tree are the same for both complete binary trees:
A complete binary tree of 2k-1 nodes is the same as complete Kary tree with (k-1) 2's:
Possible Issues (1)
The length of the input must be at least one. Otherwise the function returns unevaluated:
Neat Examples (2)
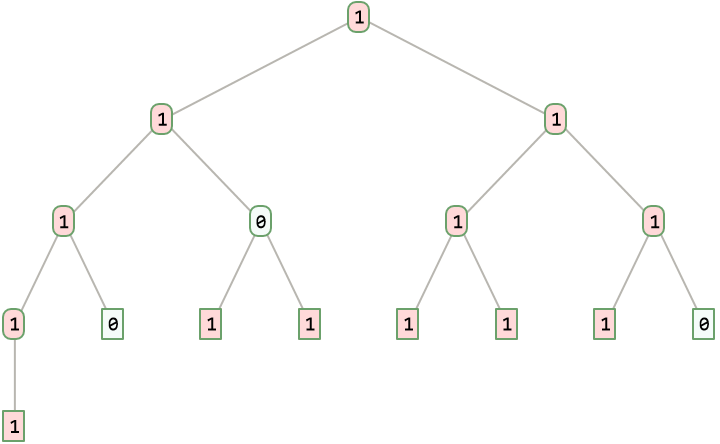
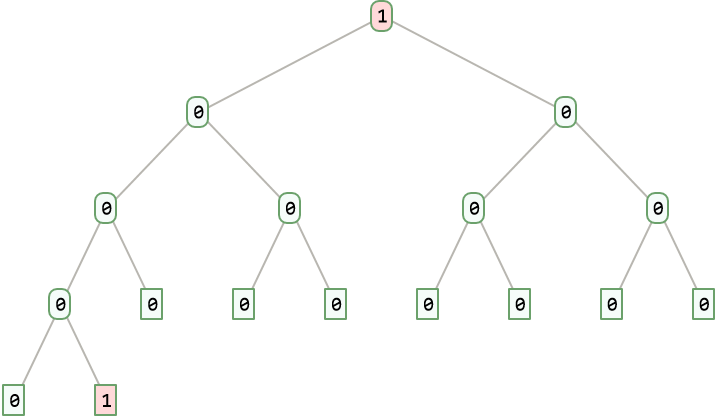
Use binary expansion of n as input to create a complete binary tree and then read those bits in pre-order (OEIS A380856):
Specify TreeTraversalOrder to implement pre-order traversal:
The new number and its associated complete binary tree:
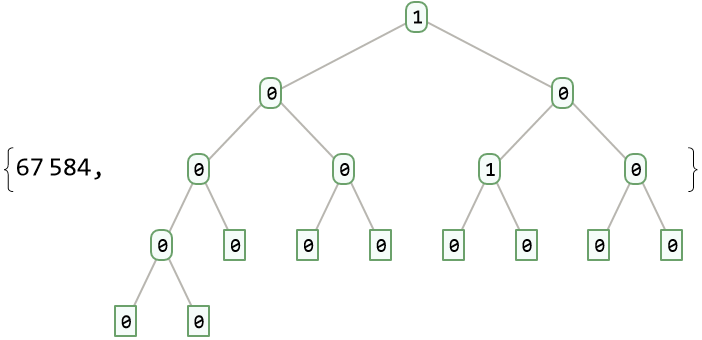
Every integer is associated with a permutation group using the operation from OEIS A380856:
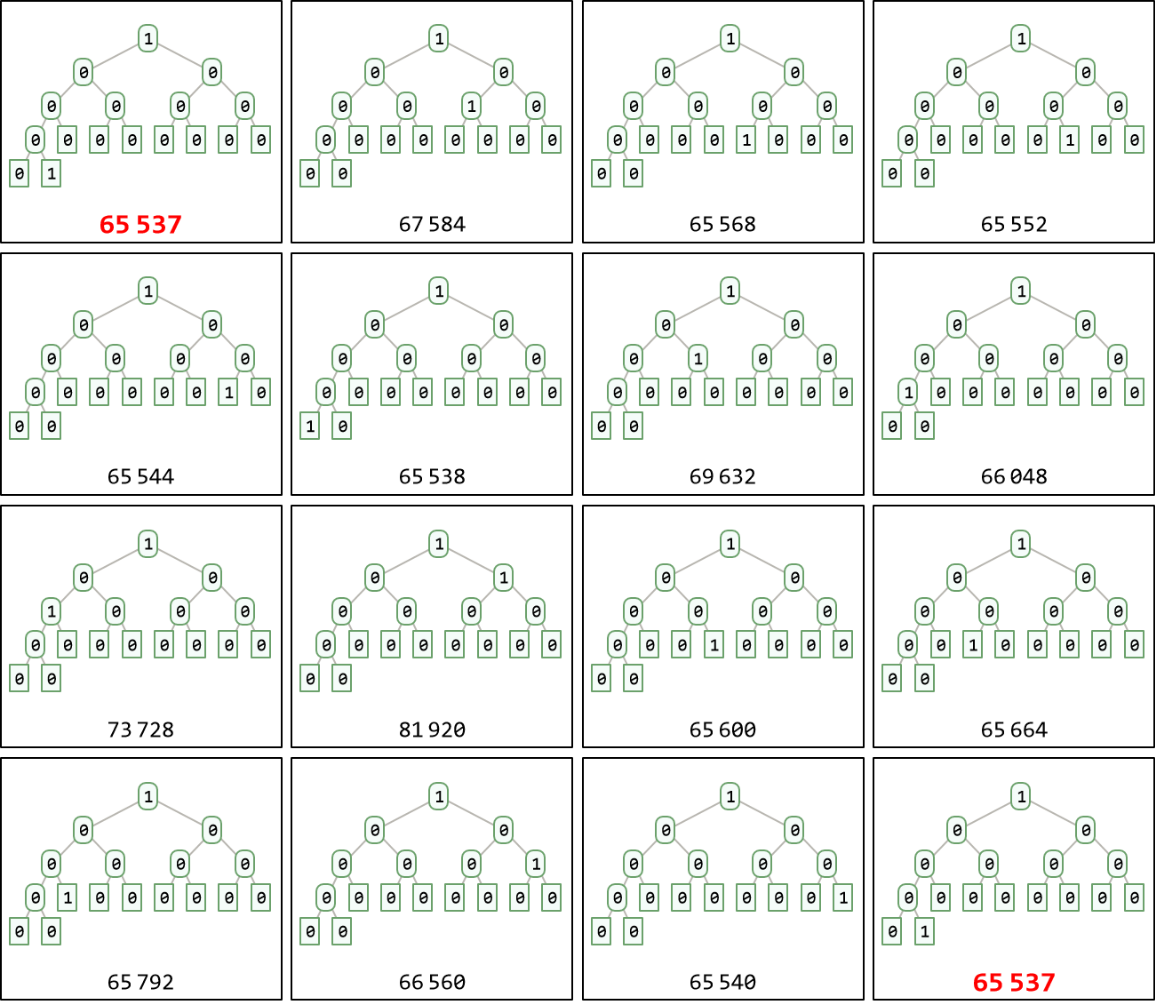
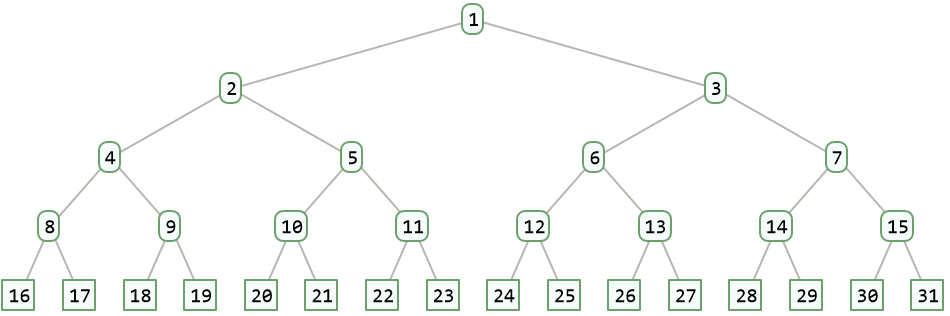
Use n=65537 for example:
The order of the permutation group associated with 65537 is 15:
Repeat 15 times the rearrangement of binary bits of 65537 on complete binary tree using pre-order traversal will return to the original number:
List the numbers and their complete binary tree representation:
Remove unused items in the deque:
Publisher
Shenghui Yang
Related Links
Requirements
Wolfram Language 14.0
(January 2024) or above
Version History
-
1.0.1
– 18 March 2025
-
1.0.0
– 07 March 2025
Related Resources
![ResourceFunction["ListToCompleteBinaryTree"][IntegerDigits[63357, 2], TreeElementStyle -> {TreeCases[1] -> LightRed}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d17/d173d4d8-821f-4950-a1f1-023d459f1aa3/1-0-0/516a73e3179148b2.png)
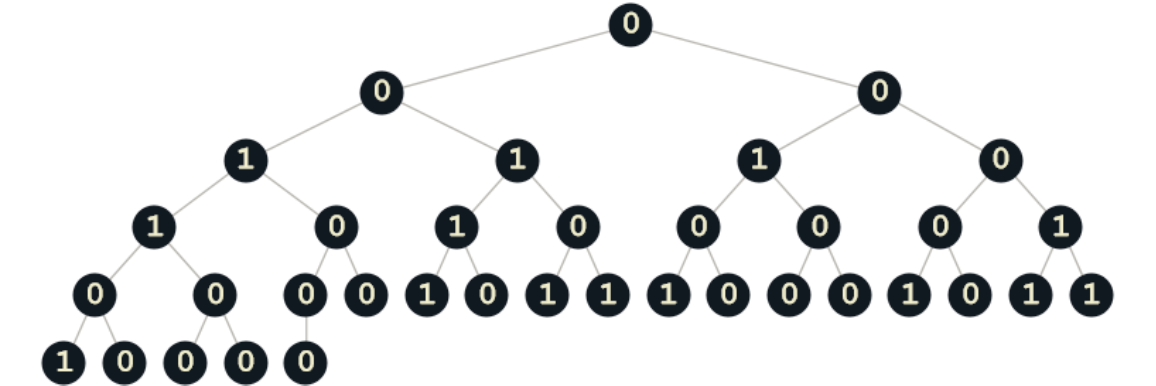
![ResourceFunction["ListToCompleteBinaryTree"][RandomInteger[{0, 1}, 36],
TreeElementShape -> All -> Graphics[{RGBColor["#101820"], Disk[{0, 1}, 1]}],
TreeElementSize -> All -> Scaled[0.12],
TreeElementLabelFunction -> All -> (Placed[
Style[#, 18, Bold, FontFamily -> "Courier", RGBColor["#F0EDCC"]],
Center] &)
]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d17/d173d4d8-821f-4950-a1f1-023d459f1aa3/1-0-0/6f3323eb95fc991d.png)

![cbt = ResourceFunction["ListToCompleteBinaryTree"][
IntegerDigits[65537, 2], TreeElementStyle -> {TreeCases[1] -> LightRed}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d17/d173d4d8-821f-4950-a1f1-023d459f1aa3/1-0-0/640c6348d2b6132d.png)
![permGroup[n_Integer] := Module[{bits, len, perm},
bits = IntegerDigits[n, 2];
len = Length[bits];
perm = Reap[TreeScan[Sow, ResourceFunction["ListToCompleteBinaryTree"][Range[len]], TreeTraversalOrder -> {"DepthFirst", "TopDown", "LeftRight"}]][[
2, 1]];
PermutationGroup[{FindPermutation[perm]}]
]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d17/d173d4d8-821f-4950-a1f1-023d459f1aa3/1-0-0/790eb30c4a607ccd.png)
![If[# == 65537, Highlighted[#], #] & /@ (
perm = NestList[
(cbt = ResourceFunction["ListToCompleteBinaryTree"][
IntegerDigits[#, 2]];
res = Reap[TreeScan[Sow, cbt, TreeTraversalOrder -> {"DepthFirst", "TopDown", "LeftRight"}]][[2, 1]];
ds["PushBack", res];
FromDigits[res, 2]) &
, 65537, 15])](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d17/d173d4d8-821f-4950-a1f1-023d459f1aa3/1-0-0/2aed381be434fdf5.png)

![Grid[Partition[MapThread[
Framed@Labeled[ResourceFunction["ListToCompleteBinaryTree"]@#1,
If[#2 == 65537, Style[#2, 16, Bold, Red], #2]
] &, {ds["Elements"], perm}], 4]
]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/d17/d173d4d8-821f-4950-a1f1-023d459f1aa3/1-0-0/34506960ca98c18d.png)
