Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Sort keys of an Association in the same order as another set of keys
ResourceFunction["KeySortLike"][assoc,order] sorts elements of assoc so their keys match order. | |
ResourceFunction["KeySortLike"][order] gives an operator that sorts associations like order. |
Sort an Association like a List:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
Create an operator:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
Sort some fruit:
| In[3]:= | ![sorter[<|"Watermelon" -> Entity[
"Food", {EntityProperty[
"Food", "FoodType"] -> ContainsExactly[{
Entity[
"FoodType", "Watermelon"]}], EntityProperty[
"Food", "AddedFoodTypes"] -> ContainsExactly[{}]}], "Grapes" -> Entity[
"Food", {EntityProperty[
"Food", "FoodType"] -> ContainsExactly[{
Entity[
"FoodType", "Grape"]}], EntityProperty[
"Food", "AddedFoodTypes"] -> ContainsExactly[{}]}], "Apples" -> Entity[
"Food", {EntityProperty[
"Food", "FoodType"] -> ContainsExactly[{
Entity[
"FoodType", "Apple"]}], EntityProperty[
"Food", "AddedFoodTypes"] -> ContainsExactly[{}]}], "Blueberries" -> Entity[
"Food", {EntityProperty[
"Food", "FoodType"] -> ContainsExactly[{
Entity[
"FoodType", "Blueberry"]}], EntityProperty[
"Food", "AddedFoodTypes"] -> ContainsExactly[{}]}]|>]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/c92/c9294236-189a-43da-a5e2-f91b5d125305/5d9875ef1833eda3.png) |
| Out[3]= |  |
Associations can be used to specify the order as well. Create two associations:
| In[4]:= |  |
Sort the all-time Major League Baseball home run records in the order of the all time runs batted in records:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
Sort integers based on an existing List:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |
Sort names according to an existing List containing only some of the keys:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
Sort names according to an existing List containing extra keys:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
Create an operator from an Association where the values are ignored:
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
Apply it to data:
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= |
Sort rows of a Dataset using the operator form:
| In[12]:= | ![Dataset[{
<|"a" -> 1, "b" -> "x", "c" -> {1}|>,
<|"a" -> 2, "b" -> "y", "c" -> {2, 3}|>}][All, ResourceFunction["KeySortLike"][{"b", "c", "a"}]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/c92/c9294236-189a-43da-a5e2-f91b5d125305/1392b0e572ff9d9a.png) |
| Out[12]= | 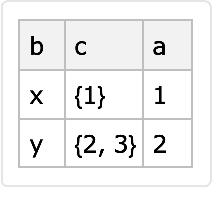 |
KeySortLike works on a Dataset which contains indexed tables (associations of associations). Get an indexed table dataset:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= | 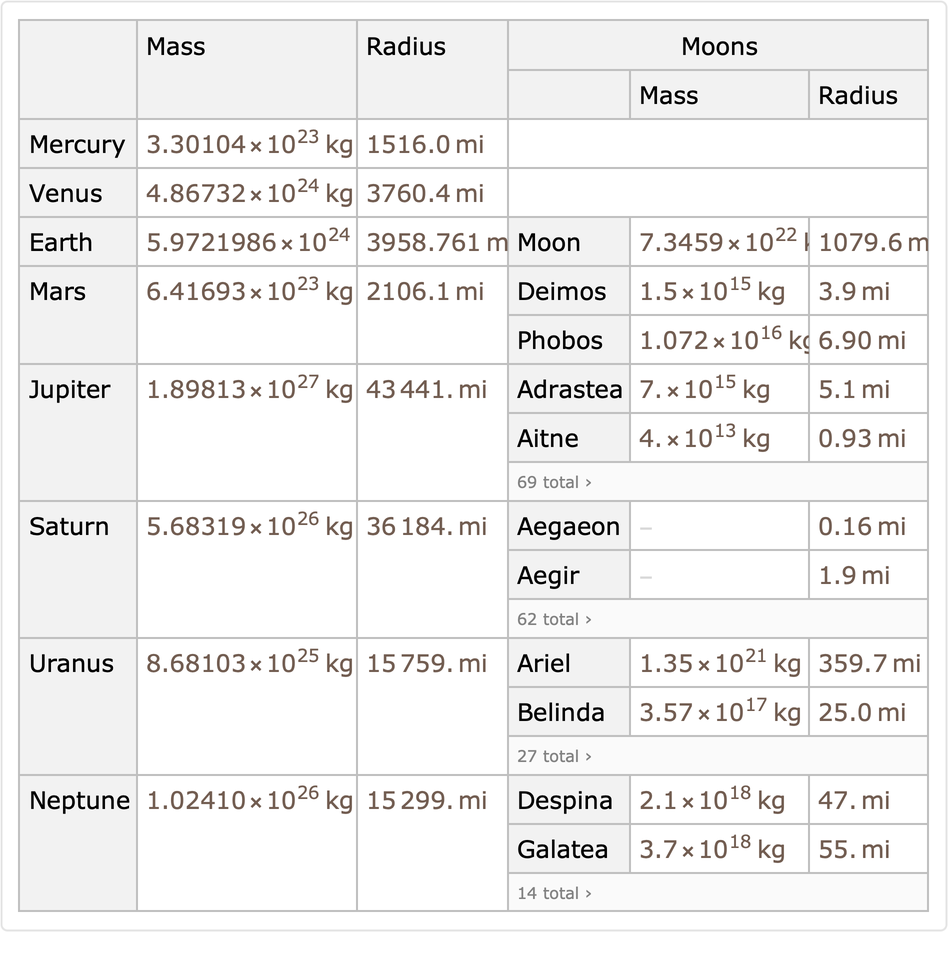 |
Sort the planets in the order that their names appear on the Wikipedia page for Roman deities:
| In[14]:= |
| Out[14]= | 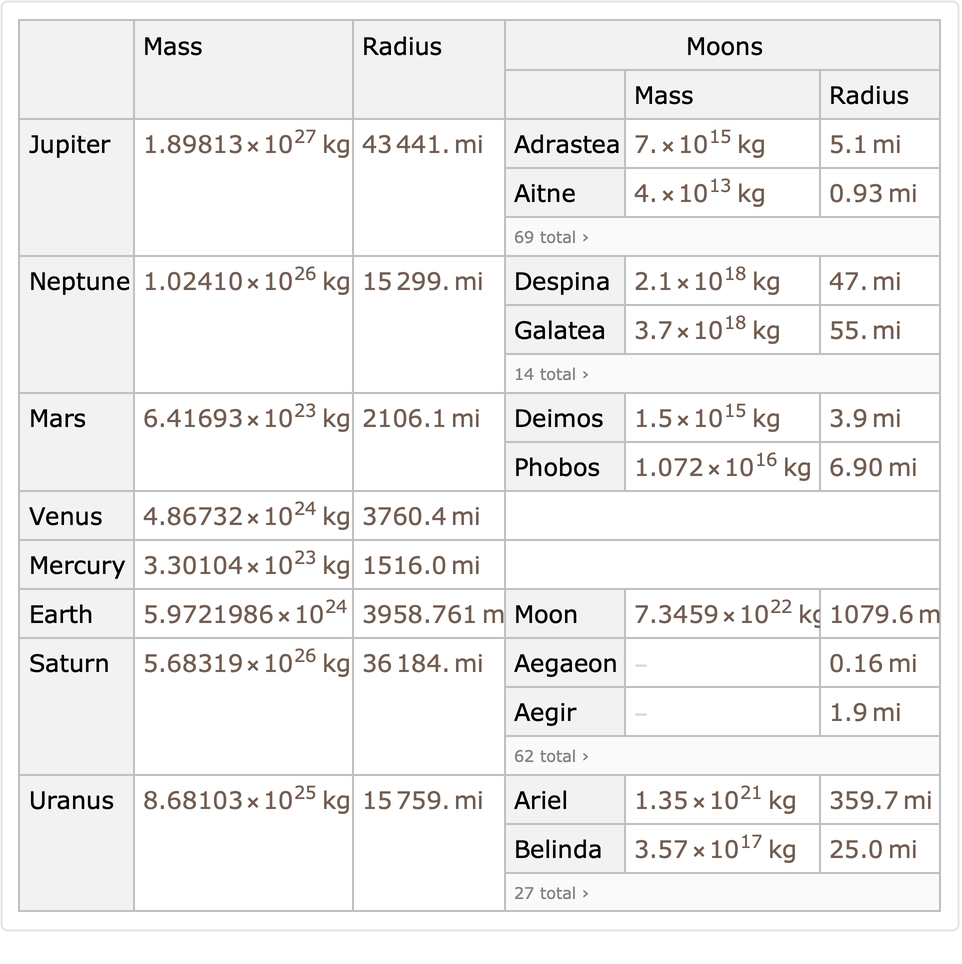 |
KeySortLike effectively applies the resource function SortLike to the keys of an Association:
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= |
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= |
KeySortLike fails for non-indexed datasets:
| In[17]:= | ![ds = Dataset[{
<|"a" -> 1, "b" -> "x", "c" -> {1}|>,
<|"a" -> 2, "b" -> "y", "c" -> {2, 3}|>}];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/c92/c9294236-189a-43da-a5e2-f91b5d125305/02032054bfbd5570.png) |
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= |
It can work as an operator at lower levels:
| In[19]:= |
| Out[19]= | 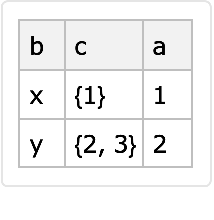 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License