Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Return a canonical rotation/reflection for a point set
ResourceFunction["DihedralCanonicalization"][points] find a canonical rotation, reflection and ordering for 2D pointset points. |
Canonicalize a set of points:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
Verify that applying the function to a canonicalized set returns the same set:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
Show before/after to reveal the pattern has rotated counterclockwise:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= | 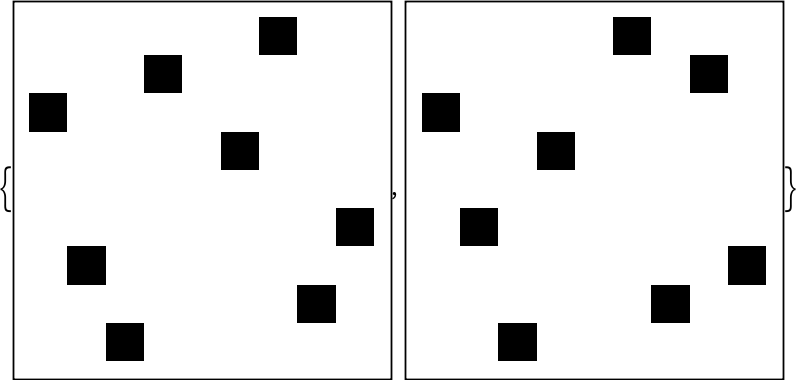 |
Find invariant pairs of points:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[5]= |
Find invariant pairs of points with maximal absolute value 2:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[7]= | 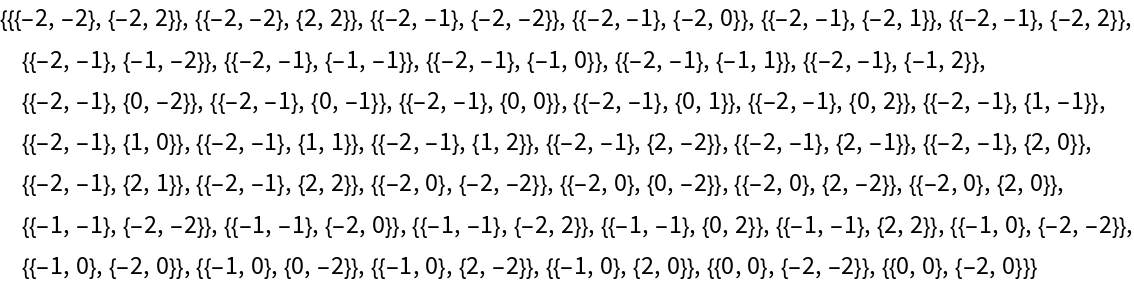 |
There are a few hundred of pairs2:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
The canonical invariants are a much smaller set:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
Count the number of invariants with maximal absolute value n:
| In[10]:= | ![pairs7 = Subsets[Tuples[Range[-7, 7], {2}], {2}];
invariants7 = Union[ResourceFunction["DihedralCanonicalization"] /@ pairs7];
Length /@ GatherBy[SortBy[invariants7, Max[Abs[Flatten[#]]] &], Max[Abs[Flatten[#]]] &]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/9f5/9f52959c-4ff1-448d-9d7a-ba24065bd818/006a5f66f5904216.png) |
| Out[11]= |
Obtain values for a related cubic:
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |
Find invariant triples:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[14]= | 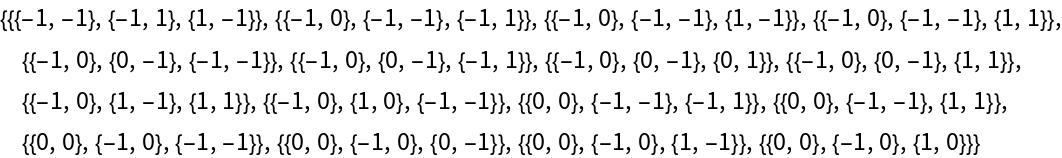 |
Show the 16 invariant triples:
| In[15]:= | ![Grid[Partition[
Graphics[{EdgeForm[Black], {White, Rectangle[{-1.1, -1.1}, {1.1, 1.1}]}, Point[#], Circle[{0, 0}, .1]}, ImageSize -> 80] & /@ invariants1, 4]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/9f5/9f52959c-4ff1-448d-9d7a-ba24065bd818/313ea9b85e1e93d0.png) |
| Out[15]= | 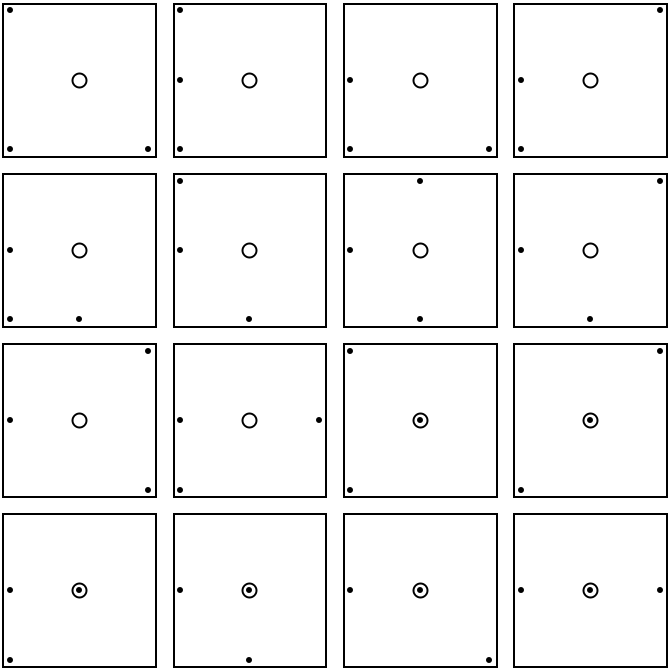 |
Curiously, the number of invariant triples grows as follows:
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= |
Repeated points will be tossed out:
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= |
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= |
Wolfram Language 14.0 (January 2024) or above
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License