Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Get data about various black hole models
ResourceFunction["BlackHoleModelData"][solution] returns the metric for the specified solution of the Einstein field equations. | |
ResourceFunction["BlackHoleModelData"][solution,property] returns the symbolic expression for the specified property in the given metric. | |
ResourceFunction["BlackHoleModelData"][solution,property,{var1→quantity1,var2→quantity2, …}] inserts the specified values quantityi for the variables vari into expressions. | |
ResourceFunction["BlackHoleModelData"][solution,property,attribute] gives the value of the specified attribute. |
| "Coordinates" | the coordinate system of the solution |
| "Entropy" | entropy |
| "HorizonArea" | area of the event horizon |
| "HorizonRadius" | radius of the event horizon |
| "Metric" | Association of nonzero metric components for the solution |
| "PenroseDiagram" | Penrose diagram |
| "SurfaceGravity" | gravity at the event horizon boundary |
| "Temperature" | temperature |
| "QuantityVariableDimensions" | list of base dimensions for all variables |
| "QuantityVariableNames" | English names for all variables |
| "QuantityVariablePhysicalQuantities" | physical quantities for all variables |
| "QuantityVariables" | list of all variables in the formula |
| "QuantityVariableTable" | details on all variables for the formula |
Obtain the metric for a particular solution to the Einstein field equations:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= | 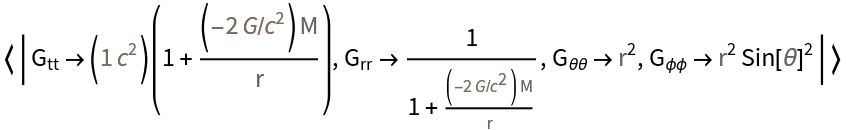 |
Learn the expression for the entropy of a black hole in the Reissner–Nordstrom solution:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= | 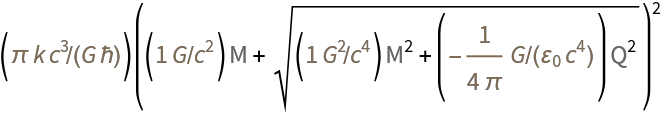 |
Determine the temperature of a rotating charged black hole with the mass of a million suns:
| In[3]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"BlackHoleModelData"]["KerrNewman", "Temperature", {"M" -> 10^6 StarData["Sun", "Mass"], "J" -> Quantity[10^9, "Joules" "Seconds"], "Q" -> Quantity[10^6, "Coulombs"]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/b78/b782f7bf-708e-42de-85ce-74f9f53a436e/70865ae6165c163d.png) |
| Out[3]= |
List all supported solutions:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |
List the available properties:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
Look up the metric to a particular solution:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= | 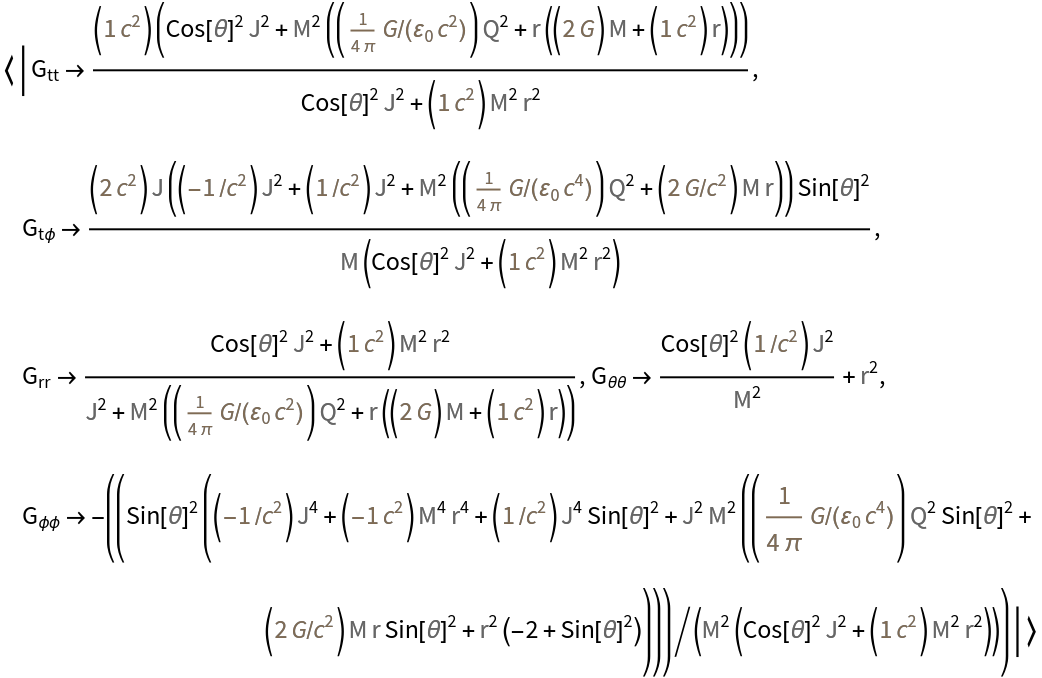 |
Obtain the expressions for various black hole properties:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= | 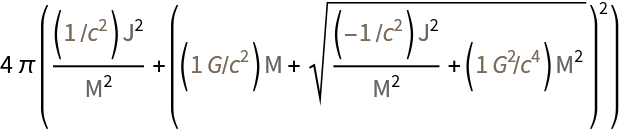 |
Extract information on the physical quantities used to calculate the properties of black holes:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= |
Explore Penrose diagrams for different black hole geometries:
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= | 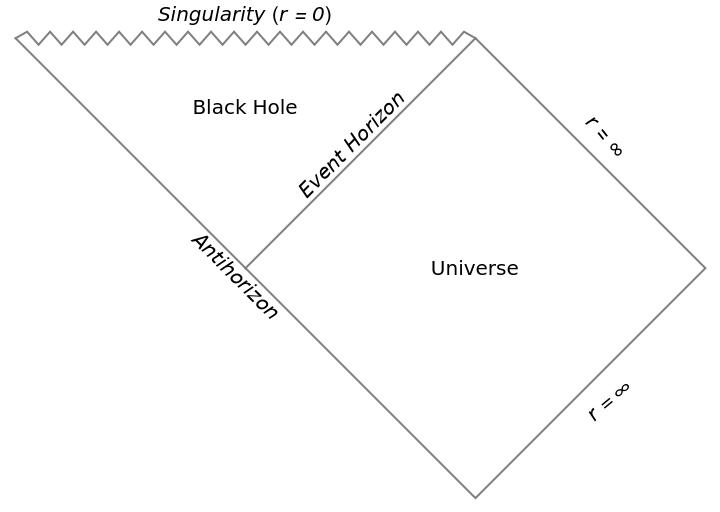 |
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= | 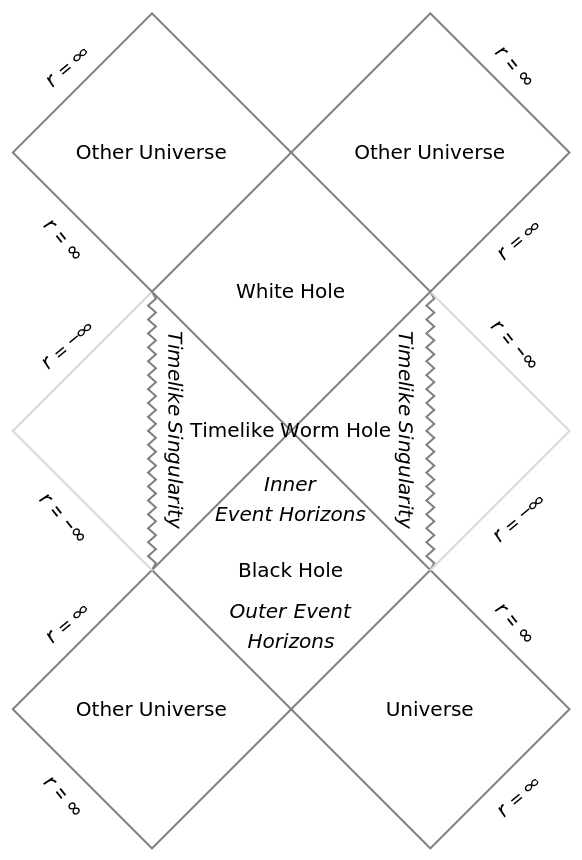 |
Insert values for the important physical quantities of a black hole to learn the surface gravity on the event horizon:
| In[14]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"BlackHoleModelData"]["ReissnerNordstrom", "SurfaceGravity", {"M" -> 10 StarData["Sun", "Mass"], "Q" -> Quantity[10^13, "Coulombs"]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/b78/b782f7bf-708e-42de-85ce-74f9f53a436e/6491ec0d69be9d37.png) |
| Out[14]= |
Convert that to units of standard gravity:
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= |
Physical quantities can be specified as Quantity objects or numbers:
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= |
Quantity input is checked for the correct units:
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= |
Only valid physical quantities are used:
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= |
Some values are not physically realizable:
| In[19]:= | ![ResourceFunction[
"BlackHoleModelData"]["KerrNewman", "Temperature", {"M" -> StarData["Sun", "Mass"], "J" -> Quantity[10^10, "Joules" "Seconds"], "Q" -> Quantity[10^30, "Coulombs"]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/b78/b782f7bf-708e-42de-85ce-74f9f53a436e/764b7ae49e85ee65.png) |
| Out[19]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License