Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Serialize an expression along with any dependent definitions
ResourceFunction["BinarySerializeWithDefinitions"][expr] serializes expr to a ByteArray object along with its dependent definitions. |
| Method | Automatic | details of serialization methods to use |
| PerformanceGoal | Automatic | aspects of performance to try to optimize |
| "Speed" | optimize for serialization and deserialization speed |
| "Size" | optimize for smallness of serialized output |
| Automatic | automatically pick serialization strategy |
| {typespec1→enc1,…} | specify encodings for particular types |
| Automatic | pick encodings automatically based on data |
| "PackedArrayIntegerType" | integer packed arrays |
| "PackedArrayRealType" | real-valued packed arrays |
| "PackedArrayComplexType" | complex-valued packed arrays |
Serialize an expression with dependent definitions:
| In[1]:= | ![f[x_] := g[x] + 1;
g[x_] := 2 x;
bytes = ResourceFunction["BinarySerializeWithDefinitions"][f]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/036/036b5832-2ec0-4bd6-90ef-50733d6946b5/1b03012b0c2ec783.png) |
| Out[3]= |
Definitions are restored when deserialized:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[5]= |
The serialized expression is an evaluation that restores definitions before returning the output:
| In[6]:= | ![ClearAll[f, g];
f[x_] := g[x] + 1;
g[x_] := 2 x;
bytes = ResourceFunction["BinarySerializeWithDefinitions"][f];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/036/036b5832-2ec0-4bd6-90ef-50733d6946b5/2515031d4b8c85d5.png) |
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= | 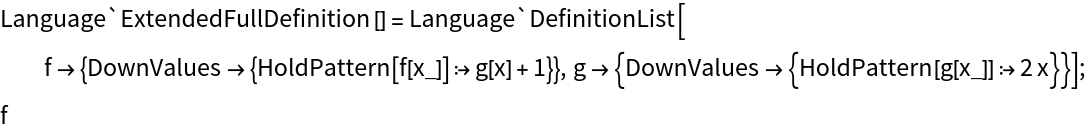 |
BinarySerialize by itself does not preserve definitions:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
| In[10]:= |
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= |
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |
Serialize a Dataset:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |  |
Serialize the same Dataset with PerformanceGoal set to "Size":
| In[14]:= | ![compressed = ResourceFunction["BinarySerializeWithDefinitions"][
ResourceData["Meteorite Landings"], PerformanceGoal -> "Size"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/036/036b5832-2ec0-4bd6-90ef-50733d6946b5/0ef418af95f77d79.png) |
| Out[14]= |
Both forms represent the same expression:
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= |
Create a packed array of integer values:
| In[16]:= |
By default, BinarySerializeWithDefinitions uses the smallest integer type that fits the data:
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= |
Serialize the packed array using a bigger integer type:
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= |
Create a packed array of real values:
| In[19]:= |
| Out[19]= |
Serialize the array:
| In[20]:= |
| Out[20]= |
Serialize the array using machine floats, trading precision for a smaller output:
| In[21]:= |
| Out[21]= |
Create a packed array of complex values:
| In[22]:= |
| Out[22]= |
Serialize the array:
| In[23]:= |
| Out[23]= |
Serialize the array using lower precision:
| In[24]:= |
| Out[24]= |
CloudPut an evaluation that runs each time you use CloudGet on it:
| In[25]:= | ![CloudSymbol["count"] = 0;
info[] := With[{i = <|"Time" -> Now, "Count" -> (CloudSymbol["count"] += 1)|>}, PutAppend[i, CloudObject["log.wl"]]; i];](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/036/036b5832-2ec0-4bd6-90ef-50733d6946b5/4d2cfc992b4eb048.png) |
| In[26]:= | ![With[{b = ResourceFunction["BinarySerializeWithDefinitions"][
Unevaluated[info[]]]},
CloudPut[Unevaluated[BinaryDeserialize[b]], "info"]
]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/036/036b5832-2ec0-4bd6-90ef-50733d6946b5/1e688032df7e2b00.png) |
| Out[26]= |
| In[27]:= |
| Out[27]= |
| In[28]:= |
| Out[28]= |
Check the log:
| In[29]:= |
| Out[29]= | 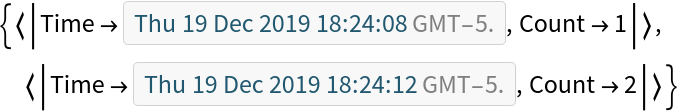 |
When there are no dependent symbols, BinarySerializeWithDefinitions will produce the same ByteArray as BinarySerialize:
| In[30]:= |
| Out[23]= |
The results are different when definitions need to be included:
| In[31]:= |
| Out[27]= |
For small expressions, definitions add a significant amount of overhead relative to the total size:
| In[32]:= |
| In[33]:= |
| Out[33]= |
| In[34]:= |
| Out[34]= |
This overhead becomes insignificant for larger expressions:
| In[35]:= |
| In[36]:= |
| Out[36]= |
| In[37]:= |
| Out[37]= |
Wolfram Language 11.3 (March 2018) or above
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License