Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Compute the generalized outer product of lists and get an association keyed by arguments
ResourceFunction["AssociationOuter"][f,list1,list2,…] gives the generalized outer product of the listi as a nested association, forming all possible combinations of the lowest-level elements in each of them as keys, and feeding them as arguments to f for values. | |
ResourceFunction["AssociationOuter"][f,list1,list2,…,n] treats as separate elements only sublists at level n in the listi. | |
ResourceFunction["AssociationOuter"][f,list1,list2,…,n1,n2,…] treats as separate elements only sublists at level ni in the corresponding listi. |
Compute an outer product:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
Compare to Outer:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
Outer product of vectors:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |
Outer product of matrices:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |
The keys are nested so that values can be retrieved in argument order:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |
Treat nested lists as rank-1 vectors of sublists:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |
Arrays can be ragged:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
Outer product of SparseArray objects:
| In[10]:= |
| In[11]:= |
| Out[11]= |
Word combinations:
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |  |
Function combinations:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= | 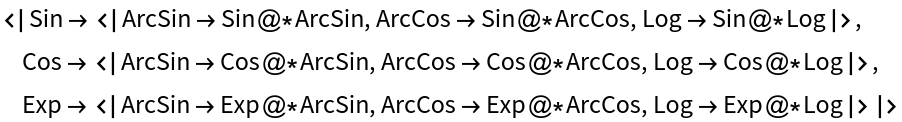 |
| In[14]:= |
| Out[14]= | 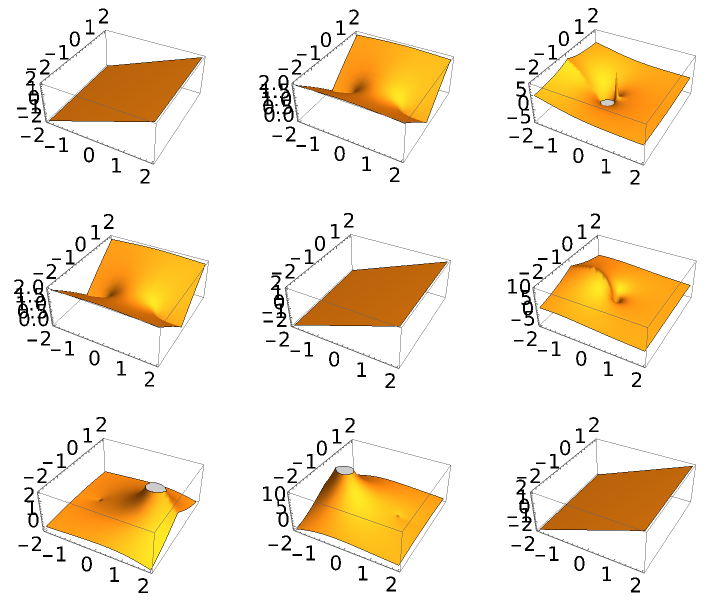 |
Complete bipartite graph:
| In[15]:= | ![Graphics[Values[
ResourceFunction["AssociationKeyFlatten"][
ResourceFunction["AssociationOuter"][Line[ {##}] &, Table[{x, 1}, {x, 4}], Table[{x, 2}, {x, 4}], 1]]]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/354/354a1f72-7066-4dfa-b465-2751d6b71756/4a6989b53a809f81.png) |
| Out[15]= | 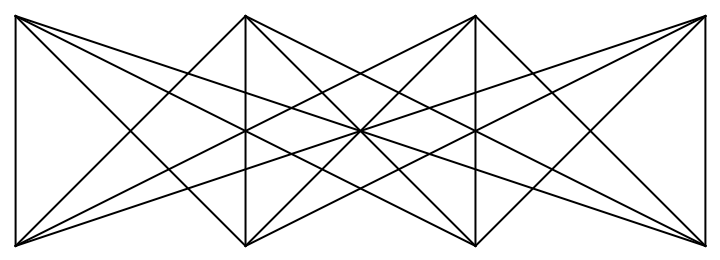 |
Generate all possible binary trees with nodes from f and leaves from e to depth n:
| In[16]:= | ![trees[f_, e_, 1] = e;
trees[f_, e_, n_] := Flatten[Table[
ResourceFunction["AssociationOuter"][#, trees[f, e, r], trees[f, e, n - r]], {r, n - 1}] & /@ f]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/354/354a1f72-7066-4dfa-b465-2751d6b71756/07c075fc3eef7647.png) |
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= | 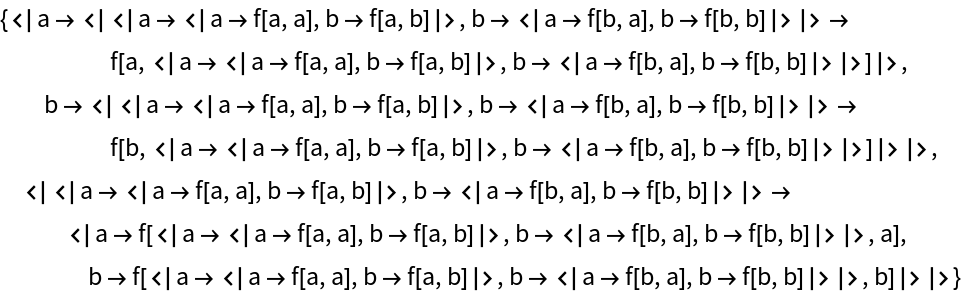 |
If each of the listi are duplicate-free, dimensions of the result are a concatenation of the dimensions of the inputs:
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= |
| In[19]:= |
| Out[19]= |
If there are duplicates, the dimensions will correspond to the number of unique elements in each listi:
| In[20]:= |
| Out[20]= |
| In[21]:= |
| Out[21]= |
Compare to Outer, which is unaffected by duplicates:
| In[22]:= |
| Out[22]= |
| In[23]:= |
| Out[23]= |
Use Map and Values to convert the result into the format given by Outer:
| In[24]:= |
| Out[24]= |
| In[25]:= |
| Out[25]= |
| In[26]:= |
| Out[26]= |
AssociationKeyFlatten can be used to convert the result into a flat association:
| In[27]:= |
| Out[27]= |
| In[28]:= |
| Out[28]= |
Restore the nested structure with AssociationKeyDeflatten:
| In[29]:= |
| Out[29]= |
Distribute forms the same combinations of all elements, but in a flat structure:
| In[30]:= |
| Out[30]= |
| In[31]:= |
| Out[31]= |
Use AssociationKeyFlatten and Values to get the same result:
| In[32]:= |
| Out[32]= |
AssociationOuter relates to Outer much like AssociationMap relates to Map:
| In[33]:= |
| Out[33]= |
| In[34]:= |
| Out[34]= |
| In[35]:= |
| Out[35]= |
| In[36]:= |
| Out[36]= |
Unlike Outer, the head must be List:
| In[37]:= |
| Out[37]= |
| In[38]:= |
| Out[38]= |
Unlike Outer, at least two arguments are required:
| In[39]:= |
| Out[39]= |
| In[40]:= |
| Out[40]= |
Values are nested by arguments in the order they were given to f, even if f is Orderless:
| In[41]:= |
| Out[41]= |
| In[42]:= |
| Out[42]= |
| In[43]:= |
| Out[43]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License