Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Compute the Knuth-Bendix completion for a given multiway system
ResourceFunction["KnuthBendixCompletion"][rules,init,n] generates a list of Knuth-Bendix completion rules for the multiway system with the specified rules after n steps, starting with initial conditions init. | |
ResourceFunction["KnuthBendixCompletion"][rules→sel,init,n] uses the function sel to select which of the events obtained at each step to include in the evolution. |
| {"lhs1"->"rhs1",…} | string substitution system |
| {{l11,l12,…}->{r11,r12,..},…} | list substitution system |
| WolframModel[rules] | Wolfram Model system |
| CellularAutomaton[rules] | cellular automaton system |
| "type"→rules | system of the specified type |
| "StringSubstitutionSystem" | rules given as replacements on strings |
| "ListSubstitutionSystem" | rules given as replacements on lists |
| "CellularAutomaton" | rules given as a list of CellularAutomaton rule specifications |
| "WolframModel" | rules given as replacements on hypergraphs |
| "StateEvolutionFunction" | gives the list of successors to a given state |
| "StateEquivalenceFunction" | determines whether two states should be considered equivalent |
| "StateEventFunction" | gives the list of events applicable to a given state |
| "EventApplicationFunction" | applies an event to a given state |
| "EventDecompositionFunction" | decomposes an event into creator and destroyer events for individual elements |
| "SystemType" | system type name |
| "EventSelectionFunction" | determines which events should be applied to a given state |
| "Sequential" | applies the first possible replacement (sequential substitution system) |
| "Random" | applies a random replacement |
| {"Random",n} | applies n randomly chosen replacements |
| "MaxScan" | applies the maximal set of spatially-separated replacements (strings only) |
| "IncludeStepNumber" | False | whether to label states and events with their respective step numbers |
| "IncludeStateID" | False | whether to label states and events with unique IDs |
Generate the list of all Knuth-Bendix completion rules for two string substitution systems:
| In[1]:= |
|
| Out[1]= |
|
| In[2]:= |
|
| Out[2]= |

|
Different event selection functions can lead to different lists of Knuth-Bendix completion rules:
| In[3]:= |
|
| Out[3]= |
|
| In[4]:= |
|
| Out[4]= |
|
KnuthBendixCompletion can handle Wolfram models and other system types:
| In[5]:= |
|
| Out[5]= |
|
Provide a cellular automaton as input:
| In[6]:= |
|
| Out[6]= |

|
Preventing identical states from being merged, by including step numbers and/or state IDs, can change the resulting Knuth-Bendix completions:
| In[7]:= |
|
| Out[7]= |

|
| In[8]:= |
|
| Out[8]= |

|
KnuthBendixCompletion supports both string and list substitution systems:
| In[9]:= |
|
| Out[9]= |
|
Use substitutions on lists:
| In[10]:= |
|
| Out[10]= |
|
Lists can contain arbitrary symbolic elements:
| In[11]:= |
|
| Out[11]= |
|
Give an explicit substitution system rule:
| In[12]:= |
|
| Out[12]= |

|
An alternative method of specifying that a substitution system should be used:
| In[13]:= |
|
| Out[13]= |

|
KnuthBendixCompletion also supports multiway generalizations of cellular automata:
| In[14]:= |
|
| Out[14]= |
|
Generate a Knuth-Bendix completion for left- and right-shift cellular automaton rules after 3 steps:
| In[15]:= |
|
| Out[15]= |

|
Determine that the rule 30 cellular automaton is not causal invariant:
| In[16]:= |
|
| Out[16]= |

|
KnuthBendixCompletion also supports multiway generalizations of Wolfram Models:
| In[17]:= |
|
| Out[17]= |
|
| In[18]:= |
|
| Out[18]= |
|
Construct a multiway evolution by explicitly specifying an association:
| In[19]:= |
![ResourceFunction[
"KnuthBendixCompletion"][<|
"StateEvolutionFunction" -> (StringReplaceList[#, {"A" -> "AA", "B" -> "AB"}] &), "StateEquivalenceFunction" -> SameQ, "StateEventFunction" -> Identity, "EventDecompositionFunction" -> Identity, "EventApplicationFunction" -> Identity, "SystemType" -> "None", "EventSelectionFunction" -> Identity|>, {"ABA"}, 3]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/91e/91ecc1bd-3f1d-4801-ba6c-de8478903c14/47157a6c55a5541b.png)
|
| Out[19]= |
|
KnuthBendixCompletion accepts both individual rules and lists of rules:
| In[20]:= |
|
| Out[20]= |
|
| In[21]:= |
|
| Out[21]= |

|
Likewise for initial conditions:
| In[22]:= |
|
| Out[22]= |

|
Apply only the first possible event at each step:
| In[23]:= |
|
| Out[23]= |
|
Apply the first and last possible events at each step:
| In[24]:= |
|
| Out[24]= |
|
Use a greedy-style algorithm to apply the maximal set of non-conflicting events at each step (strings only):
| In[25]:= |
|
| Out[25]= |
|
Explicitly specify the type of rule:
| In[26]:= |
|
| Out[26]= |

|
| In[27]:= |
|
| Out[27]= |

|
By default, equivalent states are merged across all time steps:
| In[28]:= |
|
| Out[28]= |
|
Merging of equivalent states across different time steps can be prevented by including step numbers:
| In[29]:= |
|
| Out[29]= |
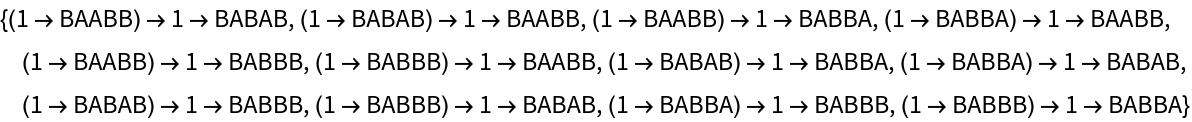
|
Merging of equivalent states at the same time step can be prevented by also including state IDs:
| In[30]:= |
|
| Out[30]= |

|
KnuthBendixCompletion returning an empty list of Knuth-Bendix completion rules is a sufficient (but not necessary) condition for causal invariance:
| In[34]:= |
|
| Out[34]= |
|
| In[35]:= |
|
| Out[35]= |
|
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License