Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Find the equation for an ellipse given two foci and a point
ResourceFunction["FociPointEllipse"][{f1,f2,p},{x,y}] returns the ellipse A x2+B x y+C y2+D x+E y+F in the variables x and y, given the foci f1,f2 and a point p through which the ellipse passes. | |
ResourceFunction["FociPointEllipse"][{f1,f2,p},t] returns a parametric equation in the variable t. | |
ResourceFunction["FociPointEllipse"][{f1,f2,p}] returns an Ellipsoid object representing the ellipse. |
Find the Cartesian equation of an ellipse with foci (3,3) and ![]() ) that goes through point
) that goes through point ![]() ):
):
| In[1]:= | ![{F, G, H} = {{3, 3}, {7/3, 11/3}, {5/2, 5/2}};
eq = ResourceFunction["FociPointEllipse"][{F, G, H}, {x, y}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/813/81382fb7-ca72-45e2-95f7-bbe5e6665f9d/00e130097ff1ec34.png) |
| Out[2]= |
Show the ellipse:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= | 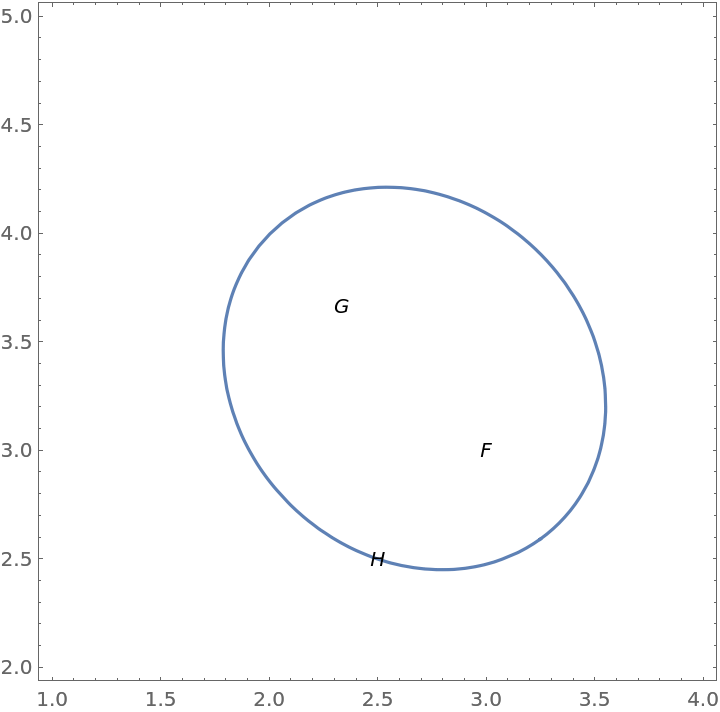 |
Generate the parametric equations of an ellipse with foci (3,3) and ![]() ) that goes through point
) that goes through point ![]() ):
):
| In[4]:= | ![{F, G, H} = {{3, 3}, {7/3, 11/3}, {5/2, 5/2}};
ell = ResourceFunction["FociPointEllipse"][{F, G, H}, t]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/813/81382fb7-ca72-45e2-95f7-bbe5e6665f9d/27701a6bc9322d4e.png) |
| Out[5]= | 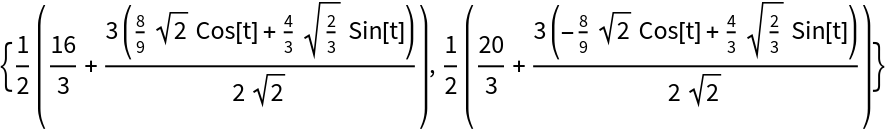 |
Show the ellipse:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= | 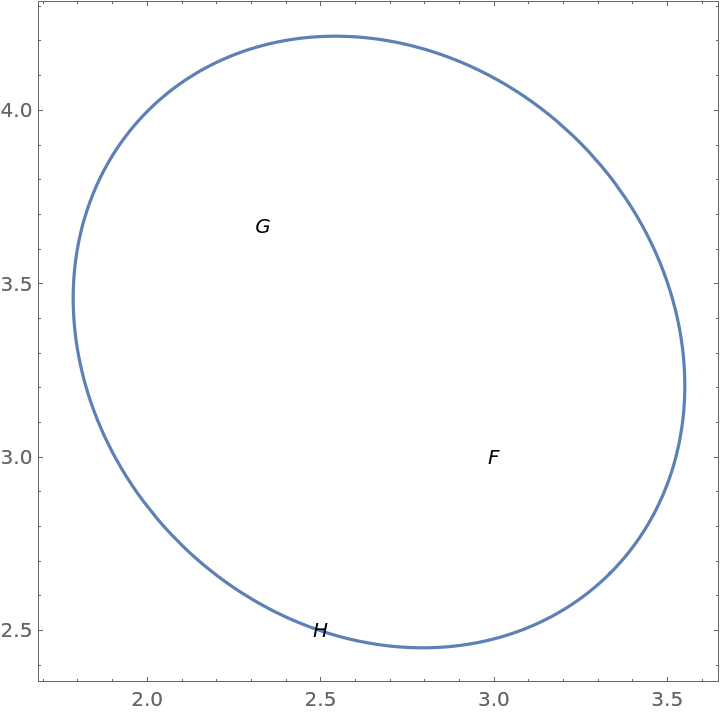 |
Generate the corresponding Ellipsoid object:
| In[7]:= |
| Out[7]= |
Show the ellipse:
| In[8]:= |
| Out[8]= |  |
Use a different set of variables:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
Use formal variables:
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
Use FociPointEllipse to generate the implicit Cartesian equation of an ellipse:
| In[11]:= |
| Out[12]= |
Use GroebnerBasis to get an equivalent result:
| In[13]:= | ![First[GroebnerBasis[
Sqrt[# . # &[{x, y} - F]] + Sqrt[# . # &[{x, y} - G]] == Sqrt[# . # &[H - F]] + Sqrt[# . # &[H - G]], {x, y}]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/813/81382fb7-ca72-45e2-95f7-bbe5e6665f9d/26fc4e34ffa86194.png) |
| Out[13]= |
Generate an equivalent parametric equation:
| In[14]:= |
| Out[14]= |
Use GroebnerBasis to derive the implicit Cartesian equation from the parametric equation:
| In[15]:= |
| Out[15]= |
Use the resource function EllipseProperties to generate properties of the ellipse:
| In[16]:= |
| Out[16]= |  |
Get an ellipse equation:
| In[17]:= |
| Out[17]= |
Show positions for coefficients in A x2+B x y+C y2+D x+E y+F=0:
| In[18]:= |
| Out[18]= |
Get the coefficients:
| In[19]:= |
| Out[19]= |
See the coefficients in the standard order:
| In[20]:= |
| Out[20]= |
Construct an ellipse from given foci and a point:
| In[21]:= | ![{F, G, H} = {{3, 3}, {7/3, 11/3}, {5/2, 5/2}};
ell = ResourceFunction["FociPointEllipse"][{F, G, H}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/813/81382fb7-ca72-45e2-95f7-bbe5e6665f9d/39b89c96ae85675f.png) |
| Out[22]= |
Use three mysterious points to create a complex cubic, take the derivative and solve the quadratic to find foci that happen to be F and G:
| In[23]:= |
| Out[24]= |
In Marden's theorem, the above step finds the foci of an inellipse that is tangent to the midpoints of the sides of the triangle generated by vertices PQR:
| In[25]:= | ![Graphics[{{Directive[EdgeForm[Black], White], Polygon[{P, Q, R}]}, {Directive[
FaceForm[],
EdgeForm[
Directive[
RGBColor[0.368417, 0.506779, 0.709798],
AbsoluteThickness[1.6]]]], ell}, {Blue, Style[Text[#[[1]], #[[2]]], 18] & /@ Transpose[{Characters["FGHPQR"], {F, G, H, P, Q, R}}]}}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/813/81382fb7-ca72-45e2-95f7-bbe5e6665f9d/3384cc9ffc526ca3.png) |
| Out[25]= |  |
The resulting inellipse is a scaled version of the Steiner circumellipse, with a scaling factor of 1/2. Use the resource function SteinerCircumellipse to produce an equivalent figure:
| In[26]:= | ![ell2 = ResourceFunction["SteinerCircumellipse"][{P, Q, R}];
Graphics[{{Directive[EdgeForm[Black], White], Polygon[{P, Q, R}]}, {Directive[
FaceForm[],
EdgeForm[
Directive[
RGBColor[0.368417, 0.506779, 0.709798],
AbsoluteThickness[1.6]]]], Scale[ell2, {1/2, 1/2}, First[ell2]]}, {Blue, Style[Text[#[[1]], #[[2]]], 18] & /@ Transpose[{Characters["FGHPQR"], {F, G, H, P, Q, R}}]}}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/813/81382fb7-ca72-45e2-95f7-bbe5e6665f9d/4af6e2336d0dc0f0.png) |
| Out[27]= | 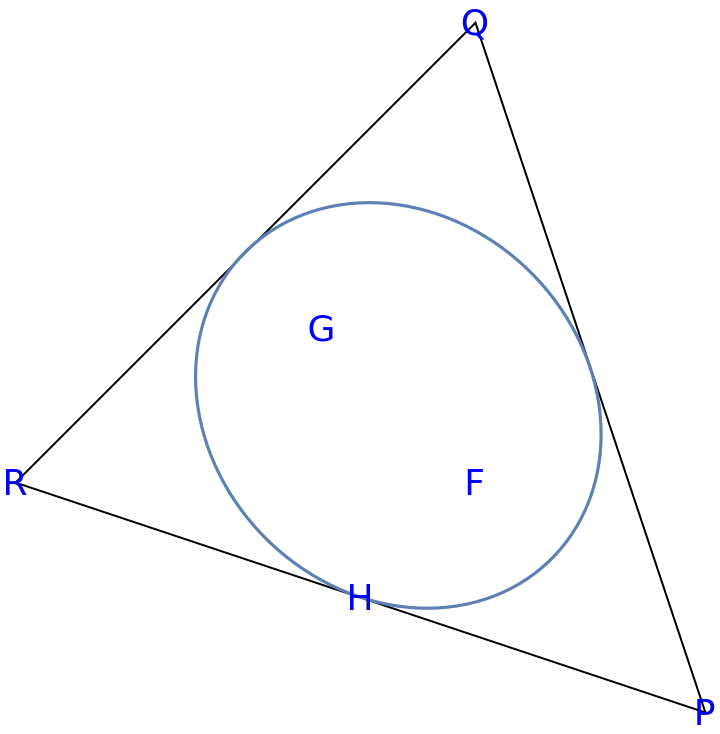 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License