Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Give the index of a subset or return the subset with that index
ResourceFunction["IndexedSubset"][choose,index] returns a subset of length choose with given index. | |
ResourceFunction["IndexedSubset"][list] gives the index of subset list. |
The following 3-subset ordering can be extended to infinity:
| In[1]:= |
| Out[1]= |
The function returns the same subsets in the same order:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |
The function can return subsets of a large index:
| In[3]:= |
| Out[3]= |
Applying the function to a subset returns the index:
| In[4]:= |
| Out[4]= |
Any strictly increasing list of integers can be considered as a subset with a unique index:
| In[5]:= |
| Out[5]= |
The index above generates a unique 9-subset:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= |
Some binomial representations of the number 320:
| In[7]:= | ![Column[Row[
Riffle[Table[
TraditionalForm[
Binomial[(ToString /@ #)[[n]], ToString[n]]], {n, 1, Length[#]}], "+"]] & /@ Table[ResourceFunction["IndexedSubset"][n, 321], {n, 2, 7}], Alignment -> Center]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/6f0/6f05e839-f7ec-42d3-b09e-20a7bc25cee0/2489460e6e86d9fd.png) |
| Out[7]= | 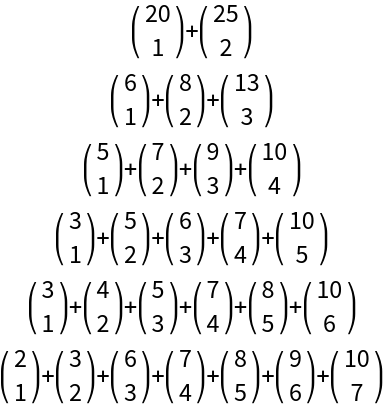 |
Here are some two item subsets with their indices to show their structure:
| In[8]:= | ![doubles = SortBy[Subsets[Range[0, 5], {2}], Reverse];
Graphics[{Text[
Style[Column[{StringJoin[ToString /@ #], ResourceFunction["IndexedSubset"][#]},
Alignment -> Center], 20], #] & /@ doubles, Blue, Line[doubles]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/6f0/6f05e839-f7ec-42d3-b09e-20a7bc25cee0/78f109da75d55c3f.png) |
| Out[8]= | 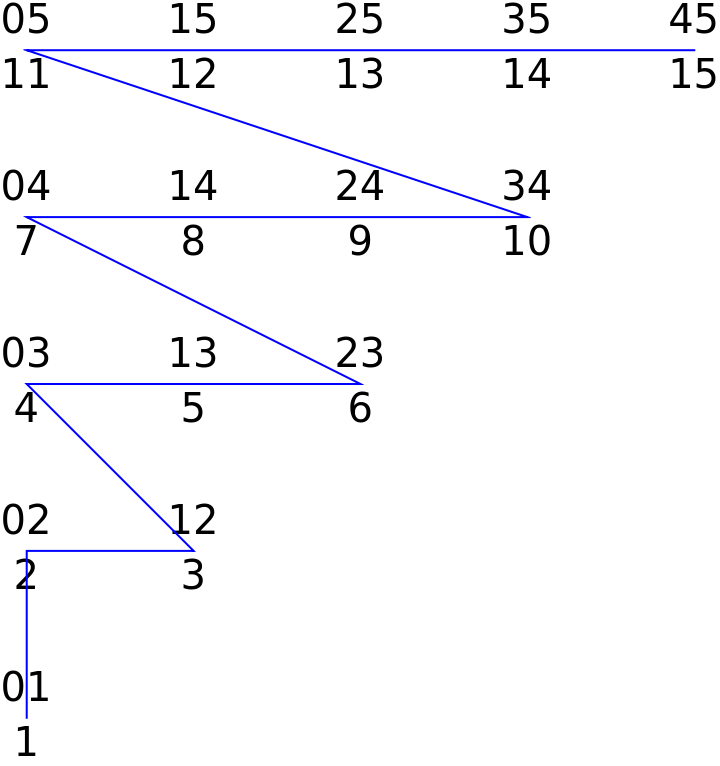 |
The 2-subset {4,5} has an index of ![]() :
:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= |
Recover the same information using IndexedSubset:
| In[10]:= |
| Out[10]= |
The structure of 3-subsets in 3D:
| In[11]:= | ![triples = SortBy[Subsets[Range[0, 5], {3}], Reverse];
Graphics3D[{Text[
Style[Column[{StringJoin[ToString /@ #], ResourceFunction["IndexedSubset"][#]},
Alignment -> Center], 20], #] & /@ triples, Blue, Line[triples]}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/6f0/6f05e839-f7ec-42d3-b09e-20a7bc25cee0/7ec406c4165956f8.png) |
| Out[11]= | 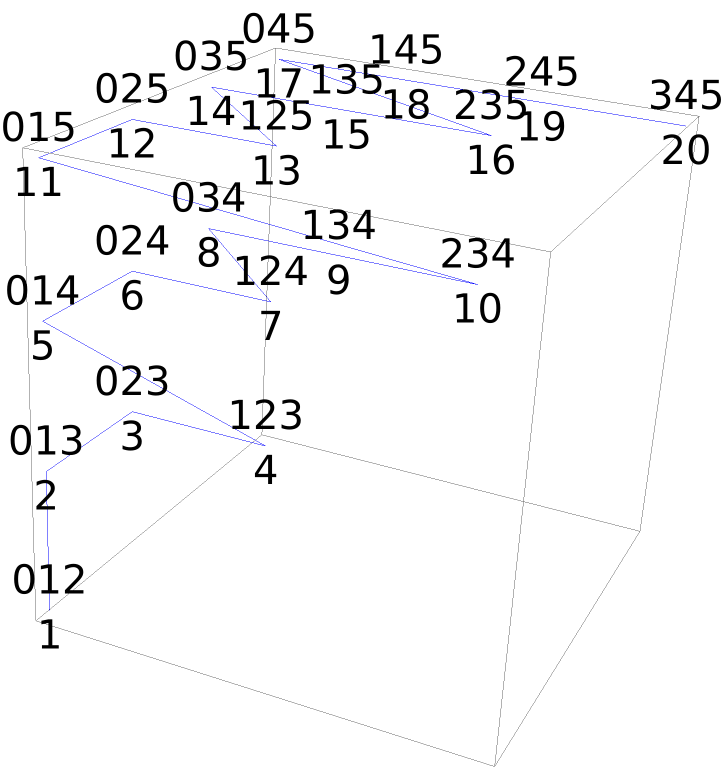 |
Find the trillionth number with binary weight eight:
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |
Find the index of an eight-term subset:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License