Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Compute the evolution of a multiway system and many associated properties
ResourceFunction["MultiwaySystem"][rules,init,n] generates the results of n steps in the evolution of the multiway system with the specified rules, starting from initial conditions init. | |
ResourceFunction["MultiwaySystem"][rules,init,n,"prop"] gives the property "prop" for the specified multiway system evolution. | |
ResourceFunction["MultiwaySystem"][rules→sel,init,n,…] uses the function sel to select which of the events obtained at each step to include in the evolution. |
| {"lhs1"→"rhs1",…} | string substitution system |
| {{l11,l12,…}→{r11,r12,..},…} | list substitution system |
| SubstitutionSystem[rules] | string or list substitution system |
| CellularAutomaton[rules] | cellular automaton system |
| "type"→rules | system of the specified type |
| assoc | system with properties defined by an Association |
| "StringSubstitutionSystem" | rules given as replacements on strings |
| "ListSubstitutionSystem" | rules given as replacements on lists |
| "CellularAutomaton" | rules given as a list of CellularAutomaton rule specifications |
| "WolframModel" | rules given as replacements on hypergraphs |
| "StateEvolutionFunction" | gives the list of successors to a given state |
| "StateEquivalenceFunction" | determines whether two states should be considered equivalent |
| "StateEventFunction" | gives the list of events applicable to a given state |
| "EventApplicationFunction" | applies an event to a given state |
| "EventDecompositionFunction" | decomposes an event into creator and destroyer events for individual elements |
| "SystemType" | system type name |
| "EventSelectionFunction" | determines which events should be applied to a given state |
| "Sequential" | applies the first possible replacement (sequential substitution system) |
| "Random" | applies a random replacement |
| {"Random",n} | applies n randomly chosen replacements |
| "MaxScan" | applies the maximal set of spatially separated replacements (strings only) |
| "AllStatesList" | the list of all states generated at each successive step (default) |
| "StatesCountsList" | the number of distinct states generated at each successive step |
| "AllStatesListUnmerged" | the list of all states without any merging |
| "PredecessorRulesList" | the list of states and their corresponding predecessor states at each successive step |
| "EvolutionGraph" | graph formed by the evolution process, with no merging between different time steps |
| "EvolutionGraphStructure" | evolution graph without labeling |
| "EvolutionGraphFull" | graph formed by the evolution process, including equivalent events |
| "EvolutionGraphFullStructure" | full evolution graph without labeling |
| "EvolutionGraphUnmerged" | graph formed by the evolution process, with no merging of equivalent states |
| "EvolutionGraphUnmergedStructure" | unmerged evolution graph without labeling |
| "EvolutionGraphWeighted" | graph formed by the evolution process, with edges weighted by event multiplicity |
| "EvolutionGraphWeightedStructure" | weighted evolution graph without labeling |
| "StatesGraph" | graph of how each distinct state leads to other states |
| "StatesGraphStructure" | states graph without labeling |
| "AllEventsList" | the list of all events that occur at each successive step |
| "EvolutionEventsGraph" | graph showing the evolution process with updating events explicitly included |
| "EvolutionEventsGraphStructure" | evolution events graph without labeling |
| "CausalGraph" | graph of all causal relations between updating events |
| "CausalGraphStructure" | causal graph without labeling |
| "EvolutionCausalGraph" | combined graph of evolution process and causal relationships between events |
| "EvolutionCausalGraphStructure" | evolution causal graph without labeling |
| "CausalGraphInstances" | list of distinct causal graphs for all possible choices of event sequences |
| "CausalGraphStructureInstances" | causal graph instances without labeling |
| "EvolutionCausalGraphInstances" | list of distinct evolution causal graphs for all possible choices of events sequences |
| "EvolutionCausalGraphStructureInstances" | evolution causal graph instances without labeling |
| "BranchPairsList" | list of all branch pairs (i.e. critical pairs) generated in the states graph |
| "NewBranchPairsList" | list of all new branch pairs generated at each successive step |
| "EvolutionBranchPairsList" | list of all branch pairs generated in the evolution graph |
| "NewEvolutionBranchPairsList" | list of all new evolution branch pairs generated at each successive step |
| "BranchPairEventsList" | list of all events yielding branch pairs |
| "NewBranchPairEventsList" | list of all events yielding new branch pairs at each successive step |
| "EvolutionBranchPairEventsList" | list of all events yielding evolution branch pairs |
| "NewEvolutionBranchPairEventsList" | list of all events yielding new evolution branch pairs at each successive step |
| "BranchialGraph" | graph of branch pair ancestry at a given step |
| "BranchialGraphStructure" | branchial graph without labeling |
| "AllStatesBranchialGraph" | graph of branch pair ancestry across all steps |
| "AllStatesBranchialGraphStructure" | all states branchial graph without labeling |
| "EvolutionBranchialGraph" | graph of evolution branch pair ancestry at a given step |
| "EvolutionBranchialGraphStructure" | evolution branchial graph without labeling |
| "AllStatesEvolutionBranchialGraph" | graph of evolution branch pair ancestry across all steps |
| "AllStatesEvolutionBranchialGraphStructure" | all states evolution branchial graph without labeling |
| "EventBranchialGraph" | graph of branch pair event ancestry at a given step |
| "EventBranchialGraphStructure" | event branchial graph without labeling |
| "AllEventsBranchialGraph" | graph of branch pair event ancestry across all steps |
| "AllEventsBranchialGraphStructure" | all events branchial graph without labeling |
| "EvolutionEventBranchialGraph" | graph of evolution branch pair event ancestry at a given step |
| "EvolutionEventBranchialGraphStructure" | evolution event branchial graph without labeling |
| "AllEventsEvolutionBranchialGraph" | graph of evolution branch pair event ancestry across all steps |
| "AllEventsEvolutionBranchialGraphStructure" | all events evolution branchial graph without labeling |
| "BranchPairResolutionsList" | association of all resolved and unresolved branch pairs up to a given step |
| "EvolutionBranchPairResolutionsList" | association of all resolved and unresolved evolution branch pairs up to a given step |
| "CausalInvariantQ" | whether the system is causal invariant (all branch pairs converge) |
| "EvolutionCausalInvariantQ" | whether the system is evolution causal invariant (all evolution branch pairs converge) |
| "KnuthBendixCompletion" | list of Knuth–Bendix completion rules required to force causal invariance |
| "EvolutionKnuthBendixCompletion" | list of Knuth–Bendix completion rules required to force evolution causal invariance |
| "CanonicalBranchPairsList" | list of canonical (initial condition-independent) branch pairs |
| "CanonicalBranchPairResolutionsList" | association of all resolved and unresolved canonical branch pairs up to a given step |
| "TotalCausalInvariantQ" | whether the system is total causal invariant (all canonical branch pairs converge) |
| "CanonicalKnuthBendixCompletion" | minimal list of canonical Knuth–Bendix completion rules required to force total causal invariance |
| "StateWeights" | list of weights for all vertices in the states graph |
| "IncludeStepNumber" | False | whether to label states and events with their respective step numbers |
| "IncludeStateID" | False | whether to label states and events with unique IDs |
| "IncludeInitializationEvents" | False | whether to include pseudoevents that set up initial conditions |
| "IncludeEventInstances" | False | whether to show distinct updating events that connect the same states as separate edges |
| "IncludeStateWeights" | False | whether to weight state vertices by their rate of occurrence at a particular time step |
| "IncludeStatePathWeights" | False | whether to weight state vertices by the number of distinct evolution paths that lead to them |
| "StateRenderingFunction" | Automatic | how to label states that appear in graphs |
| "EventRenderingFunction" | Automatic | how to label events that appear in graphs |
| MaxItems | Infinity | how many instances of a causal graph or evolution causal graph to return |
| "GivePredecessors" | False | whether to label branch pairs with their predecessor state |
| "GiveResolvents" | False | whether to label branch pairs with their resolvent state |
| "IncludeSelfPairs" | False | whether to include trivial branch pairs |
| "IncludeFullBranchialSpace" | False | whether to show all possible states in a given branchial graph |
| "LineThickness" | 1 | absolute line thickness for graph edges |
| Automatic | make a label from the name of the vertex |
| Inherited | use the explicit vertex name as the label |
| None | use no label for the vertex |
| "string" | use a shape from the VertexShapeFunction collection |
| func | apply the function func to the name of the vertex |
Show basic multiway system evolution:
| In[1]:= |
|
| Out[1]= |
|
| In[2]:= |
|
| Out[2]= |
|
| In[3]:= |
|
| Out[3]= |
|
Generate a graph showing how each state is obtained from the others:
| In[4]:= |
|
| Out[4]= |
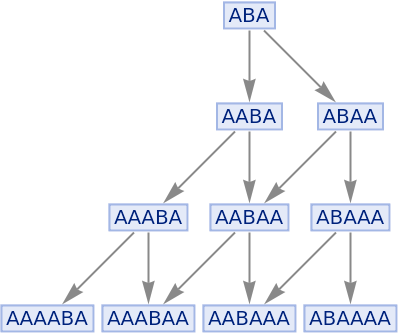
|
Show the structure of the graph, without labels:
| In[5]:= |
|
| Out[5]= |
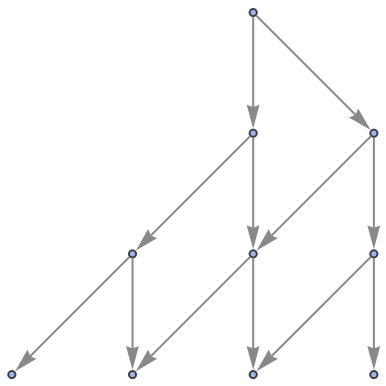
|
Generate the list of all updating events applied at each step:
| In[6]:= |
|
| Out[6]= |
|
Generate a graph of the evolution history, with updating events included:
| In[7]:= |
|
| Out[7]= |
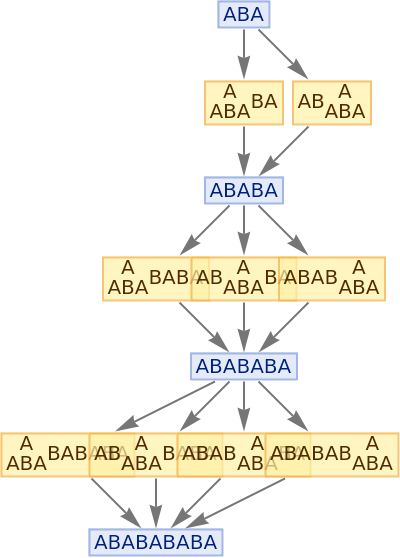
|
Show the structure of the graph, without labels:
| In[8]:= |
|
| Out[8]= |
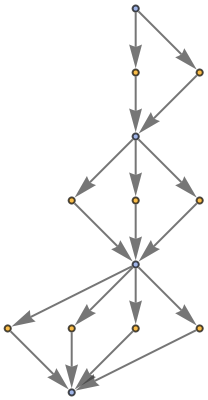
|
Generate the causal graph, showing dependencies between updating events:
| In[9]:= |
|
| Out[9]= |
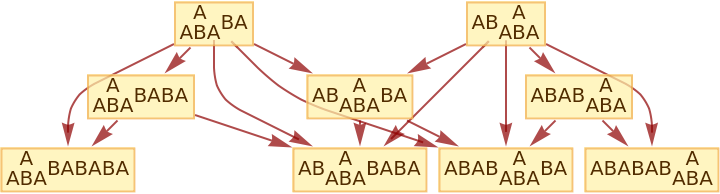
|
Show the structure of the graph, without labels:
| In[10]:= |
|
| Out[10]= |
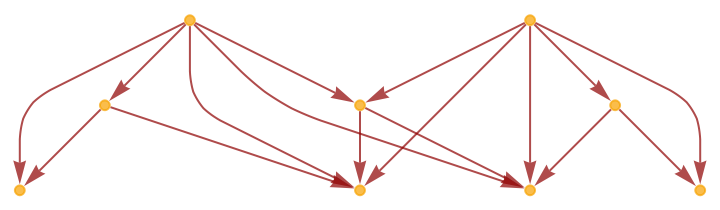
|
Generate the evolution events graph, with causal connections included:
| In[11]:= |
|
| Out[11]= |

|
Show the structure of the graph, without labels:
| In[12]:= |
|
| Out[12]= |
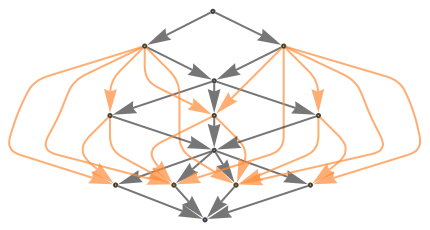
|
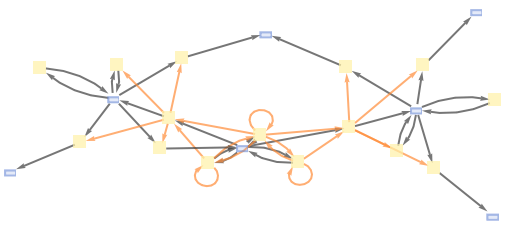
MultiwaySystem can handle Wolfram models and other rule types:
| In[13]:= |
![ResourceFunction["MultiwaySystem"][
"WolframModel" -> {{{2, 2, 1}, {2, 2, 2}} -> {{1, 1, 3}, {1, 1, 1}, {2, 1, 2}, {3, 3, 2}}}, {Table[{0, 0, 0}, 3]}, 3, "EvolutionCausalGraph", VertexSize -> 1]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/2e0/2e01e7b9-9618-41ef-95c1-ed6532f16094/6eb6fc69083e8fe0.png)
|
| Out[13]= |
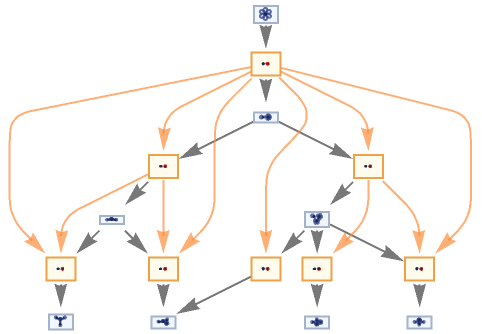
|
| In[14]:= |
|
| Out[14]= |
|
| In[15]:= |
|
| Out[15]= |
|
Specify an event selection function that picks only up to two events at each step:
| In[16]:= |
|
| Out[16]= |
|
Generate causal graphs for all possible choices of event sequences:
| In[17]:= |
|
| Out[17]= |
|
Show the structures of the graphs, without labels:
| In[18]:= |
|
| Out[18]= |
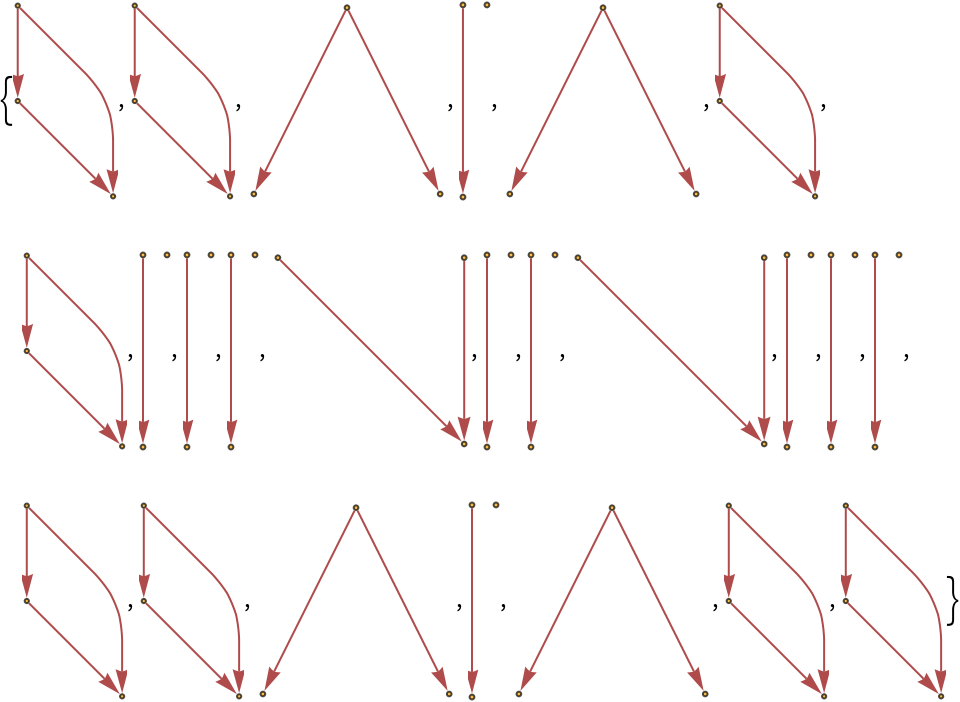
|
Generate a graph of full evolution history, with all events included:
| In[19]:= |
|
| Out[19]= |
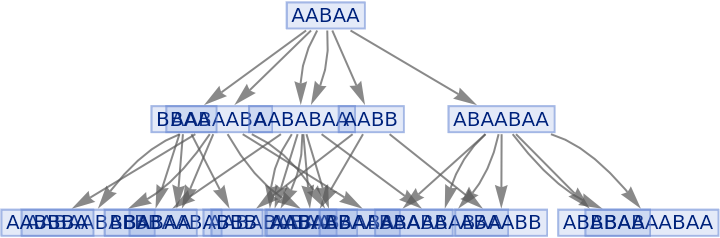
|
Show the structure of the graph, without labels:
| In[20]:= |
|
| Out[20]= |
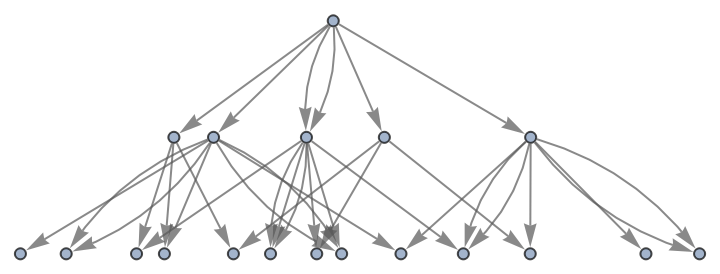
|
Generate a graph of evolution history, with no merging of equivalent states:
| In[21]:= |
|
| Out[21]= |

|
Show the structure of the graph, without labels:
| In[22]:= |
|
| Out[22]= |
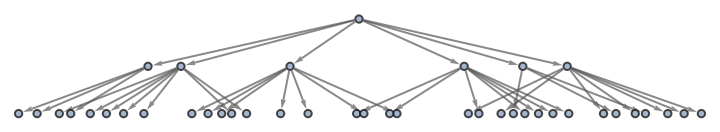
|
Generate a graph of evolution history, with edges weighted by event multiplicity:
| In[23]:= |
|
| Out[23]= |
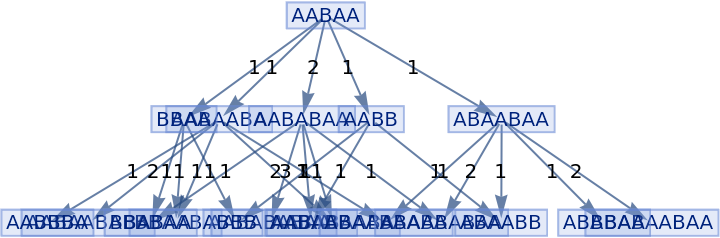
|
Show the structure of the graph, without labels:
| In[24]:= |
|
| Out[24]= |
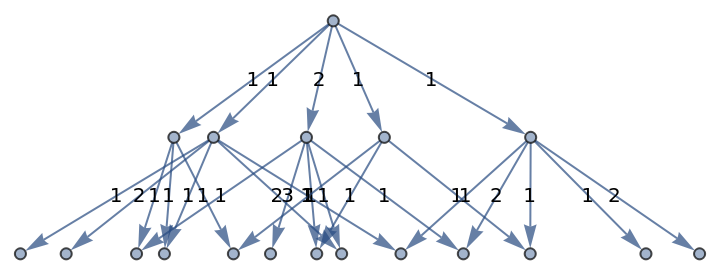
|
Generate a states graph with vertices weighted by their rate of occurrence on each time step:
| In[25]:= |
|
| Out[25]= |
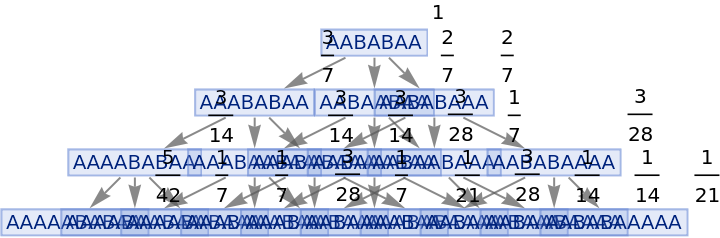
|
Show the structure of the graph, without labels:
| In[26]:= |
|
| Out[26]= |
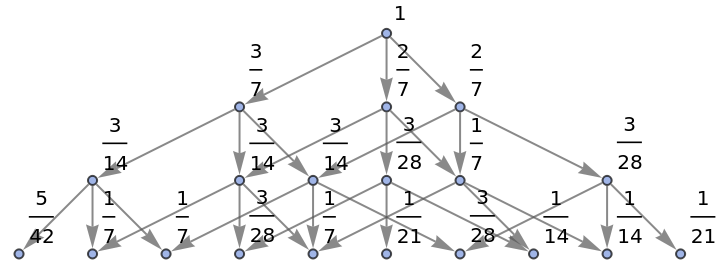
|
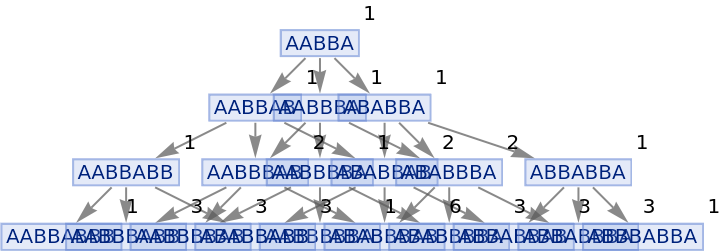
Generate a states graph with vertices weighted by the number of distinct evolution paths that lead to them:
| In[27]:= |
|
| Out[27]= |
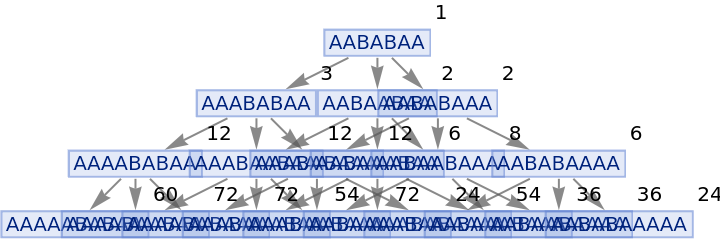
|
Show the structure of the graph, without labels:
| In[28]:= |
|
| Out[28]= |
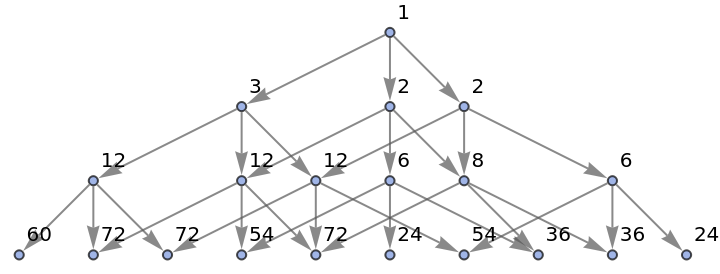
|
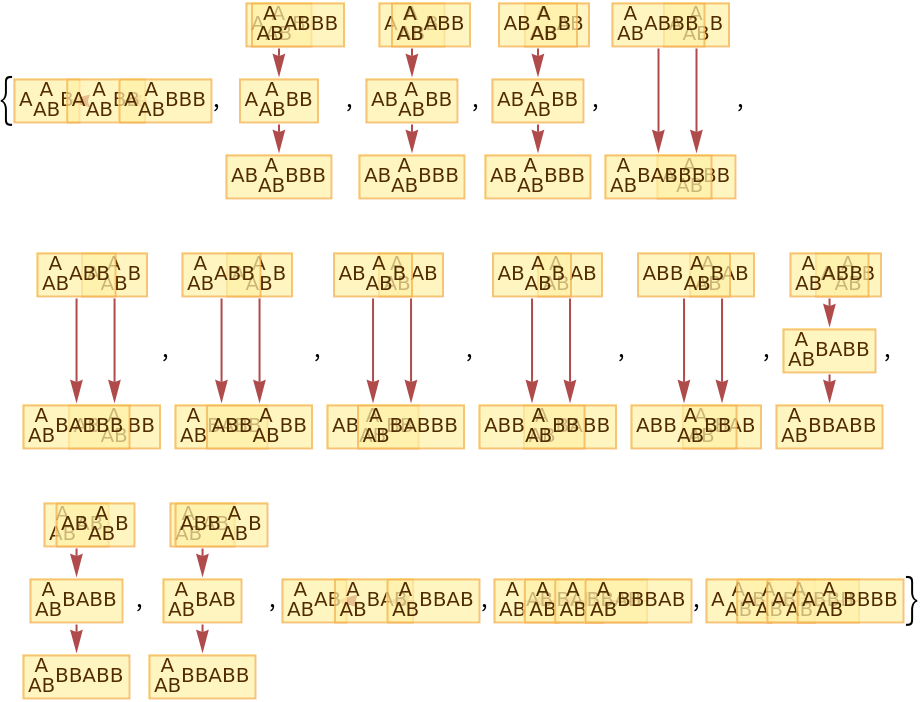
Generate the list of all branch pairs (i.e. critical pairs):
| In[29]:= |
|
| Out[29]= |

|
Generate the association showing which branch pairs converged and which did not:
| In[30]:= |
|
| Out[30]= |

|
Prove that the system is not causal invariant:
| In[31]:= |
|
| Out[31]= |
|
Generate a graph showing branch pair ancestry:
| In[32]:= |
|
| Out[32]= |
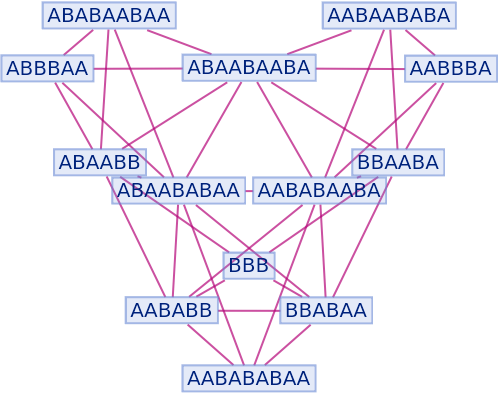
|
Show the structure of the graph, without labels:
| In[33]:= |
|
| Out[33]= |

|
Generate a graph showing branch pair event ancestry:
| In[34]:= |
|
| Out[34]= |
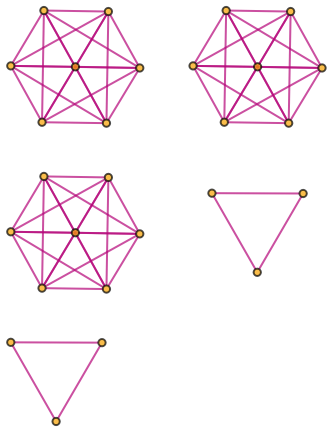
|
Prevent identical states from being merged by including step numbers and state IDs:
| In[35]:= |
|
| Out[35]= |
|
| In[36]:= |
|
| Out[36]= |

|
MultiwaySystem supports both string and list substitution systems:
| In[37]:= |
|
| Out[37]= |
|
| In[38]:= |
|
| Out[38]= |
|
Lists can contain arbitrary symbolic elements:
| In[39]:= |
|
| Out[39]= |
|
Give an explicit substitution system rule:
| In[40]:= |
|
| Out[40]= |
|
An alternative method of specifying that a substitution system should be used:
| In[41]:= |
|
| Out[41]= |
|
MultiwaySystem also supports multiway generalizations of cellular automata:
| In[42]:= |
|
| Out[42]= |
|
Lists of cellular automaton rules can also be specified directly:
| In[43]:= |
|
| Out[43]= |
|
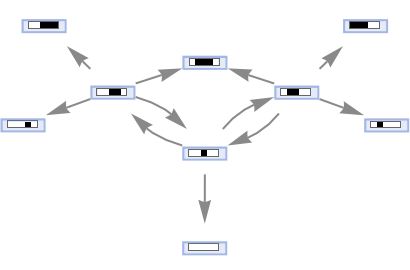
Generate a states graph from left- and right-shift cellular automaton rules:
| In[44]:= |
|
| Out[44]= |
|
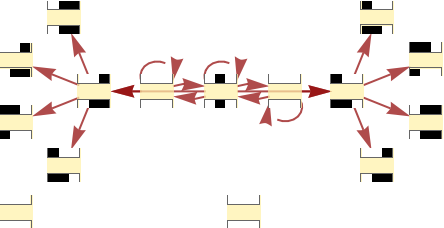
Generate a causal graph for the rule 30 cellular automaton:
| In[45]:= |
|
| Out[45]= |
|
MultiwaySystem also supports multiway generalizations of Wolfram models:
| In[46]:= |
|
| Out[46]= |

|
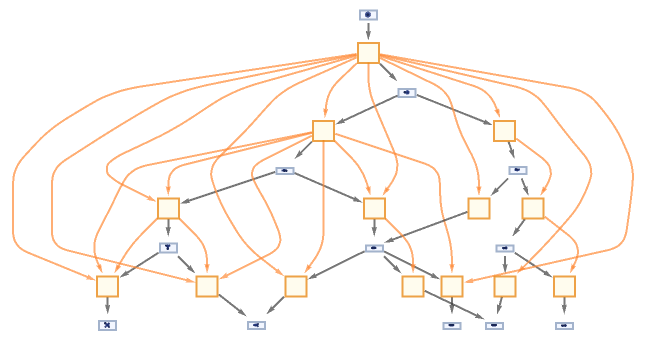
Generate an evolution causal graph for a Wolfram model rule:
| In[47]:= |
|
| Out[47]= |
|
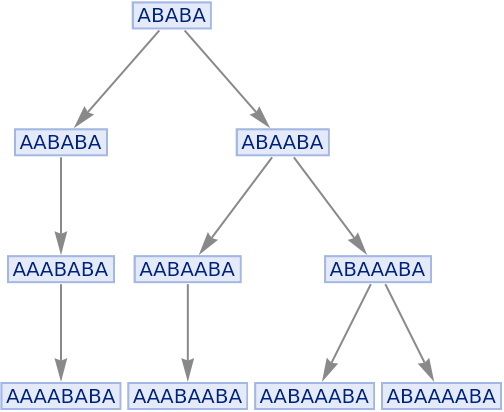
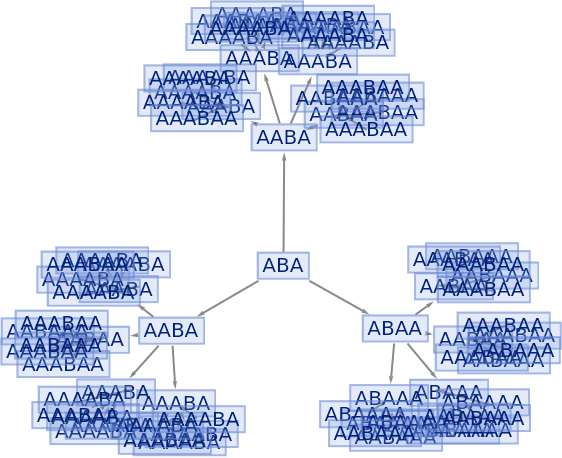
Construct a multiway system by explicitly specifying an association:
| In[48]:= |
![ResourceFunction[
"MultiwaySystem"][<|
"StateEvolutionFunction" -> (StringReplaceList[#, {"A" -> "AA", "B" -> "AB"}] &), "StateEquivalenceFunction" -> SameQ, "StateEventFunction" -> Identity, "EventDecompositionFunction" -> Identity, "EventApplicationFunction" -> Identity, "SystemType" -> "None", "EventSelectionFunction" -> Identity|>, {"ABA"}, 3]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/2e0/2e01e7b9-9618-41ef-95c1-ed6532f16094/1c6fda9e53b129eb.png)
|
| Out[48]= |
|
MultiwaySystem accepts both individual rules and lists of rules:
| In[49]:= |
|
| Out[49]= |
|
| In[50]:= |
|
| Out[50]= |

|
Likewise for initial conditions:
| In[51]:= |
|
| Out[51]= |

|
Apply only the first possible event at each step:
| In[52]:= |
|
| Out[52]= |
|
Apply the first and last possible events at each step:
| In[53]:= |
|
| Out[53]= |

|
Use a greedy-style algorithm to apply the maximal set of nonconflicting events at each step (strings only):
| In[54]:= |
|
| Out[54]= |
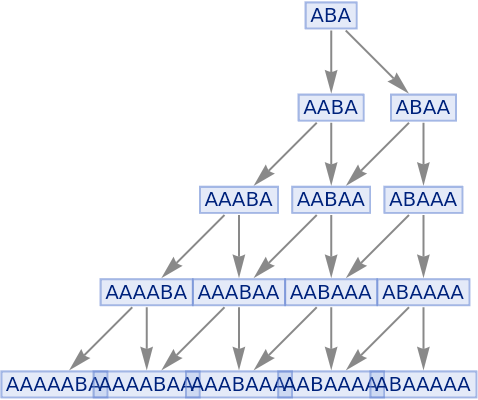
|
Compare this to the full states graph:
| In[55]:= |
|
| Out[55]= |
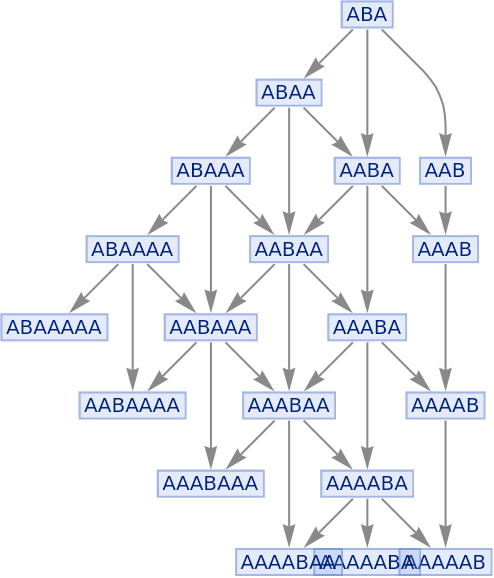
|
By default, states are labeled by their contents:
| In[56]:= |
|
| Out[56]= |
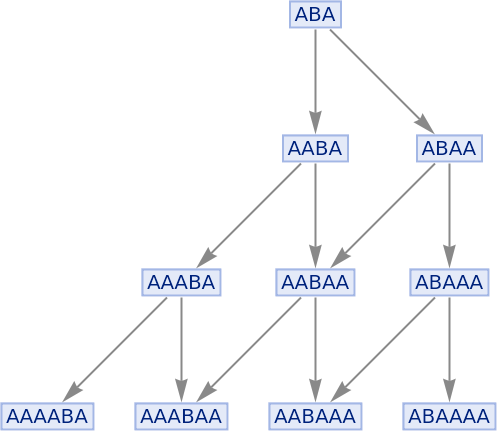
|
Use no labeling for states:
| In[57]:= |
|
| Out[57]= |
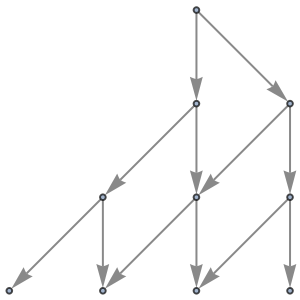
|
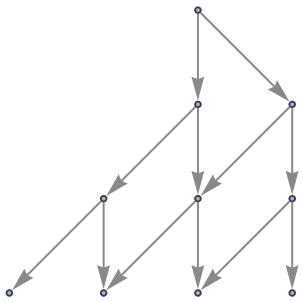
"StatesGraphStructure" yields the same result:
| In[58]:= |
|
| Out[58]= |
|
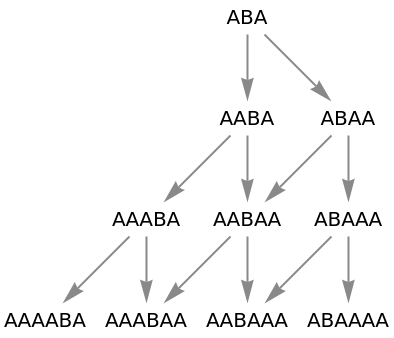
Use raw state names as node labels:
| In[59]:= |
|
| Out[59]= |
|
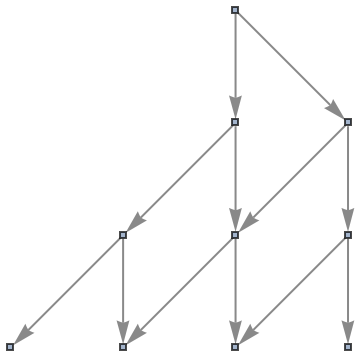
Use a named shape as each state label:
| In[60]:= |
|
| Out[60]= |
|
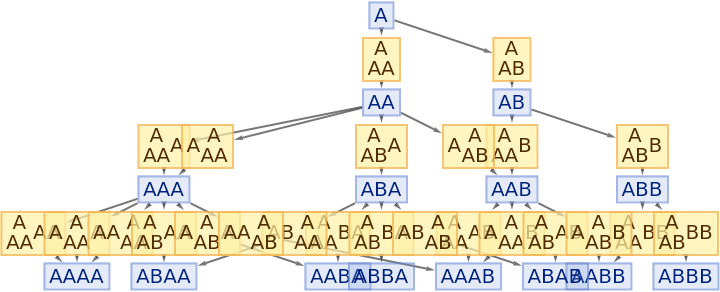
By default, both states and events are labeled by their contents:
| In[61]:= |
|
| Out[61]= |
|
Use no labeling for states:
| In[62]:= |
|
| Out[62]= |
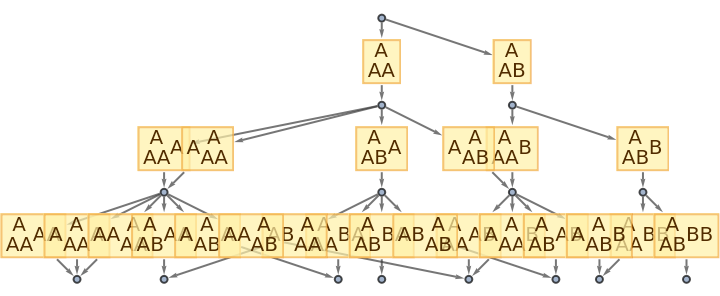
|
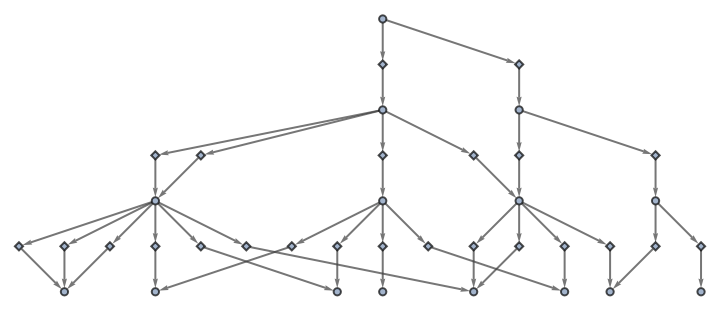
Also use no labeling for events:
| In[63]:= |
|
| Out[63]= |
|
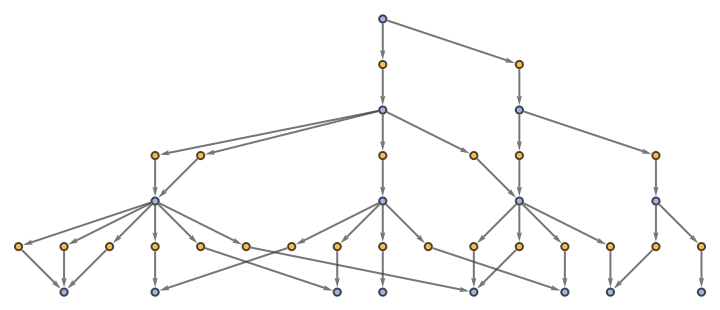
"EvolutionEventsGraphStructure" yields an equivalent result:
| In[64]:= |
|
| Out[64]= |
|
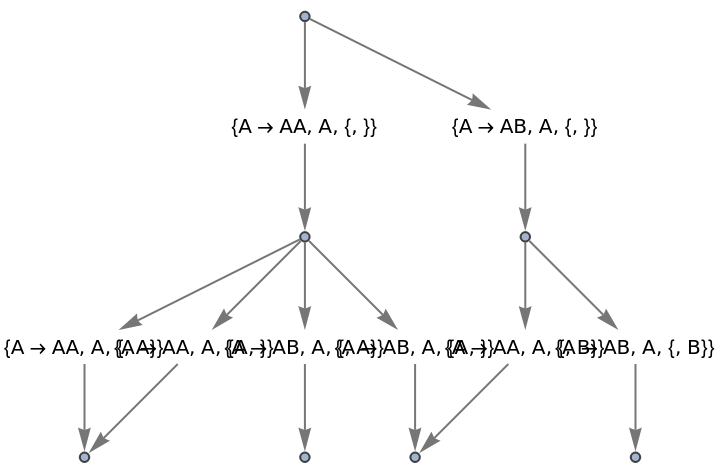
Use raw event expressions as their labels:
| In[65]:= |
|
| Out[65]= |
|
By default, "AllEventsList" does not include initialization events:
| In[66]:= |
|
| Out[66]= |
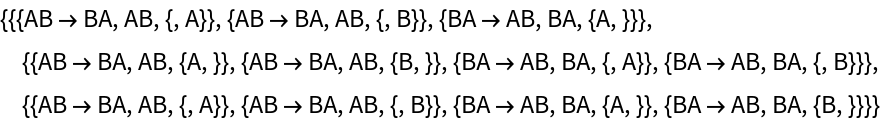
|
The option "IncludeInitializationEvents" allows one to override this default:
| In[67]:= |
|
| Out[67]= |

|
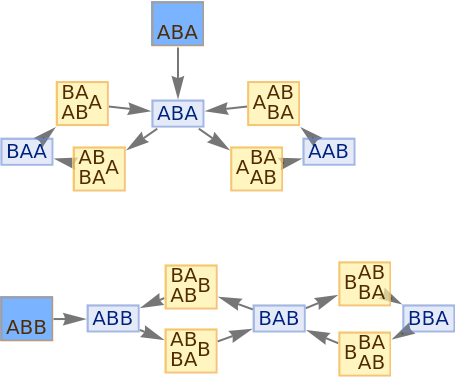
Initialization events have special default rendering:
| In[68]:= |
|
| Out[68]= |
|
Place arrows in the middle of edges:
| In[69]:= |
|
| Out[69]= |
|
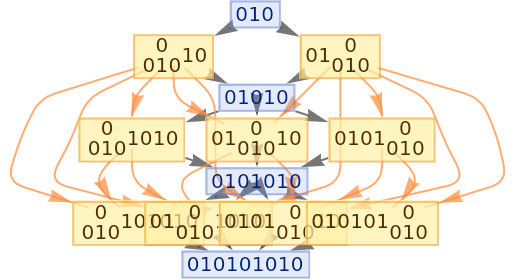
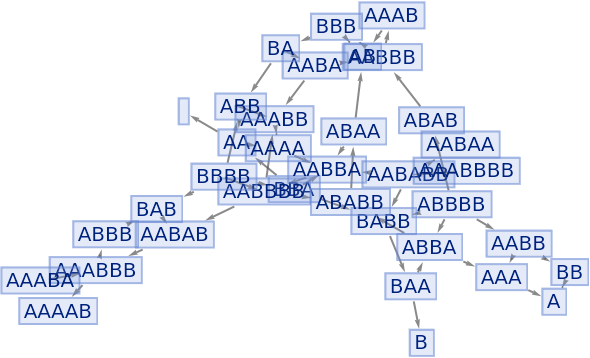
Generate an example multiway evolution from page 209 of A New Kind of Science:
| In[70]:= |
|
| Out[70]= |
|
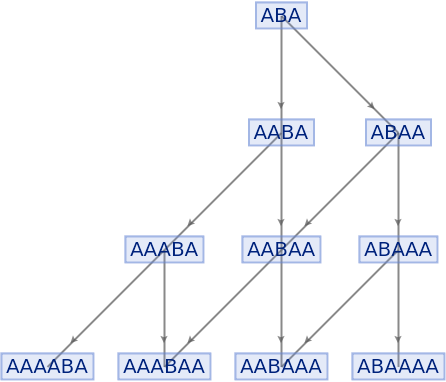
Force the initial state node to be at the top:
| In[71]:= |
|
| Out[71]= |
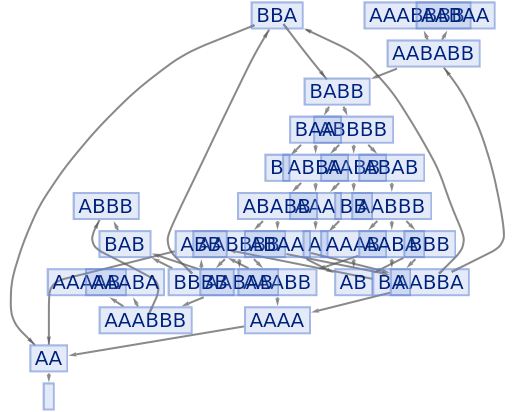
|
By default, equivalent states are merged across all time steps:
| In[72]:= |
|
| Out[72]= |
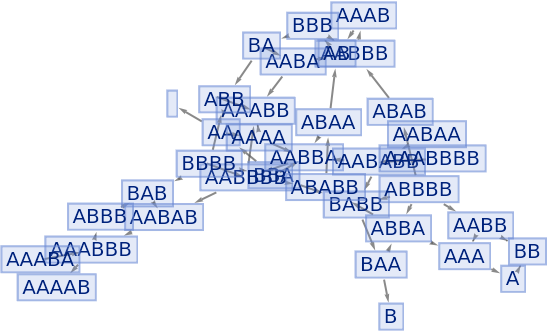
|
| In[73]:= |
|
| Out[73]= |

|
Merging of equivalent states across different time steps can be prevented by including step numbers:
| In[74]:= |
|
| Out[74]= |
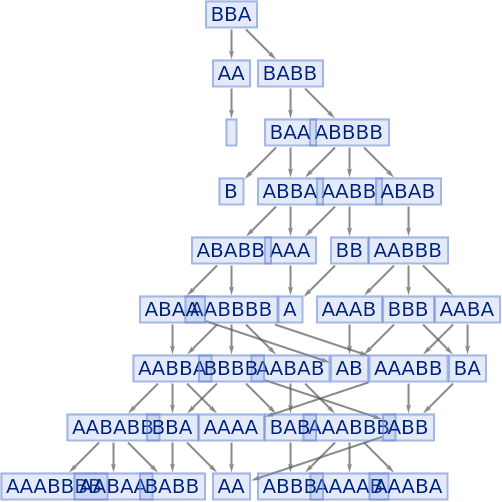
|
| In[75]:= |
|
| Out[75]= |

|
Merging of equivalent states at the same time step can be prevented by also including state IDs:
| In[76]:= |
|
| Out[76]= |
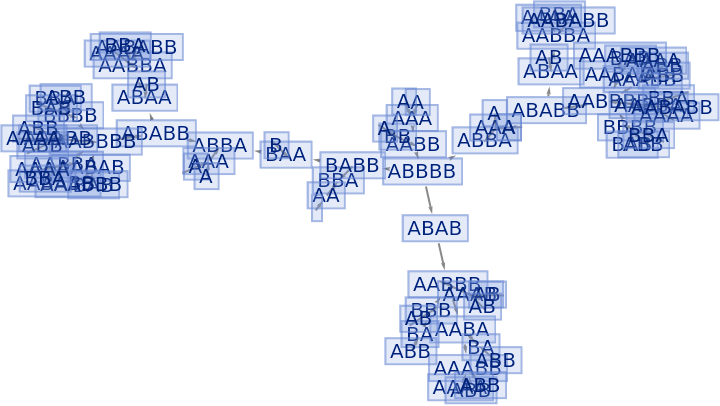
|
| In[77]:= |
|
| Out[77]= |

|
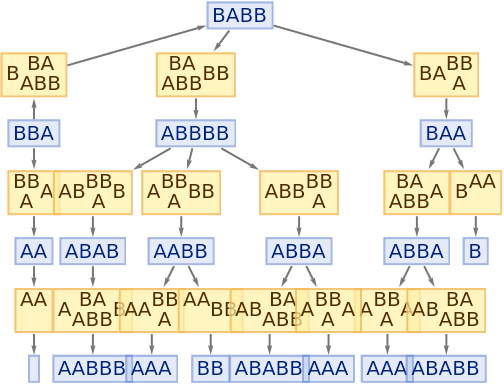
Step numbers and IDs also apply to events:
| In[78]:= |
|
| Out[78]= |
|
| In[79]:= |
|
| Out[79]= |

|
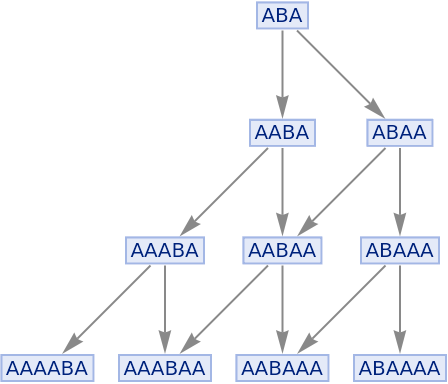
By default, multiple instances of equivalent updating events are merged in the states graph:
| In[80]:= |
|
| Out[80]= |
|
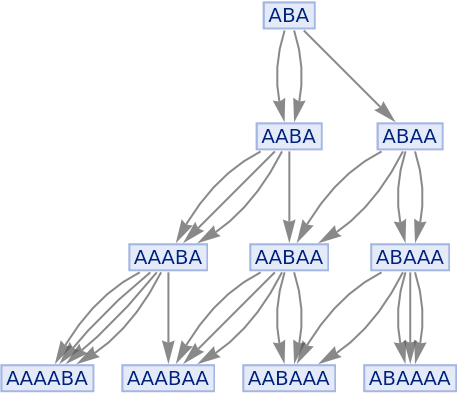
Merging of equivalent events can be prevented by including event instances:
| In[81]:= |
|
| Out[81]= |
|
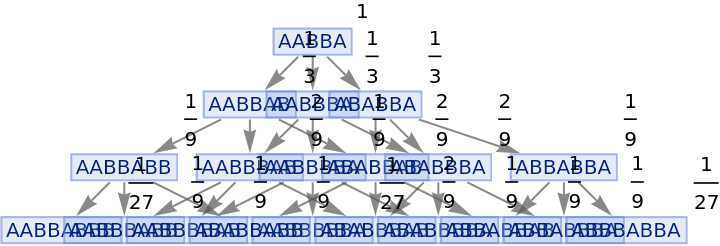
Vertices of a states graph can be weighted by their relative rate of occurrence at each time step:
| In[82]:= |
|
| Out[82]= |
|
Vertices can also be weighted by the number of distinct evolution paths that lead to them:
| In[83]:= |
|
| Out[83]= |
|
By default, "CausalGraphInstances" returns all possible causal graphs:
| In[84]:= |
|
| Out[84]= |
|
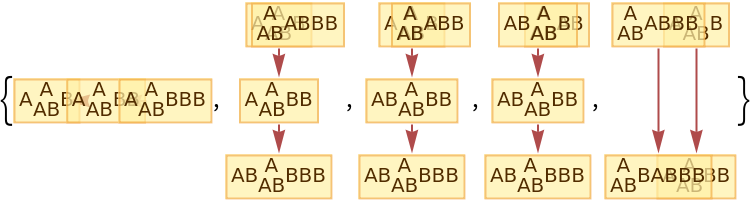
The number of causal graphs returned can be limited using MaxItems:
| In[85]:= |
|
| Out[85]= |
|
By default, "BranchPairsList" returns only a list of branch pairs:
| In[86]:= |
|
| Out[86]= |

|
Common predecessor states can be shown using "GivePredecessors":
| In[87]:= |
|
| Out[87]= |

|
Similarly, "BranchPairResolutionsList" by default lists only resolved and unresolved branch pairs:
| In[88]:= |
|
| Out[88]= |

|
Common resolvents of resolved branch pairs can be shown using "GiveResolvents":
| In[89]:= |
|
| Out[89]= |

|
Show both common predecessors and common resolvents, where appropriate:
| In[90]:= |
|
| Out[90]= |

|
By default, "CanonicalBranchPairsList" does not include self-pairs (i.e. trivial critical pairs):
| In[91]:= |
|
| Out[91]= |
|
Self-pairs can be included using "IncludeSelfPairs":
| In[92]:= |
|
| Out[92]= |
|
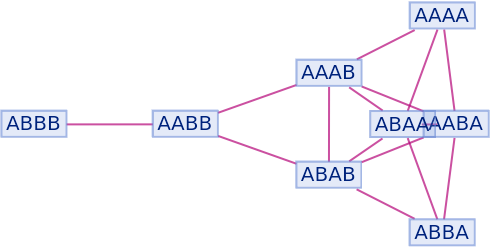
By default, non-branch pair states are not shown as part of the branchial graph:
| In[93]:= |
|
| Out[93]= |
|
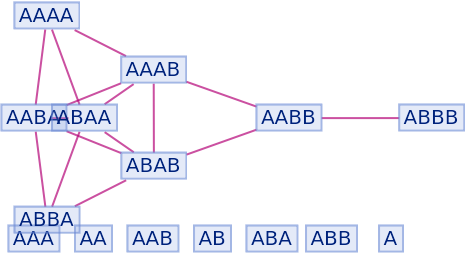
They can be shown using "IncludeFullBranchialSpace":
| In[94]:= |
|
| Out[94]= |
|
Investigate a multiway system from A New Kind of Science:
| In[95]:= |
|
| Out[95]= |
|
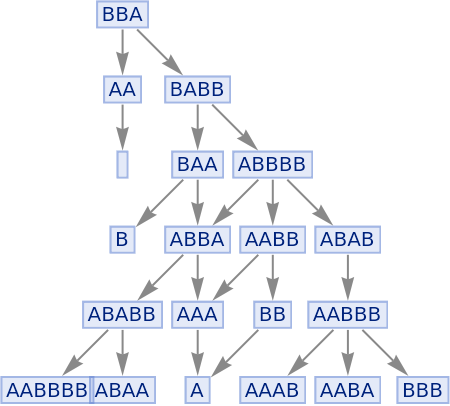
Illustrate the evolution:
| In[96]:= |
|
| Out[96]= |
|
The rule exhibits irregular growth in the total number of states at each step:
| In[97]:= |
|
| Out[97]= |

|
Its multiway causal graph is relatively complicated:
| In[98]:= |
|
| Out[98]= |

|
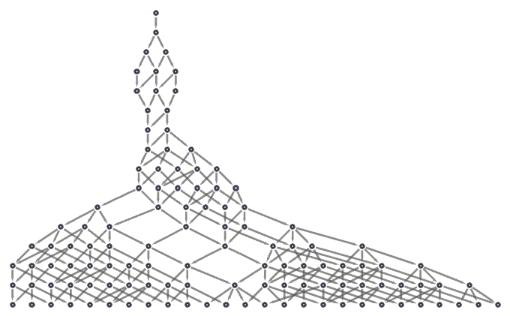
Show the state graph structure for a multiway system:
| In[99]:= |
![LayeredGraphPlot[
ResourceFunction["MultiwaySystem"][{"AAB" -> "ABBBAA"}, "AAABBB", 15,
"StatesGraphStructure"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/2e0/2e01e7b9-9618-41ef-95c1-ed6532f16094/0416d3ef79dfa10c.png)
|
| Out[99]= |
|
Show the causal graph structure:
| In[100]:= |
|
| Out[100]= |
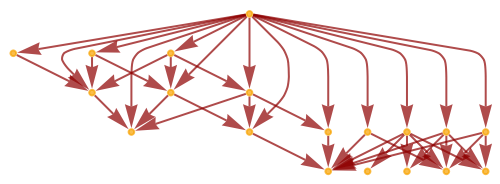
|
Show that this multiway evolution is both causal invariant and total causal invariant:
| In[101]:= |
|
| Out[101]= |
|
| In[102]:= |
|
| Out[102]= |
|
Illustrate a simple sorting rule:
| In[103]:= |
|
| Out[103]= |
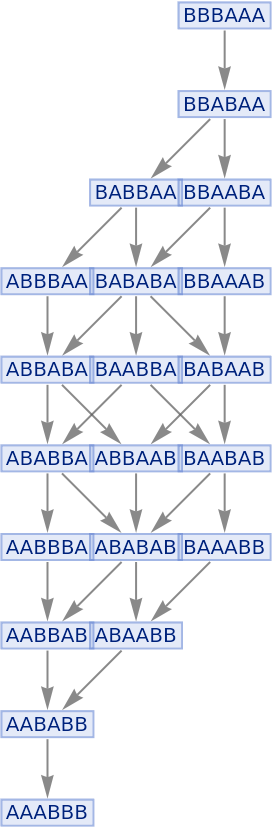
|
| In[104]:= |
|
| Out[104]= |
|
| In[105]:= |
|
| Out[105]= |
|
Generate string replacements rules corresponding to the Xor function:
| In[106]:= |
|
| Out[106]= |
|
The multiway system has many paths, but due to causal invariance all lead to the same eventual result:
| In[107]:= |
|
| Out[107]= |
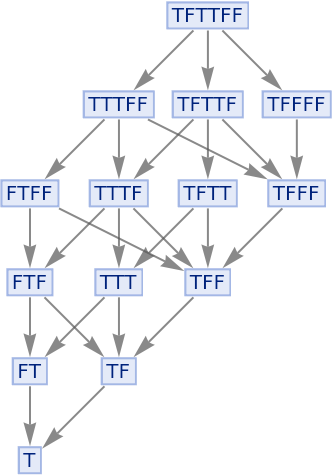
|
| In[108]:= |
|
| Out[108]= |
|
| In[109]:= |
|
| Out[109]= |
|
The And function is also confluent, since it too is associative:
| In[110]:= |
|
| Out[110]= |
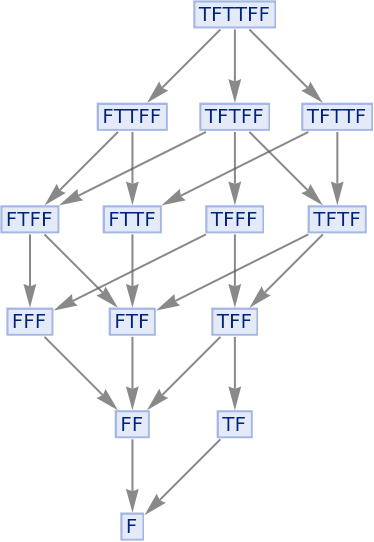
|
| In[111]:= |
|
| Out[111]= |
|
| In[112]:= |
|
| Out[112]= |
|
The Nand function is not associative, so can lead to different results:
| In[113]:= |
|
| Out[113]= |
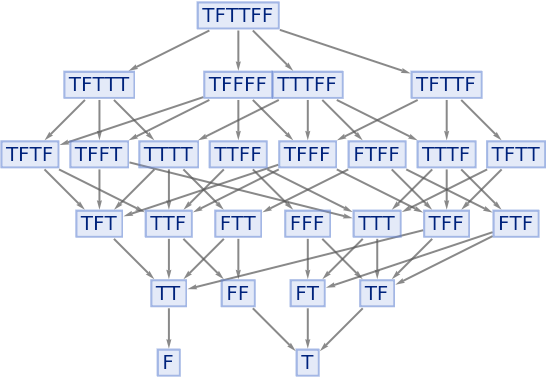
|
| In[114]:= |
|
| Out[114]= |
|
| In[115]:= |
|
| Out[115]= |
|
"StatesCountsList" is equivalent to mapping Length over the lists of generated states:
| In[116]:= |
|
| Out[116]= |
|
| In[117]:= |
|
| Out[117]= |
|
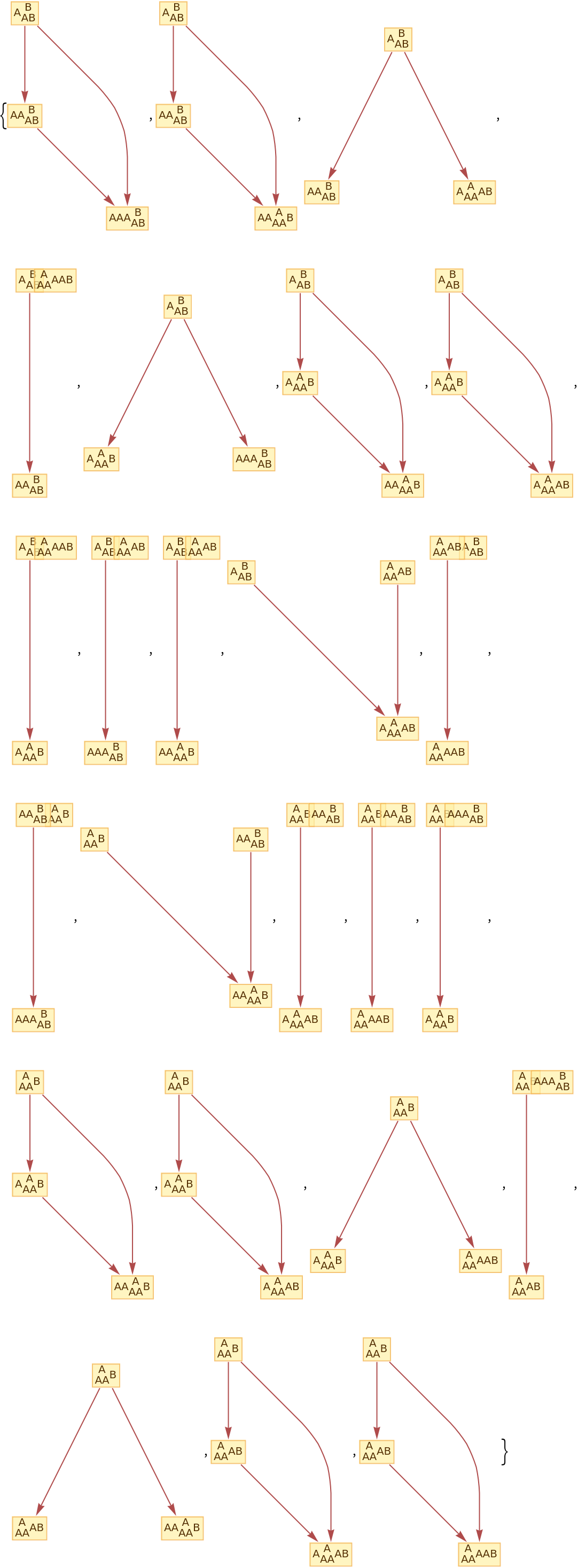
Find all possible states, including multiplicities:
| In[118]:= |
|
| Out[118]= |
|
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License