Wolfram Function Repository
Instant-use add-on functions for the Wolfram Language
Function Repository Resource:
Convert a three-channel color RGB image to a one-channel grayscale image or matrix
ResourceFunction["OneChannelGrayscale"][img] converts color image img to a single-channel grayscale image. | |
ResourceFunction["OneChannelGrayscale"][img,"ImageData"] returns the image data matrix of the grayscale image. |
| "Luminosity" (default) | uses the luminosity algorithm, which is a weighted average |
| "Mean" | uses the mean algorithm on the 3 channel RGB colors pixels |
Convert a color image to a grayscale:
| In[1]:= | ![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/1e116a42-d09b-4d09-b5b6-225e2ea5a7f3"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/275/2753919b-f36e-4ec2-8754-ab34fa818754/66a0afea7c7ab42a.png) |
| Out[1]= |  |
Look at the image information:
| In[2]:= |
| Out[2]= |  |
Convert the same image to grayscale using the mean algorithm:
| In[3]:= | ![(* Evaluate this cell to get the example input *) CloudGet["https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/67db657b-b7ca-468f-afe5-4ca2e056f9b5"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/275/2753919b-f36e-4ec2-8754-ab34fa818754/6a200c8ffa70df53.png) |
| Out[3]= |  |
2D numerical matrix can be seen with ArrayPlot:
| In[4]:= | ![# -> ArrayPlot[
ResourceFunction["OneChannelGrayscale"][#, "Matrix", Method -> "Mean"], Frame -> None, ColorFunction -> GrayLevel] &[
ResourceFunction["GetLoremFlickrImage"]["dometic cat"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/275/2753919b-f36e-4ec2-8754-ab34fa818754/57f187749c1b8c0c.png) |
| Out[4]= | 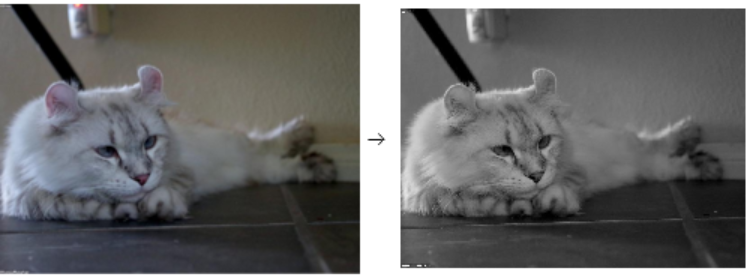 |
Convert an AI image synthesis to grayscale:
| In[5]:= | ![GraphicsGrid[{{#, ArrayPlot[
ResourceFunction["OneChannelGrayscale"][#, "Matrix", Method -> "Mean"], Frame -> None, ColorFunction -> GrayLevel]}}] &[
ImageSynthesize[
"White cat with red hat, blue glasses in a green forest background photo realistic"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/275/2753919b-f36e-4ec2-8754-ab34fa818754/74bf7d22518c87a6.png) |
| Out[5]= |  |
Image exams, such as X-rays or mammograms, are in gray scale. Still, the images are usually 3-channel RGB, it is better to convert to one channel grayscale for faster computation and clean up data:
| In[6]:= |
| Out[6]= | 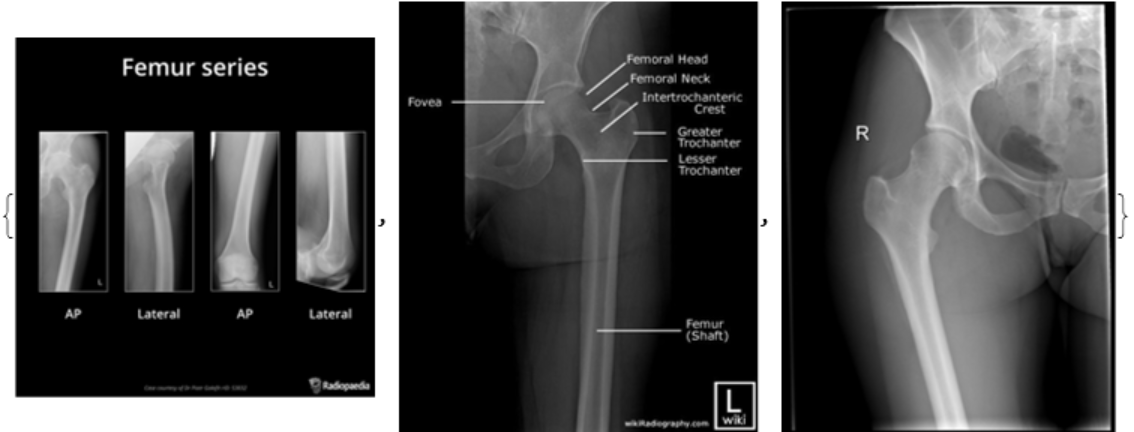 |
Find a general test image and convert to grayscale:
| In[7]:= | ![dog = Entity["TaxonomicSpecies", "CanisLupusFamiliaris::4t62p"][
EntityProperty["TaxonomicSpecies", "Image"]];
golden = ResourceFunction["OneChannelGrayscale"][dog];
GraphicsRow[{dog, golden}]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/275/2753919b-f36e-4ec2-8754-ab34fa818754/16db1947a9bec0c7.png) |
| Out[8]= |  |
Compare information for the images:
| In[9]:= |
| Out[9]= | 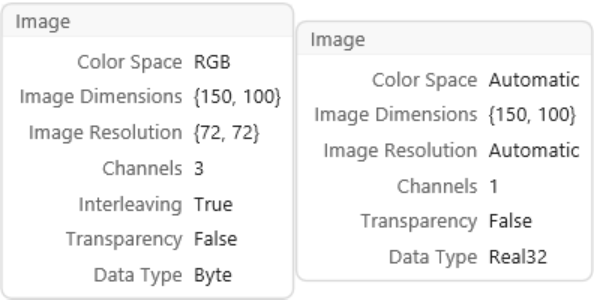 |
Convert an image to grayscale and then colorize it using ArrayPlot:
| In[10]:= | ![ArrayPlot[
ResourceFunction["OneChannelGrayscale"][
GeoGraphics[{Entity["HistoricalSite", "ChristTheRedeemer::g488w"]}],
"Matrix", Method -> "Mean"], Frame -> None, ColorFunction -> "Rainbow"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/obj/resourcesystem/images/275/2753919b-f36e-4ec2-8754-ab34fa818754/1801564075a5e8fe.png) |
| Out[10]= | 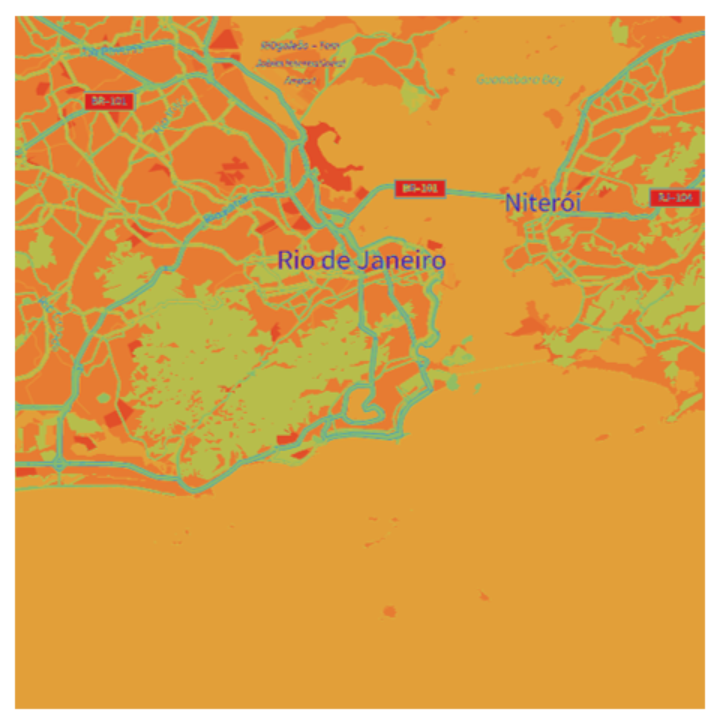 |
Convert three faces to grayscale:
| In[11]:= |
| In[12]:= |
| Out[12]= |  |
Convert the same faces using the unweighted mean:
| In[13]:= |
| Out[13]= |  |
Compare to the resource function "FaustGrayscaleConvert":
| In[14]:= |
| Out[14]= |  |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License