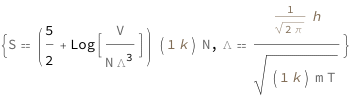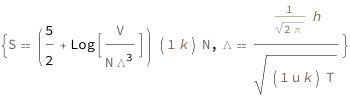Sackur–Tetrode Equation Using Thermal de Broglie Wavelength
The Sackur–Tetrode equation is an expression for the entropy of a monatomic classical ideal gas, which incorporates quantum considerations that give a more detailed description of its regime of validity.
The absolute entropy increases logarithmically with the volume and the reciprocal of the thermal de Broglie wavelength cubed. Higher values of the particle number also increase absolute entropy at the rate of the particle number times the logarithm of the reciprocal of the particle number. The thermal de Broglie wavelength is proportional to the reciprocal of the square root of the mass times the temperature.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 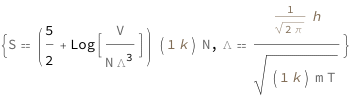 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 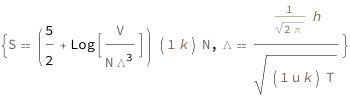 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard {QuantityVariable["S", "Entropy"] == (5/2 + Log[QuantityVariable["V", "Volume"]/(QuantityVariable["N", "Unitless"]*QuantityVariable["Λ", "Wavelength"]^3)])*Quantity[1, "BoltzmannConstant"]*QuantityVariable["N", "Unitless"], QuantityVariable["Λ", "Wavelength"] == Quantity[1/Sqrt[2*Pi], "PlanckConstant"]/Sqrt[Quantity[1, "BoltzmannConstant"]*QuantityVariable["m", "Mass"]*QuantityVariable["T", "Temperature"]]}](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/ff1/ff17662a-2cc0-4ec0-ab8a-1ec367b4edbe/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)