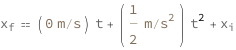Constant Translational Acceleration in a Straight Line
Constant translational acceleration in a straight line describes the equation of motion of an object moving under constant acceleration along a straight line as a function of time.
The final position for constant acceleration in a stright line equals the initial position plus the initial velocity times the time plus half the acceleration times the time squared.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 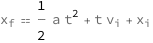 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 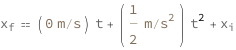 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable[Subscript["x", "f"], "Length"] == (QuantityVariable["a", "Acceleration"]*QuantityVariable["t", "Time"]^2)/2 + QuantityVariable["t", "Time"]*QuantityVariable[Subscript["v", "i"], "Speed"] + QuantityVariable[Subscript["x", "i"], "Length"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/f45/f45e219c-d89f-4445-a664-06d22ea680f8/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Constant Translational Acceleration in a Straight Line"], \
{QuantityVariable["a","Acceleration"] ->
Quantity[1, ("Meters")/("Seconds")^2], QuantityVariable[
\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\("v"\), \("i"\)]\),"Speed"] ->
Quantity[0, ("Meters")/("Seconds")]}]](images/f45/f45e219c-d89f-4445-a664-06d22ea680f8-io-3-i.en.gif)