Parallel Resistor-Inductor Circuit
A resistor–inductor circuit is an electric circuit composed of resistors and inductors driven by a voltage or current source. The parallel version places resistor and inductor in parallel.
The resistor current equals the input voltage divided by the resistance. The inductor current equals the input voltage divided by the product of 2\[Pi] times the frequency and the magnetic inductance.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 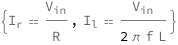 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 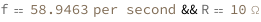 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard {QuantityVariable[Subscript["I", "r"], "ElectricCurrent"] == QuantityVariable[Subscript["V", "in"], "ElectricPotential"]/QuantityVariable["R", "ElectricResistance"], QuantityVariable[Subscript["I", "l"], "ElectricCurrent"] == QuantityVariable[Subscript["V", "in"], "ElectricPotential"]/(2*Pi*QuantityVariable["f", "Frequency"]*QuantityVariable["L", "MagneticInductance"])}](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/f3a/f3a6f668-ad2b-4d9a-87cf-9db5a647e6ac/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

![FormulaData[
ResourceObject[
"Parallel Resistor-Inductor Circuit"], {QuantityVariable[
\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\("V"\), \("in"\)]\),"ElectricPotential"] ->
Quantity[10, "Volts"],
QuantityVariable["L","MagneticInductance"] ->
Quantity[1, "Henries"], QuantityVariable[
\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\("I"\), \("l"\)]\),"ElectricCurrent"] ->
Quantity[0.027`, "Amperes"], QuantityVariable[
\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\("I"\), \("r"\)]\),"ElectricCurrent"] ->
Quantity[1, "Amperes"]}]](images/f3a/f3a6f668-ad2b-4d9a-87cf-9db5a647e6ac-io-3-i.en.gif)