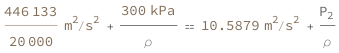Bernoulli's Energy Equation
Bernoulli's energy equation derives from Bernoulli's principle, which states that an increase in the speed of a fluid across a surface will result in a decrease of the force exerted (pressure) on that surface, or a decrease in the fluid's potential energy vectored toward that surface.
Bernoulli's energy equation states that the sum of the pressure divided by the fluid density, the kinetic energy divided by the mass and the potential energy due to gravity divded by mass remains constant.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 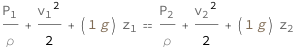 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 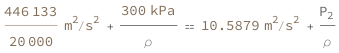 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable[Subscript["P", "1"], "Pressure"]/QuantityVariable["ρ", "MassDensity"] + QuantityVariable[Subscript["v", "1"], "Speed"]^2/2 + Quantity[1, "StandardAccelerationOfGravity"]*QuantityVariable[Subscript["z", "1"], "Height"] == QuantityVariable[Subscript["P", "2"], "Pressure"]/QuantityVariable["ρ", "MassDensity"] + QuantityVariable[Subscript["v", "2"], "Speed"]^2/2 + Quantity[1, "StandardAccelerationOfGravity"]*QuantityVariable[Subscript["z", "2"], "Height"]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/eed/eeda0558-2666-4374-ad9f-23cf422869a3/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)

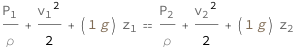
![FormulaData[
ResourceObject["Bernoulli's Energy Equation"], {QuantityVariable[
\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\("z"\), \("2"\)]\),"Height"] ->
Quantity[1, "Meters"], QuantityVariable[
\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\("z"\), \("1"\)]\),"Height"] ->
Quantity[1, "Meters"], QuantityVariable[
\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\("v"\), \("2"\)]\),"Speed"] ->
Quantity[1.25`, ("Meters")/("Seconds")], QuantityVariable[
\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\("v"\), \("1"\)]\),"Speed"] ->
Quantity[5, ("Meters")/("Seconds")], QuantityVariable[
\!\(\*SubscriptBox[\("P"\), \("1"\)]\),"Pressure"] ->
Quantity[300, "Kilopascals"]}]](images/eed/eeda0558-2666-4374-ad9f-23cf422869a3-io-3-i.en.gif)