Johnson–Nyquist Noise Voltage
The Johnson–Nyquist noise is the electronic noise generated by the thermal agitation of the charge carriers (usually the electrons) inside an electrical conductor at equilibrium, which happens regardless of any applied voltage.
The Johnson-Nyquist noise voltage equals two times the square root of the product of the Boltzmann constant, the electric resistance, the frequency bandwidth and the temperature.
Examples
Get the resource:
| Out[1]= |  |
Get the formula:
| Out[2]= | 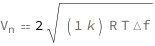 |
Use some values:
| Out[3]= | 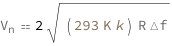 |
External Links
Publisher Information
![Copy to Clipboard QuantityVariable[Subscript["V", "n"], "ElectricPotential"] == 2*Sqrt[Quantity[1, "BoltzmannConstant"]*QuantityVariable["R", "ElectricResistance"]*QuantityVariable["T", "Temperature"]*QuantityVariable["Δf", "Frequency"]]](https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/resourcesystem/marketplacestorage/resources/edd/eddb49a1-c144-4a4b-9318-2a9048f7a67f/Webpage/FormulaImage.png)
